Maps of India
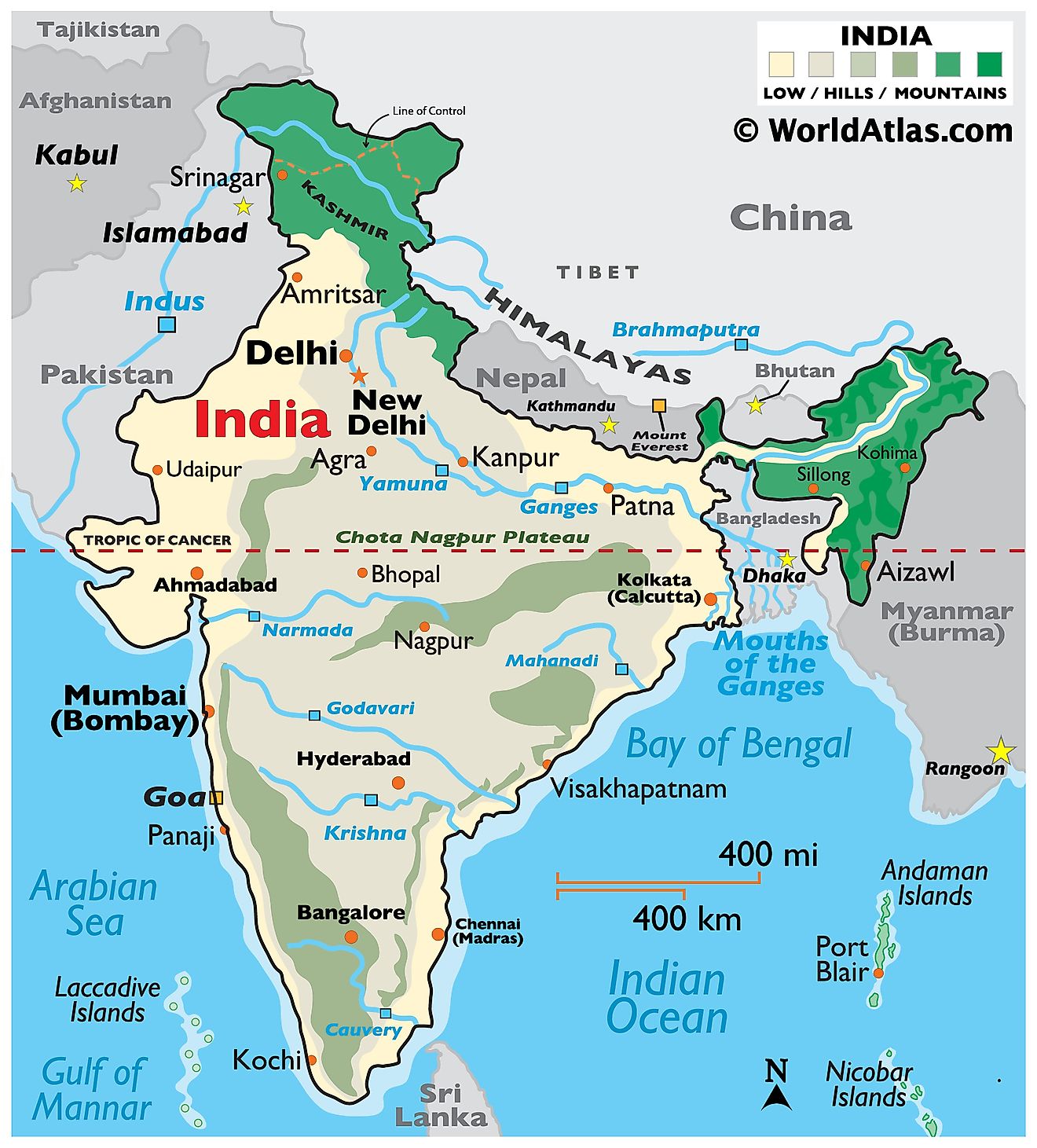
India, located in Southern Asia, covers a total land area of about 3,287,263 sq. km (1,269,219 sq. mi). It is the 7th largest country by area and the 2nd most populated country in the world. To the north, India borders Afghanistan and Pakistan, while China, Nepal, and Bhutan sit to its north and northeast. It also shares its eastern borders with Bangladesh and Myanmar. The southwestern and southern parts of India are surrounded by the Indian Ocean, with the Arabian Sea to the west and the Bay of Bengal to the east.
India is divisible into four particular regions: the Himalayan Region, the Northern Plains, the Peninsular Plateau, the Coastal Plains, and the Islands.
The Himalayan Region, in the north of India, comprises the world's highest mountain ranges, including the formidable Himalayas. These mountain ranges not only contribute to the country's scenic beauty but also play a crucial role in influencing India's climate, particularly acting as a barrier against the cold central Asian winds. This region is home to many prominent peaks, including Mount Kanchenjunga and Nanda Devi, with the world's highest peak of 8,848 m (29,029 ft) above sea level, Mount Everest, located on the Nepal-China border in close proximity to India. However, the highest point in India is Mount Kanchenjunga which rises to 28,208 ft. (8,598 m).
The Northern Plains, south of the Himalayan Region, is made up of the Gangetic Plains formed by the Indus, Ganges, and Brahmaputra river systems. This region is a large and fertile alluvial plain that stretches across several states and is the country's primary agricultural hub.
The Peninsular Plateau: South of the Northern Plains is the Peninsular Plateau, an ancient landmass composed of the Malwa plateau in the north and the Deccan plateau in the south. This region is rich in minerals and is bordered by the Western and Eastern Ghats, a range of hills running along the coasts.
The Coastal Plains include the Western Coastal Plains, which stretch from Gujarat to Kerala, and the Eastern Coastal Plains, extending from West Bengal to Tamil Nadu. These regions, located between the peninsular plateau and the respective seas, feature wide and fertile deltas formed by the rivers flowing into the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal.
Major bodies of water in India include the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal, part of the larger Indian Ocean. The country's significant rivers are the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and the Indus, all of which play a crucial role in India's agriculture, providing the needed water resources and enriching the soil with silt.
The Indian Islands consist of two major groups: the Lakshadweep Islands in the Arabian Sea and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal. The former is a group of coral islands, whereas the latter is a group of volcanic islands.
States of India Map
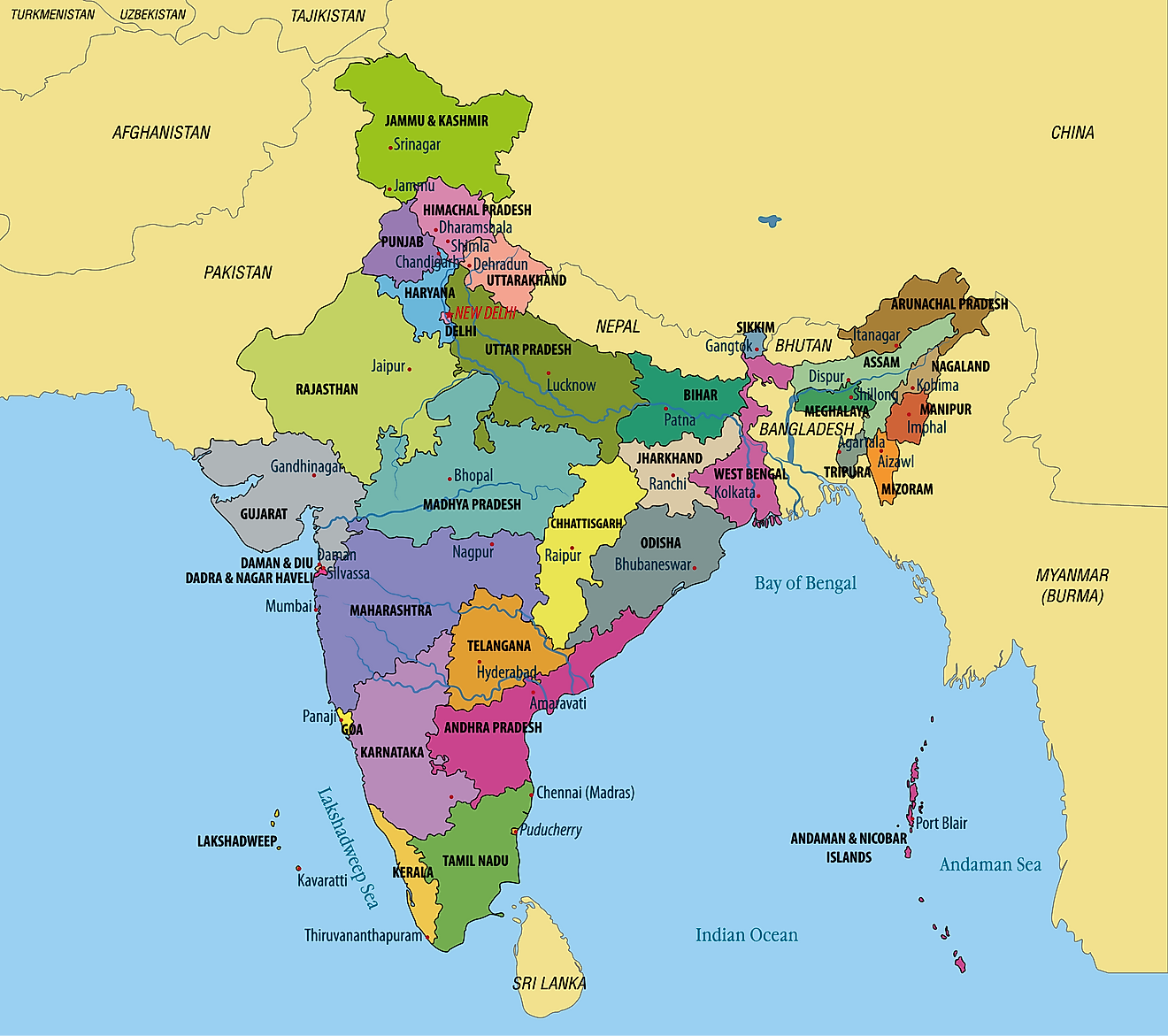
India is divided into 28 states and 8 Union Territories. The states are: Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Goa, Gujarat, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Odisha, Punjab, Rajasthan, Sikkim, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and West Bengal. The Union Territories are: Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Chandigarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, National Capital Territory of Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Lakshadweep and Puducherry.
Covering a total land area of 3,287,263 sq.km, India is the world’s 7th largest and the 2nd-most populous country. Located in the north-central part of the country in the National Capital Territory of Delhi is, New Delhi – the capital of India. Situated in the western coast of the country is Mumbai – the largest and the most-populated city of India. It is also the country’s chief port as well as the industrial and commercial center.
Where is India?
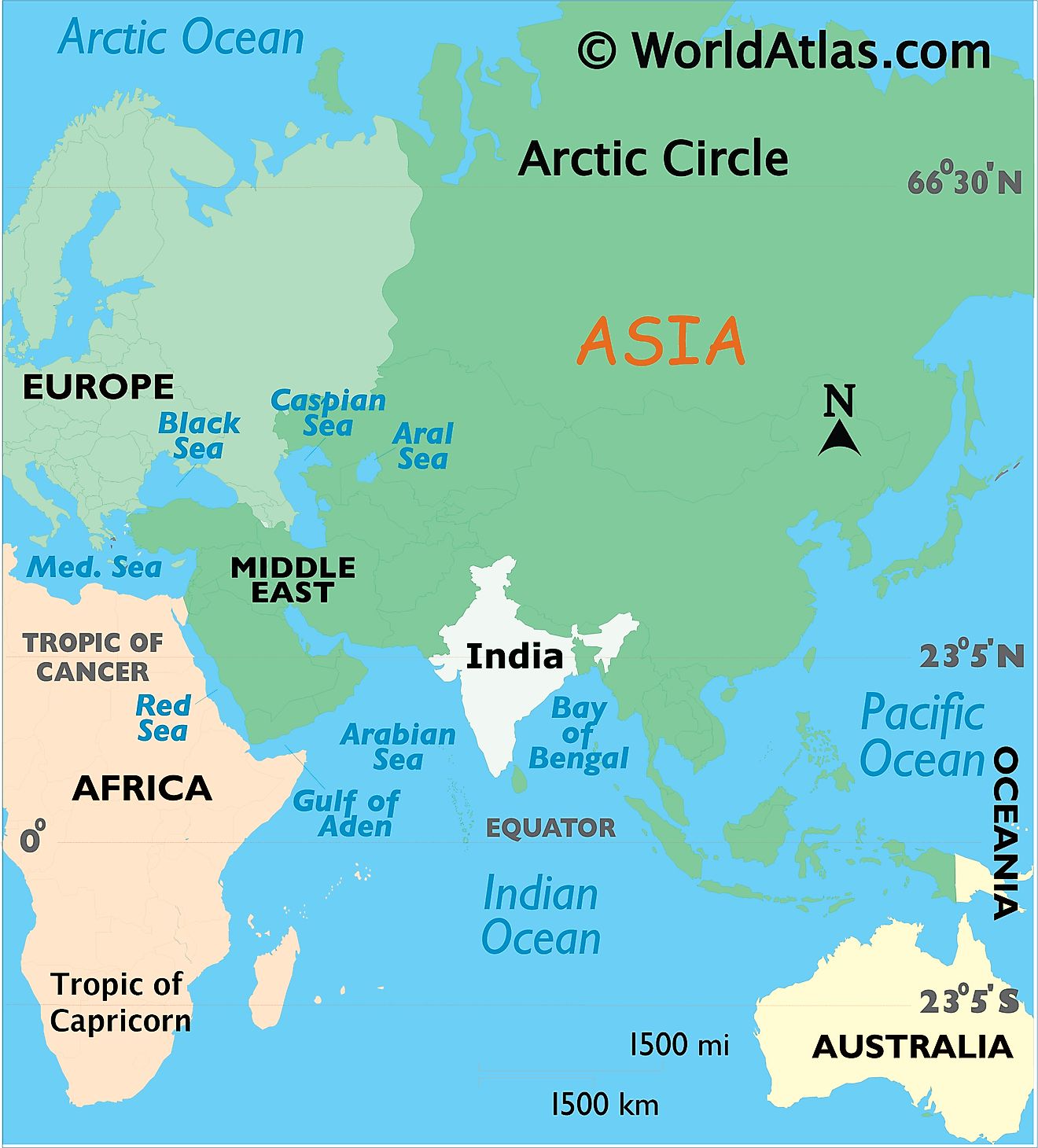
India is a large country located on the Indian subcontinent in south-central Asia. India is geographically positioned both in the Northern and Eastern hemispheres of the Earth. It is bordered by Afghanistan and Pakistan in the north-west; by China, Nepal and Bhutan in the north; and by Bangladesh and Burma (Myanmar) in the east. It is bounded by the Arabian Sea in the southwest; by Bay of Bengal in the southeast; and by the Indian Ocean in the south. The narrow channel of Palk Strait and the Gulf of Mannar separates the island nation of Sri Lanka from the Indian mainland.
India Bordering Countries: China, Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Myanmar, Pakistan.
Regional Maps: Map of Asia
Outline Map of India
The above blank map represents India - a large country located on the Indian subcontinent in south-central Asia. The above map can be downloaded, printed and used for geography education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.
The above outline map represents India - a large country located on the Indian subcontinent in south-central Asia. It is one of the world's most ethnically diverse countries.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Republic of India |
|---|---|
| Flag |

|
| Capital City | New Delhi |
| 28 36 N, 77 12 E | |
| Total Area | 3,287,263.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 2,973,193.00 km2 |
| Water Area | 314,070.00 km2 |
| Population | 1,366,417,754 |
| Major Cities |
|
| Currency | Indian rupees (INR) |
| GDP | $2.88 Trillion |
| GDP Per Capita | $2,104.15 |
This page was last updated on July 6, 2023











