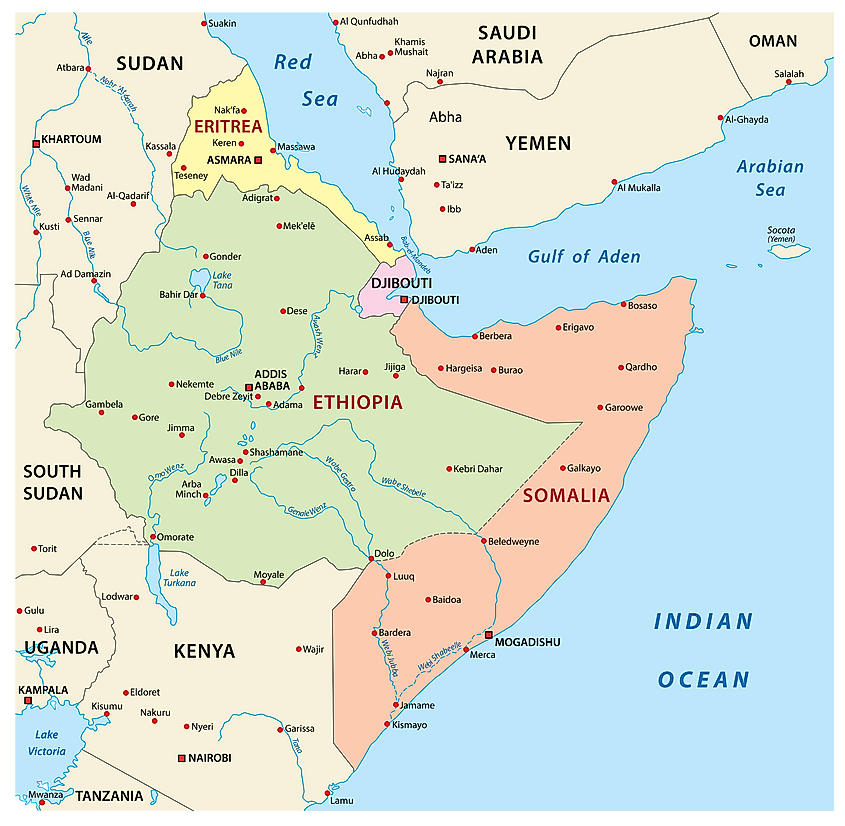
Gulf Of Aden
The Gulf of Aden is an extension of the Indian Ocean, tucked between the Arabian Peninsula and the African continent. The gulf connects the Red Sea to the Arabian Sea via the Strait of Bab el Mandeb. It has a long history as part of the Erythraean Sea and a critical oil shipping route linking the Far East and Europe. The Gulf of Aden is also a critical part of the Suez Canal shipping route, which connects the Red Sea and the Mediterranean Sea. Thus, the gulf’s importance declined in the 1960s when the Egyptian government temporarily closed the Suez Canal for renovation.
Origin Of The Name
The name “Gulf of Aden” is a fairly new and modern name given to the gulf. The gulf is named after “Aden,” a port city on Yemen’s coast. However, in ancient days, the water body was considered part of the Erythraean Sea. It was also referred to as “the Gulf of Berbera” by various sources, including Ibn Majid, an Arab navigator, and Abu’l-Fida, a Kurdish geographer. Berbera is a prominent port city in the Sahil region
Geography
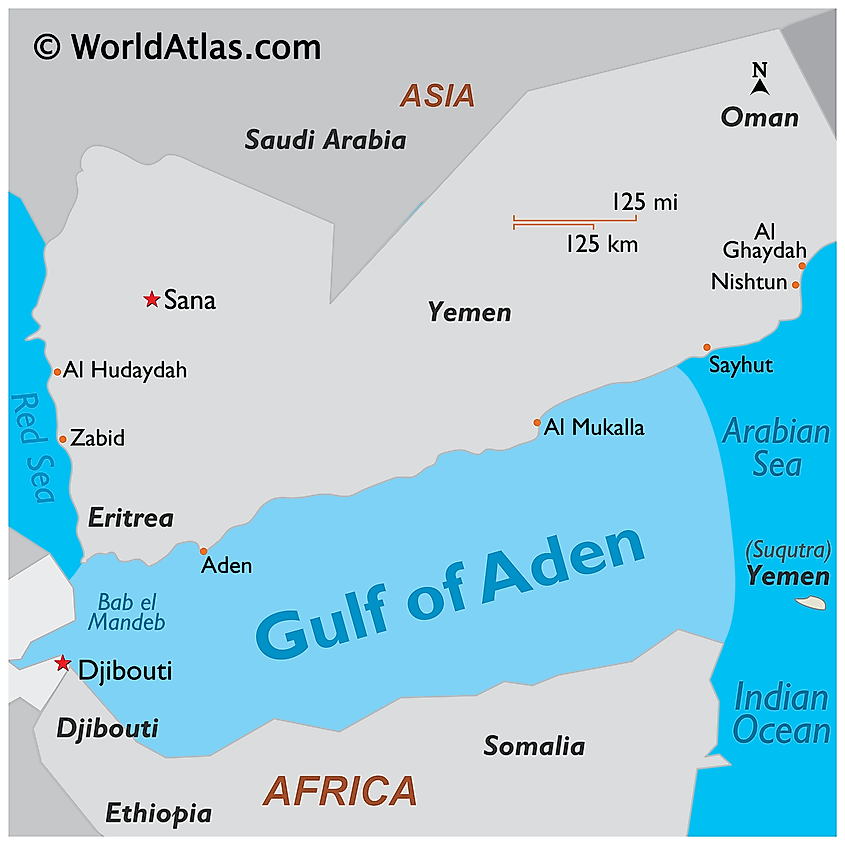
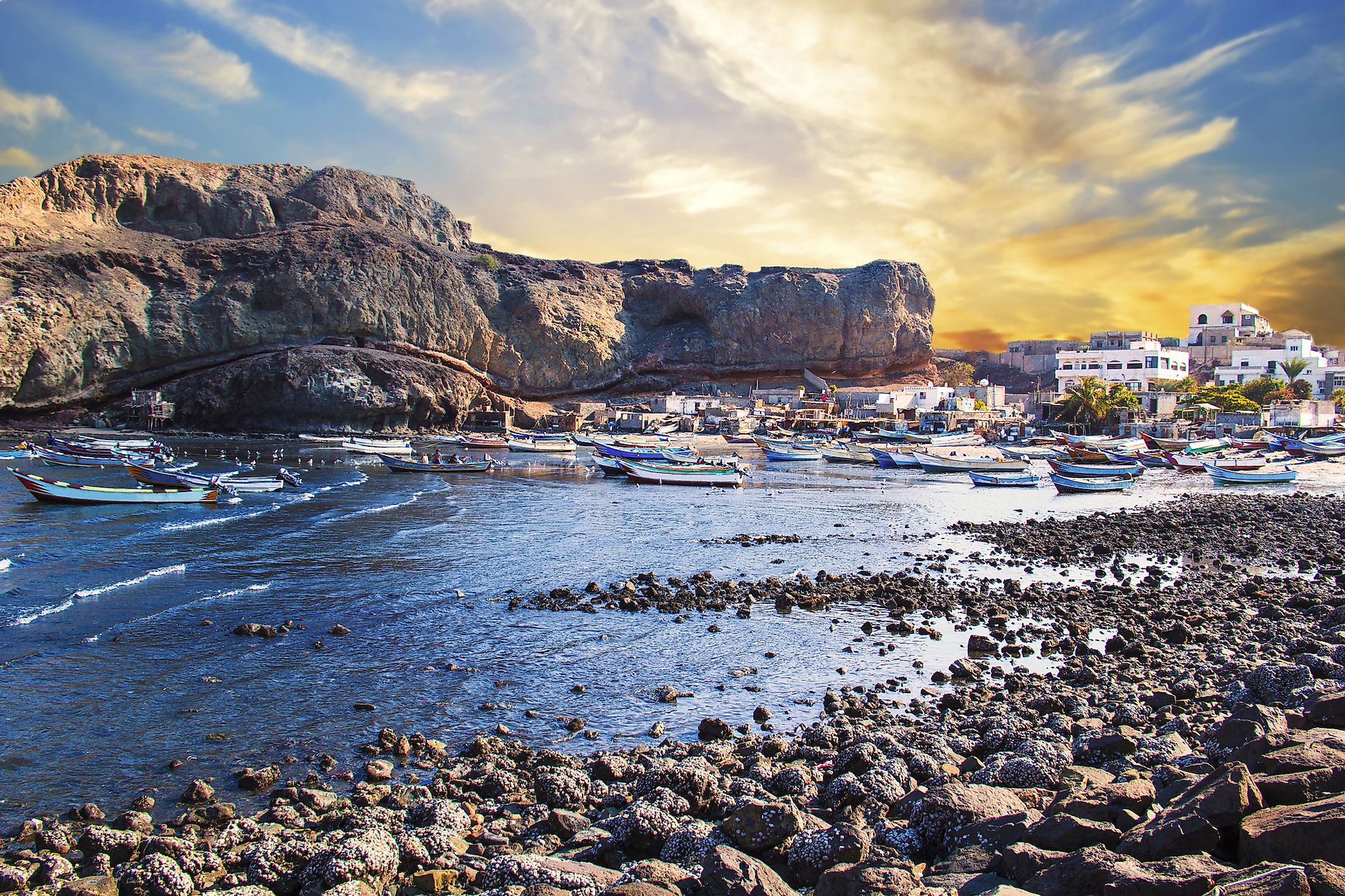
The Gulf of Aden is located between the Arabian Peninsula (north) and the Horn of Africa (south). It is bounded to the south by Somali and the Socotra Islands, north by Yemen, east by the Arabian Sea, and west by Djibouti. The gulf is connected to the Somali Sea to the south by the Guardafui Channel, and to the Red Sea on the west by the Strait of Bab el Mandeb. Some of the major cities near the gulf include Aden, Mukalla, Ahnwar, Balhaf, Berbera, Bosaso, and Djibouti City.
The Gulf of Aden is approximately 900 km long and 500 km wide and covers roughly 410,000 square kilometers. It has an average depth of 500 meters and a maximum depth of 2,700 meters. The water temperature ranges from 59 degrees Fahrenheit to 82 degrees Fahrenheit, depending on the monsoons and seasons. The salinity varies from 35.3% (near the Somali coast) to 37.3% (in the gulf’s central region).
Economy

The Gulf of Aden is mainly shared by three countries-Yemen, Somali, and Djibouti- whose exclusive economic zones extend into the water body. Somali’s EEZ extends 831,059 square kilometers, Yemen covers about 509,000 square kilometers, and Djibouti has less than 10,000 square kilometers. The Gulf of Aden is an important shipping route, with over 20,000 vessels passing through the Gulf annually, making it an important seaway in the world economy.
The main commodity transported through the gulf is the Persian Gulf oil, with about 11% of the world’s total petroleum transported over water passing through it. India alone ships over $60 billion in export and $50 billion in imports through the Gulf of Aden. The major harbors along the gulf include Aden, Mukalla, Djibouti City, Balhaf, and Berbera.
Dangers
In recent years, the Gulf of Aden has media and international attention due to refugee smuggling, terrorism, and piracy. In 2000, a US vessel was nearly destroyed and sunk by a suicide bomber, while in 2002 MIV Limburg, a French oil tanker, was also attacked. However, the attacks have declined since 2013. Hundreds of illegal emigrants have also drowned while trying to cross the Gulf into Yemen.