Maps of Spain
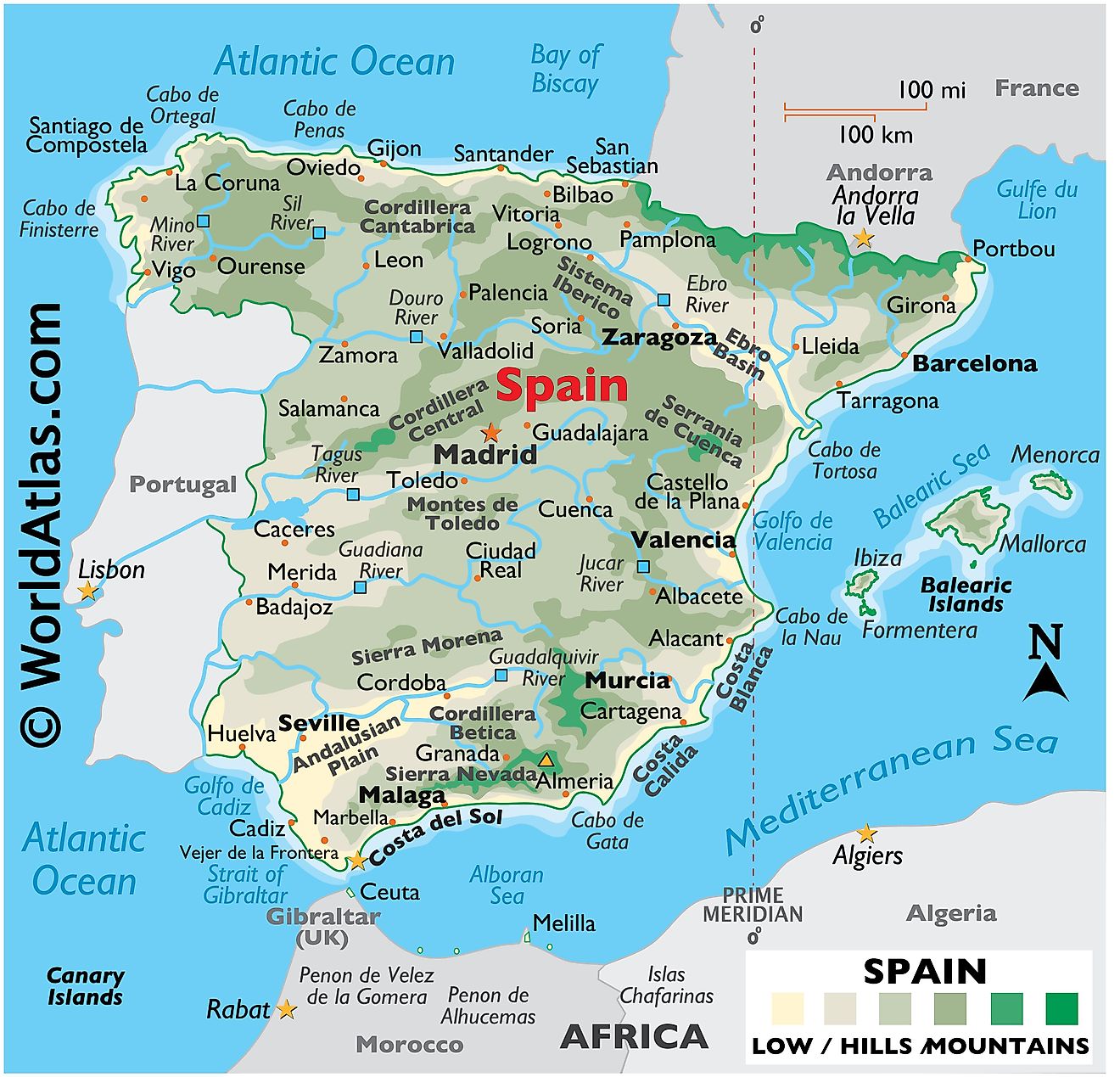
Spain is located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula, which it shares with its western neighbor, Portugal. To the north, it borders France and Andorra, with the Pyrenees mountain range acting as a natural boundary. Towards the south, Morroco lies just across the Strait of Gibraltar. The Mediterranean Sea lines its eastern coast, while the Atlantic Ocean lies to the north and west. The total area of Spain is about 505,994 km2 (195,365 mi2).
Mainland Spain comprises eight geographic regions, but the notable territories of the Balearic and Canary Islands are also significant enough to merit inclusion.
Meseta Central: The Meseta Central is a vast plateau in the heart of Spain. This expansive high plain covers a significant portion of the country's interior and is characterized by its relatively flat terrain interspersed with rolling hills. The Tagus and Duero Rivers cut across this region, providing crucial water sources for agriculture. The altitude of the Meseta Central averages about 660 meters (2,165 feet), giving it a continental climate with hot summers and cold winters.
Cantabrian Mountains (Cordillera Cantabrica) and the Northwest Region: The Cantabrian Mountains extend across northern Spain, running parallel to the Bay of Biscay. These mountains are characterized by their rugged peaks, deep valleys, and dense forests. They act as a climatic barrier, bringing heavy rainfall to the northern coastal regions. The northwest region, including Galicia, benefits from these mountains, which ensures that the surrounding area receives adequate rainfall.
Ibérico Region: The Ibérico region, featuring the Iberian Mountains, is located in northeastern Spain. These mountains, though not as high as the Pyrenees, contain significant mineral deposits, especially in their northern parts. The Ebro River, one of Spain's most important rivers, originates from this region, providing an essential waterway for transportation and irrigation. This region is known for its varying landscapes, from rocky peaks to fertile valleys.
The Pyrenees: The Pyrenees mountain range acts as a natural boundary between Spain and France. Stretching approximately 300 miles (490 kilometers) from the Mediterranean Sea to the Bay of Biscay, these mountains are known for their towering peaks, some reaching over 11,000 feet (3,400 meters). Several major rivers, including the Garonne and the Aude, originate from the Pyrenees.
Penibético Region in the Southeast: The Penibético region encompasses the Baetic Mountain Range in southern Spain. This region features two primary mountain systems: the Sierra Nevada and the Sierra de los Filabres. The Sierra Nevada boasts the highest peak in mainland Spain, Mulhacén, which rises to 3,482 meters (11,424 feet). These mountain ranges are notable for supporting various ecosystems and serving as water catchments.
Andalusian Plain: The Andalusian Plain, situated in southern Spain, is a flat, fertile expanse. The Guadalquivir River, one of the country's major rivers, flows through this plain, making the land especially suitable for agriculture. Historically, this region has been significant for crop production, particularly olives, cereals, and grapes. Its strategic location near the Strait of Gibraltar also makes it a critical economic region.
Ebro Basin: The Ebro Basin is centered around the Ebro River, which flows into the Mediterranean Sea. This basin is one of Spain's primary agricultural regions, producing a variety of crops thanks to its fertile soils. The river and its tributaries have been essential for the development of the region's agriculture and transportation networks. The Ebro Delta, where the river meets the Mediterranean, is of ecological significance, supporting numerous bird species.
Coastal Plains: Spain's coastal plains stretch along both its Mediterranean and Atlantic coastlines. These plains are often narrow, squeezed between the sea and nearby mountain ranges. With mild climates and fertile soils, they support agriculture, particularly citrus fruits, olives, and vineyards. Moreover, large settlements dot these coastal plains, and over time, they have grown into significant centers of trading, political concentration, and social infrastructure.
Balearic Islands: This autonomous community is an archipelago in the Mediterranean Sea, east of the Spanish mainland. Comprising major islands like Mallorca, Menorca, Ibiza, and Formentera, these islands are characterized by their limestone landscapes, fertile plains, and coastal cliffs. They play a significant role in Spain's tourism industry, attracting millions of visitors annually. The surrounding sea also contributes to the islands' mild climate and rich marine biodiversity.
Canary Islands: The Canary Islands are another autonomous archipelago that belongs to Spain, despite being located off the northwest coast of Africa. These volcanic islands, including major ones like Tenerife, Gran Canaria, and Lanzarote, harbor striking landscapes, from black sand beaches to towering volcanoes. Interestingly, Teide Peak of Tenerife is the highest point on Spanish soil, at 3,715 m (12,188 ft). The Canary Islands have a subtropical climate, which has made them a popular tourist destination. The Canary Current, a major ocean current of the North Atlantic, impacts the climate and marine life around these islands.
Bodies of Water: Besides the Atlantic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, the Bay of Biscay to the north, and the Alboran Sea, the country has a series of major rivers. The Tagus River originates in Spain and flows into Portugal, making it the longest. The Ebro River runs through the northeast, draining into the Mediterranean, and the Guadalquivir River winds through southern Andalusia, aiding agriculture. Other notable rivers include the Duero and the Júcar, each playing significant geographical roles.
Regarding lakes, Lake Sanabria is the Iberian Peninsula's largest glacial lake. The Albufera Lake, near Valencia, is a shallow lagoon, while the Lakes of Covadonga consist of Lake Enol and Lake Ercina in the Picos de Europa range. Catalonia's Lake Banyoles is another major natural lake. Spain also contains several reservoirs, crucial for water management.
Communities of Spain Map
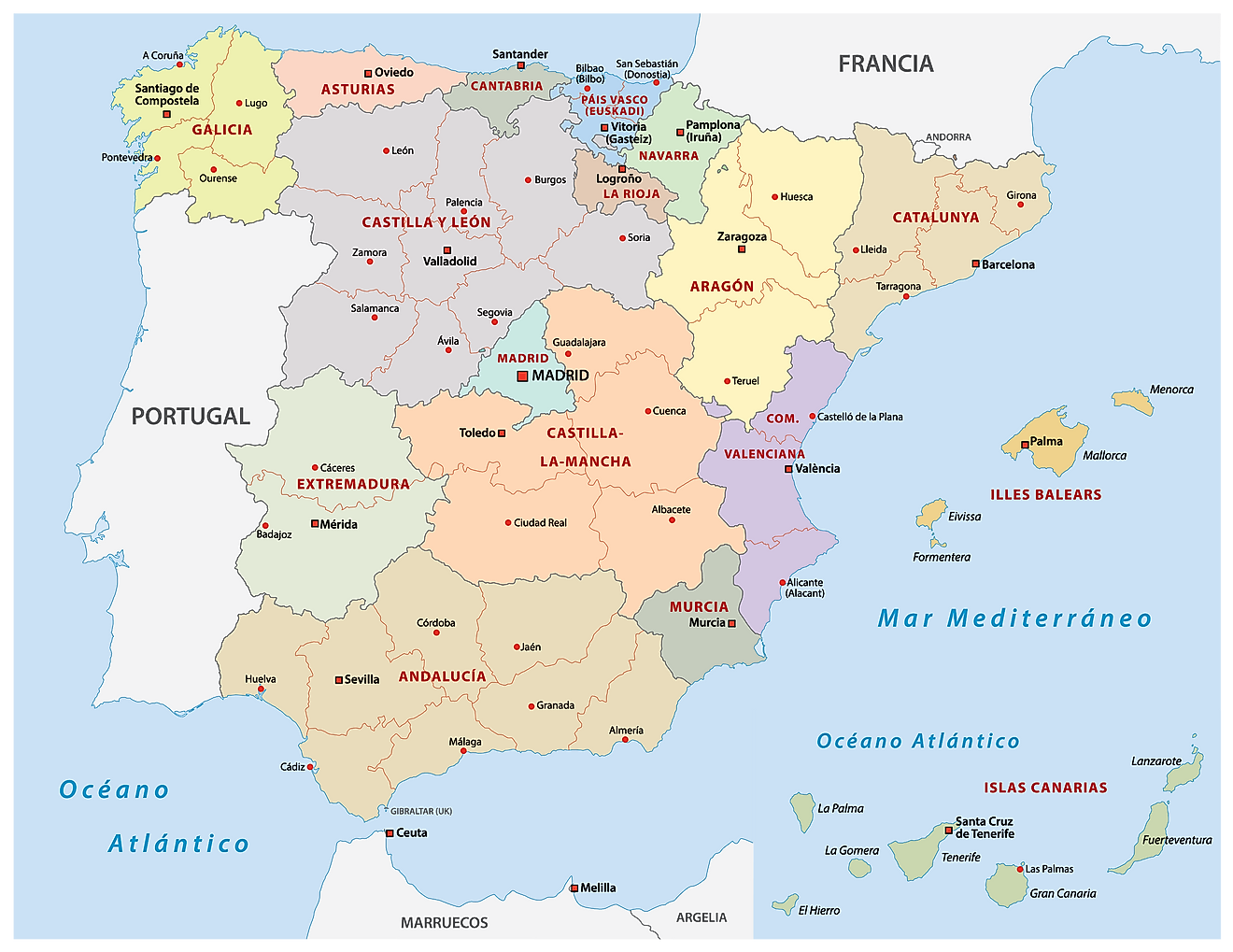
Spain (officially, the Kingdom of Spain) is divided into 17 autonomous communities (comunidades autonomas, sing. comunidad autonoma) and 2 autonomous cities (ciudades autonomas, sing. ciudad autonoma). The autonomous communities are: Andalusia, Catalonia (Catalan), Madrid, Comunitat Valenciana [Valencian Community], Galicia, Castilla-Leon, Euskadi (Basque) [Basque Country], Castilla-La Mancha, Canarias (Canary Islands), Murcia, Aragon, Extremadura, Illes Baleares (Balearic Islands), Asturias, Navarre (Castilian), Cantabria, and La Rioja. The 2 autonomous cities are: Ceuta and Melilla. The autonomous communities are further subdivided into provinces and smaller subdivisions.
With an area of 505,990 sq. km, Spain is the largest country in Southern Europe and the 4th largest country in the continent of Europe. It is also the 2nd largest country in Western Europe and EU. Spain has a population of over 47 million, making it the 6th most populous country in Europe and the 4th most populous country in EU. Located in the central part of the country is, Madrid – the capital, the largest and the most populous city of Spain. Madrid is also the cultural, administrative and economic center of Spain. Madrid functions as an important financial hub of Southern Europe.
Where is Spain?
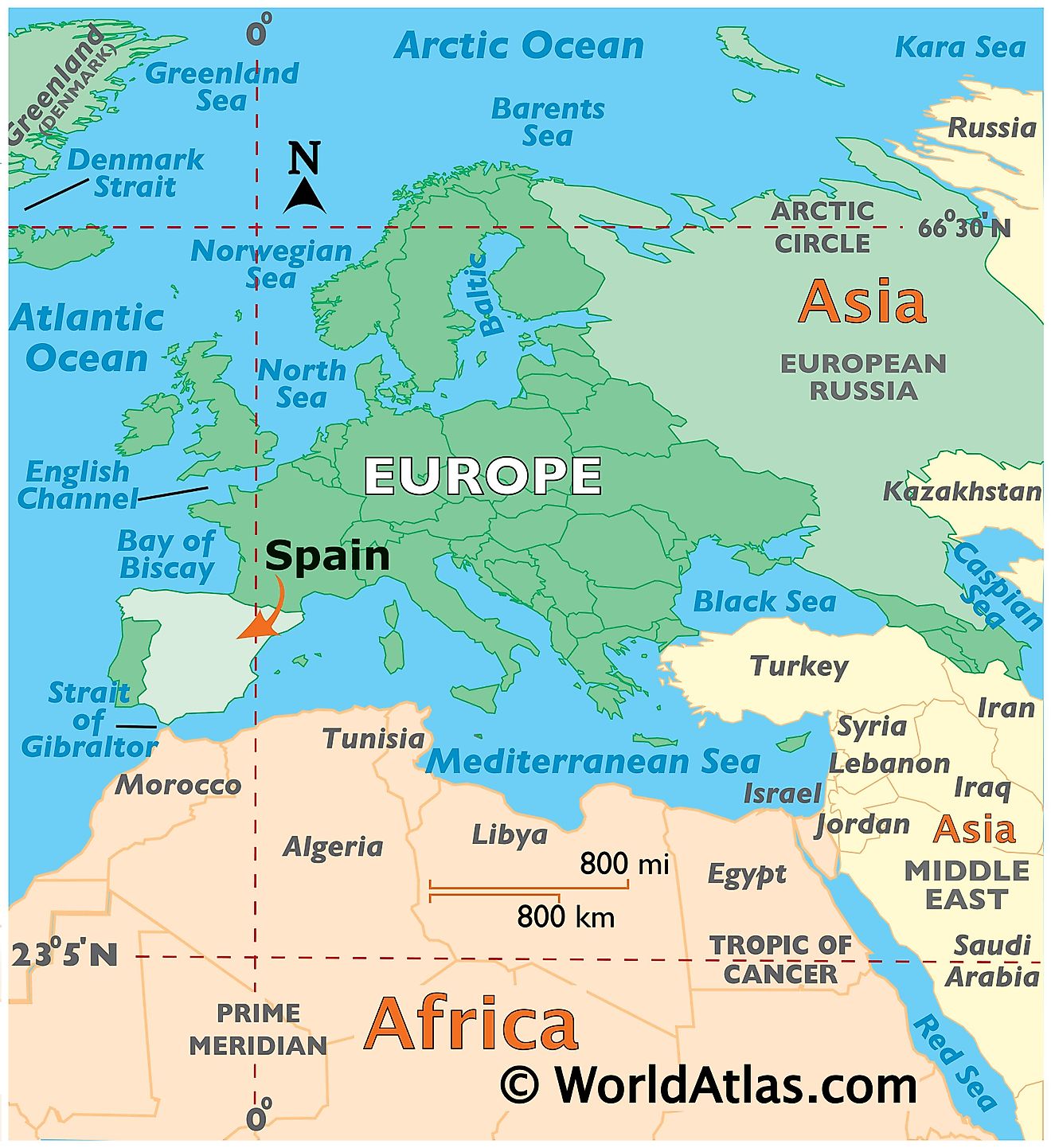
Spain is a country located on the Iberian Peninsula in southwestern Europe. It is situated in both Northern and Eastern hemispheres of the Earth. Spain is bordered by 5 countries: by Portugal in the west, by France and Andorra in the northeast, by Gibraltar and Morocco (the Spanish territories of Ceuta and Melilla in North Africa), in the south. The country is bounded by the Mediterranean Sea in the east and southeast, by the Atlantic Ocean in the northwest and southwest and by the Bay of Biscay in the north. Spain shares its maritime borders with Algeria and Italy.
Spain Bordering Countries: Morocco, Gibraltar, Portugal, Andorra.
Regional Maps: Map of Europe
Outline Map of Spain
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Kingdom of Spain |
|---|---|
| Flag |

|
| Capital City | Madrid |
| 40 24 N, 3 41 W | |
| Total Area | 505,370.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 498,980.00 km2 |
| Water Area | 6,390.00 km2 |
| Population | 47,076,781 |
| Major Cities |
|
| Currency | Euros (EUR) |
| GDP | $1.39 Trillion |
| GDP Per Capita | $29,613.67 |
This page was last updated on August 18, 2023