Maps of Utah
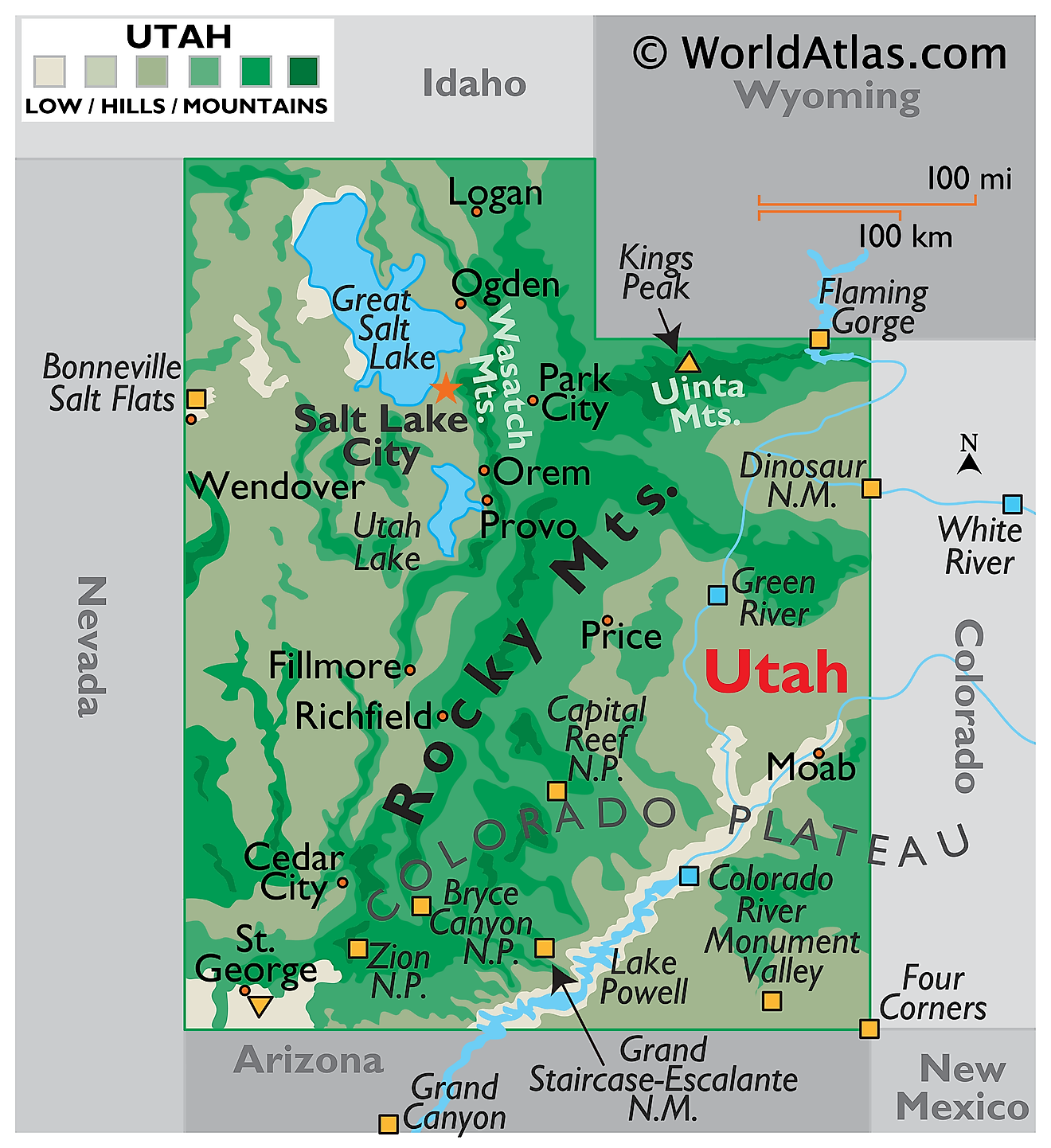
Utah, a state in the western United States, shares borders with Idaho and Wyoming to the north, Colorado to the east, Arizona to the south, New Mexico to the southeast, and Nevada to the west. The state covers a total area of approximately 84,899 mi2 (219,882 km2).
Utah, from northwest to southeast, is divisible into four primary geographic regions:
Basin and Range characterizes the western part of Utah, a region marked by a series of north-south mountain ranges separated by desert basins. These ranges are the remnants of ancient volcanic activity and subsequent erosion. The topography features narrow mountain chains interspersed with flat valleys and basins. This region extends into Nevada and is known for its arid climate and sparse vegetation, which is predominantly sagebrush and shadscale.
Middle Rocky Mountains: The Middle Rocky Mountains dissect the northern central part of Utah and consist of rugged mountain ranges such as the Uintas, which run east to west, unlike most ranges in North America. This area also includes the Wasatch Range, which serves as a dramatic backdrop to the urbanized Wasatch Front, where the majority of Utah's population resides. The highest peak in Utah, Kings Peak, with an elevation of 13,528 feet (4,123 meters), is located in the Uinta Mountains.
Basin & Range Colorado Plateau Transition encompasses a complex region where the topography gradually shifts from the Basin and Range to the elevated landforms of the Colorado Plateau. The terrain here is diverse, featuring deep canyons, high plateaus, and isolated mountain ranges.
Colorado Plateau dominates the eastern and southern portions of Utah and is renowned for its landscapes that include arches, natural bridges, canyons, mesas, and buttes. This high, semi-arid plateau is cut by numerous river systems, creating significant vertical relief. The San Rafael Swell, an anticline or "bulge" in the Earth's crust, is a notable feature in this region. The plateau includes prominent national parks like Arches and Canyonlands.
Major Bodies Of Water: The Great Salt Lake, located in the northern part of the Basin and Range region, is the largest saltwater lake in the Western Hemisphere. Bear Lake, often called the "Caribbean of the Rockies" for its intense turquoise-blue water, straddles the border between Utah and Idaho. The Colorado River, which carves out the dramatic Canyonlands National Park, is a significant waterway that flows through the eastern part of the state. The Green River, a major tributary of the Colorado River, also winds through the Colorado Plateau.
Counties Map
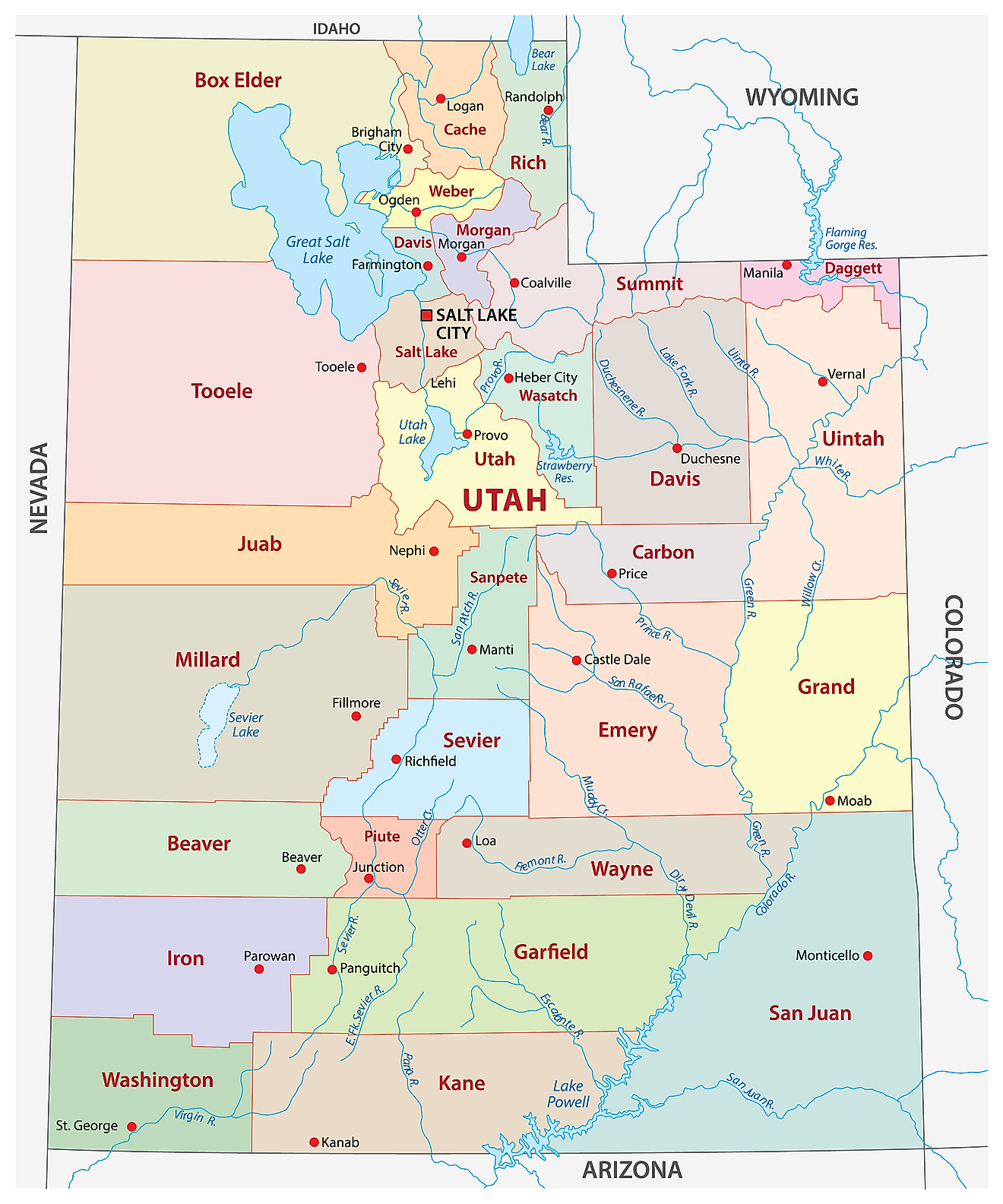
Utah is divided into 29 counties. In alphabetical order, the counties are: Beaver, Box Elder, Cache, Carbon, Daggett, Davis, Duchesne, Emery, Garfield, Grand, Iron, Juab, Kane, Millard, Morgan, Piute, Rich, Salt Lake, San Juan, Sanpete, Sevier, Summit, Tooele, Uintah, Utah County, Wasatch, Washington, Wayne, Weber.
With an area of 219,890 sq. km, Utah is the 13th largest and the 31st most populous state in the USA. Located in the north-central part of the state is Salt Lake City – the capital, the largest and the most populous city in Utah. The capital city hosts the world headquarters of the LDS Church. It also serves as the national hub of industrial banking. The city is a major tourist spot in the US that offers many outdoor recreation activities like skiing for attracting tourists.
Where is Utah?
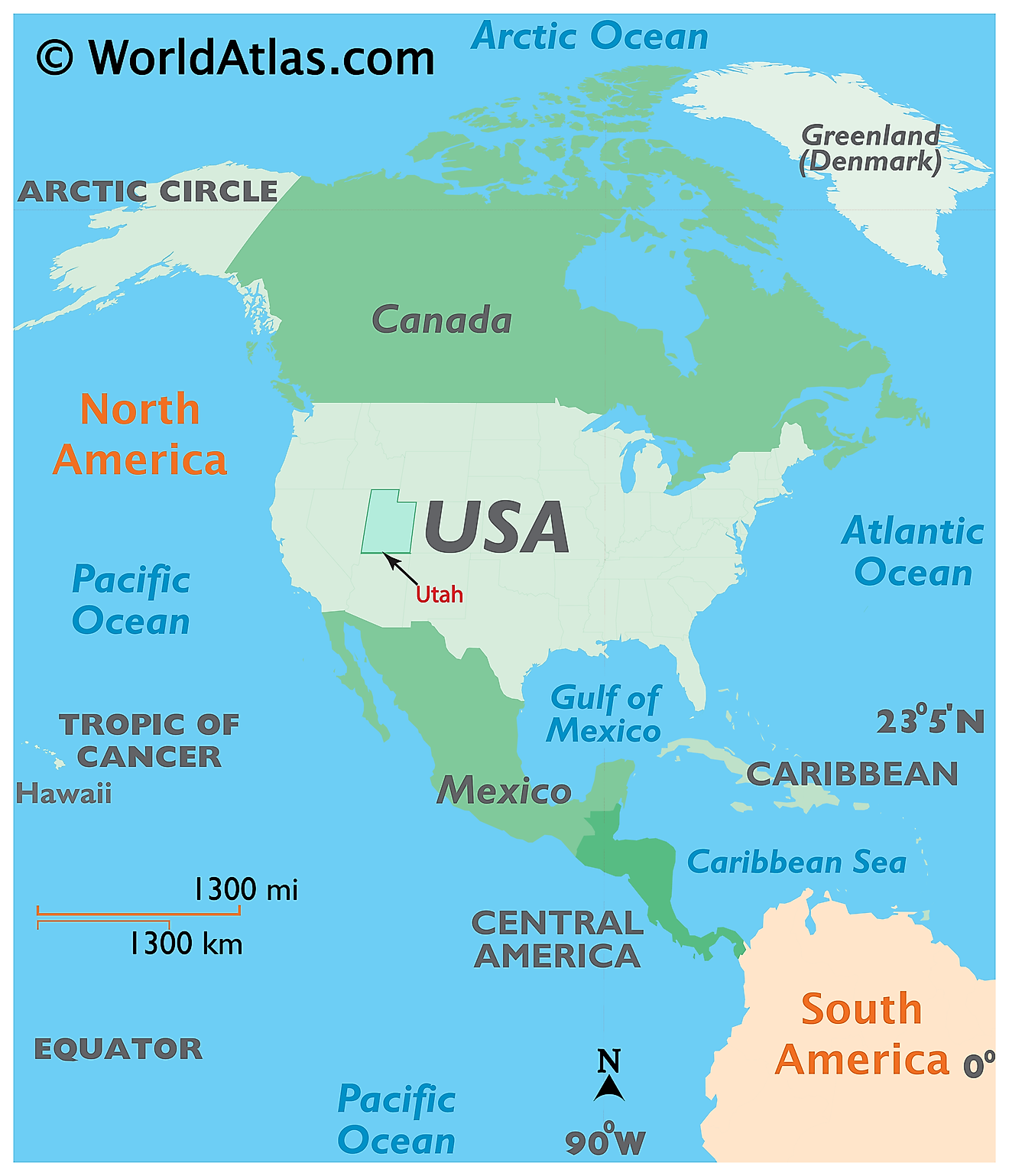
The State of Utah is located in the west-central region (or Mountain States area) of the United States. The landlocked state of Utah is bordered by the states of Nevada in the west; by Idaho in the north; by Wyoming in the northeast; by Colorado in the east; by Arizona in the south and by New Mexico (at a single point, in the Four Corners) in the southeast.
Regional Maps: Map of North America
Outline Map of Utah
The above blank map represents the State of Utah, located in the west-central region (or Mountain States area) of the United States. The above map can be downloaded, printed and used for geography education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.
The above outline map represents the State of Utah, located in the west-central region (or Mountain States area) of the United States.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | State of Utah |
|---|---|
| ISO 3166 Code | US-UT |
| Capital City | Salt Lake City |
| Major Cities |
|
This page was last updated on February 9, 2024







