Maps of Tasmania
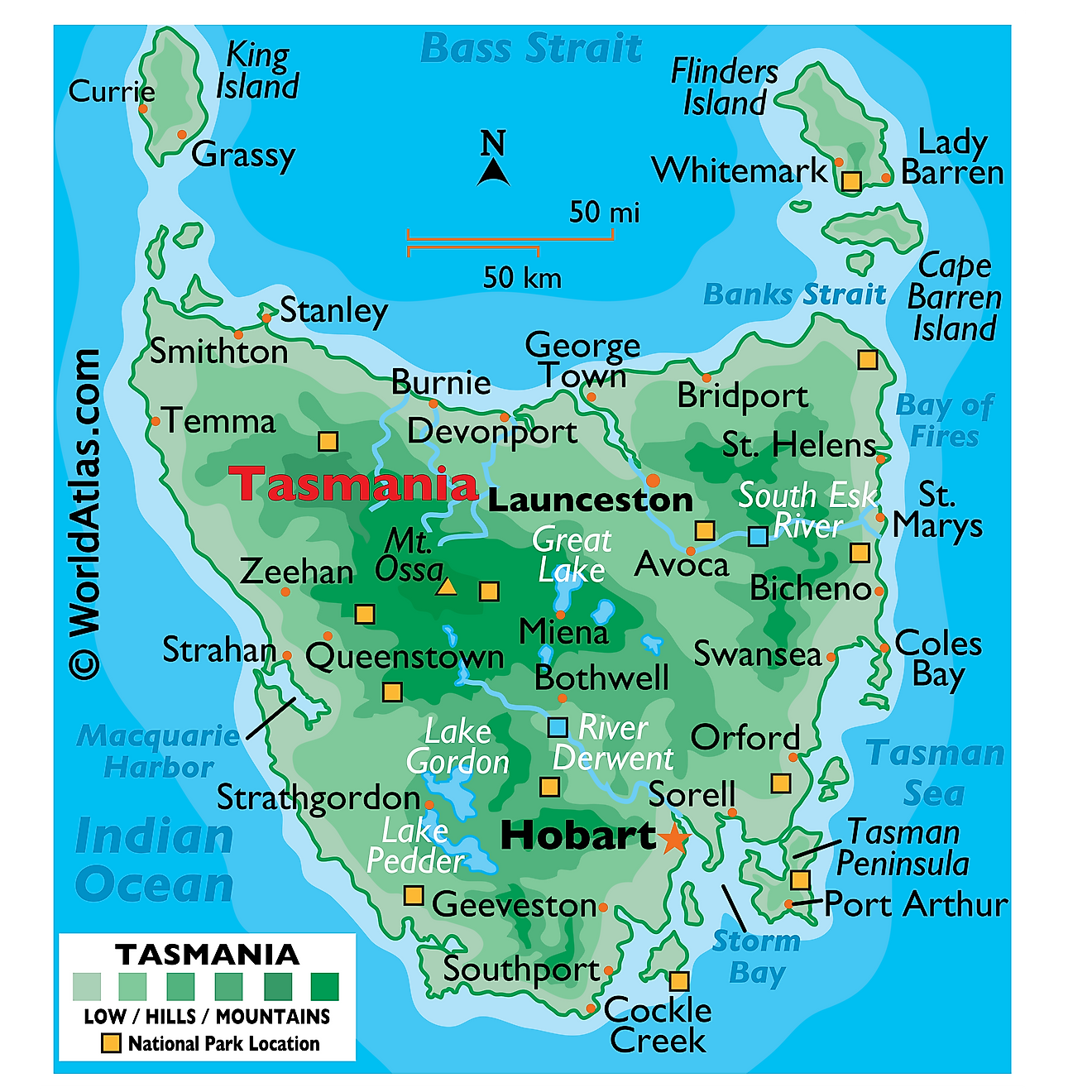
Covering a land area of 68,401 sq. km, the island state of Tasmania is Australia’s smallest state that is located off the southern coast of Australia. As observed on the map, Tasmania is the most mountainous state in Australia. The central and western parts of the island state are dominated by the Central Highlands. Mount Ossa, which rises to an elevation of 1,617m is the highest point in Tasmania. The central-eastern parts of the island state are occupied by the flat Midlands. Most parts of Tasmania are covered by dense forests and the Southwest National Park supports some of the Southern Hemisphere’s remaining temperate rainforests. With an area of 3,800sq.km, Tarkine which is located in the island’s extreme northwestern part hosts Australia’s largest temperate rainforest. Due to the island’s rugged topography, there are many rivers in Tasmania such as the Derwent, South Esk, etc. Some of the notable lakes in Tasmania include Great Lake, Gordon Lake, and Pedder Lake. The lowest point in Tasmania is the Indian Ocean (0m).
Counties Map
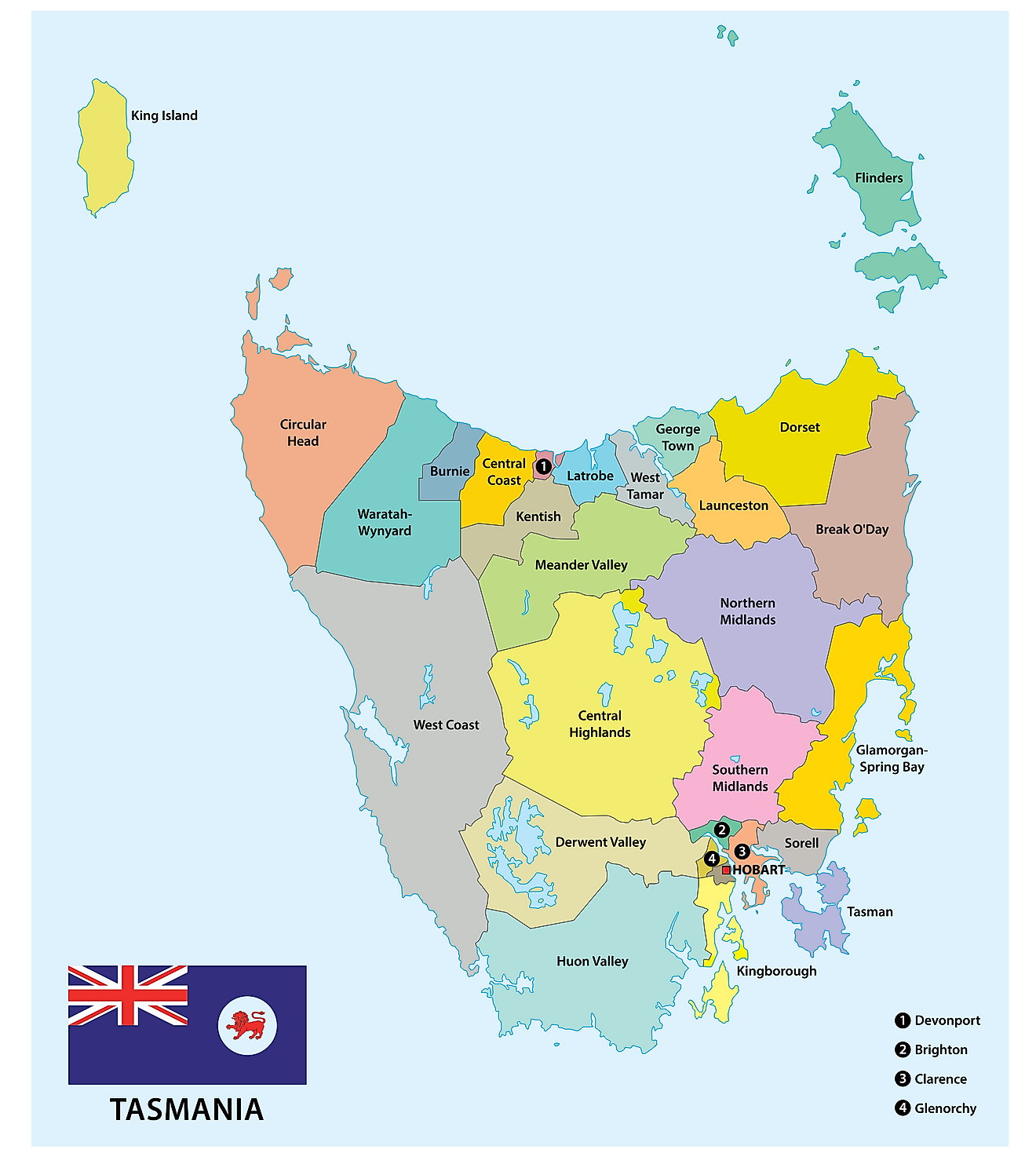
Tasmania, an island state of Australia, lies approximately 150 miles to the southeast of the mainland, separated by the Bass Strait. Covering an area of about 26,410 square miles, Tasmania is the 26th largest island globally. It borders the Indian Ocean to the west and south and the Tasman Sea to the east. The island state comprises about 334 surrounding smaller islands.
The geography of Tasmania divides into several distinct regions, which include the West Coast, the Central Plateau, the Midlands, the East Coast, and the Southeast. Each of these regions features unique topography, climate, and natural features.
The West Coast of Tasmania is predominantly rugged and mountainous, characterized by dense rainforests and steep terrain. The region is abundant with a variety of minerals, making it a significant center for mining in the past. Major rivers in the West Coast region include the Franklin, Gordon, and Pieman Rivers. These rivers have carved deep gorges and valleys throughout the landscape, creating stunning vistas and providing natural habitats for diverse flora and fauna.
The Central Plateau, also known as the Central Highlands, is a significant elevated region in Tasmania, with an average elevation of 2,952 feet above sea level. This region hosts a variety of alpine vegetation and several glacial lakes. Great Lake, the largest freshwater lake in Tasmania, is located within the Central Plateau, covering an area of approximately 61 square miles. The region also includes the Cradle Mountain-Lake St Clair National Park, which is home to Tasmania's highest peak, Mount Ossa, standing at 5,305 feet.
The Midlands region lies in the central part of Tasmania and features a predominantly flat, agricultural landscape. The region experiences a drier and warmer climate compared to the West Coast, making it suitable for farming. The South Esk and the Macquarie Rivers are two significant rivers that traverse the Midlands, providing essential water sources for irrigation and supporting the agriculture-dependent economy.
The East Coast of Tasmania is renowned for its picturesque coastline, white sandy beaches, and mild climate. The region features several stunning bays and inlets, including Wineglass Bay and the Bay of Fires. The Freycinet Peninsula, a popular tourist destination, is home to the scenic Freycinet National Park. Several rivers flow through the East Coast, such as the Prosser, Swan, and Ansons Rivers, which contribute to the region's diverse and lush vegetation.
Lastly, the Southeast region of Tasmania is home to the state capital, Hobart, situated along the Derwent River. This region features a mix of coastal landscapes and rugged mountainous terrain, including the Tasman Peninsula, known for its towering sea cliffs and unique rock formations. The Huon and the Derwent Rivers are two major rivers that run through the Southeast region, providing essential water resources for both urban and rural communities.
Where is Tasmania?
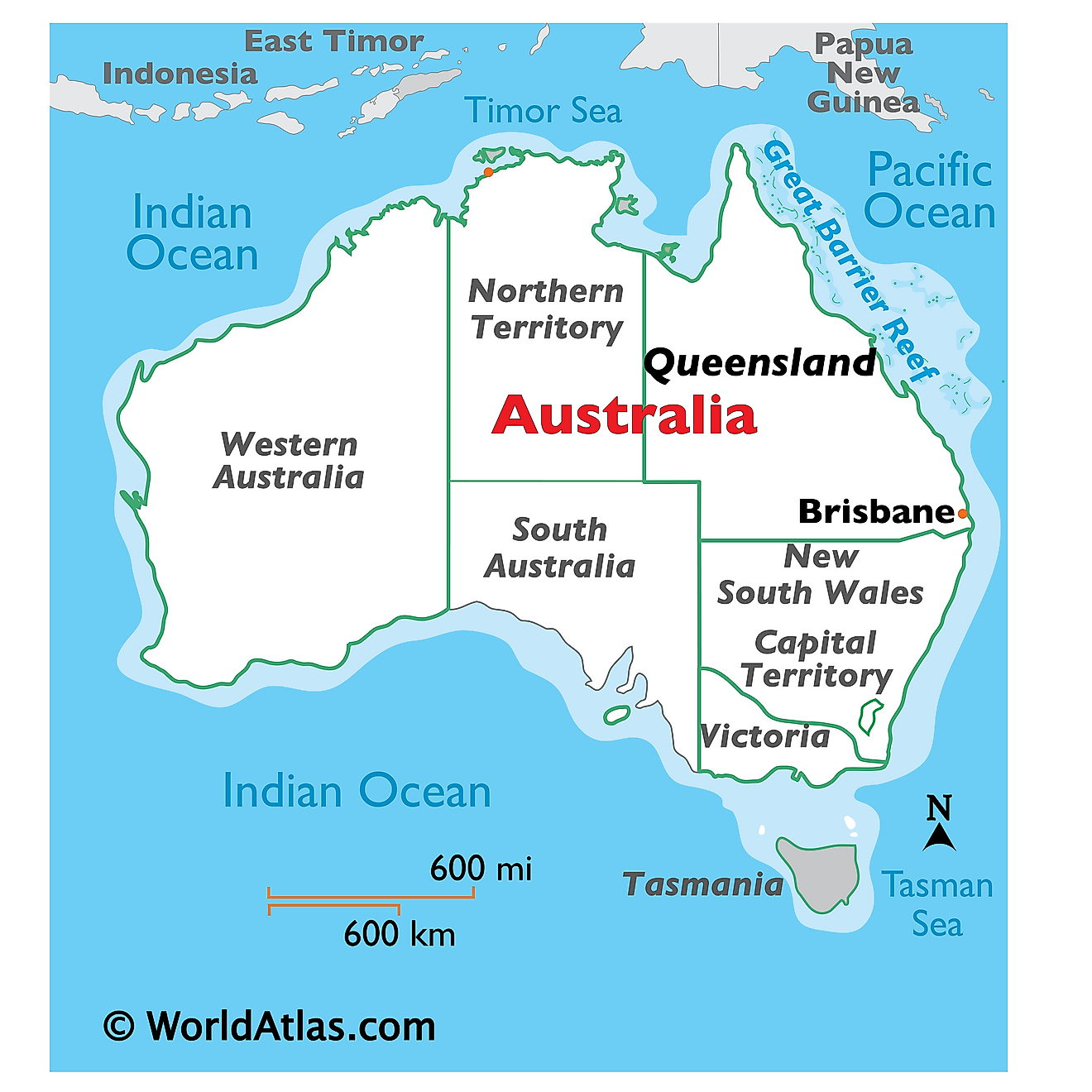
Tasmania is an island state located off the southern coast of Australia. It is geographically positioned both the Southern and Eastern hemispheres of the Earth. Tasmania is bordered by the Indian Ocean in the west, and by the Tasman Sea in the east. In the north, the shallow Bass Strait separates Tasmania from the Australian mainland.
Regional Maps: Map of Oceania
Outline Map of Tasmania
The above blank map represents Tasmania, an island state located off the southern coast of Australia. The above map can be downloaded, printed, and used for geography education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.
The above outline map represents Tasmania, an island state located off the southern coast of Australia.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | State of Tasmania |
|---|---|
| ISO 3166 Code | AU-AU_TS |
| Capital City | Hobart |
This page was last updated on April 12, 2023







