Africa
African History
African Origin of Modern Humans
As for Africa, scientists have formerly concluded that it is the birthplace of mankind, as large numbers of human-like fossils (discovered no where else) were found on the continent, some dating back 3.5 million years.
About 1.75 million years ago, early man spread throughout parts of Africa. They became aggressive hunters, lived in caves and used fire and their ability to create stone tools just to survive.
The Neanderthals arose some 200,000 years ago and inhabited regions in northern Africa and across parts of southern Europe. There is also clear evidence that they had control of fire, lived in caves, as well as open-air structures of stone and vegetation.
One of the most important developments of primitive man was the creation of stone tools. By 5000 BC farming was somewhat common in the northern areas of Africa, as people were growing crops and herding livestock. During that time the Sahara Desert was a fertile area.
Ancient African History
In 3200 BC the Egyptian culture emerged along the lower reaches of the Nile River; it was among the earliest civilizations and their tools and weapons were made of bronze. They also pioneered the building of massive pyramids and temples.
Egyptians also developed mathematics, an innovative system of medicine, irrigation and agricultural production techniques, writing and the first ships. In short, the Egyptians left a lasting legacy upon the world.
Around 600 BC the use of metal tools spread across small population bases and farming groups in North Africa, and their use gradually spread south into what is now called South Africa.
The Phoenicians were an enterprising maritime trading culture from Lebanon who spread across the Mediterranean from 1550 BC to 300 BC. In 814 BC, they founded the city of Carthage in what is now Tunisia in north Africa; only to be destroyed by the Romans in 146 BC.
Meanwhile, the Egyptians continued to spread their culture across Northern Africa, and kingdoms were created in Ethiopia and Sudan. The then-growing Roman Empire continued to expand its influence, and in 30 BC Egypt became a province of Rome; Morocco the same in 42 AD.
Before the Middle Ages began, the Roman Empire collapsed and the Arabs quickly took their place on the continent. In 698-700 they invaded Tunis and Carthage and soon controlled all of coastal North Africa. The Arabs were Muslims, and most of North Africa converted to Islam; Ethiopia was the exception.
Soon kingdoms emerged in Africa; they traded with the Arabs using gold plus a valuable commodity - slaves. One of the first kingdoms was Ghana, located in what is now southeastern Mauritania and western Mali. The empire grew rich from the trans-Saharan trade in gold and salt, but then lost its power in the 11th century.
Additional kingdoms developed across the continent, including those in Benin and Mali. Both became rich by trading in gold, horse salt, and of course, slaves. And like most kingdoms before them on any continent, they were invaded and in the end destroyed.
Mogadishu, the now largest city in Somalia, was settled by Arabs who traveled and traded on the east coast of Africa. The Arabs' reach extended to Zanzibar, which was used as a base for voyages between the Middle East and India.
As other organized kingdoms were formed in central and southern Africa, the Portuguese began to explore the western coast of Africa. By 1445 they reached the Cape Verde Islands and the coast of Senegal, and the mouth of the River Congo in 1482. They even sailed around the Cape of Good Hope.

African Colonization and the Slave Trade
The continent-changing 16th Century began with Europeans transporting African slaves to the Americas for profit. A slave purchased on the African coast for the equivalent of 14 English pounds in bartered goods could sell for 45 pounds in the American market.
The best-known method of commerce at the time was called the Triangular Trading System. It involved British and other European countries' manufactured goods which were shipped to Africa, then slaves from there to the West Indies and then sugar and other products back to Europe.
At the same time, Barbary pirates along the North African coast captured thousands of ships. From the 16th to 19th century, an estimated 800,000 to 1.25 million people were taken captive as slaves. The pirates' impact on the continent, however, peaked in the early to mid-17th century.
As tales of African riches spread north, the Europeans founded their first real colonies in the early 16th century, when the Portuguese settled in what is now Angola. Later, the Dutch founded a colony in what is now South Africa.
Strong movements to end slavery began in the late 18th century. France became one of the first countries to abolish slavery in 1794. Britain banned slave trade in 1807, but it was not officially abolished for good until 1848. In some parts of Africa, slave-like practices continue to this day and have proven difficult to eliminate.
Wholesale colonization of Africa by European countries began in 1814 when the British snatched the Dutch Colony of South Africa. Carved up like a large pie, the Brits, Dutch,French, Germans and Portuguese grabbed all of the available pieces.
By the end of the 19th century, from Algeria to Zimbabwe, and from Botswana to Niger, the continent was now all but controlled by European powers. In the early 20th century the land grab continued as the British took control of Egypt.
By 1920, the forced occupation of African lands began to sour in Europe, and change was in the wind. Africans were also driven by their passionate desire for independence and the movement for same became unstoppable. By mid-century most of the continent was independent, with Angola finally free in 1975.
Post-Colonial Africa
Self-government brought more than its share of civil wars, coup d'états and ethnic conflicts to the newly emerged countries. Add to that mix some horrible genocides, along with famines and out-of-control disease (HIV/AIDS), and Africa was teetering on the edge, and in many areas still does today.
Although Africa remains the world's poorest inhabited continent, there are many bright spots in this land of over one billion people and its 2,000 + languages. Significant economic and social gains have taken place over the last few years, with South Africa, Nigeria, Morocco and Egypt leading the way.
The largest segments of modern Africa's economies are agriculture and mining, with tourism growing in some areas. Manufacturing industries have grown large enough to ship products across the planet, and the oil export revenues of Angola, Libya and Nigeria have the potential to change the lives of millions.
Today the 54 countries of Africa have great potential, but this question must be asked: "Can it change soon enough to meet the needs of its people?" We can only hope so.
Africa Geography Facts
For additional geography details please use the yellow navigation bar at the top of this page.
- Algeria is Africa's largest country
- The Seychelles are Africa's smallest country
- Nigeria is Africa's largest country by population
- The Seychelles are Africa's smallest country by population
- Africa's highest point is Mt Kilimanjaro in Tanzania
- Africa's lowest point is Lake Assal in Djibouti
Interesting Facts About Africa
Two of Africa's most interesting geographical features are the Nile River System and Sahara Desert; both impressive in so many ways.
Nile River System: The Nile is a north-flowing river considered the longest river in the world at 6,650 km (4,130 mi) long. It is shared by and benefits eleven countries. The White Nile and Blue Nile are its major tributaries. The White Nile is longer and rises in the Great Lakes region of central Africa, flowing north from Tanzania to South Sudan. The Blue Nile is the source of most of the water and both rivers join near Khartoum, Sudan The northern section of the river flows almost entirely through desert, from Sudan into Egypt. The Nile ends in a large delta that empties into the Mediterranean Sea.
Sahara Desert: It's the world's hottest desert, the third largest desert after Antarctica and the Arctic, and almost as large as China. Covering almost one-third of the continent, the Sahara is the largest hot desert in the world at approximately 3,500,000 sq. miles (9,065,000 sq. km) in total size. Topography includes areas of rock-strewn plains, rolling sand dunes and numerous sand seas. It ranges in elevation from 100 ft. below sea level, to peaks in the Ahaggar and Tibesti Mountains, that exceed 11,000 ft. (3,350m). Regional deserts include the Libyan, Nubian and the Western desert of Egypt, just to the west of the Nile. Almost completely without rainfall, a few underground rivers flow from the Atlas Mountains, helping to irrigate isolated oases. In the east, the waters of the Nile help fertilize smaller parts of the landscape.
Africa Information
- Africa famous native sons and daughters
- Africa facts and figures, capital cities and currency
- Africa country flags
- Africa land statistics, highest and lowest points
- Africa landforms, lakes, mountains and rivers
- Africa latitude, longitude and relative locations
- Africa links to major attractions and points of interest
- Africa maps, outline, political and topographical
- Africa symbols, coat of arms and flags
- Africa time zones and current times
- Africa timeline of events and history
- Africa travel information, airfares, cruises and train travel
- Africa weather forecasts and current conditions
Maps of Africa
Africa, the planet's 2nd largest continent and the second most-populous continent (after Asia) includes (54) individual countries, and Western Sahara, a member state of the African Union whose statehood is disputed by Morocco. Note that South Sudan is the continent's newest country.
With a 2011 population of 1,032,532,974, it accounts for just over 14% of the world's human population. It also contains the Nile River system, the world's longest, and the massive Sahara Desert, the world's largest.
Africa is surrounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, both the Suez Canal and the Red Sea along the Sinai Peninsula to the northeast, the Indian Ocean to the east and southeast, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west.
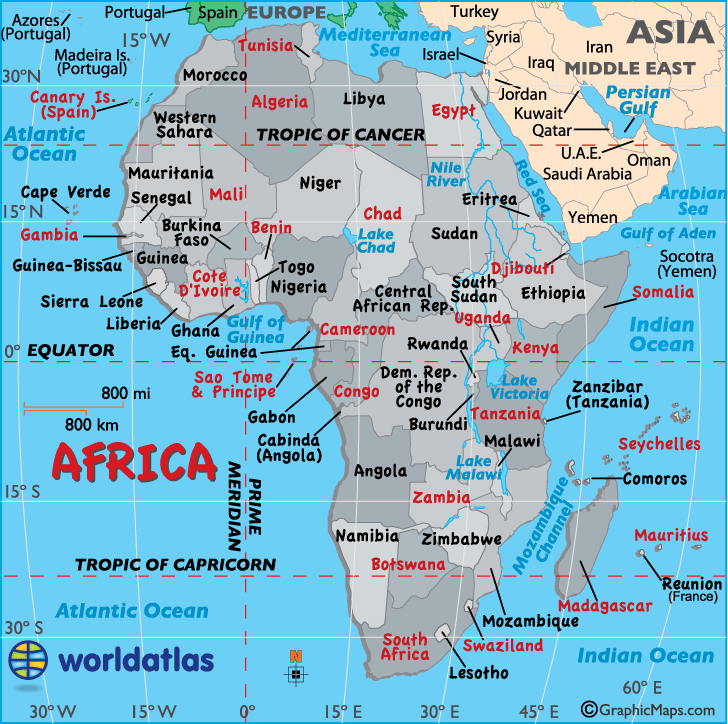
Country Map of Africa Outline
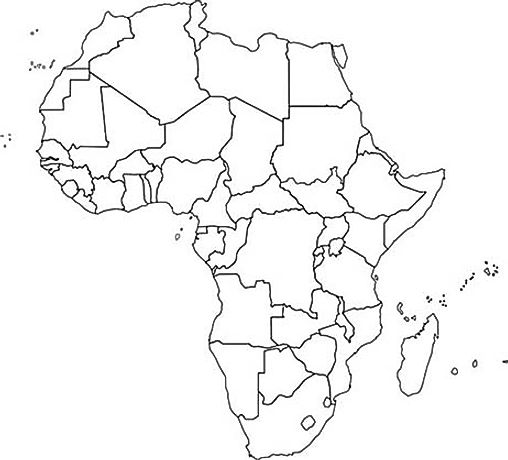
Outline map of the Africa continent including the disputed territory of Western Sahara
Political Map of Africa
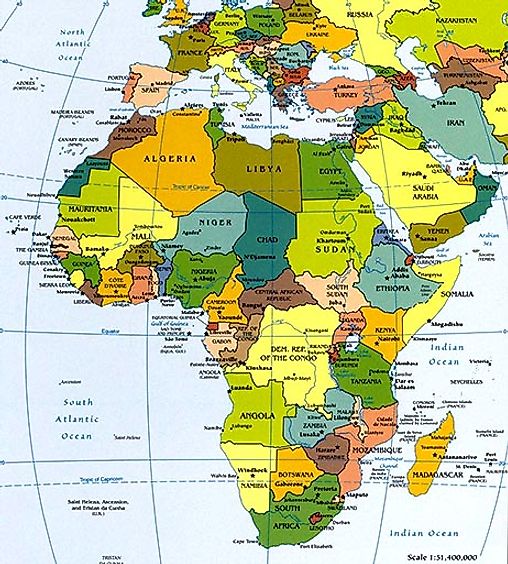
Political maps are designed to show governmental boundaries of countries, states, and counties, the location of major cities, and they usually include significant bodies of water. Like in the sample, bright colors are often used to help the user find the borders. A larger version of this map here.
Topographical Map of Africa
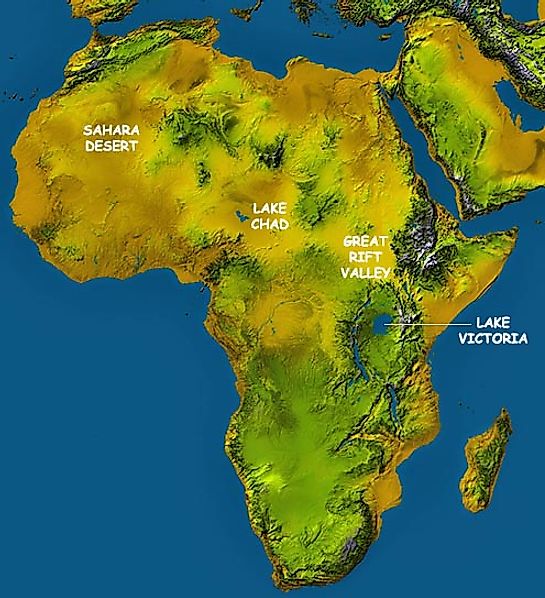
A topographic map highlights hills, mountains and valleys of a specific land area by exaggerated shading rather than by using contour lines. This topo map clearly shows the flatness of the Sahara Desert, the depression that Lake Chad sits in, the high mountains of the Great Rift Valley, and it also highlights Lake Victoria, all but surrounded by mountains.
Great Rift Valley African Map
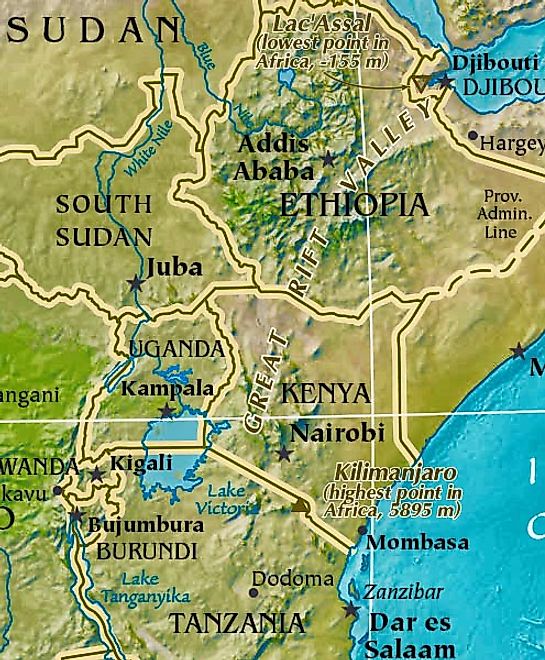
This is a slice of a larger topographical map that highlights the Great Rift Valley, a dramatic depression on the earth's surface, approximately 4,000 miles (6,400 km) in length, extends from the Red Sea area near Jordan in the Middle East,, south to the African country of Mozambique. In essence, it's a series of geological faults caused by huge volcanic eruptions centuries back, that subsequently created what we now call the Ethiopian Highlands, and a series of perpendicular cliffs, mountain ridges, rugged valleys and very deep lakes along its entire length. Many of Africa's highest mountains front the Rift Valley, including Mount Kilimanjaro,Mount Kenya and Mount Margherita.
For additional details on many of the landforms of Africa, this page will help
Africa Satellite View Map
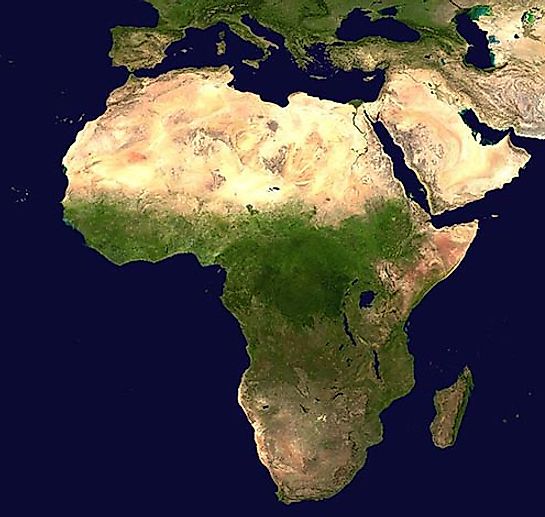
This NASA satellite view of Africa can be useful in many applications, including agriculture, geology, forestry, meteorology, intelligence and warfare. In addition, it's a great education tool as it provides an overview of Africa, with the desert areas of the north, the central fertile areas and the varied topography of the southern regions of the continent are clearly visible.
Historical African Map 1570
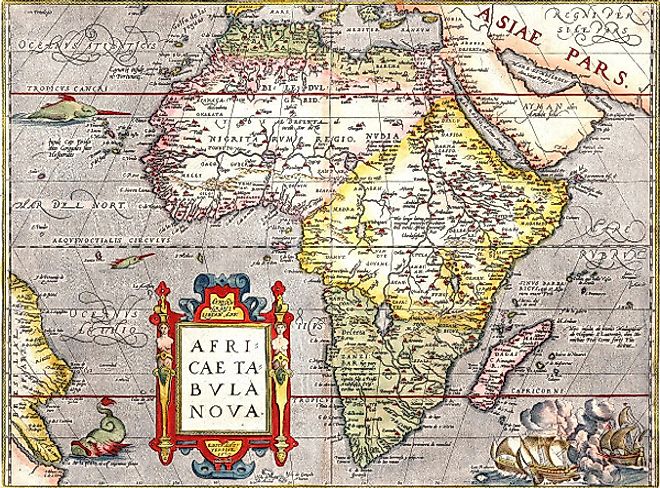
Beautifully designed the map represents a high mark of 16th-century mapmaking, it shows Africa in a recognizable shape, with a more pointed southern cape. Madagascar appears, as do the place-names of numerous towns along the coasts and in the interior, although large empty spaces begin to dominate there. No animal or plant life is indicated, but the oceans contain swordfish and a whale. Three ships in the lower right are caught in the smoke of battle. The map was designed by Abraham Ortelius who published the Theatrum, the worlds first atlas.
Map of Africa Prior to Colonization
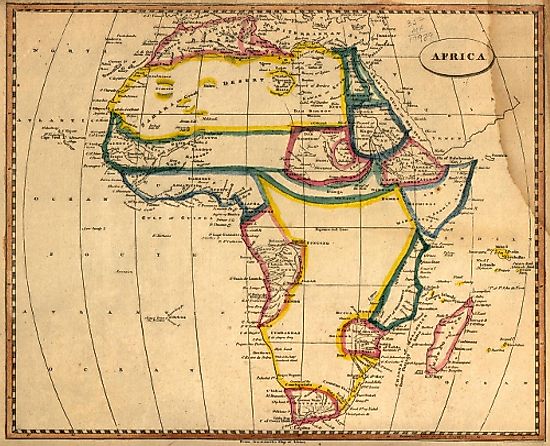
A map depicting Africa before colonization in 1812 by Arrowsmith and Lewis, printed in Boston by Thomas & Andrews.
1910 Map of the Colonization of Africa
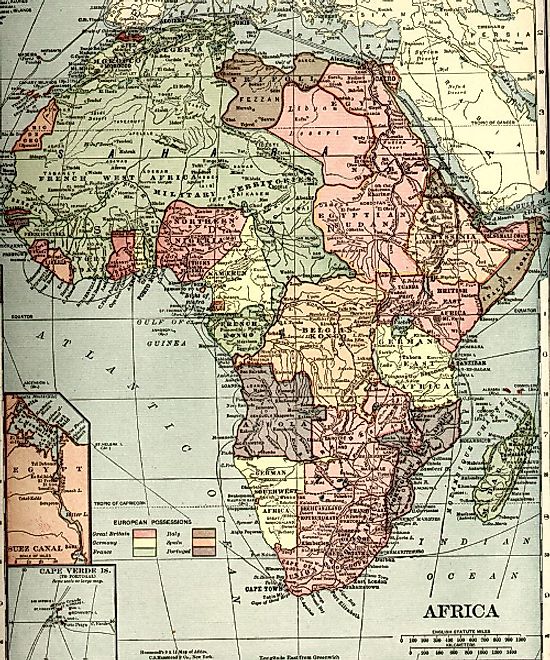
Historical map of Africa shows the possessions of the different European Powers in 1910
What Countries are in Africa?
There are 54 countries the are internationally recognized. Full list bellow, for individual country maps follow the links
| Country | Capital | Population |
| Algeria | Algiers | 33333267 |
| Angola | Luanda | 16941000 |
| Benin | Porto-Novo | 8439000 |
| Botswana | Gaborone | 1839833 |
| Burkina | Ouagadougou | 13228000 |
| Burundi | Bujumbura | 7548000 |
| Cameroon | Yaoundé | 17795000 |
| Cape Verde | Praia | 420979 |
| Central African Republic | Bangui | 4216666 |
| Chad | N'Djamena | 10146000 |
| Comoros | Moroni | 798000 |
| Congo | Kinshasa | 75507308 |
| Congo, Democratic Republic of | Brazzaville | 4012809 |
| Djibouti | Djibouti City | 906000 |
| Egypt | Cairo | 84550000 |
| Equatorial Guinea | Malabo | 504000 |
| Eritrea | Asmara | 5880000 |
| Ethiopia | Addis Ababa | 85237338 |
| Gabon | Libreville | 1384000 |
| Gambia | Banjul | 1517000 |
| Ghana | Accra | 23000000 |
| Guinea | Conakry | 10057975 |
| Guinea-Bissau | Bissau | 1586000 |
| Ivory Coast | Yamoussoukro | 17654843 |
| Kenya | Nairobi | 34707817 |
| Lesotho | Maseru | 2067000 |
| Liberia | Monrovia | 4128572 |
| Libya | Tripoli | 6036914 |
| Madagascar | Antananarivo | 18606000 |
| Malawi | Lilongwe | 12884000 |
| Mali | Bamako | 13518000 |
| Mauritania | Nouakchott | 3069000 |
| Mauritius | Port Louis | 1219220 |
| Morocco | Rabat | 35757175 |
| Mozambique | Maputo | 20366795 |
| Namibia | Windhoek | 2031000 |
| Niger | Niamey | 13957000 |
| Nigeria | Abuja | 174507539 |
| Rwanda | Kigali | 7600000 |
| Sao Tome and Principe | Sao Tome | 183176 |
| Senegal | Dakar | 11658000 |
| Seychelles | Victoria | 80654 |
| Sierra Leone | Freetown | 6144562 |
| Somalia | Mogadishu | 10532017 |
| South Africa | Bloemfontein | 52981991 |
| South Sudan | Juba | 8260490 |
| Sudan | Khartoum | 36787012 |
| Swaziland | Lobamba | 1032000 |
| Tanzania | Dodoma | 44929002 |
| Togo | Lomé | 7154237 |
| Tunisia | Tunis | 10102000 |
| Uganda | Kampala | 27616000 |
| Zambia | Lusaka | 14668000 |
| Zimbabwe | Harare | 13010000 |
World Facts
Useful information on populations and more that are updated weekly.











