Maps of US Virgin Islands
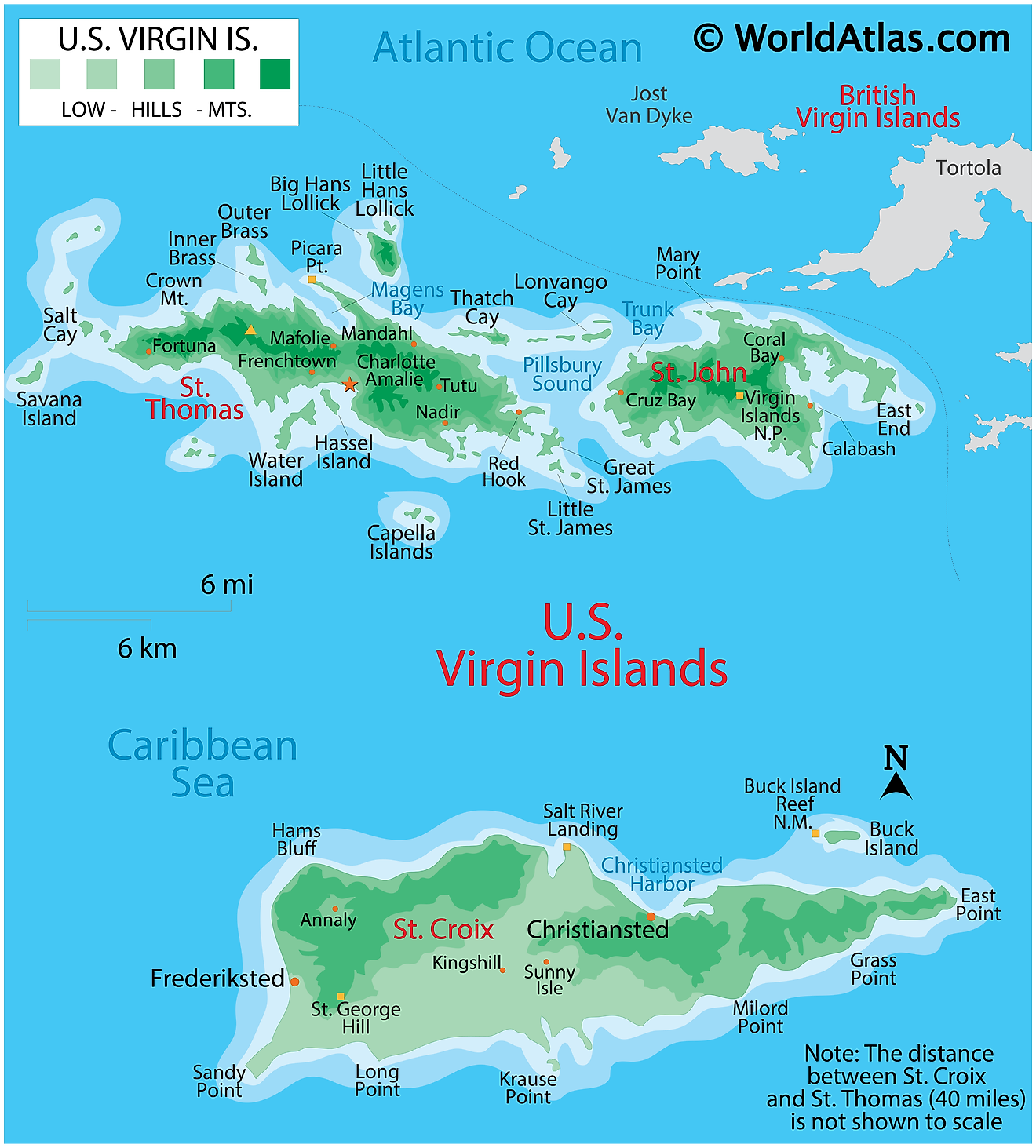
The U.S. Virgin Islands is an organized and unincorporated island territory of the United States of America, located between the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea.
Covering a total land area of 346.36 sq. km. As observed on the physical map of the US Virgin Islands above, the territory consists of three main islands: Saint Thomas, Saint John, Saint Croix, as well as several dozen smaller islands.
Most of the islands are volcanic in origin and as observed on the map, the islands of Saint Thomas and Saint John are quite hilly. Saint Croix is the largest of the US Virgin Islands and comparatively has a much flatter terrain.
The highest point is Crown Mountain on Saint Thomas at 1,555 ft. (474 m). The lowest point is at the sea level.
Scattered streams help to drain the islands, while white sand beaches and coral reefs are common.
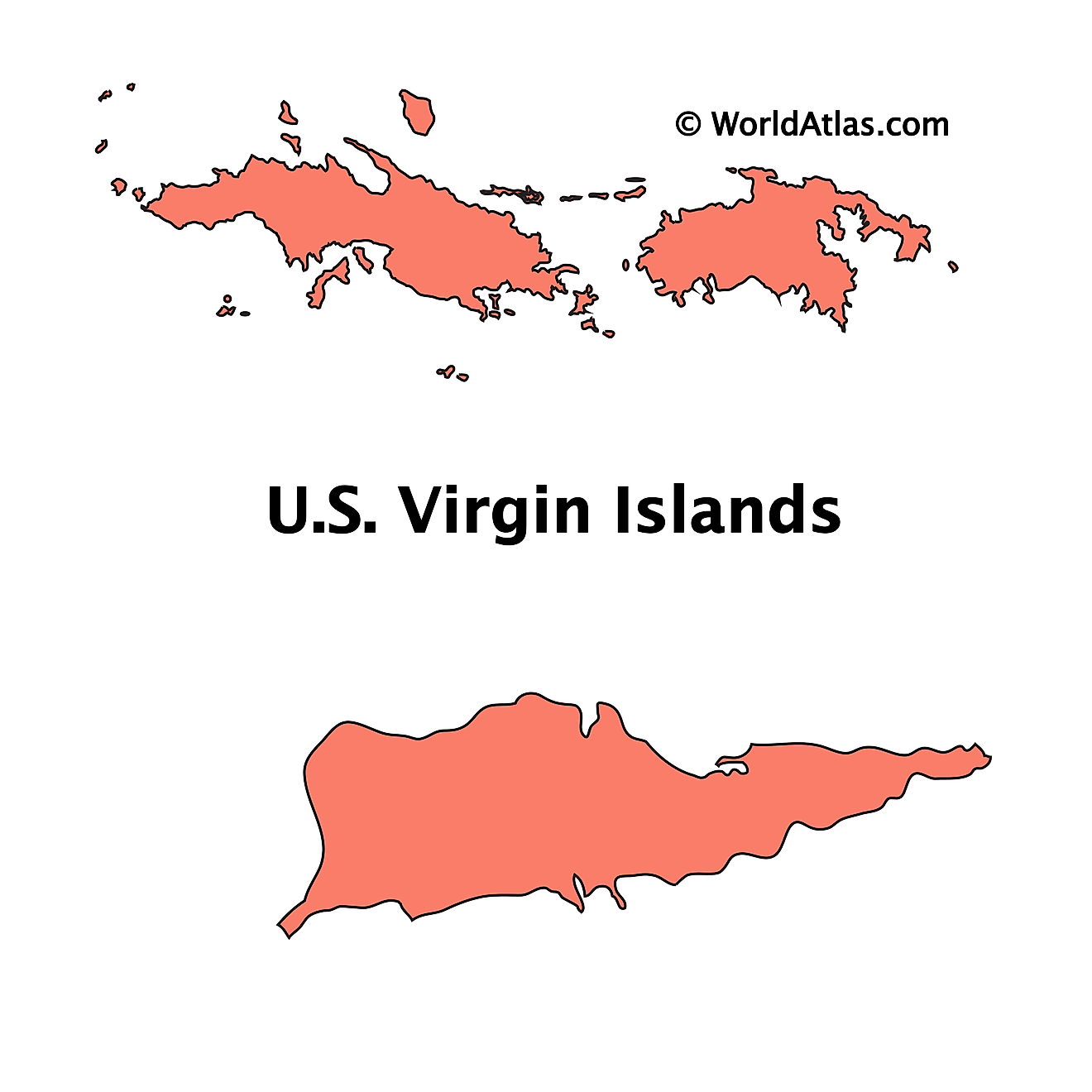
Islands of US Virgin Islands Map
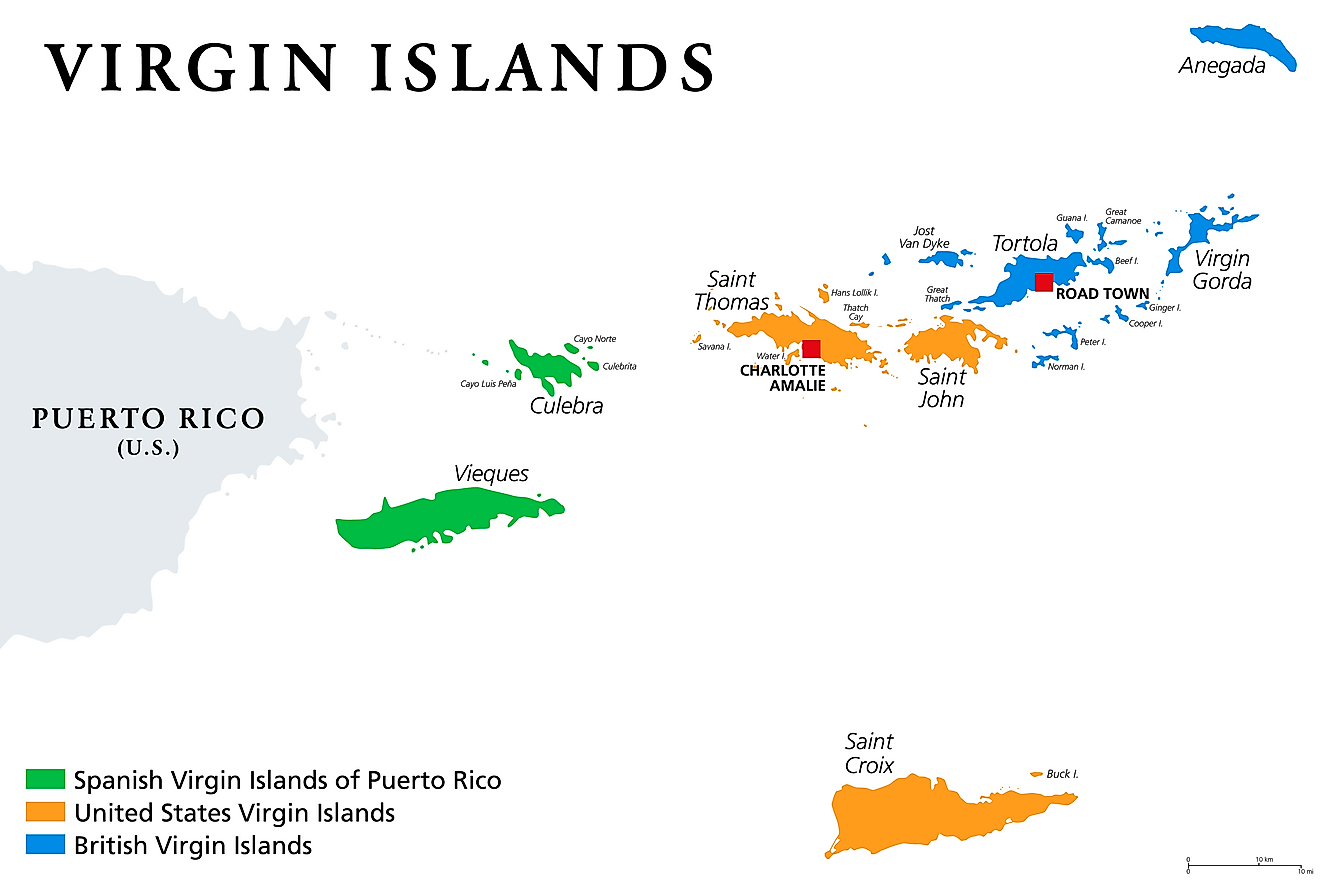
There are no first-order administrative divisions of the US Virgin Islands as defined by the US Government, but there are 3 islands at the second order; Saint Croix, Saint John, Saint Thomas.
Where is US Virgin Islands?
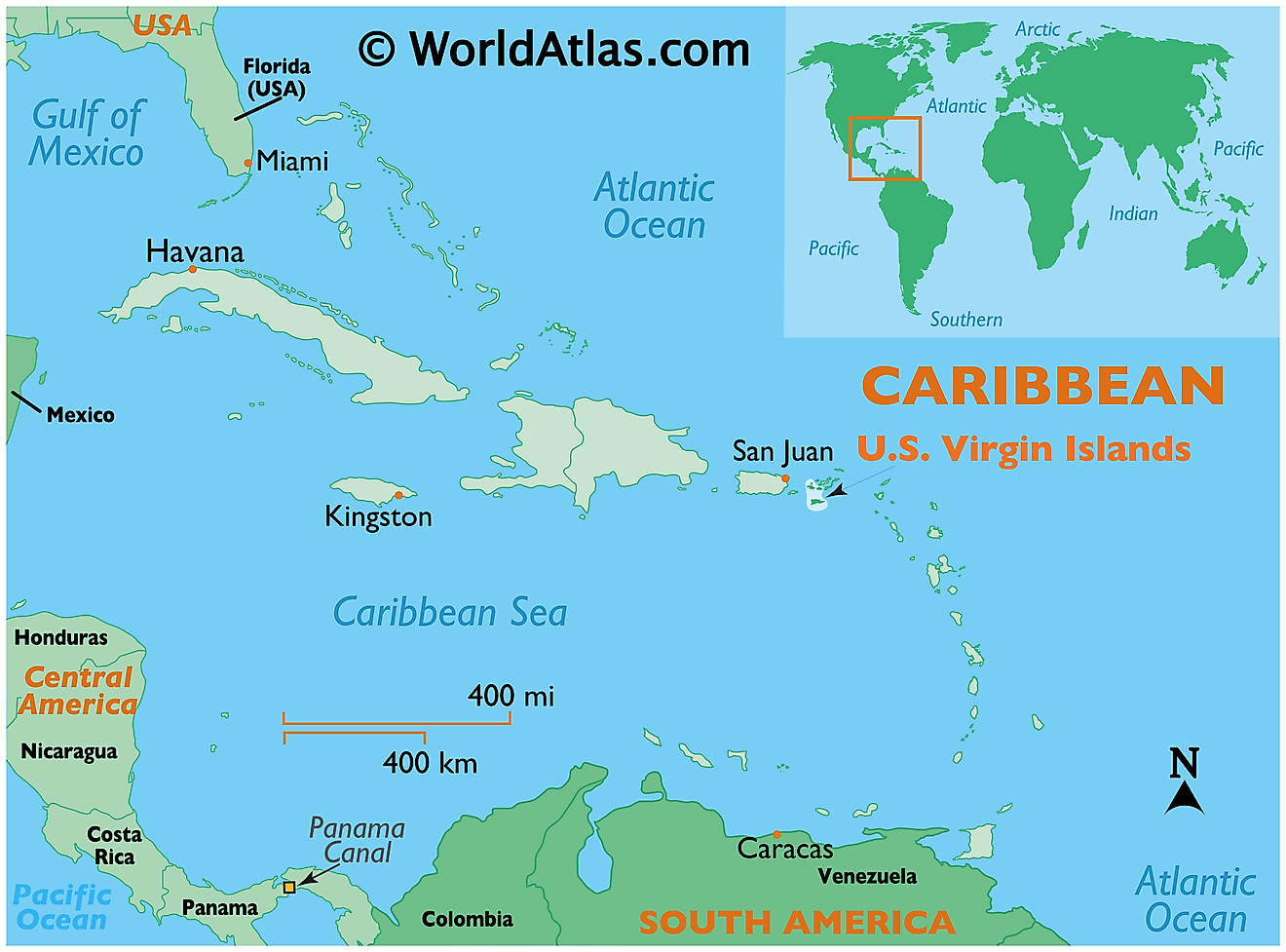
The U.S. Virgin Islands is an organized and unincorporated island territory of the United States of America. Geographically, a part of the archipelago of Virgin Islands, the island territory is situated in the Leeward islands of the Lesser Antilles chain in the north-eastern Caribbean Sea. The island territory is positioned both in the Northern and Western hemispheres of the Earth. The U.S. Virgin Islands are located in the east of Puerto Rico; in the southeast of Miami and in the west of British Virgin Islands.
Regional Maps: Map of North America
Outline Map of US Virgin Islands
The above blank map represents The U.S. Virgin Islands - an unincorporated island territory of The United States of America, located between the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea. The above map can be downloaded, printed and used for geographical educational purposes.
The above outline map represents The U.S. Virgin Islands - an unincorporated island territory of The United States of America, located between the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Virgin Islands |
|---|---|
| Flag |

|
| Capital City | Charlotte Amalie |
| 18 21 N, 64 56 W | |
| Total Area | 1,910.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 346.00 km2 |
| Water Area | 1,564.00 km2 |
| Population | 106,631 |
| Currency | US Dollar (USD) |
| GDP | $3.86 Billion |
| GDP Per Capita | $35,938.02 |
This page was last updated on February 25, 2021







