Maps of Tanzania
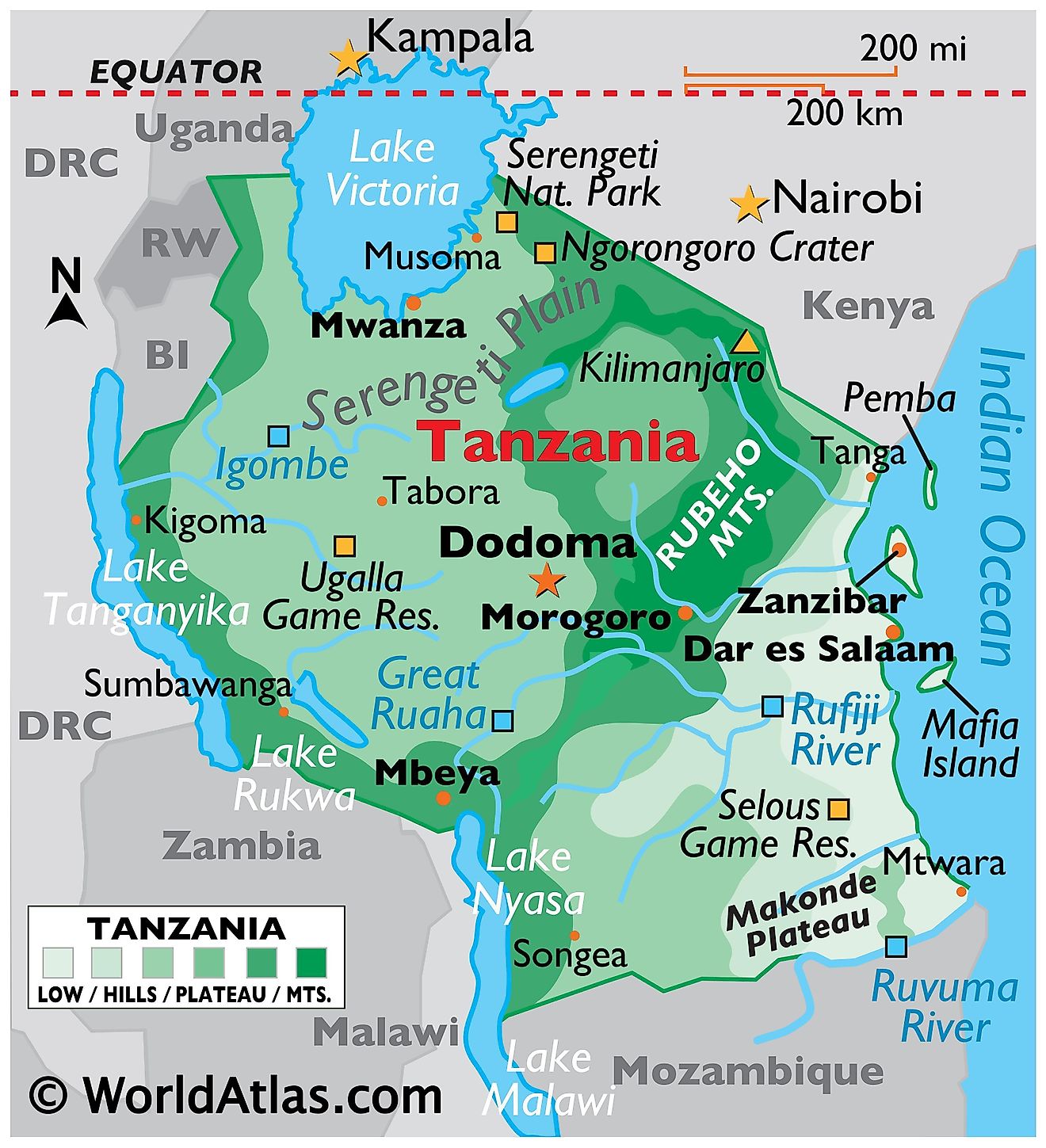
Tanzania is situated in East Africa and encompasses an area of approximately 945,087 km2 (364,900 mi2). It shares borders with eight countries: Kenya and Uganda to the north, Rwanda, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west, and Zambia, Malawi, and Mozambique to the south. The eastern border of Tanzania meets the Indian Ocean.
The East African Rift Valley is one of Tanzania's most prominent geographical regions. It is a significant tectonic feature that extends into the country from the north, splitting into the Eastern Rift and the Western Rift. The Eastern Rift runs along the edge of the Tanzanian plateau, and its western wall forms a series of mountains, such as Mount Meru and the globally famous Mount Kilimanjaro, the highest peak in Africa at 5,895 m. The Rift Valley region contains large, shallow lakes, including Lake Natron in the northeast and Lake Manyara further south.
The Western Rift, also known as the Albertine Rift in neighboring countries like Rwanda and Burundi, is characterized by some of the deepest lakes in Africa, including Lake Tanganyika, which is the continent's deepest and the world's second deepest freshwater lake. It creates a natural border with the Democratic Republic of Congo. The Western Rift also houses the Mahale and Gombe Stream National Parks, notable for their populations of wild chimpanzees.
The Central Plateau lies in the interior of Tanzania and has an average elevation of about 1,200 meters (3,937 feet) above sea level. It is characterized by large grasslands and scattered woodland. This region houses the Serengeti National Park, a crucial wildlife area known for the migration of millions of wildebeest and zebras.
The Southern Highlands contain the Kipengere, Poroto, and Livingstone mountain ranges. This region has a cool climate and fertile soils, making it a key area for agriculture, including tea, coffee, and tobacco production.
The Coastal Plain: Bordering the Indian Ocean, the Tanzanian coastal plain is a narrow, low-lying region characterized by sandy and clay soils. It extends from the country's northern border with Kenya to the Ruvuma River in the south, marking the border with Mozambique. The coastal region includes hubs like its largest city Dar es Salaam.
Bodies of Water. In addition to the lakes within the Rift Valley, Tanzania also includes a portion of Lake Victoria, the largest lake in Africa and a source of the Nile River. Lake Victoria lies to the north of the country, providing a natural boundary with Uganda and Kenya. Several rivers course through Tanzania, including the Great Ruaha, Rufiji, and Kagera rivers. The 600 km Rufiji River is the largest river in the country, flowing through the Selous Game Reserve and creating a large delta as it meets the Indian Ocean. These rivers are critical for the country's agriculture, transportation, and hydroelectric power generation.
Islands: The country also includes a number of major islands and archipelagos. The most significant are Zanzibar, Pemba, and Mafia, all located off the eastern coast in the Indian Ocean. These islands are famous for their spice production and hold significant historical and cultural importance. The archipelago Zanzibar, particularly, serves as a significant tourist destination with its well-preserved Stone Town, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Regions of Tanzania Map
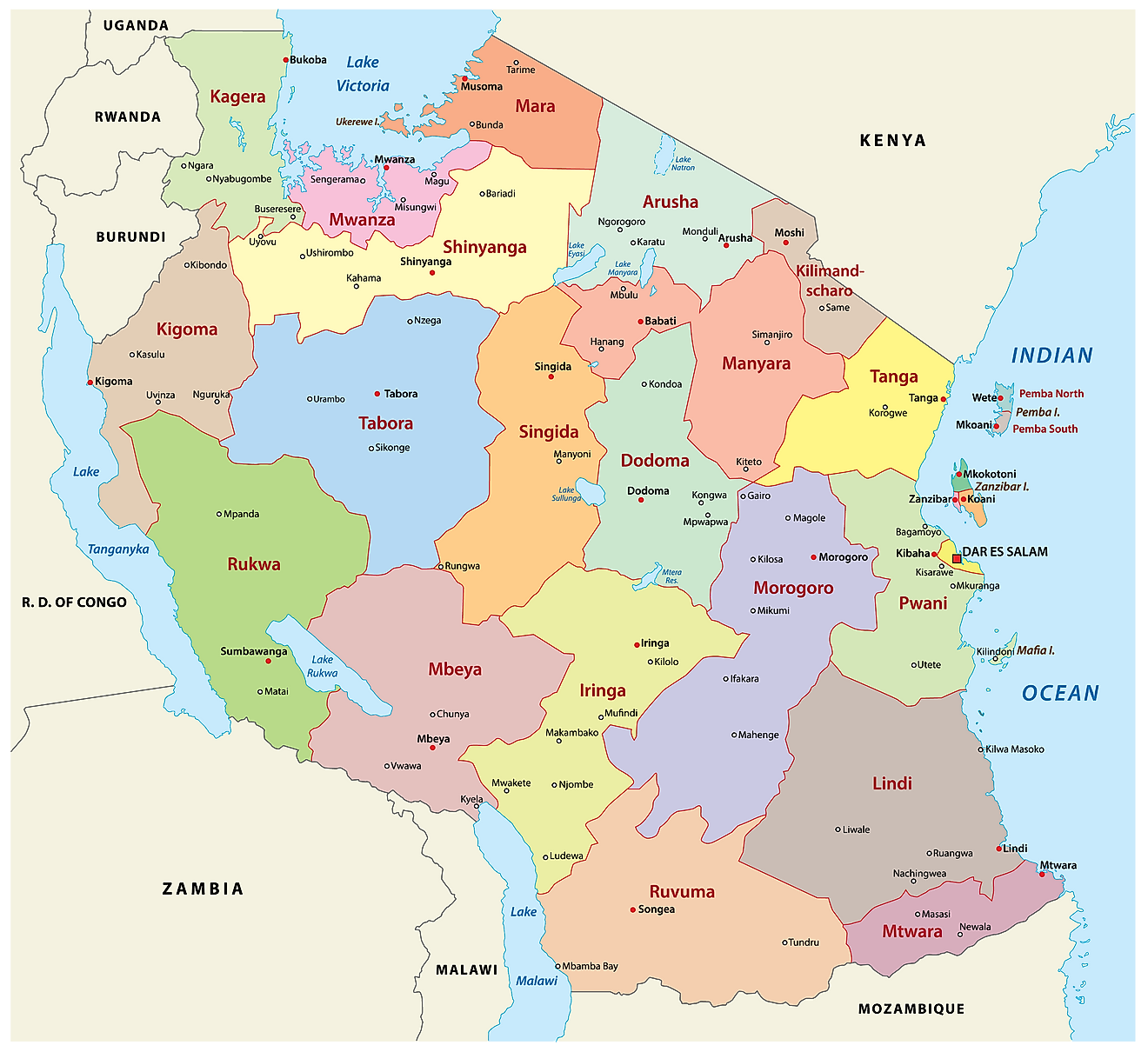
Tanzania is divided into 31 regions as visible on the political map above. In alphabetical order, these regions are as follows: Arusha, Dar es Salaam, Dodoma, Geita, Iringa, Kagera, Kaskazini Pemba (Pemba North), Kaskazini Unguja (Zanzibar North), Katavi, Kigoma, Kilimanjaro, Kusini Pemba (Pemba South), Kusini Unguja (Zanzibar Central/South), Lindi, Manyara, Mara, Mbeya, Mjini Magharibi (Zanzibar Urban/West), Morogoro, Mtwara, Mwanza, Njombe, Pwani (Coast), Rukwa, Ruvuma, Shinyanga, Simiyu, Singida, Songwe, Tabora, Tanga
Each region of the country is further sub-divided into districts, and districts into divisions which are further sub-divided into local wards. It does not stop there. Wards are further divided into streets (in urban areas) and villages (in rural areas).
With an area of 76,150 sq. km, Tabora is the largest region in Tanzania by area. Dar-es-Salaam Region that hosts Dar-es-Salaam city, the former capital of Tanzania, is the country's largest region by population.
Dodoma, the current capital of the country is part of the Dodoma Region.
Where is Tanzania?
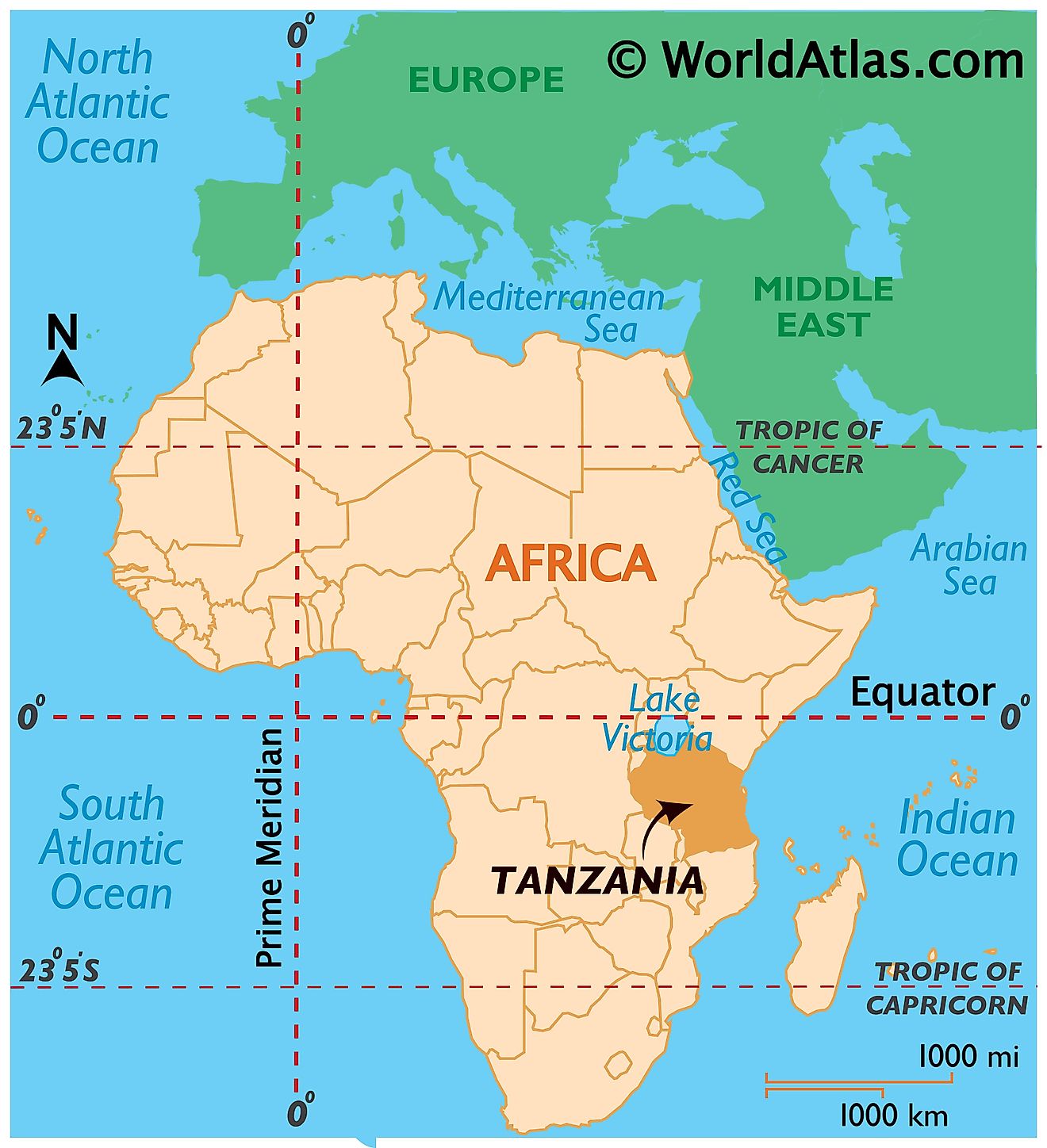
Tanzania is a country in East Africa's Great Lakes Region. As observed on the location map above, Tanzania is located just below the Equator in the Southern and Eastern Hemisphere. It is one of the 10 countries with the most international borders in the world. As represented in the map, it is bordered by 8 countries. Uganda bounds it to the north, Kenya to the northeast, Malawi and Mozambique to the south, and Zambia to the southwest. The three countries of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Burundi, and Rwanda border Tanzania to the west. The country's eastern borders are formed by the Indian Ocean.
Tanzania Bordering Countries: Kenya, Mozambique, Zambia, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, The Democratic Republic Of The Congo, Malawi.
Regional Maps: Map of Africa
Outline Map of Tanzania
The blank outline map respresents mainland Tanzania. The country also has several islands on the Indian Ocean which cannot be observed on this map. The above map can be downloaded for free, and used for educational purposes like map-pointing activities.
The outline map of Tanzania represents mainland Tanzania, a country located in Eastern Africa. The country also has several islands on the Indian Ocean.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | United Republic of Tanzania |
|---|---|
| Flag |

|
| Capital City | Dar es Salaam (administrative capital), Dodoma (legislative capital); note - Dodoma was designated the national capital in 1996 and serves as the meeting place for the National Assembly; Dar es Salaam remains the de facto capital, the country's larges |
| 6 48 S, 39 17 E | |
| Total Area | 947,300.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 885,800.00 km2 |
| Water Area | 61,500.00 km2 |
| Population | 58,005,463 |
| Major Cities |
|
| Currency | Tanzanian shillings (TZS) |
| GDP | $63.18 Billion |
| GDP Per Capita | $1,122.12 |
This page was last updated on August 9, 2023







