Maps of Indonesia
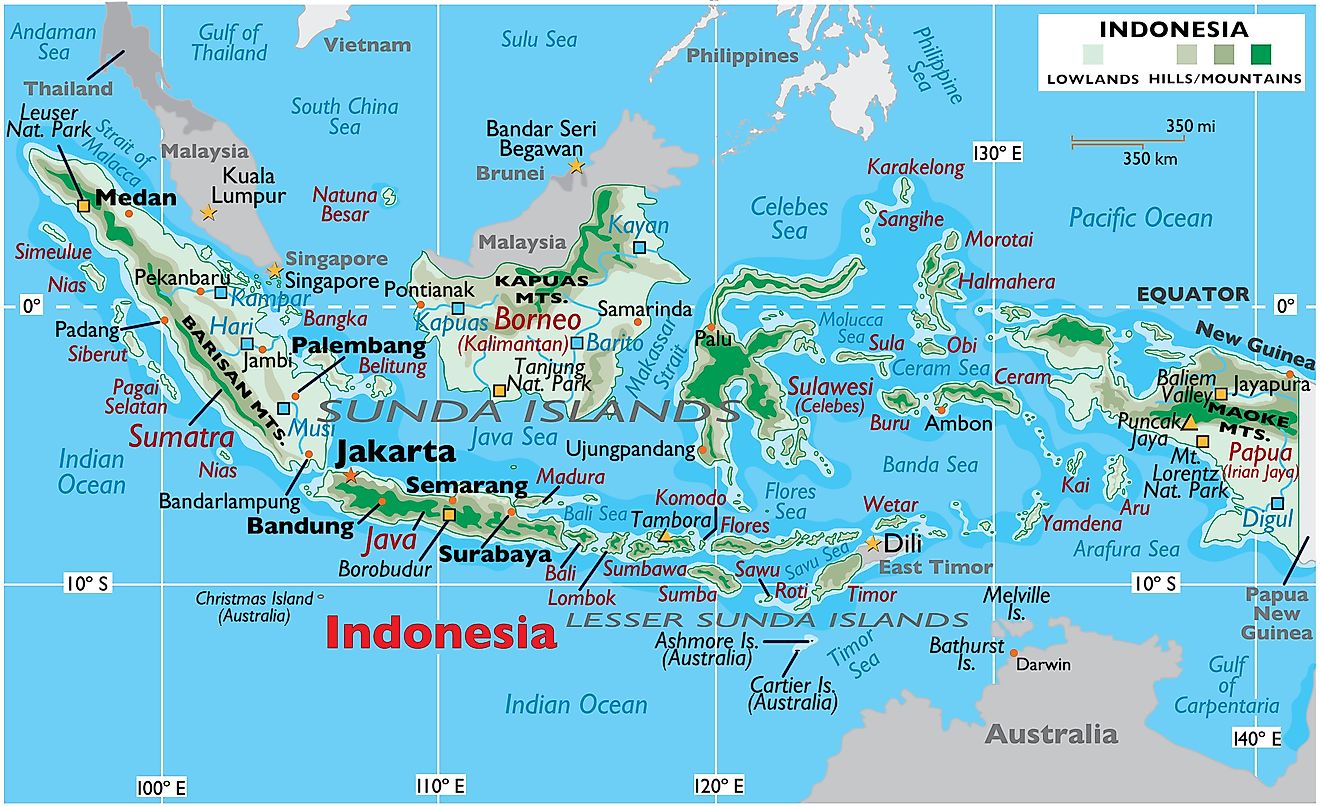
Covering an area of 1,904,569 sq. km, and strategically positioned between the Pacific and Indian Oceans, Indonesia comprises over 17,504 islands and is by far the largest and the most varied archipelago on Earth. Despite being a nation made up of various islands, Indonesia does share three separate land borders with East Timor, Papua New Guinea, and Malaysia.
The larger islands of Sumatra, Java, Kalimantan (which comprises two-thirds of the island of Borneo), Sulawesi, and Irian Jaya are quite mountainous, with some peaks reaching 12,000 ft. These mountains on the major Indonesian Islands are densely forested and volcanic in origin. The mountains with the highest elevations (over 16,000 ft) are found on Irian Jaya in the east. Located in the Papua province and as a part of the Sudirman mountain range is Puncak Jaya – the highest point in Indonesia. At an elevation of 16,502 ft. (5,030 m), Puncak Jaya is also the world’s highest island peak and the Southwestern Pacific’s tallest mountain. The lowest point is the Indian Ocean (0m). Indonesia's former tallest peak, Mount Tambora (8,930 ft, 2,722 m), is an active stratovolcano whose 1815 eruption was the largest ever in recorded history - killing nearly 71,000 people. The explosion alone was heard as far west as Sumatra island, some 1,200 miles (2,000 km) away, and ashfalls were recorded on the islands of Borneo, Sulawesi, Java, and Maluku.
Thick tropical rainforests cover much of the islands in Indonesia that eventually give way to coastal plains. The islands tend to be quite hot, wet, and humid for most of the year and experience intense tropical storms between September and December each year. The significant rivers of Indonesia include the Barito, Digul, Hari, Kampar, Kapuas, Kayan, and Musi. There are also some scattered inland lakes as well which are relatively small in size.
The Ring of Fire, a long chain of volcanoes that circles the Pacific Ocean is how many of Indonesia's islands came into being. Indonesia has about 400 volcanoes within its borders, with at least 90 still active in some capacity. The most active volcanoes are Mount Kelud (which has erupted more than 30 times since 1000 AD) and Mount Merapi (which has erupted more than 80 times since 1000 AD) on Java island. For its location between numerous tectonic plates, including the two continental plates: the Eurasian Plate (Sunda Shelf) and the Australian Plate (Sahul Shelf), and two oceanic plates: the Philippine Sea Plate and Pacific Plate; natural disasters are common in Indonesia. The most notable natural disaster is the 9.2 earthquake that struck the Indian Ocean and which triggered the Tsunami of December 2004 and devastated many of the islands within Indonesia's archipelago.
Provinces of Indonesia Map
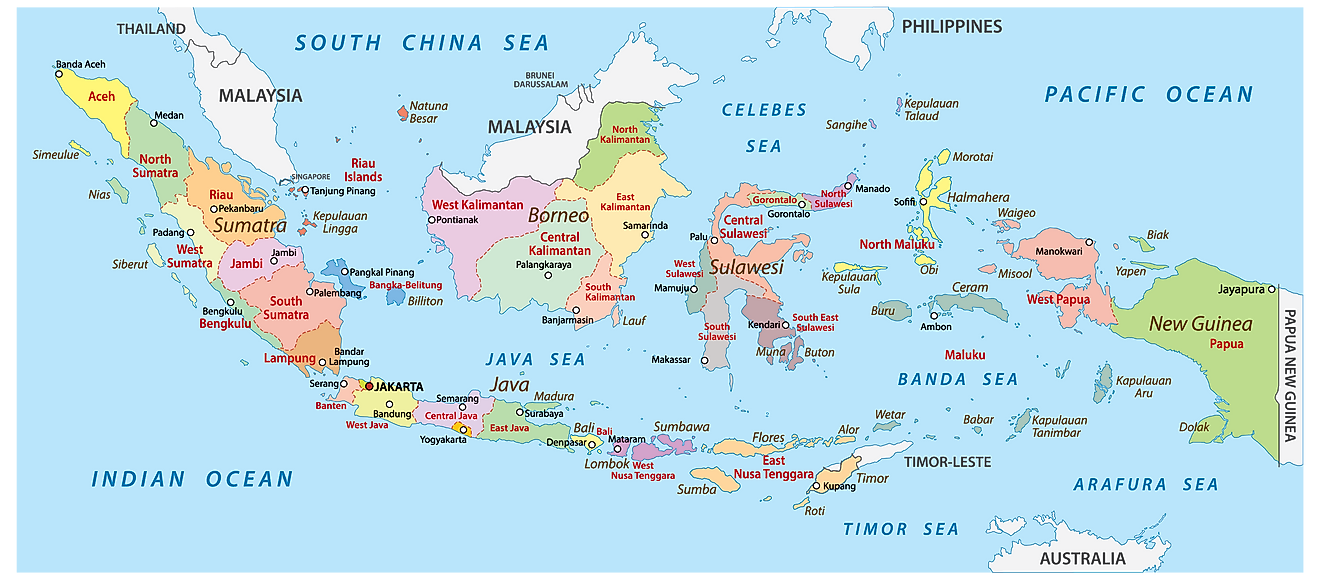
Indonesia is divided into 34 administrative provinces. These provinces are: Aceh, Bali, Banten, Bengkulu, Gorontalo, Jakarta, Jambi, Jawa Barat (West Java), Jawa Tengah (Central Java), Jawa Timur (East Java), Kalimantan Barat (West Kalimantan), Kalimantan Selatan (South Kalimantan), Kalimantan Tengah (Central Kalimantan), Kalimantan Timur (East Kalimantan), Kalimantan Utara (North Kalimantan), Kepulauan Bangka Belitung (Bangka Belitung Islands), Kepulauan Riau (Riau Islands), Lampung, Maluku, Maluku Utara (North Maluku), Nusa Tenggara Barat (West Nusa Tenggara), Nusa Tenggara Timur (East Nusa Tenggara), Papua, Papua Barat (West Papua), Riau, Sulawesi Barat (West Sulawesi), Sulawesi Selatan (South Sulawesi), Sulawesi Tengah (Central Sulawesi), Sulawesi Tenggara (Southeast Sulawesi), Sulawesi Utara (North Sulawesi), Sumatera Barat (West Sumatra), Sumatera Selatan (South Sumatra), Sumatera Utara (North Sumatra), and Yogyakarta. Out of these 34 provinces, the provinces of Aceh, Jakarta (national capital district), Yogyakarta (special region), Papua and West Papua have special status.
These provinces are subdivided into regencies and cities, which are further subdivided into districts and again into rural or urban villages.
Covering an area of 1,904,569 sq. km, Indonesia comprises over 17,504 islands and is by far the largest and the most varied archipelago on Earth. Located on the north-western coast of the most populous island of Java is Jakarta – the capital and the largest city of Indonesia. It is the administrative center as well as an important industrial, financial, trading, and business hub.
Where is Indonesia?
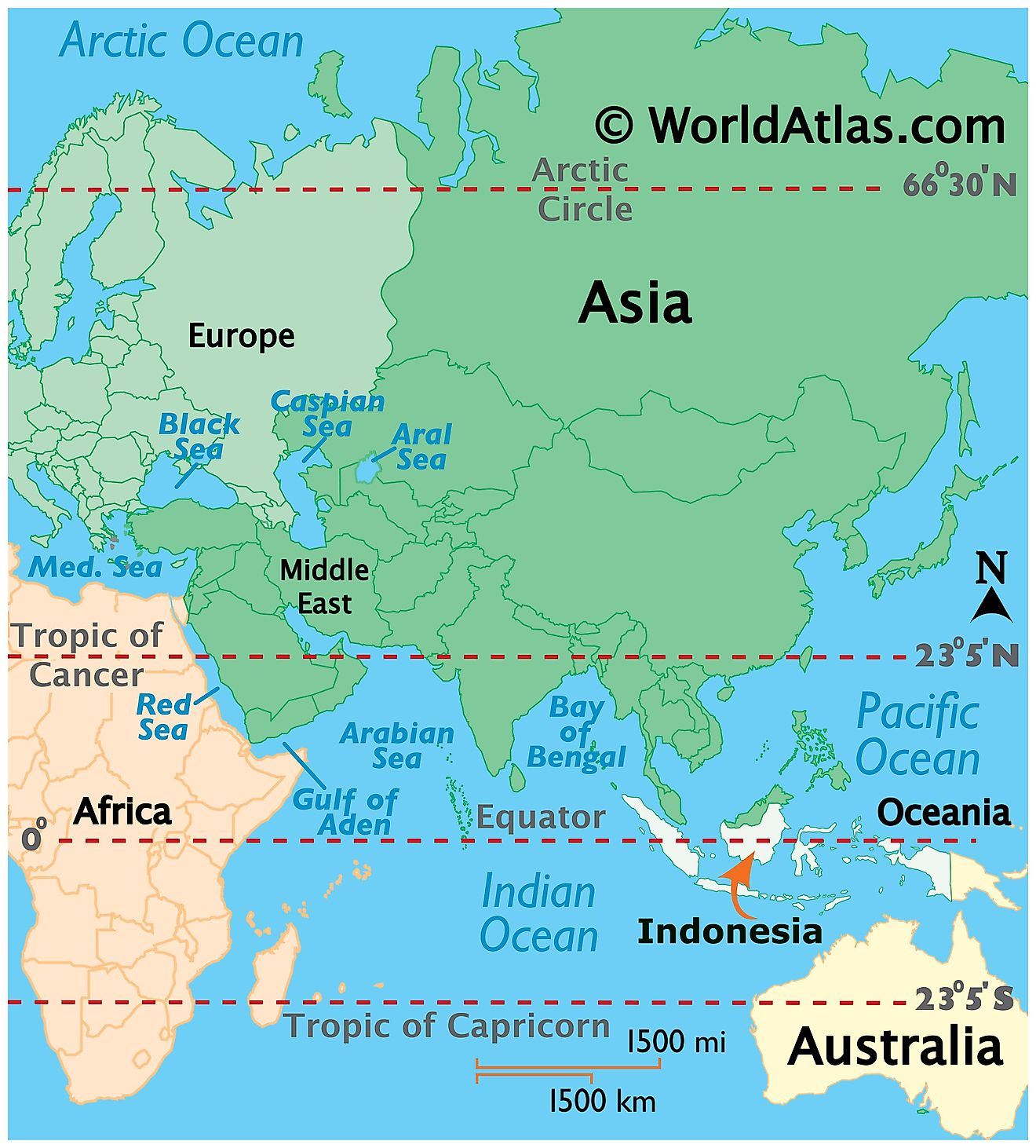
The archipelagic nation of Indonesia is located just to the north of Australia and off the Southeast Asian mainland, between the Pacific and Indian Oceans. It is placed across the Equator and hence is geographically positioned both in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres of the Earth as well as the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, and Timor-Leste. It is surrounded by the Indian Ocean in the south; by the Pacific Ocean (South China Sea) in the north, and over a dozen regional seas. Indonesia shares its maritime borders with India, Australia, Palau, Singapore, Philippines, Vietnam, and Thailand.
Indonesia Bordering Countries: Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, Timor-Leste.
Regional Maps: Map of Asia
Outline Map of Indonesia
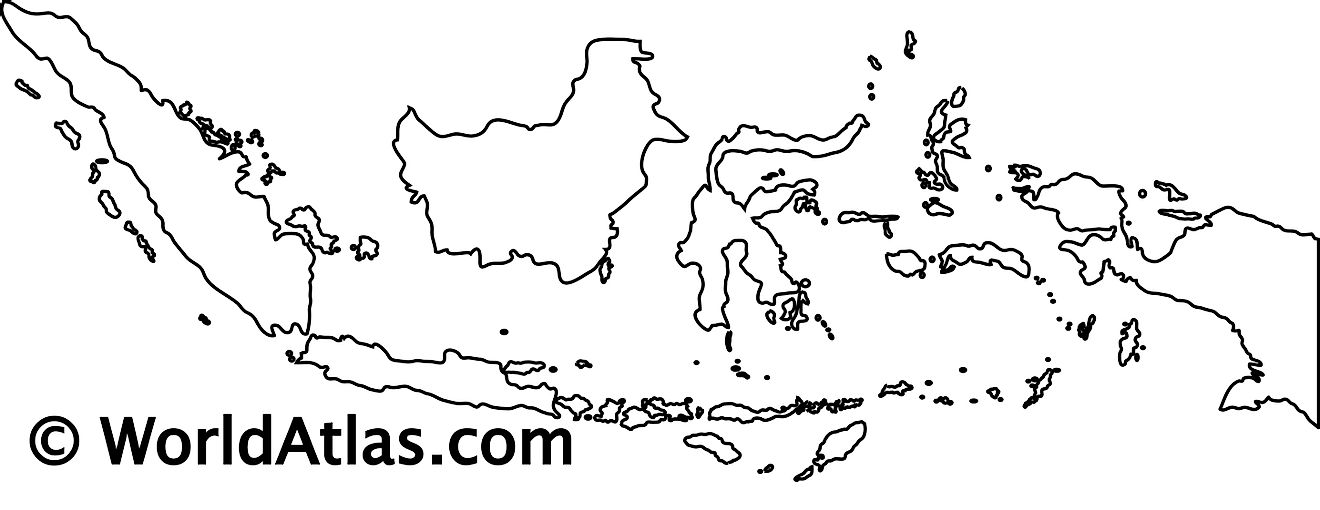
The above blank map represents the archipelagic nation of Indonesia - the world's largest island nation that is strategically positioned between the Pacific and Indian Oceans. The above map can be downloaded, printed and used for geographic education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.
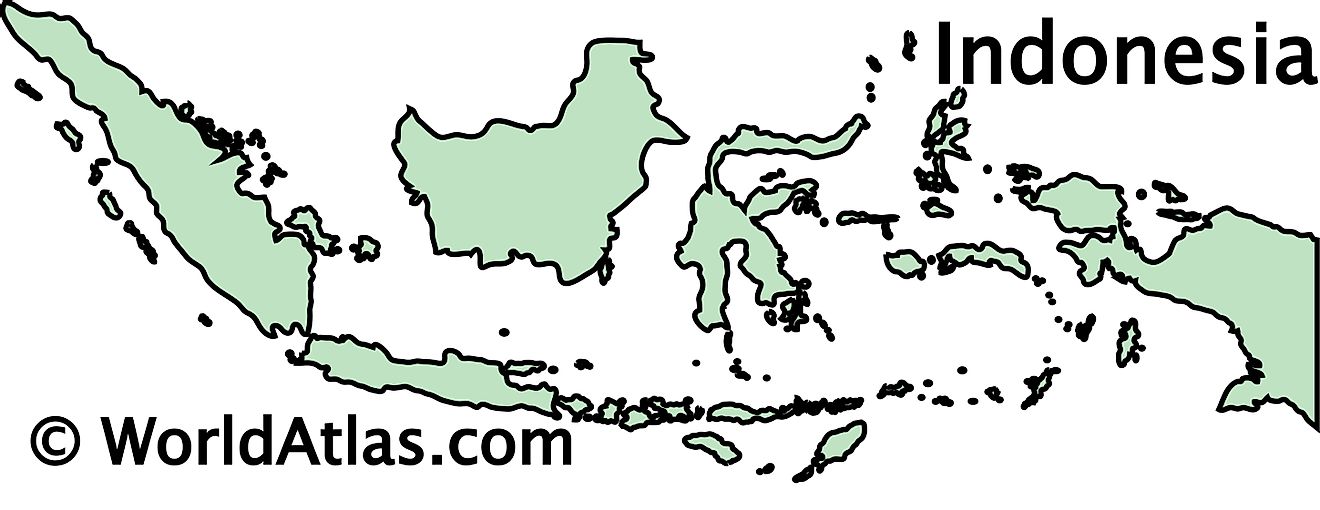
The above outline map represents the archipelagic nation of Indonesia - the world's largest island nation that is strategically positioned between the Pacific and Indian Oceans.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Republic of Indonesia |
|---|---|
| Flag |

|
| Capital City | Jakarta |
| 6 10 S, 106 49 E | |
| Total Area | 1,904,569.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 1,811,569.00 km2 |
| Water Area | 93,000.00 km2 |
| Population | 270,625,568 |
| Major Cities |
|
| Currency | Indonesian rupiah (IDR) |
| GDP | $1.12 Trillion |
| GDP Per Capita | $4,135.57 |
This page was last updated on December 16, 2023











