Maps of Arizona
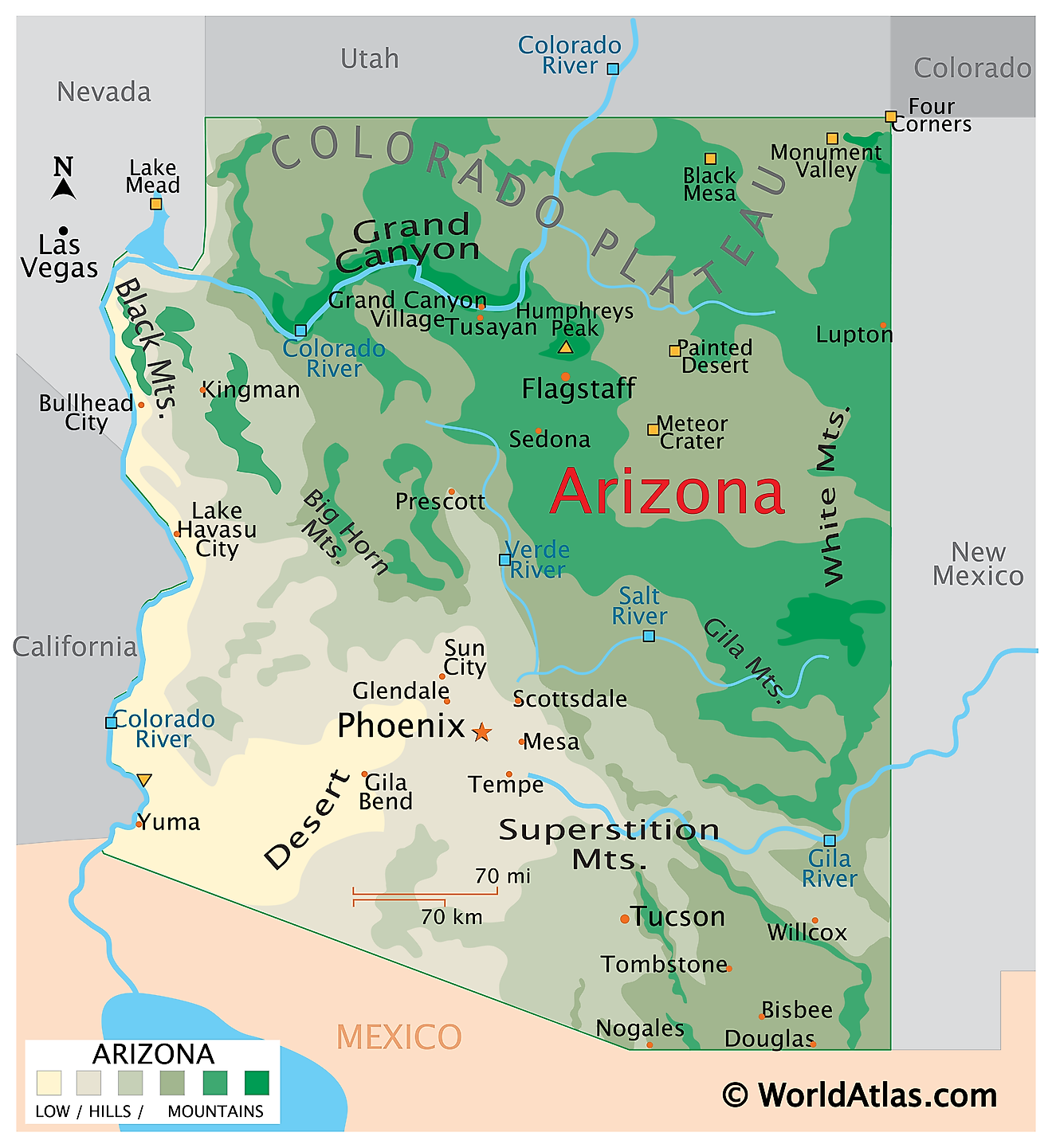
Arizona, a state in the United States, shares its borders with Utah to the north, New Mexico to the east, the Mexican states of Sonora and Baja California to the south, and California and Nevada to the west. To the southwest, Arizona also has a short coastline on the Colorado River, which forms part of the border with California. The state covers an area of approximately 113,998 mi2 (295,253 km2).
Arizona, from northeast to southwest, is divisible into three primary geographic regions:
Colorado Plateau: The Colorado Plateau spans the northern part of Arizona, characterized by a high, flat terrain interrupted by various canyons and valleys. This region is home to the Grand Canyon, one of the most famous geographical features in the United States, carved by the Colorado River over millions of years. The highest point in Arizona, Humphreys Peak, is located in this region, within the Kachina Peaks Wilderness. This peak reaches an elevation of 12,633 feet (3,851 meters) above sea level.
Transition Zone: South of the Colorado Plateau lies the Transition Zone, an area that features a mix of deep canyons and mountain ranges such as the Mogollon Rim and the White Mountains. It serves as a geographical boundary between the plateau and the deserts to the south. The region is distinguished by its significant elevation change from north to south, and it includes several important rivers that contribute to the state's water resources, including the Verde River and parts of the Salt River.
Basin and Range: The Basin and Range region occupies the southern portion of Arizona, characterized by low broad basins and narrow ridges known as sky islands. This topography is the result of crustal stretching that created north-south mountain ranges separated by valleys. Phoenix, the state's capital and largest city, is located in this region, within the Salt River Valley. The lowest point in Arizona is located near Yuma in the SSonoran Desert, where the Colorado River crosses the border with California, lying at an elevation of just 70 feet (21 meters) above sea level.
Major Bodies Of Water: Arizona's major bodies of water include the Colorado River, which defines part of its western border, and Lake Mead, formed by the Hoover Dam on the Colorado River. Other significant lakes include Lake Powell, Lake Havasu, and Roosevelt Lake, which are vital for water supply, irrigation, and recreation. The state's rivers include the Colorado River, the Salt River, and their tributaries.
Counties Map
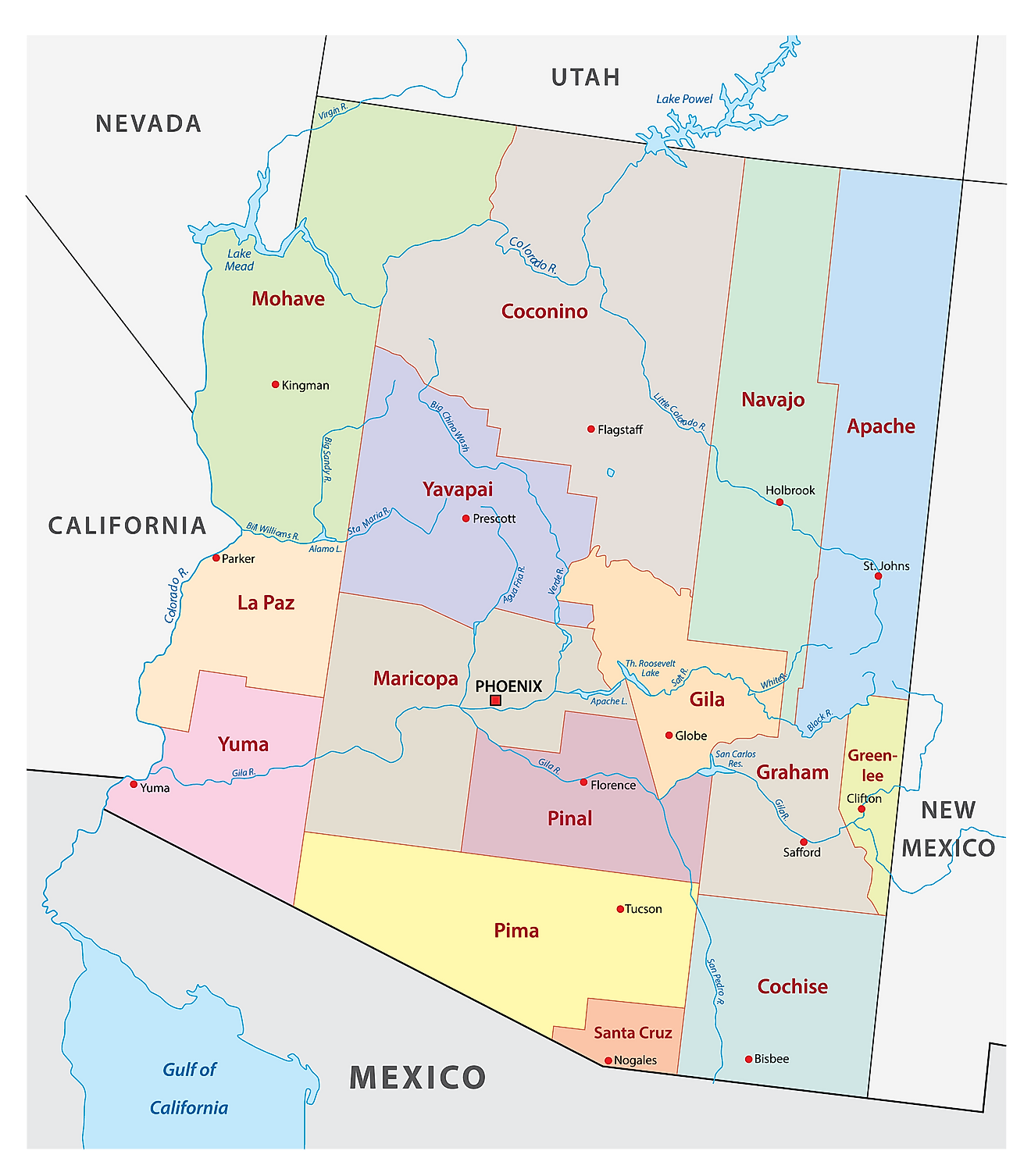
The State of Arizona is divided into 15 counties. In alphabetical order, these counties are: Apache, Cochise, Coconino, Gila, Graham, Greenlee, La Paz, Maricopa, Mohave, Navajo, Pima, Pinal, Santa Cruz, Yavapai, and Yuma.
With an area of 295,233 sq. km, Arizona is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous state in the USA. Located in the south-central part of the state, along the Salt River is Phoenix – the capital, the largest and the most populous city in Arizona. It serves as the financial, cultural, transportation and communication hub of the state. The capital city’s booming economy has been built around a strong real estate market, manufacturing and trade, health care and insurance services.
Where is Arizona?
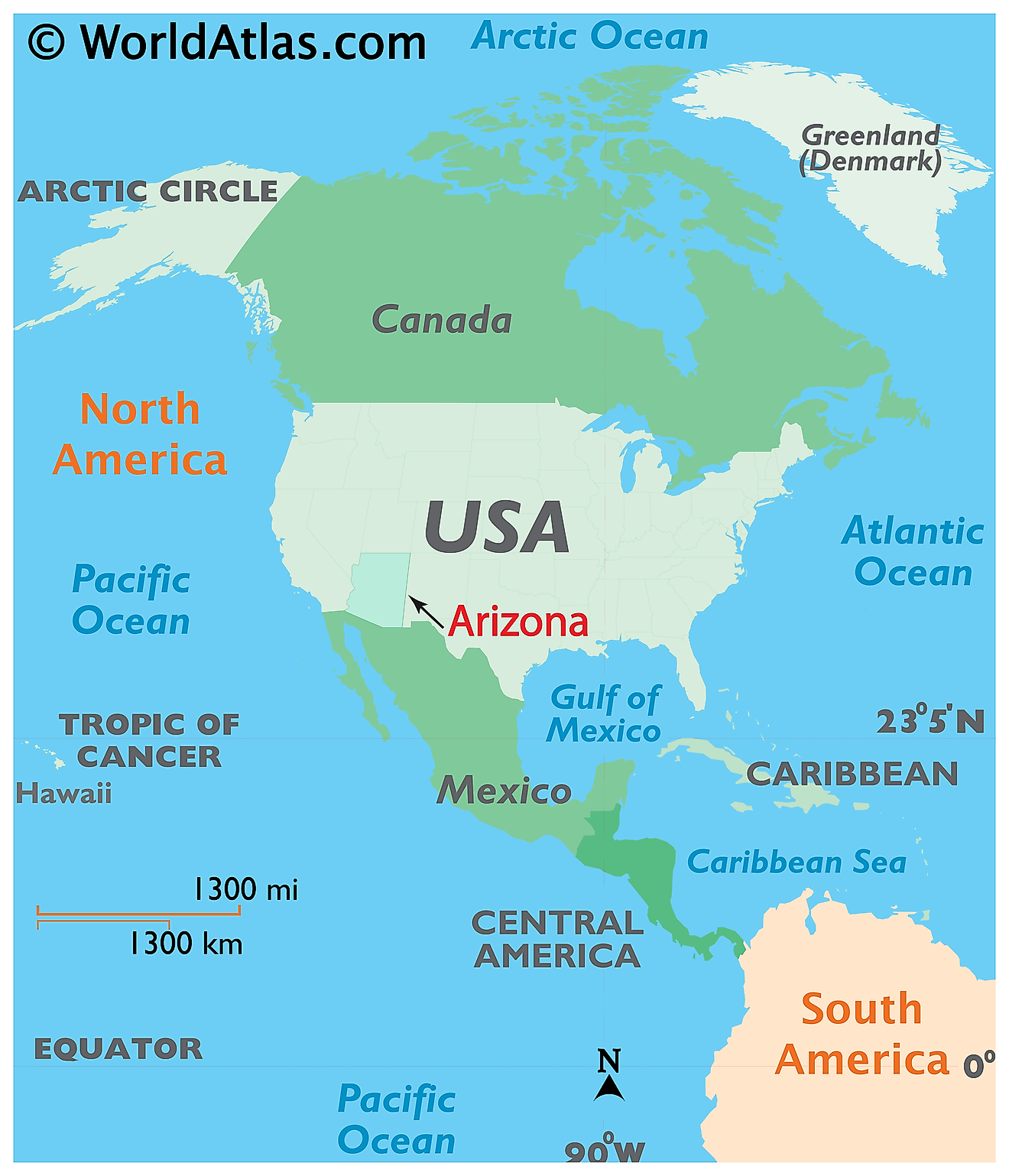
The State of Arizona is located in the southwestern region of the United States. This landlocked state is bordered by California in the west; by Nevada in the northwest; by Utah in the north; by New Mexico in the east; by the Mexican state of Sonora in the south; and by Baja California in the southwest. Arizona shares the Four Corners region, in its extreme northeastern corner, with the states of Colorado, Utah, and New Mexico.
Regional Maps: Map of North America
Outline Map of Arizona
The above blank map represents the State of Arizona, located in the southwestern region of the United States. The above map can be downloaded, printed and used for geography education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.
The above outline map represents the State of Arizona, located in the southwestern region of the United States.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | State of Arizona |
|---|---|
| ISO 3166 Code | US-AZ |
| Capital City | Phoenix |
| Major Cities |
|
This page was last updated on February 7, 2024











