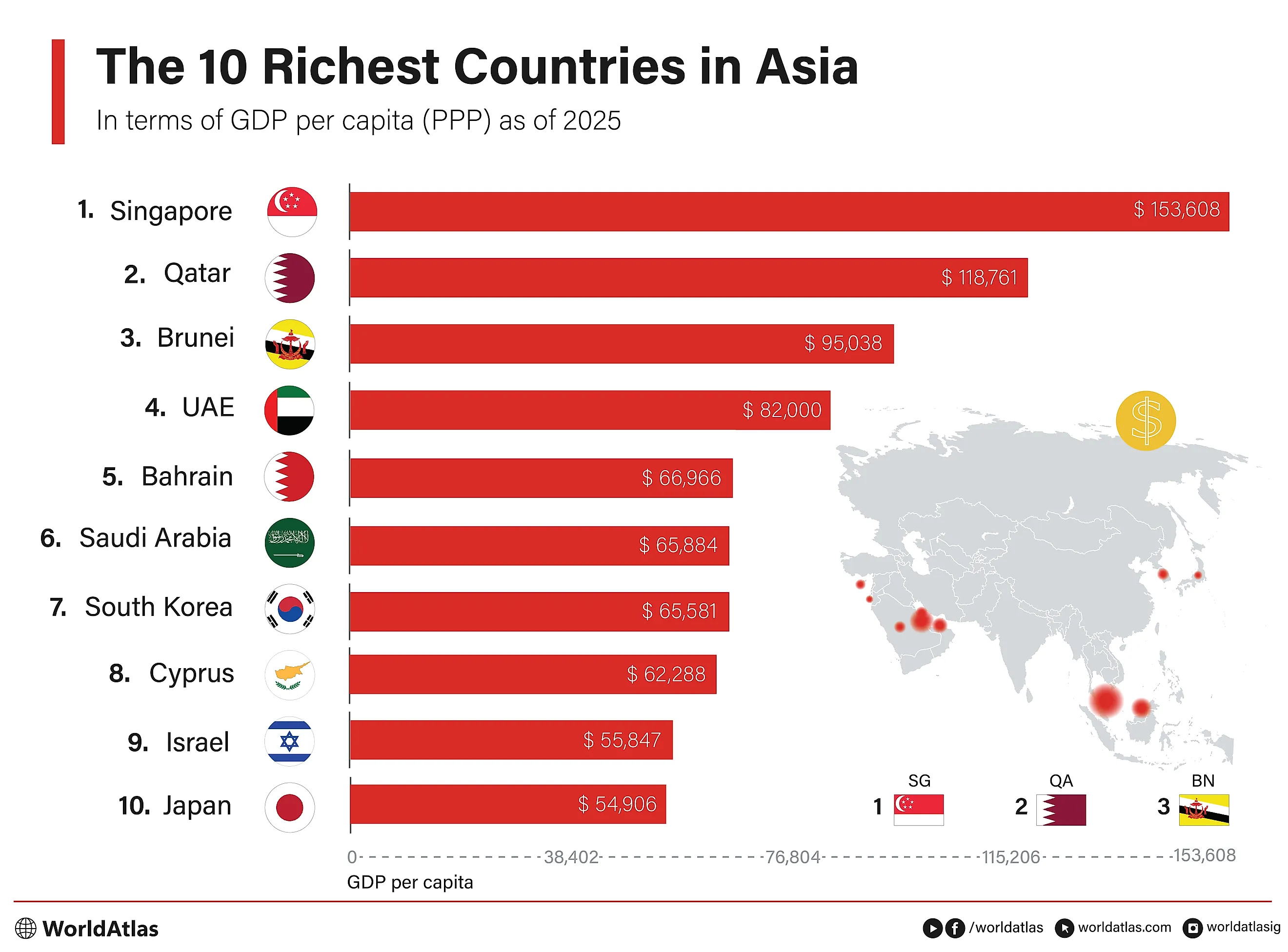
The Richest Countries in Asia
Asia is home to some of the world's richest countries by GDP per capita in purchasing power parity (PPP). These economies range from global financial powerhouses like Singapore to resource-rich countries such as Qatar and the United Arab Emirates. Despite the variety in size and population, these Asian countries share commonalities in strategic economic planning, technological innovation, and robust trade practices that have catapulted them onto the global stage as economic leaders.
Below, we delve into the ten richest countries in Asia by GDP per capita (PPP) as of 2025. You will notice that these nations excel through specialized sectors such as finance, technology, and petrochemicals, underpinned by strong infrastructures and forward-thinking policies that ensure their sustained economic growth and high standards of living. This year, Singapore, Qatar, and Brunei rank as the three richest countries in Asia, with a GDP/Capita in PPP of $153,608, $118,761, and $95,038, respectively.
10 Richest Countries In Asia
| Rank | Country | GDP/Capita (PPP) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Singapore | $153,608.8 |
| 2 | Qatar | $118,761.7 |
| 3 | Brunei Darussalam | $95,038.77 |
| 4 | United Arab Emirates | $82,000.37 |
| 5 | Bahrain | $66,966.5 |
| 6 | Saudi Arabia | $65,884.71 |
| 7 | South Korea | $65,581.6 |
| 8 | Cyprus | $62,288.05 |
| 9 | Israel | $55,847.399 |
| 10 | Japan | $54,906.86 |
Jump to the list of all Asian countries ranked by GDP/Capita (PPP)
1. Singapore - $153,608 GDP/Capita (PPP)

Singapore has the second-highest GDP per capita levels in PPP globally, driven by its status as an international finance, trade, and technology hub. Despite limited natural resources, Singapore leveraged its strategic geographic location to establish itself as a leading global port and trading center, specializing in high-value intermediary trade, such as refining imported goods for re-export. The city-state's economy is renowned for its openness, business-friendly regulations, low corruption, and attractive investment climate, drawing significant foreign direct investment from global corporations and financial institutions.
Major industries include electronics, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, finance, petroleum refining, marine engineering, and tourism. Singapore also excels in wealth management, serving as Asia’s financial nucleus. Limited land availability has led to innovative practices like vertical farming and agrotechnology parks to secure food supplies, making Singapore among the world’s most food-secure nations. Its rapid transformation into a prosperous, developed nation within mere decades, particularly under Prime Minister Lee Kuan Yew’s leadership, is frequently hailed as an economic "miracle," solidifying its position among the richest countries globally.
2. Qatar - $118,761 GDP/Capita (PPP)

Qatar, consistently among Asia's richest nations by GDP per capita (PPP), owes its immense wealth to its vast natural gas and petroleum reserves, holding the world's third-largest proven gas reserves. The hydrocarbon sector contributes over 60% of GDP, more than 70% of government revenues, and approximately 85% of exports. Qatar strategically invests its substantial resource revenues through initiatives like Qatar National Vision 2030, aiming for economic diversification beyond hydrocarbons.
The nation’s economy survived regional sanctions, largely due to robust trade relationships with major Asian economies, notably Japan, South Korea, India, and China. QatarEnergy’s ambitious North Field LNG expansion projects underline Qatar’s intent to significantly increase LNG production, securing its position as the leading global LNG exporter. Additionally, the state promotes industrial diversification, notably in petrochemicals, fertilizers, and steel, supported by infrastructure investments around Ras Laffan and Mesaieed industrial cities. Despite challenges such as fluctuating oil markets, Qatar’s prudent economic policies and extensive sovereign wealth investments bolster its status as one of Asia’s wealthiest economies.
3. Brunei - $95,038 GDP/Capita (PPP)

Brunei ranks among Asia's richest nations due to its substantial wealth derived from oil and natural gas exports. Petroleum and liquefied natural gas (LNG) dominate its economy, contributing over 50% of the nation's GDP and nearly all export revenues. With a relatively small population, Brunei enjoys a high GDP per capita, placing it third in Asia by purchasing power parity (PPP). The country's economic strength is reinforced by significant foreign reserves managed by the Brunei Investment Agency, providing financial security despite fluctuations in global oil prices.
Efforts to diversify the economy beyond hydrocarbons have seen limited progress, although investments have been made in petrochemicals, agriculture, fisheries, and halal industries. Brunei actively encourages foreign investment, offering incentives such as tax exemptions for pioneering enterprises. However, economic growth remains sensitive to oil price volatility and production rates, reflecting ongoing reliance on hydrocarbons. The government provides generous welfare services, subsidizing healthcare, housing, and food, underpinning a stable social environment.
4. United Arab Emirates - $82,000 GDP/Capita (PPP)

The United Arab Emirates (UAE) ranks among Asia's richest countries, driven predominantly by its petroleum and natural gas reserves, particularly in Abu Dhabi. Historically reliant on oil revenues, the UAE has pursued aggressive diversification, notably in Dubai, focusing on tourism, finance, real estate, and logistics. Dubai's proactive diversification has positioned it as a global business hub, hosting the Dubai International Financial Centre and major tourism and real estate projects such as Burj Khalifa and Palm Islands.
The UAE has one of the region's most open economies, with advanced infrastructure, high competitiveness, and a business-friendly environment. Despite diversification efforts, oil exports still significantly fund the government's budget. The COVID-19 pandemic temporarily impacted the UAE's economy, prompting structural reforms to enhance resilience. Recently, the UAE accelerated investment in renewable energy and nuclear power, exemplified by projects like Masdar City and Barakah nuclear power plant.
Continued investment in trade, tourism, infrastructure, and sustainable energy illustrates the UAE’s strategic shift toward long-term economic stability, reinforcing its status as a wealthy, dynamic economy within Asia.
5. Bahrain - $66,966 GDP/Capita (PPP)

Bahrain, one of Asia's wealthiest countries by GDP per capita, primarily owes its economic prosperity to petroleum and natural gas, which contribute significantly to government revenues and exports. However, unlike its resource-rich neighbors, Bahrain possesses limited oil reserves, prompting aggressive diversification efforts, notably in banking, finance, and tourism. The capital, Manama, has become an influential global financial hub, specializing in Islamic finance, attracting numerous international banks and financial institutions.
Bahrain's government actively supports economic liberalization, becoming the first Gulf state to sign a free trade agreement with the United States. Despite challenges posed by fluctuating oil prices, Bahrain maintains a robust economy through strategic investments in infrastructure, aluminum production, petrochemicals, and ship repair industries. The government also promotes foreign investment, expanding sectors that permit full foreign ownership.
The country's economic strategy emphasizes reducing reliance on hydrocarbons, reflected in significant growth within the non-oil sector, especially finance and tourism. Supported by modern infrastructure and pro-business policies, Bahrain continues its trajectory toward sustainable economic diversification, strengthening its position among Asia's richest nations.
6. Saudi Arabia - $65,884 GDP/Capita (PPP)

Saudi Arabia’s vast petroleum reserves, the second-largest globally, have long underpinned the kingdom's wealth and global influence. Oil accounts for roughly 30% of GDP, over half of government revenues, and the vast majority of exports. Saudi Aramco, the state-owned oil giant, is the world’s largest oil exporter and manages these critical resources.
However, recognizing the risks of oil dependence, Saudi Arabia initiated the ambitious Vision 2030 strategy to diversify its economy. Efforts have focused on expanding sectors such as petrochemicals, manufacturing, and mining, alongside investments in infrastructure, tourism, and technology. The kingdom has attracted significant foreign investment by liberalizing trade regulations and permitting 100% foreign ownership in selected industries.
Despite diversification initiatives, challenges persist, including a high youth unemployment rate, dependency on foreign labor, and bureaucratic inefficiencies. Nevertheless, substantial financial reserves, strategic economic reforms, and investments in mega-projects have solidified Saudi Arabia’s status as an economic powerhouse in Asia, with GDP per capita among the region's highest at over $33,000 nominally, projected for 2025.
7. South Korea - $65,581 GDP/Capita (PPP)

South Korea’s economy is among the most advanced in Asia, ranking as the 12th largest globally by nominal GDP ($1.95 trillion projected for 2025). Its remarkable transformation from a war-torn nation in the 1950s to a high-income, developed economy within decades, dubbed the "Miracle on the Han River," is primarily attributed to strategic investments in technology, manufacturing, and export-led industrialization. South Korea is a global leader in electronics, shipbuilding, automotive production, telecommunications, and steel, driven by world-renowned conglomerates like Samsung, Hyundai, LG, and SK.
The country’s robust economic performance is supported by substantial investments in research and development, which accounts for nearly 5% of GDP, among the highest globally. South Korea is recognized for its highly educated workforce and sophisticated infrastructure. Challenges facing the economy include a declining and rapidly aging population, high youth unemployment, and persistent economic inequality.
South Korea maintains strong resilience during global economic downturns, buoyed by substantial fiscal reserves, relatively low government debt (around 40% of GDP), and continued innovation in high-tech industries.
8. Cyprus - $62,288 GDP/Capita (PPP)

Cyprus's economy is classified as high-income and advanced by the World Bank and IMF and has undergone significant transformation since adopting the Euro in 2008. The nation faced a financial crisis in 2013, resulting in a €10 billion bailout and a controversial haircut on uninsured deposits, leading to a recession that lasted until 2015. Post-crisis, Cyprus has seen a steady economic recovery, driven by its service-based economy which includes tourism, business services, and light manufacturing.
With a GDP per capita of $40,557 (nominal) and $62,288 (PPP) projected for 2025, Cyprus ranks well in global economic standings. The services sector dominates the economy, contributing approximately 85.5% to the GDP, followed by industry and agriculture. Cyprus enjoys a "very high" Human Development Index score and a relatively low unemployment rate of 4.9% as of February 2025. The nation's trade dynamics are also noteworthy, with significant import and export activities, particularly with European Union countries.
Investment flows from the West into Eastern Europe, and increasingly into Asia and the Middle East, characterize Cyprus as a pivotal financial hub, although it has faced criticism for allegedly allowing sanction breaches. The country's legal and business frameworks are well-aligned with EU standards, providing a favorable environment for international finance and investment.
9. Israel - $55,847 GDP/Capita (PPP)

Israel's economy is characterized by its dynamic free-market system, strong technological innovation, and robust venture capital sector. With a projected GDP of $550.91 billion (nominal, 2025) and a GDP per capita of $54,379, Israel has developed rapidly from an agriculturally driven economy into a global technology and innovation hub. The country has the world's second-largest concentration of startup companies after the U.S., hosting major R&D centers for leading corporations such as Intel, Microsoft, and Google.
Despite limited natural resources, Israel has leveraged its highly educated workforce and entrepreneurial culture to create competitive industries in technology, pharmaceuticals, defense, and diamond processing. Its high-tech sector, known as "Silicon Wadi," is a key economic driver. Additionally, recent discoveries of offshore natural gas reserves promise greater energy independence.
Economic challenges include income inequality, poverty rates of about 20%, and demographic pressures from growing ultra-Orthodox populations with low workforce participation. Geopolitical tensions and recent conflicts have impacted economic forecasts, leading to reduced growth estimates and downgraded credit ratings.
10. Japan - $54,906 GDP/Capita (PPP)

Japan is home to the world’s fourth-largest economy with a nominal GDP projected at $4.39 trillion in 2025. Known for its highly industrialized, innovative, and service-oriented economy, Japan leads globally in automobile manufacturing, electronics, robotics, and advanced technology, with Toyota as the world’s largest carmaker. Despite limited natural resources, Japan maintains significant global influence as the world’s largest creditor nation, with extensive foreign reserves exceeding $1.2 trillion. The Tokyo Stock Exchange is Asia's second-largest and globally ranks third by market capitalization.
Historically, Japan experienced rapid economic growth after World War II, achieving the world's second-largest economy status by 1968 and sustaining robust trade surpluses. However, following the bursting of the 1990s asset-price bubble, Japan faced prolonged economic stagnation known as the "Lost Decades," characterized by deflation and slow growth. Today, it faces substantial economic challenges, including a high public debt of approximately 260% of GDP and a declining, aging population.
Countries In Asia Ranked By GDP/Capita in PPP
| Rank | Country | GDP/Capita (PPP) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Singapore | $153,608.8 |
| 2 | Qatar | $118,761.7 |
| 3 | Brunei Darussalam | $95,038.77 |
| 4 | United Arab Emirates | $82,000.37 |
| 5 | Bahrain | $66,966.5 |
| 6 | Saudi Arabia | $65,884.71 |
| 7 | South Korea | $65,581.6 |
| 8 | Cyprus | $62,288.05 |
| 9 | Israel | $55,847.4 |
| 10 | Japan | $54,906.86 |
| 11 | Kuwait | $51,287.07 |
| 12 | Kazakhstan | $43,610.17 |
| 13 | Malaysia | $43,095.31 |
| 14 | Oman | $42,361.9 |
| 15 | Turkey | $41,913.65 |
| 16 | Maldives | $35,984.3 |
| 17 | Georgia | $29,533.15 |
| 18 | China, People's Republic of | $28,008.2 |
| 19 | Turkmenistan | $27,669.54 |
| 20 | Thailand | $26,416.43 |
| 21 | Azerbaijan | $25,476.59 |
| 22 | Armenia | $24,968.34 |
| 23 | Mongolia | $20,514.33 |
| 24 | Iran | $20,368.82 |
| 25 | Bhutan | $18,113.51 |
| 26 | Indonesia | $17,520.28 |
| 27 | Vietnam | $17,348.93 |
| 28 | Iraq | $15,256.47 |
| 29 | Philippines | $12,913.37 |
| 30 | Uzbekistan | $12,224.49 |
| 31 | India | $11,937.8 |
| 32 | Jordan | $11,380 |
| 33 | Bangladesh | $10,366.62 |
| 34 | Lao P.D.R. | $10,112.55 |
| 35 | Cambodia | $8,677.668 |
| 36 | Kyrgyz Republic | $8,134.34 |
| 37 | Pakistan | $6,921.519 |
| 38 | Tajikistan | $5,788.797 |
| 39 | Nepal | $5,613.554 |
| 40 | Myanmar | $5,330.054 |
| 41 | Timor-Leste | $4,862.772 |
| 42 | Yemen | $2,017.474 |
| - | Afghanistan | no data |
| - | Lebanon | no data |
| - | Sri Lanka | no data |
| - | North Korea | no data |
| - | Palestine | no data |
| - | Syria | no data |
Based on IMF data for 2025
Discover More Rich Countries
The Richest Countries In The World
Luxembourg, Singapore, and Ireland stand out as the richest countries for 2025, with GDP/Capita in PPP of $154,910, $153,610, and $131,550, respectively.
The Richest Countries In Europe
Luxembourg, Ireland, and Norway rank as the three richest countries in Europe for 2025 with a GDP/Capita in PPP of $154,914, $131,548, and $106,540, respectively.
The Richest Countries In North America
The United States, Canada, and Panama are the richest countries in North America for 2025, with GDP/Capita in PPP of $89,680, $64,570, and $42,770, respectively.
The Richest Countries In South America
Guyana, Uruguay, and Chile are the richest countries in South America for 2025, with GDP/Capita in PPP of $91,380, $36,010, and $34,790, respectively.
The Richest Countries In Africa
Seychelles, Mauritius, and Gabon are the richest countries in Africa for 2025, with GDP/Capita in PPP of $43,070, $33,950, and $24,680, respectively.
The Richest Countries In South Asia
The Maldives, Bhutan and India are the richest countries in South Asia for 2025, with GDP/Capita in PPP of $35,980, $18,110, and $11,940, respectively.











