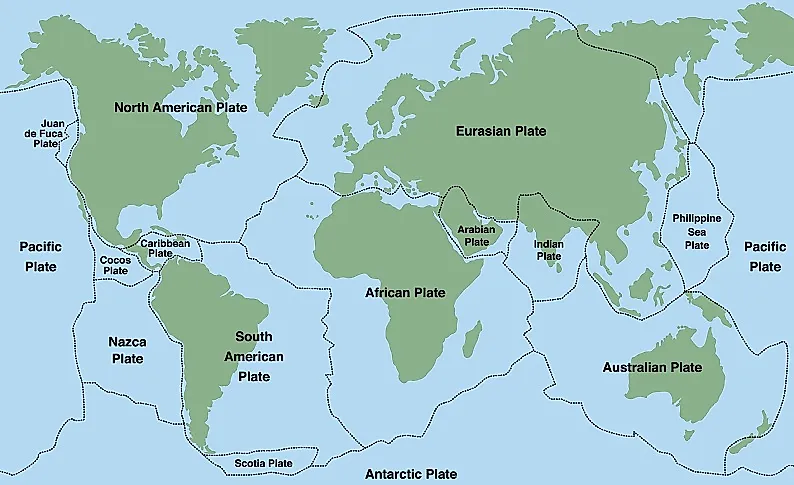
How Many Tectonic Plates Are There?
Tectonic plates are gigantic segments or pieces of the Earth's crust and uppermost mantle that together constitute the Lithosphere. Tectonic Plates are of two types, namely oceanic crust and continental crust that differ in composition. Tectonic plates are not fixed but move above the molten mantle below them.Tectonic plates form either divergent, transform, or convergent boundaries when they come in contact. Such boundaries are highly susceptible to earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. Orogeny also takes place at such boundaries. Tectonic plates are defined as major and minor plates depending on their size. There are a total of seven major tectonic plates which cover nearly 95% of the Earth's surface.
Major Tectonic Plates By Size
Pacific Plate - 103,300,000 sq km
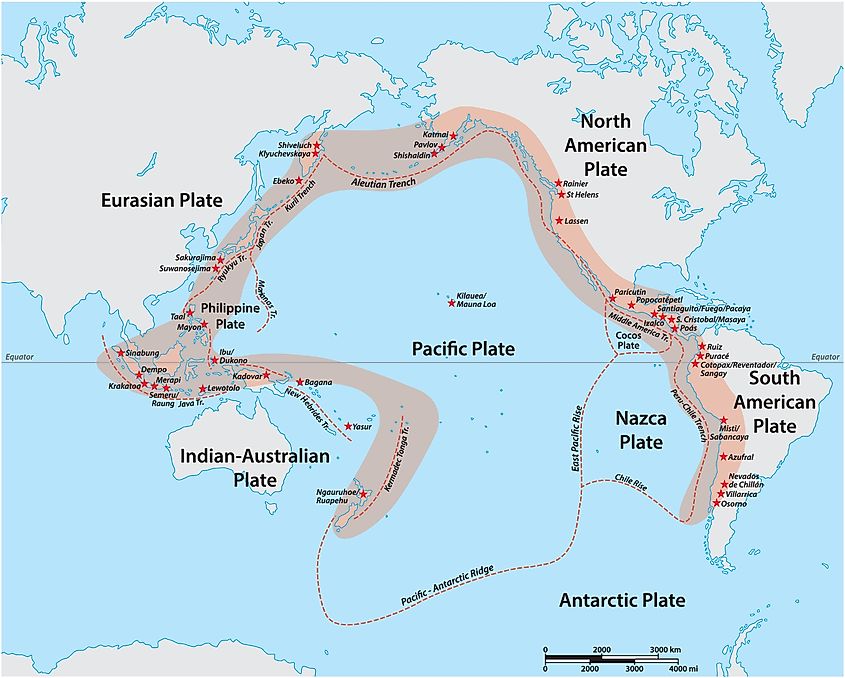
The Pacific Plate ranks as the largest tectonic plate on Earth, covering about one-third of the planet's surface and including most of the Pacific Ocean floor from Asia to the Americas. Surrounding this extensive oceanic plate are highly active subduction zones and transform faults that contribute to the "Ring of Fire," where it submerges under adjacent continental plates, resulting in significant volcanic activity, frequent earthquakes, and tsunami hazards that impact billions throughout the Pacific Rim. The plate advances northwestward at speeds of 3-4 inches per year, with its edges producing some of the most powerful earthquakes and volcanic eruptions globally, particularly affecting major population centers in Japan, Indonesia, the Philippines, and the western coastlines of North and South America.
North American Plate - 75,900,000 sq km
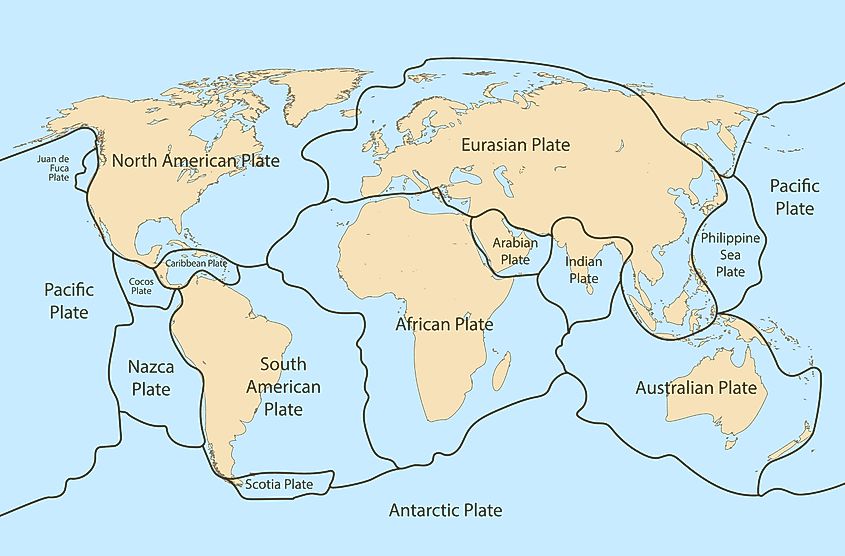
The North American Plate is a major tectonic plate on Earth, covering most of North America from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Coast. It includes the United States, Canada, Mexico, and extends into parts of the Atlantic and Arctic oceans. This mainly continental plate is bordered by several active plate boundaries, such as the San Andreas Fault system along California's coast, where it interacts with the Pacific Plate, posing significant earthquake risks. Additionally, the Cascadia Subduction Zone in the Pacific Northwest sees oceanic plates subduct beneath it, leading to volcanic activity and tsunami hazards. The eastern boundary at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge is gradually spreading, interactions with the Pacific, Juan de Fuca, and Caribbean plates result in varied geological dangers, from earthquakes in California to the volcanic Cascade Range and seismic risks associated with the New Madrid fault zone in the central United States.
Eurasian Plate - 67,800,000 sq km
The Eurasian Plate is the largest tectonic plate on Earth, encompassing most of Europe and Asia from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific, including major population centers from London to Beijing. This massive continental plate is bounded by highly active collision zones, particularly along its southern margin where it collides with the Indian, Arabian, and African plates, creating major mountain ranges including the Himalayas, Alps, and Caucasus, while generating significant seismic activity across regions like Turkey, Iran, and Central Asia. The plate's northern boundary extends into the Arctic Ocean, while its complex interactions with surrounding plates produce some of the world's most devastating earthquakes, affecting densely populated areas and critical infrastructure across multiple continents.
African Plate - 61,300,000 sq km
The African Plate is one of Earth's largest tectonic plates, encompassing the entire African continent and extending into the surrounding Atlantic and Indian oceans. This predominantly continental plate is bounded by mid-ocean ridges along its western and southern margins where it is slowly separating from the South American and Antarctic plates, while its northern boundary involves complex interactions with the Eurasian and Arabian plates across the Mediterranean region. The plate is being internally split by the East African Rift System, which is gradually dividing eastern Africa and will eventually create a new ocean basin, generating significant volcanic activity and seismic hazards throughout the rift zone.
Antarctic Plate - 60,900,000 sq km
The Antarctic Plate is one of Earth's largest tectonic plates, encompassing the entire Antarctic continent and extending outward beneath the surrounding Southern Ocean to form a roughly circular plate. This primarily continental plate is bounded by mid-ocean ridges on most sides, where it is slowly spreading apart from the South American, African, Indo-Australian, and Pacific plates, making it one of the most geologically stable major plates with relatively low seismic activity.
Indo-Australian Plate - 58,900,000 sq km
The Indo-Australian Plate is among the largest tectonic plates on Earth, including the Indian subcontinent, Australia, and much of the adjacent Indian Ocean floor. Currently, it is splitting into the separate Indian and Australian plates. This vast plate collides with the Eurasian Plate at its northern edge, forming the Himalayan mountain range and causing significant seismic activity in South and Southeast Asia, leading to devastating earthquakes in areas such as Kashmir and Nepal. Its complex boundaries feature subduction zones where it sinks beneath the Eurasian Plate in Indonesia and the Philippines, contributing to the "Ring of Fire" volcanic activity that impacts hundreds of millions across the region.
South American Plate - 43,600,000 sq km
The South American Plate ranks among Earth's primary tectonic plates, covering the entire South American continent and extending into the Atlantic Ocean to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. At its western edge, this continental plate collides with the subducting Nazca and Antarctic plates, which give rise to the Andes Mountains—the longest continental mountain range on the planet—and trigger significant seismic activity that impacts major cities from Colombia to Chile. The eastern boundary is marked by the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a divergent zone where new oceanic crust is created, gradually pushing South America away from Africa at approximately 3 centimeters per year.
Minor Tectonic Plates By Size
Somali Plate - 16,700,000 sq km
The Somali Plate is a significant tectonic plate that covers the Horn of Africa, which includes Somalia, eastern Ethiopia, and parts of Kenya. It is actively pulling away from the larger African Plate along the East African Rift System. This continental plate is moving east at a rate of about 2-3 centimeters per year, establishing a divergent boundary that is slowly separating eastern Africa and will ultimately create a new ocean basin over millions of years. This plate boundary causes considerable seismic activity across the East African Rift, impacting major population centers and leading to volcanic occurrences in areas such as the Ethiopian Highlands and the Great Rift Valley of Kenya.
Nazca Plate - 15,600,000 sq km
The Nazca Plate is a significant oceanic tectonic plate situated off the western coast of South America in the Pacific Ocean, extending from the Galápagos Islands to southern Chile. It is currently subducting beneath the South American Plate along the Peru-Chile Trench at one of the fastest convergence rates on the planet, resulting in the formation of the towering Andes Mountains and causing intense seismic activity throughout the region. This subduction process renders the area one of the most earthquake-prone on Earth, leading to devastating quakes that have historically affected major cities such as Lima, Santiago, and Quito, and also contributing to the emergence of numerous active volcanoes along the Andean volcanic arc.
Philippine Sea Plate - 5,500,000 sq km
The Philippine Sea Plate is a significant oceanic tectonic plate situated in the western Pacific Ocean, covering the Philippine Sea basin and bordered by the Philippines, Japan, and the Mariana Islands. Notably, this plate features intricate subduction zones along most of its edges, where it both descends beneath and is descended upon by neighboring plates, leading to the formation of some of the world's deepest ocean trenches, including the Mariana Trench—the deepest point on Earth. The plate's high tectonic activity results in frequent earthquakes, active volcanism, and tsunami threats across the region, greatly affecting major population centers in the Philippines, Japan, and other nations in the western Pacific.
Arabian Plate - 5,000,000 sq km
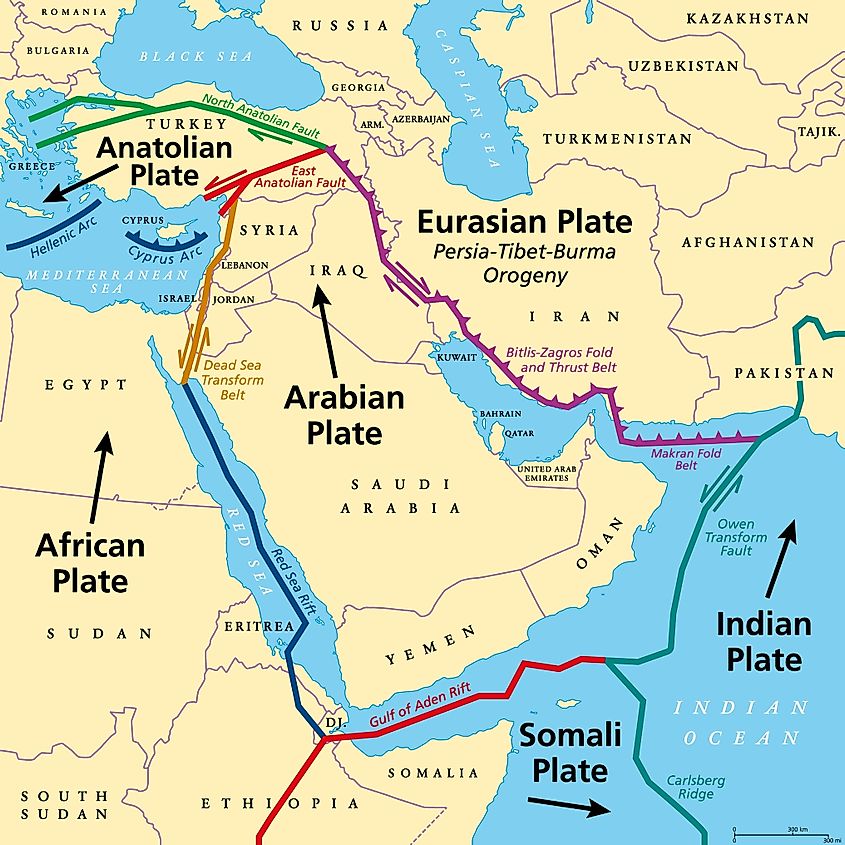
The Arabian Plate tectonic plate that covers the Arabian Peninsula and stretches beneath parts of the Persian Gulf, Red Sea, and adjacent areas. This continental plate is currently separating from the African Plate along the Red Sea Rift, resulting in the formation of new oceanic crust and gradually widening the Red Sea at a rate of approximately 1-2 centimeters annually. Additionally, the plate is colliding with the Eurasian Plate to the north, which is responsible for the formation of the Zagros Mountains in Iran and contributes to notable seismic activity throughout the Middle East. These geological processes have major implications for regional energy resources, as the movement and structure of the plate have established many of the oil and gas reservoirs vital to global energy markets, while also posing ongoing earthquake risks to major population centers in the region.
Caribbean Plate - 3,300,000 sq km
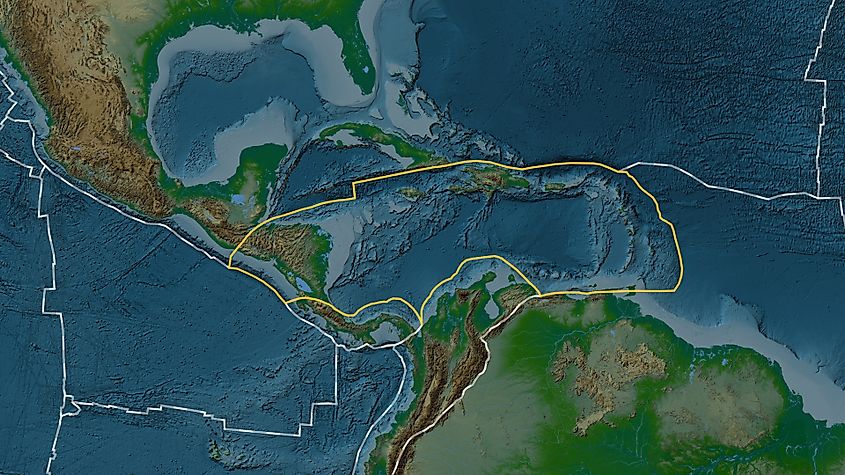
The Caribbean Plate is a relatively small tectonic plate situated between North and South America, covering most of the Caribbean Sea as well as the Greater and Lesser Antilles islands. This oceanic plate is surrounded by intricate fault systems and subduction zones, notably the Puerto Rico Trench to the north and ongoing subduction along its eastern edge, resulting in significant seismic activity and volcanic risks throughout the Caribbean. The movement of the plate causes frequent earthquakes, which threaten major population centers and vital infrastructure across the Caribbean islands, while active volcanism impacts islands such as Montserrat, Dominica, and others in the Lesser Antilles volcanic arc.
Cocos Plate - 2,900,000 sq km
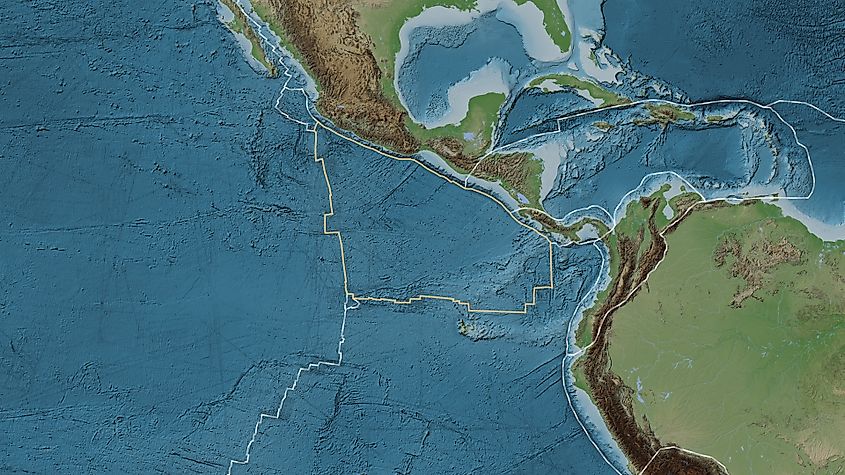
The Cocos Plate is a small oceanic tectonic plate situated off the Pacific coast of Central America, extending from southern Mexico to Costa Rica. This relatively young plate is currently being actively subducted beneath the North American and Caribbean plates along the Middle America Trench, making it one of the most seismically active areas in the Western Hemisphere. The subduction process leads to frequent earthquakes and has given rise to the volcanic arc that traverses Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica, featuring numerous active volcanoes that present ongoing risks to local populations. Furthermore, the Cocos Plate's continual descent beneath the continental plates aids in the formation of deep ocean trenches and affects tsunami risk along Central America's Pacific coast. This makes it a vital geological feature for understanding natural disaster preparedness and volcanic monitoring in this strategically important region that connects North and South America.
Caroline Plate - 1,700,000 sq km

The Caroline Plate is a small oceanic tectonic plate located in the western Pacific Ocean, situated between the Philippine Sea Plate to the west and the Pacific Plate to the east. This relatively minor plate encompasses parts of Micronesia, including the Federated States of Micronesia and portions of the Caroline Islands chain, and is characterized by complex interactions with surrounding larger plates. The Caroline Plate is being subducted along its northern boundary beneath the Philippine Sea Plate, contributing to the seismic activity in the region, while its eastern margin interacts with the Pacific Plate through a series of transform faults and spreading centers. Although smaller and less geologically active than major plates, the Caroline Plate's movements influence volcanic activity and earthquake pattern
Scotia Plate - 1,600,000 sq km
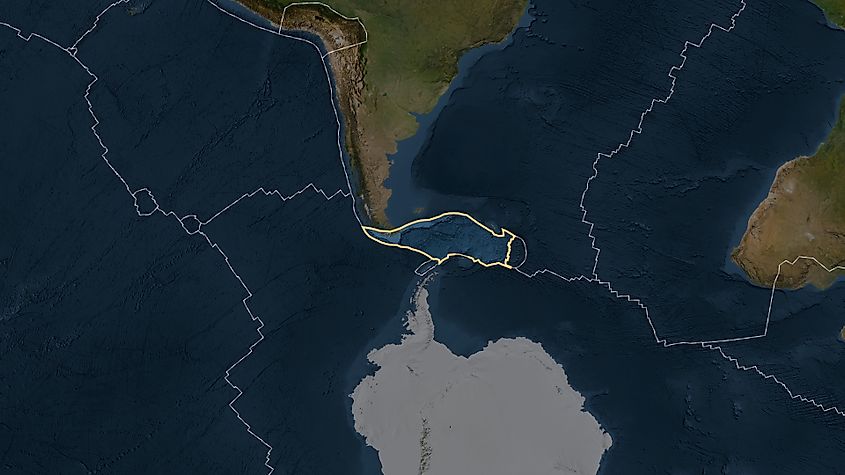
Scotia Plate is a small oceanic tectonic plate located in the South Atlantic Ocean between South America and Antarctica, encompassing the Scotia Sea and the South Sandwich Islands. This plate is bounded by the South American Plate to the north and the Antarctic Plate to the south, with its movement creating the Drake Passage—the narrow waterway that separates Cape Horn from Antarctica and serves as a critical chokepoint for global maritime navigation. The Scotia Plate's complex geology includes active spreading centers, transform faults, and subduction zones, particularly along the South Sandwich Trench where oceanic crust is being consumed, generating significant seismic activity and creating the volcanic South Sandwich Islands chain.
Burma Plate - 1,100,000 sq km
The Burma Plate is a minor tectonic plate located in Southeast Asia, encompassing Myanmar (Burma) and parts of the surrounding region between the Indian and Eurasian plates. This plate is being actively compressed and deformed due to the ongoing collision between the Indian Plate moving northward and the larger Eurasian Plate. The intense tectonic forces along the plate boundaries generate frequent earthquakes and contribute to significant seismic hazards throughout Myanmar and neighboring areas.
New Hebrides Plate - 1,100,000 sq km
The New Hebrides Plate is a small oceanic tectonic plate located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, encompassing the island nation of Vanuatu and the surrounding oceanic region. The intense tectonic activity generates frequent earthquakes and active volcanism throughout Vanuatu's island chain, making it one of the most seismically active regions in the Pacific Ring of Fire.
Bonus: Juan de Fuca Plate - 250,000 sq km
The Juan de Fuca Plate is one of the smallest of tectonic plates. At only 205,000 square km, it is technically not a minor plate but a microplate - but it may be one of the world’s most notorious ones. The Juan de Fuca Plate is part of the infamous Ring of Fire, a zone responsible for volcanic activity, orogeny, and earthquakes.
A List of Major and Minor Plates By Size
| Rank | Tectonic Plate | Type | Size (Square Km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pacific Plate | Major | 103,300,000 |
| 2 | North American Plate | Major | 75,900,000 |
| 3 | Eurasian Plate | Major | 67,800,000 |
| 4 | African Plate | Major | 61,300,000 |
| 5 | Antarctic Plate | Major | 60,900,000 |
| 6 | Indo-Australian Plate | Major | 58,900,000 |
| 7 | South American Plate | Major | 43,600,000 |
| 8 | Somali Plate | Minor | 16,700,000 |
| 9 | Nazca Plate | Minor | 15,600,000 |
| 10 | Philippine Sea Plate | Minor | 5,500,000 |
| 11 | Arabian Plate | Minor | 5,000,000 |
| 12 | Caribbean Plate | Minor | 3,300,000 |
| 13 | Cocos Plate | Minor | 2,900,000 |
| 14 | Caroline Plate | Minor | 1,700,000 |
| 15 | Scotia Plate | Minor | 1,600,000 |
| 16 | Burma Plate | Minor | 1,100,000 |
| 17 | New Hebrides Plate | Minor | 1,100,000 |