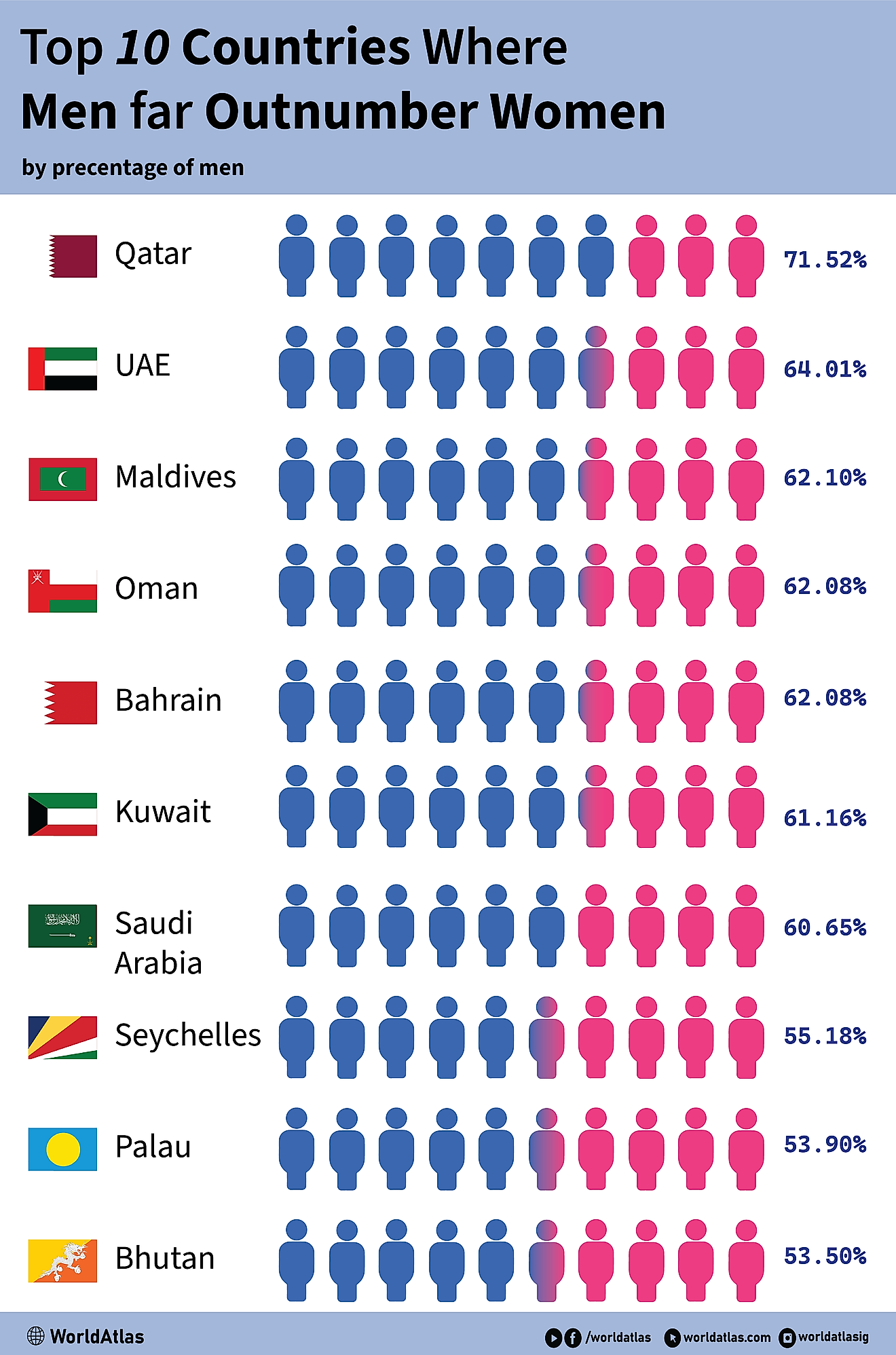
Leading Causes Of Death In Haiti
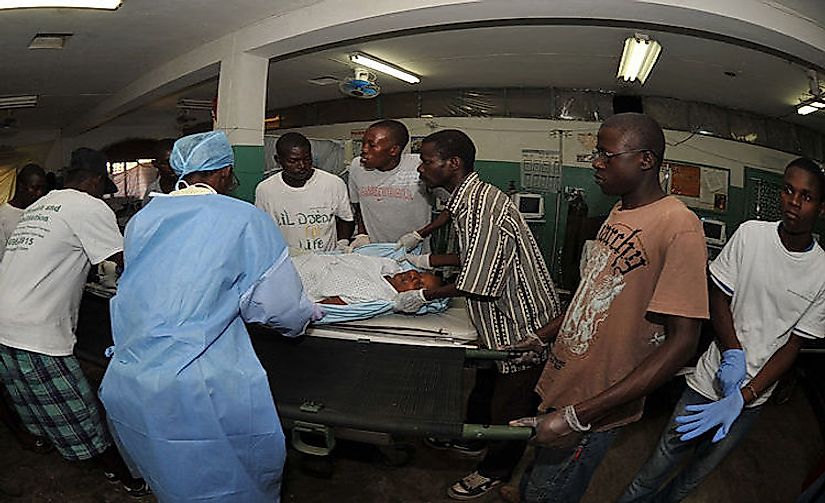
Haiti was discovered by Columbus in 1492 and by the late 1700's, Haiti was once one of the richest countries in the world. Haitian exports and economy were far superior to those of the United States of America during this time. Looking forward to the present day, Haiti is now considered a third world country and is the poorest country in the Western hemisphere. Haitian life expectancy is very low compared to the rest of the western world due to poor health facilities and infrastructure (sometimes these facilities are non-existent). Males can expect to live to 61.5 years of age, and females can expect to live to 65.5 years old. The infant mortality rate in Haiti is considered high at 52 deaths per 1000 live births. In contrast, the Dominican Republic, which is located on the same island as Haiti, has 26 deaths per 1000 live births. Haiti is always ranked at or near the bottom of the World Bank's ranking of health indicators.
Stroke
Stroke is the leading killer in Haiti, the country ranks seventh in the world for total strokes per capita, with 180 out of every 1000 deaths due to a stroke. As is true around the world, a developing country such as Haiti suffers more strokes than heart disease (which is the leading cause of death in Western nations). Approximately 12% of deaths in Haiti can be attributed to stroke.
HIV/AIDS
Haiti has the highest rate of HIV/AIDS outside of Africa. Approximately 5000 children are born with the virus annually. HIV/AIDS complications cause 20% of child deaths in Haiti. Estimates of HIV/AIDS prevalence within the population have been as high as 5% in urban areas and 3% in rural areas.
Coronary Heart Disease
Coronary heart disease has emerged as the fourth largest cause of death in the country. Approximately 95 deaths out of every 1000 can be attributed to heart disease. Although this disease in the leading cause of death in Western nations, Haiti is only ranked 77th in the world when it comes to mortality related to heart disease.
Diarrheal Diseases
Diarrheal diseases (5.1% of deaths), tuberculosis (2.8%), and lower respiratory infections (8.6%), such as pneumonia and influenza, are the leading causes of death in infants and adolescents in Haiti. In a developed country, these diseases would never be as prevalent as they are in Haiti. The lack of healthcare and sanitary facilities make it extremely hard for these types of diseases to be treated and contained.
Diabetes
Haiti ranks 13th in the world in deaths caused by diabetes, with this disease causing 72 out of every 1000 deaths (4.9% of deaths in Haiti). The high rate of mortality due to Diabetes is caused by mismanagement of the disease, lack of insulin, and traditional Haitian diets, as well as a lack of cultural understanding with regards on how to control and manage the disease.
Interpersonal Violence
Interpersonal violence causes 3.8% of deaths in Haiti. Interpersonal violence can be defined as domestic or criminal as well as sexual assault, which is all prevalent in Haiti. Physical abuse of women and children is quite common. 35 out of every 1000 deaths are caused by interpersonal violence, which reflects the lack of punishment for these criminal acts.
Preterm Birth Complications
Preterm birth complications (3.1% of Haitian deaths) and birth asphyxia/trauma (2.5%) reflect the lack of health and support systems for mothers and children in Haiti. In Haiti, it is estimated that only a quarter (25%) of births are attended by a qualified physician or nurse. This lack of professional guidance during childbirth also causes the high rate of birth asphyxia and trauma, which is when a child who is being born does not get enough oxygen during the birthing process. This can also be caused by premature birth, as the child's organs have not yet fully developed. The lack of facilities for preterm and sick babies causes a lot of health problems; sadly many premature babies die every year in Haiti.
Access To Health Facilties
With 80% of the Haitian population living below the poverty line and less than half of the population has access to clean drinking water. The World Heath Organization (WHO) estimates that only 43% of the Haitian population receives the correct immunizations. A lot of preventable diseases often cause deaths, which is caused by the lack of health and sanitation infrastructure (only 1.3 hospital beds per 1000 people). Additionally, the lack of education about health issues within Haiti cause a lot of health related problems. Most rural Haitians have no access to health facilities. In addition to these problems, Haiti has a very low rate of physicians and nurses at only 25 physicians and 11 nurses per 100,000 people.
Leading Causes Of Death In Haiti
| Rank | Cause of Death | % Of Total Deaths |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Stroke | 12% |
| 2 | Lower Respiratory Infections | 8.6% |
| 3 | HIV/AIDS 9% | 8.3% |
| 4 | Ischemic Heart Disease 6% | 6.3% |
| 5 | Diarrheal Disease | 5.1% |
| 6 | Diabetes | 4.9% |
| 7 | Interpersonal Violence | 3.8% |
| 8 | Preterm Birth Complications | 3.1% |
| 9 | Tuberculosis | 2.8% |
| 10 | Birth Asphyxia & Trauma | 2.5% |