Maps of Norway
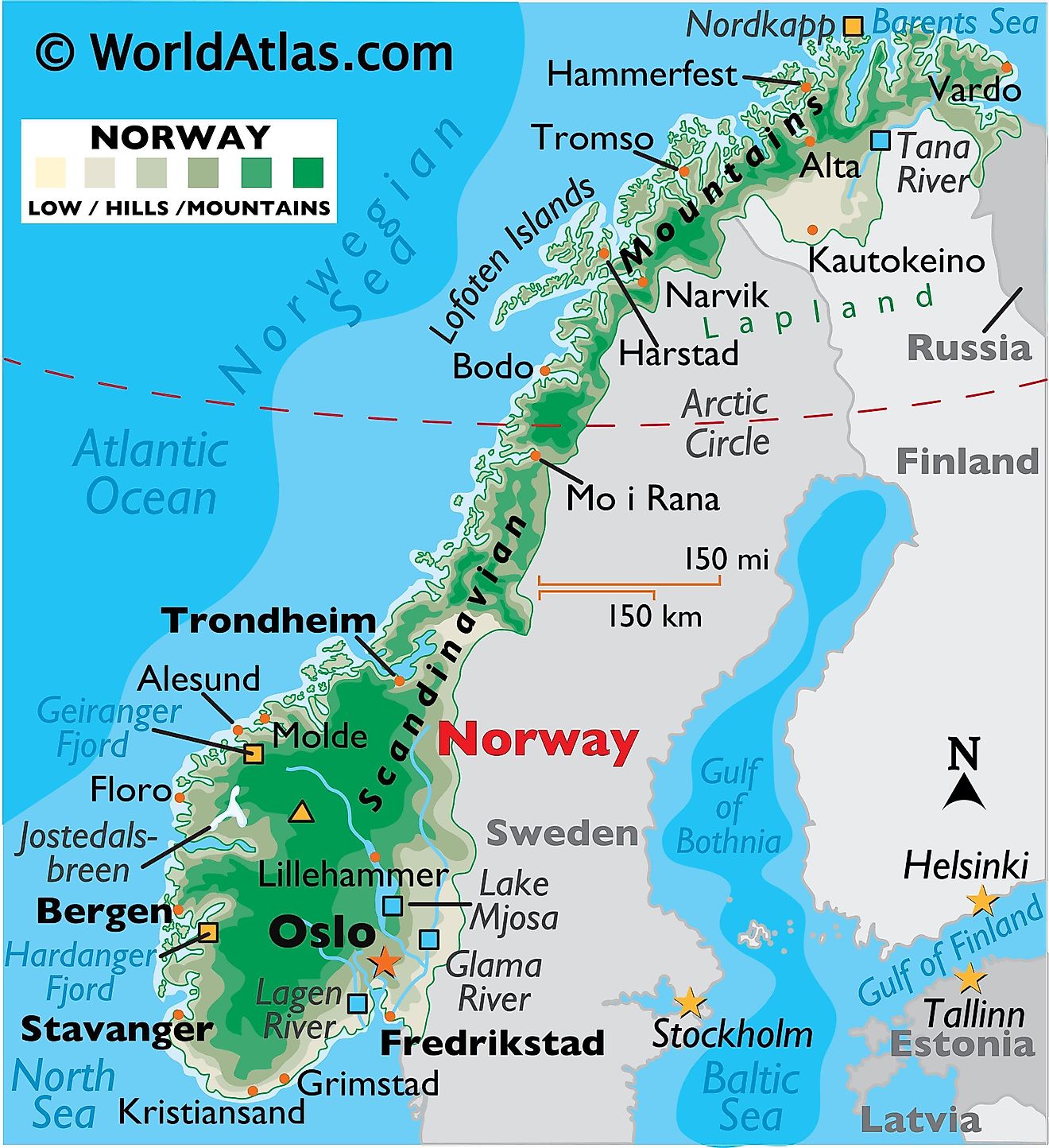
Norway is a northern European country covering an area of 385,207 sq. km on the Scandinavian Peninsula. As observed on the physical map of Norway, the country is highly mountainous and has a heavily indented coastline.
Before the last ice age ended about 10,000 years ago, Norway was covered by a thick ice sheet. When that ice finally retreated (or melted) its movement across the land formed islands, lakes, rivers and mountains. It also etched-out deep valleys that then filled with seawater forming Norway's fjords.
Norway is a rugged land of elevated plateaus, deep forested valleys and a few remaining ice age glaciers, including Folgefonna, Hardangerjokulen and Jostedalsbreen - the largest glacier on the continental Europe landmass.
Norway is one of Europe's most mountainous countries and dominated north to south by the many ranges of the Scandinavian Mountains as observed on the map above.
Its toothy-edged western coastline is a jagged expanse of (over 50,000) islands and dozens of long, deeply indented fjords; the most significant of which include Baknafjord, Geirangerfjord, Hardangerfjord, Moldefjord, Sognefjord, Trondheimfjord and Vestfjord.
In the far northeast above the Arctic Circle, frozen arctic tundra dominates the landscape, from Vardo, south and west. This tundra receives little precipitation and has a very short growing season, so it is generally a treeless plain of low shrubs and hearty grasses.
A south-central plateau slopes into the Trondelag, a hilly and mountainous farming area with strips of fertile land on the edges of the Trondheim Fjord. Additional lowlands are found in the southeast and along parts of the southern coastline.
There are reportedly over 150,000 (counted) lakes, most quite small, with the largest being Lake Mjosa.
Significant rivers include the Glama, the country's longest, and the Dramselva, Lagen (two of them) and the Tana in the far north.
The highest point in Norway (as marked on the map by a yellow triangle) is Galdhøpiggen, standing at 2,469 m (8,100 ft). The lowest point is sea level at the coast.
Regions of Norway Map
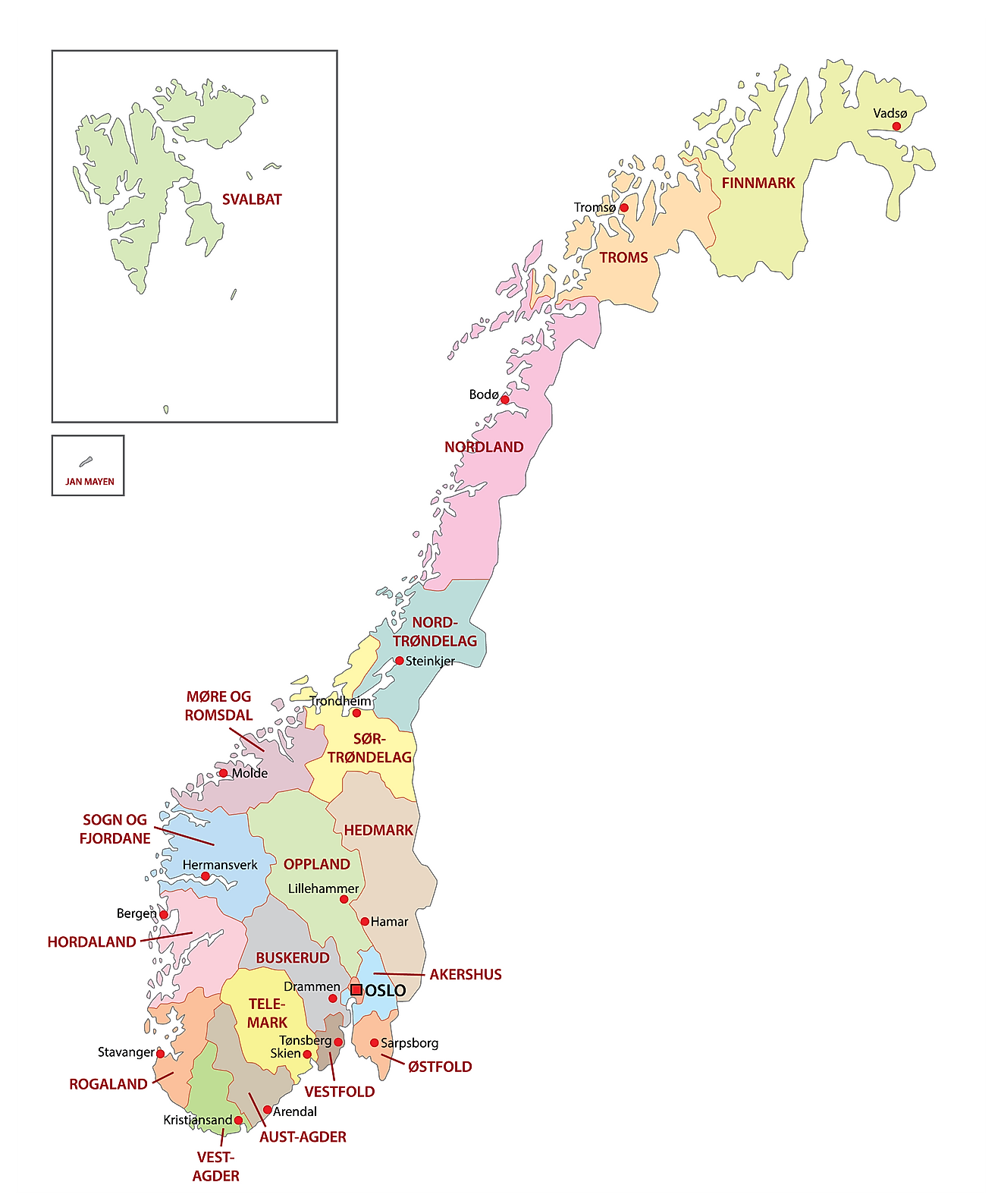
Norway is divided into 11 administrative regions or counties. In alphabetical order, the regions are: Agder, Innlandet, More og Romsdal, Nordland, Oslo, Rogaland, Troms og Finnmark, Trondelag, Vestfold og Telemark, Vestlandet and Viken. These counties are further subdivided into 356 municipalities.
[These new divisions have been reorganised and been implemented by the Norwegian Storting (Parliament), with effect from 1st January, 2020]
Located in the northwest of Oslofjord and surrounded by forested hills is, Oslo – the capital, the largest and the most populous city of Norway. It is the administrative, cultural, industrial and economic center of the country. Oslo is also an important maritime industries and trading center in Europe.
Where is Norway?
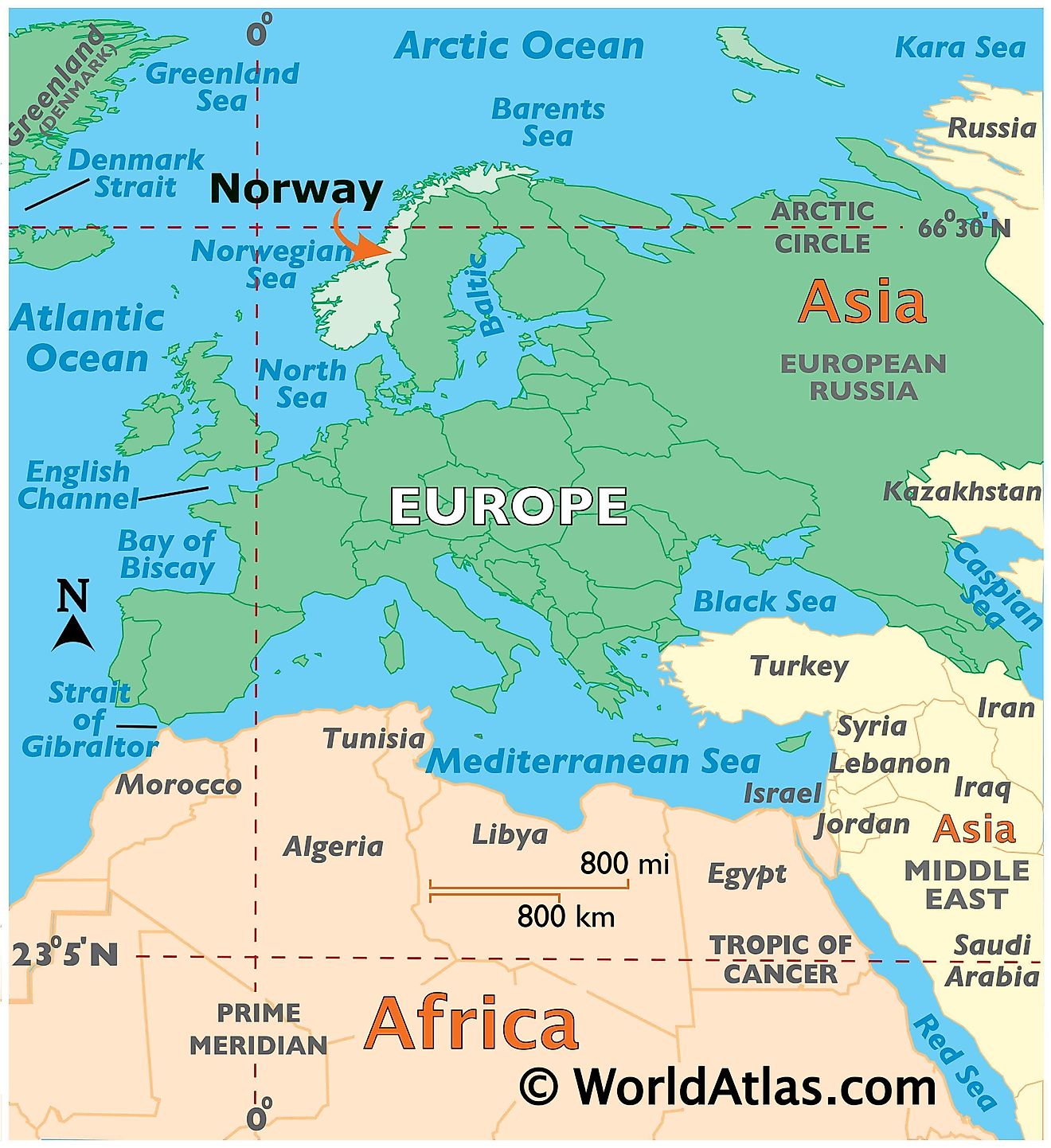
Norway is a Northern European country located on the western half of the Scandinavian Peninsula. It is geographically positioned both in the Northern and Eastern hemispheres of the Earth. Norway shares land borders with Sweden, Finland and Russia in the east and an extensive coastline facing the North Atlantic Ocean on the west. It is bounded by the Barents Sea in the north, the Norwegian Sea and the North Sea in the west and the Skagerrak (Skager Strait) in the south.
Regional Maps: Map of Europe
Outline Map of Norway
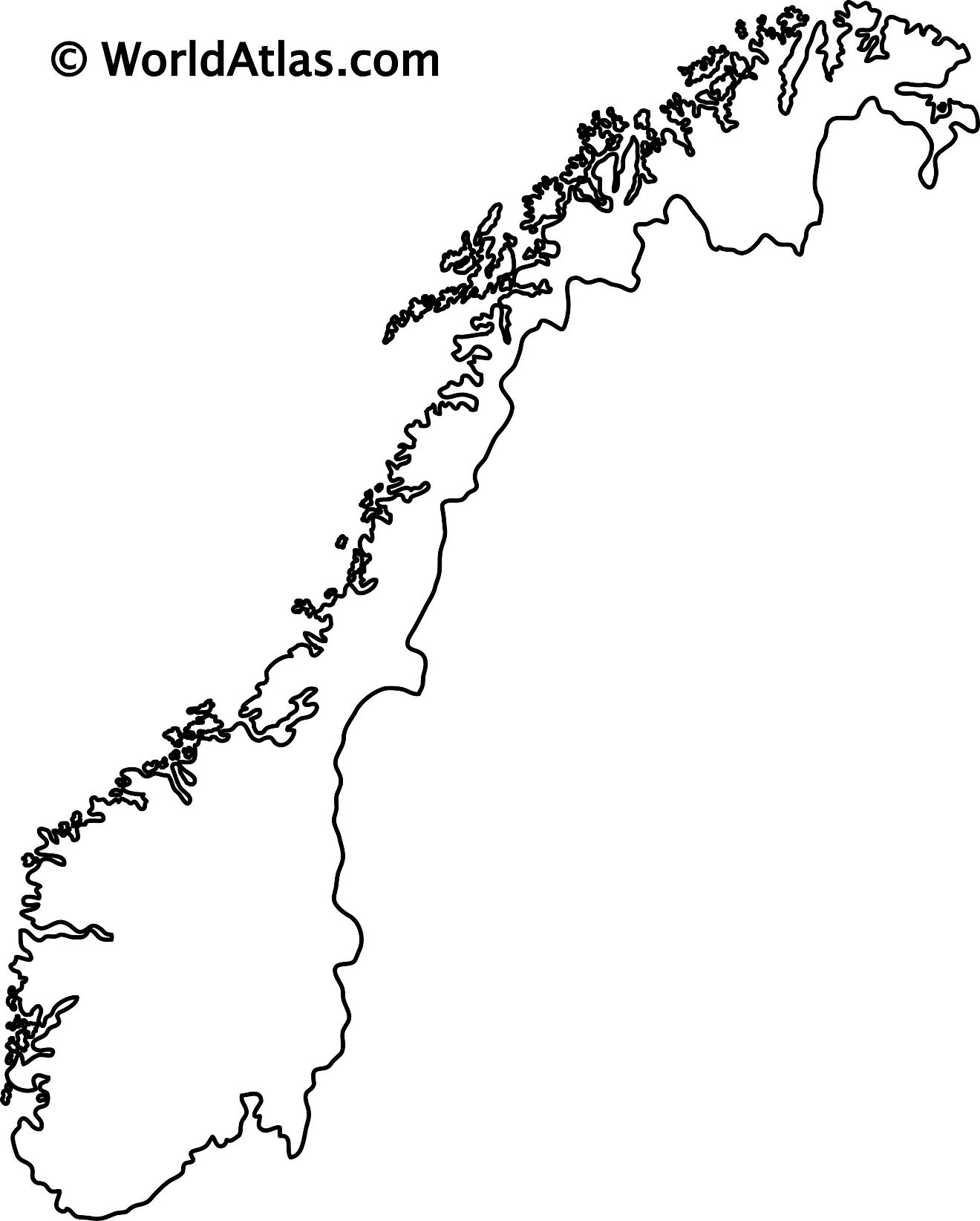
The blank outline map above is of Norway, a highly mountainous country in Northern Europe on the western half of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The map can be downloaded, printed, and used for coloring or educational purpose like map-pointing activities.
The map above represents Norway, one of the northernmost countries of the world. The country has an elongated shape with a highly rugged coastline.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Kingdom of Norway |
|---|---|
| Flag |
|
| Capital City | Oslo |
| 59 55 N, 10 45 E | |
| Total Area | 323,802.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 304,282.00 km2 |
| Water Area | 19,520.00 km2 |
| Population | 5,347,896 |
| Largest City |
Oslo (1,085,992) |
| Currency | Norwegian kroner (NOK) |
| GDP | $403.34 Billion |
| GDP Per Capita | $75,419.63 |
This page was last updated on February 24, 2021











