Maps of Minnesota
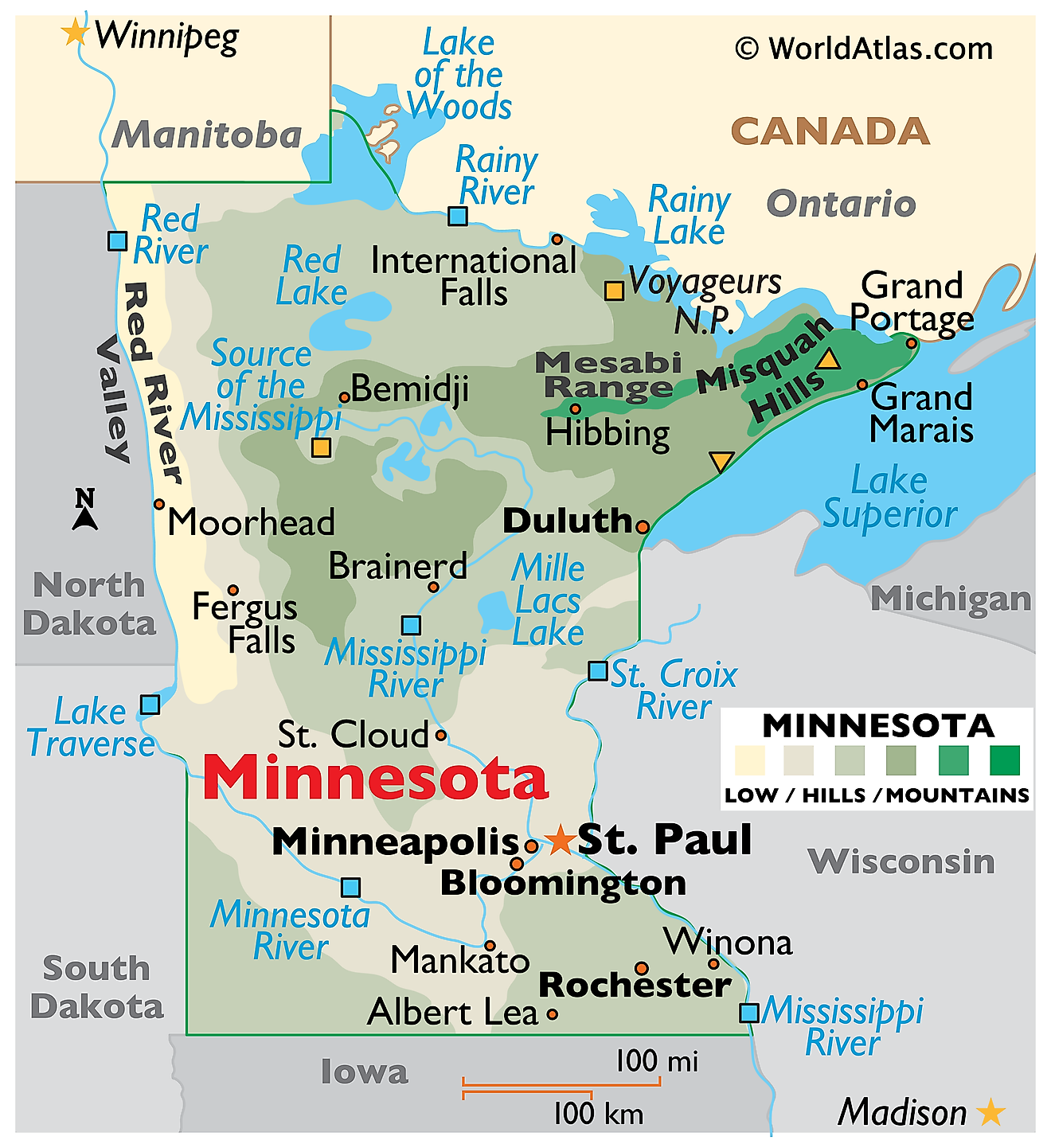
Minnesota, a state in the upper Midwest of the United States, borders Canada to the north, Lake Superior and Wisconsin to the northeast, Iowa to the south, and South Dakota and North Dakota to the west. The state spans an area of 86,935 mi2 (225,163 km2).
Minnesota, from north to south, is divisible into six primary geographic regions:
The Lake Agassiz Plain and Northern Plain region characterizes the northwesternmost part of Minnesota. This expansive region includes the remnants of the prehistoric Lake Agassiz and extends over the Lake of the Woods. Its geography is marked by flat, fertile land with occasional low rolling hills, suitable for extensive agriculture. Here, in the west along its border with North Dakota, the Red River Valley stretches from the Canadian border to the edges of South Dakota.
The Lake Superior and Northern Highland region lies to the northeast, encompassing the rugged terrain along the shores of Lake Superior. The Sawtooth Mountains here include Eagle Mountain, the highest point in Minnesota at 2,301 feet (701 meters). This area experiences more elevation changes than the rest of the state, with rocky cliffs and ridges providing dramatic landscapes.
The Central Till Plain occupies a substantial portion of the state's heartland. It is characterized by its gently rolling hills formed by glacial deposits, known as till. This region's soil is rich, benefiting from the glacial history that has influenced its topography and making it prime land for farming.
The Eastern Till Plain, running along the eastern side of the state towards its border with Wisconsin, features a landscape similar to the Central till Plain but with more pronounced rolling hills and valleys. It is in this region that the St. Croix River, a tributary of the Mississippi River, carves its way through creating a natural boundary between Minnesota and Wisconsin. This waterway complex aids greatly in commerce and transportation and is a key reason for the settlement of the capital, St. Paul, and Minneapolis.
The Northern Glaciated Plain and Western Plain encompass a large area in the southwestern part of Minnesota. This region features prairie lands and is part of the larger Great Plains of North America. The Red River forms the western boundary of Minnesota and flows northward into Canada, while the Minnesota River cuts through the southern part of this region, contributing to the state's extensive network of waterways.
Southeastern Upland is characterized by its rugged, bluff-lined river valleys and forested uplands. This region includes the Driftless Area, which escaped the flattening effects of glaciation during the last Ice Age. The Root River and the Upper Iowa River wind through this hilly landscape, which differs markedly from the plains to the west.
Maajor Bodies of Water include Lake Superior, which has a significant influence on the state's northeastern climate and geography. The state boasts a coastline of approximately 189 miles (304 kilometers) along Lake Superior. Other major lakes include Lake of the Woods, Mille Lacs Lake, and the Upper and Lower Red Lakes. The Mississippi River originates in Minnesota and flows southward, becoming one of the defining waterways of the United States.
Counties Map
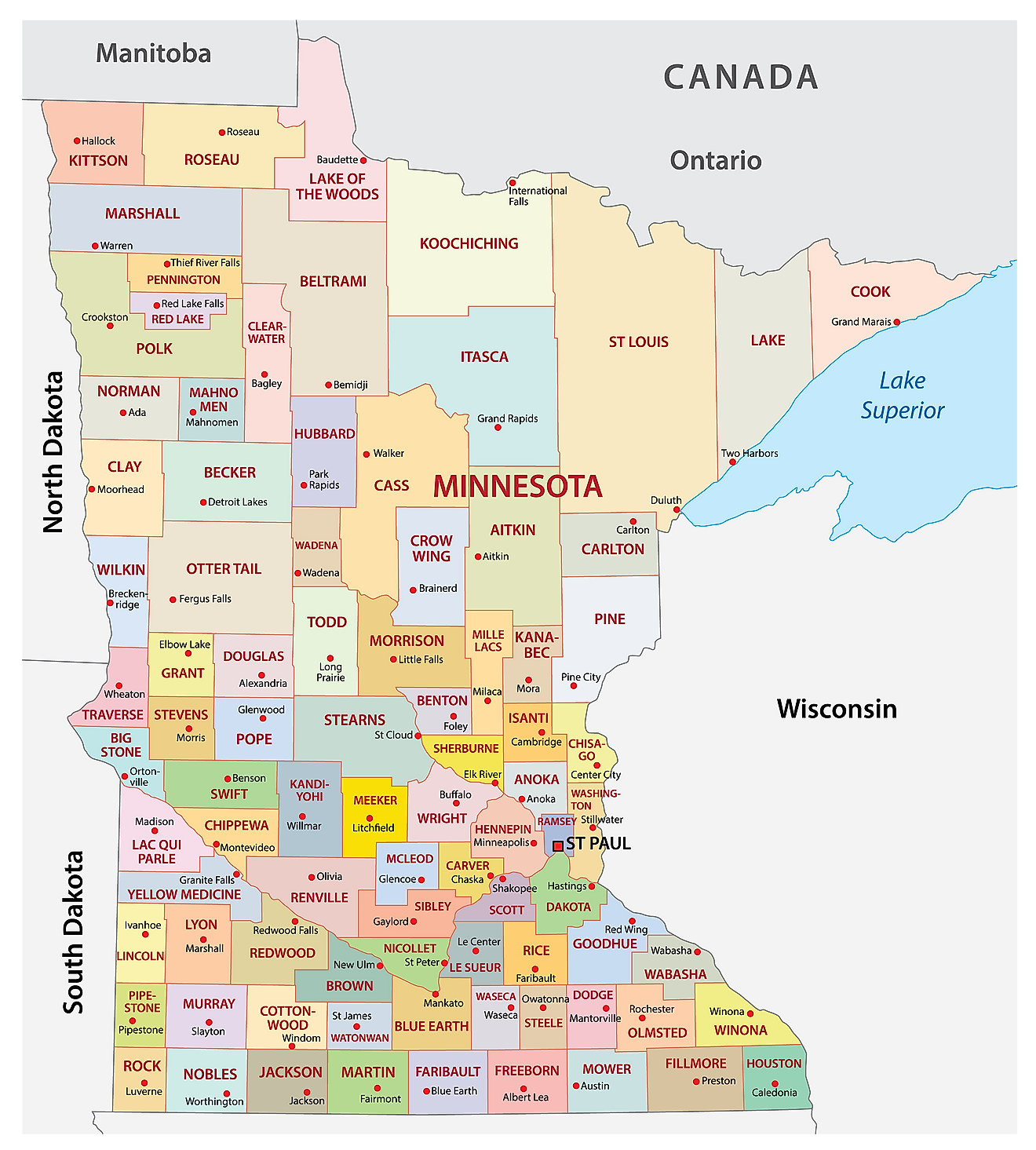
The State of Minnesota is divided into 87 counties. In alphabetical order, these counties are: Aitkin, Anoka, Becker, Beltrami, Benton, Big Stone, Blue Earth, Brown, Carlton, Carver, Cass, Chippewa, Chisago, Clay, Clearwater, Cook, Cottonwood, Crow Wing, Dakota, Dodge, Douglas, Faribault, Fillmore, Freeborn, Goodhue, Grant, Hennepin, Houston, Hubbard, Isanti, Itasca, Jackson, Kanabec, Kandiyohi, Kittson, Koochiching, Lac Qui Parle, Lake, Lake of the Woods, Le Sueur, Lincoln, Lyon, Mahnomen, Marshall, Martin, McLeod, Meeker, Mille Lacs, Morrison, Mower, Murray, Nicollet, Nobles, Norman, Olmsted, Otter Tail, Pennington, Pine, Pipestone, Polk, Pope, Ramsey, Red Lake, Redwood, Renville, Rice, Rock, Roseau, Saint Louis, Scott, Sherburne, Sibley, Stearns, Steele, Stevens, Swift, Todd, Traverse, Wabasha, Wadena, Waseca, Washington, Watonwan, Wilkin, Winona, Wright, and Yellow Medicine.
With an area of 225,163 sq. km, Minnesota is the 12th largest and the 22nd most populous state in the USA. Located in the southeastern part of the state, at the confluence of Mississippi and Minnesota Rivers is Saint Paul – the capital city of Minnesota. It serves as a major business center in the Upper Midwest region, and hosts the Xcel Energy Center – a multi-purpose arena and home of the Minnesota Wild. St. Paul city is also known for its high literacy levels and hosts the 2nd highest number of education facilities per capita in the United States. Situated on both the banks of the Mississippi River is Minneapolis – the largest and the most populous city in Minnesota. Minneapolis serves as the cultural and commercial center of the Midwest region. The cities of Saint Paul and Minneapolis together comprise the “Twin Cities Metropolitan Area”, which also functions as the chief administrative, business, industrial, education, cultural, and transportation center of the state.
Where is Minnesota?
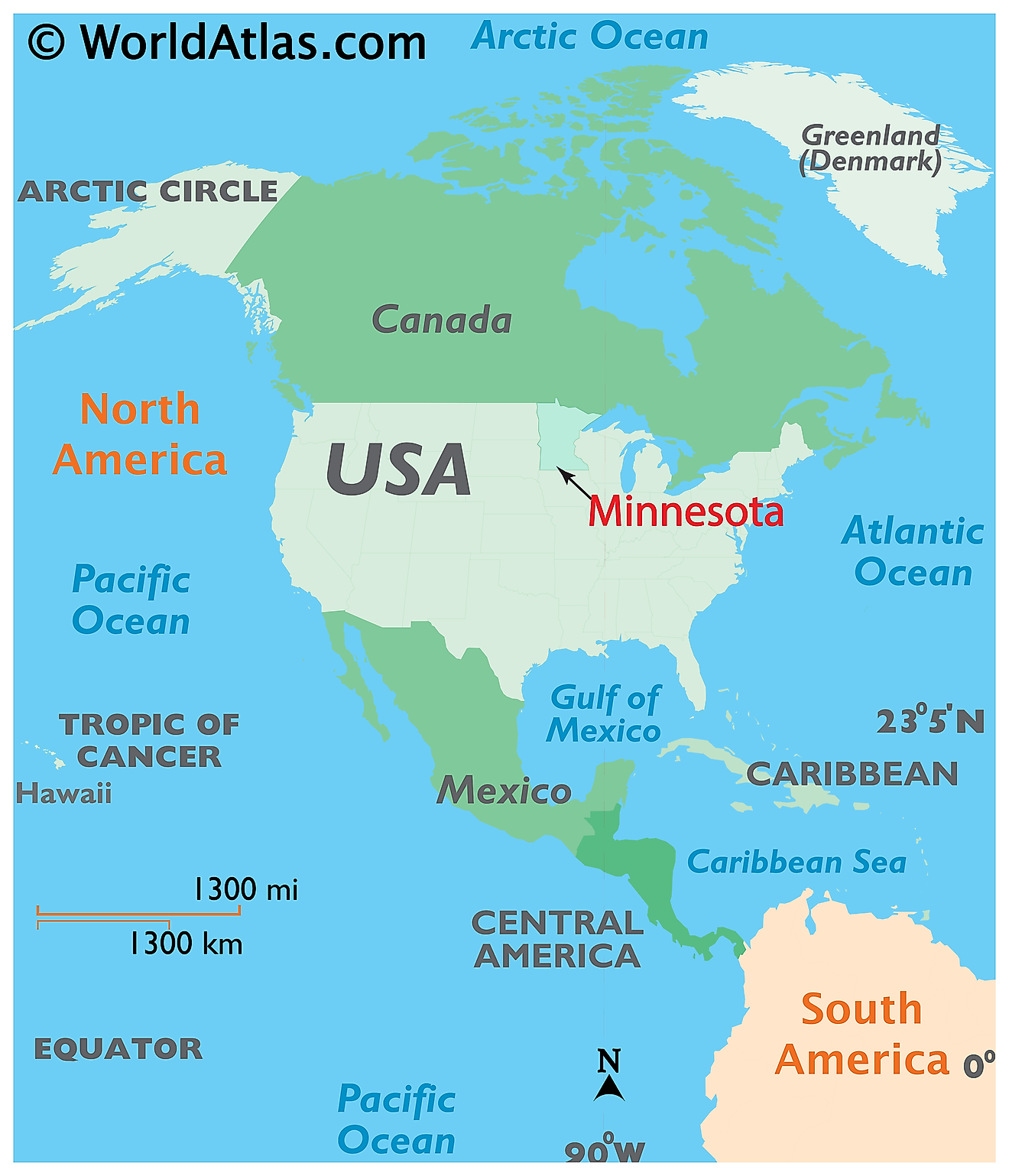
The State of Minnesota is located in the North-Central (Midwest) region of the United States. Minnesota is bordered by the states of North Dakota and South Dakota in the west; by Iowa in the south and by Wisconsin and Lake Superior in the east. It is also bordered by the Canadian provinces of Manitoba and Ontario in the north.
Regional Maps: Map of North America
Outline Map of Minnesota
The above blank map represents the State of Minnesota, located in the North-Central (Midwest) region of the United States. The above map can be downloaded, printed and used for geography education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.
The above outline map represents the State of Minnesota, located in the North-Central (Midwest) region of the United States. Minnesota is nicknamed as the "Land of 10,000 Lakes" as there are about 11,842 large-sized lakes that are scattered all over the state.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | State of Minnesota |
|---|---|
| ISO 3166 Code | US-MN |
| Capital City | Saint Paul |
| Largest City |
Minneapolis-St. Paul (2,989,669) |
This page was last updated on January 23, 2024











