Maps of Northern Mariana Islands
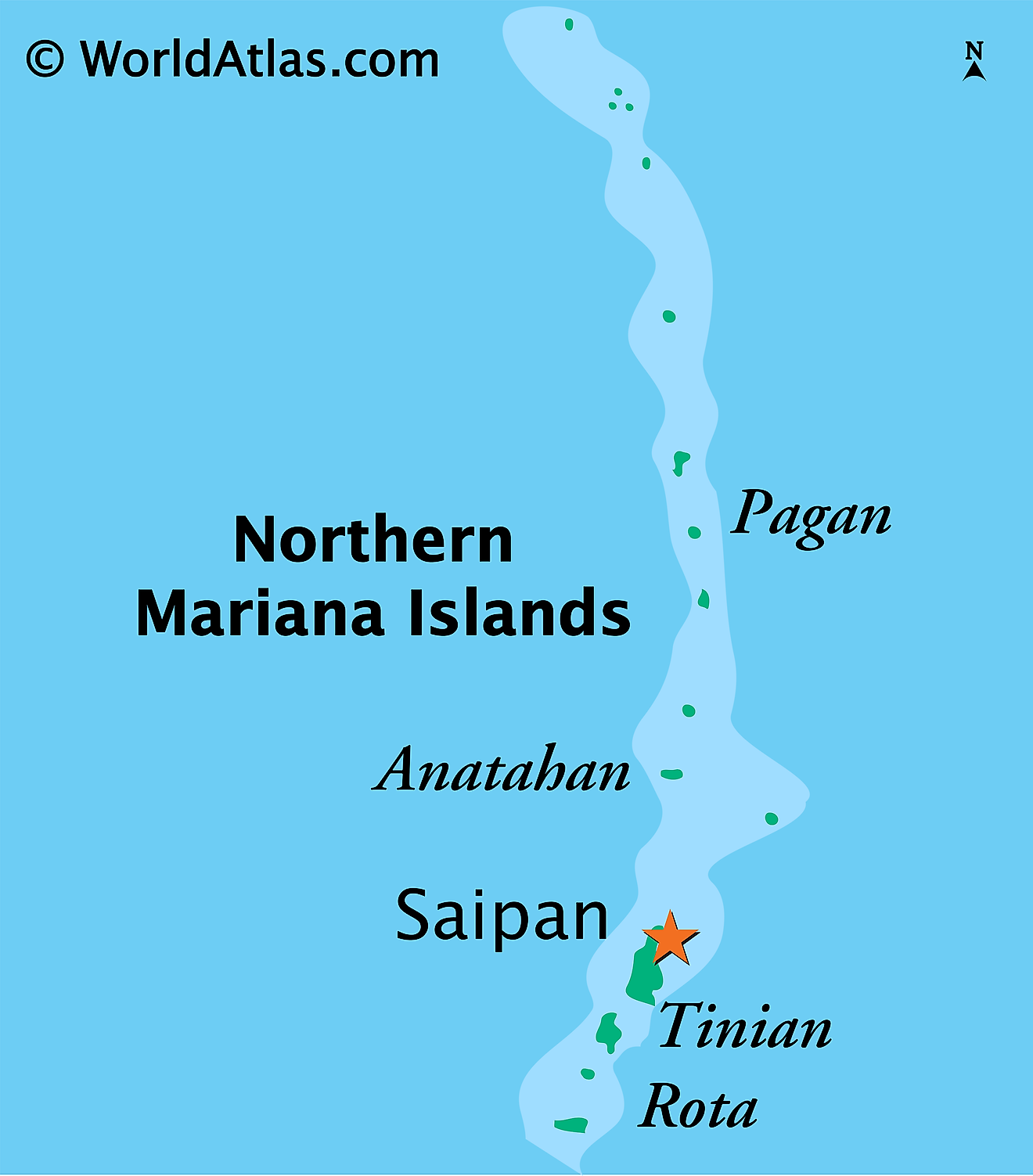
The Northern Mariana Islands, a U.S. commonwealth in the western Pacific Ocean, between the Philippine Sea to the west and the Pacific Ocean to the east. This archipelago covers a total area of about 464 km2 (179 mi2). The lowest point in the Northern Mariana Islands is at sea level, along the coastal areas. These coastal zones, particularly on the western sides of the islands, feature a combination of sandy beaches and rocky shores, shaped by the oceanic forces and coral reef structures.
Southern Region: The Southern Region of the Northern Mariana Islands includes the islands of Rota, Aguijan, and the southern part of Tinian. Rota, the southernmost island, features a rugged terrain with a mix of coastal cliffs and sandy beaches. Tinian, partially included in this region, is known for its relatively flat landscape compared to other islands, with interesting limestone formations like Taga Stone. Aguijan, a small uninhabited island, is mostly flat and covered with dense vegetation.
Central Region: Saipan, the largest island and capital of the Northern Mariana Islands, dominates the Central Region. Characterized by its limestone plateaus and volcanic ridges, Saipan has a varied topography. The western and southern coasts are lined with sandy beaches and coral reefs, while the northern coast is marked by steep cliffs. Mount Tapochau, the highest point in Saipan at 474 meters (1,555 feet), is located in this region. Saipan also encompasses a range of karst formations and caverns, notably in its northern areas.
Northern Region: The Northern Region is composed of the islands of Alamagan, Pagan, Agrihan, Asuncion, Maug Islands, and Farallon de Pajaros (Uracas). This region is predominantly volcanic, with several active volcanoes including Mount Pagan on Pagan Island and Mount Agrihan on Agrihan Island, which is the archipelago's highest volcanic peak at 965 meters (3,166 feet). The Maug Islands, forming a partially submerged caldera, has shallow hydrothermal vents close to its coral reefs. Farallon de Pajaros, the northernmost island, is also volcanic and has steep, rugged terrain.
Municipalities Map of Northern Mariana Islands
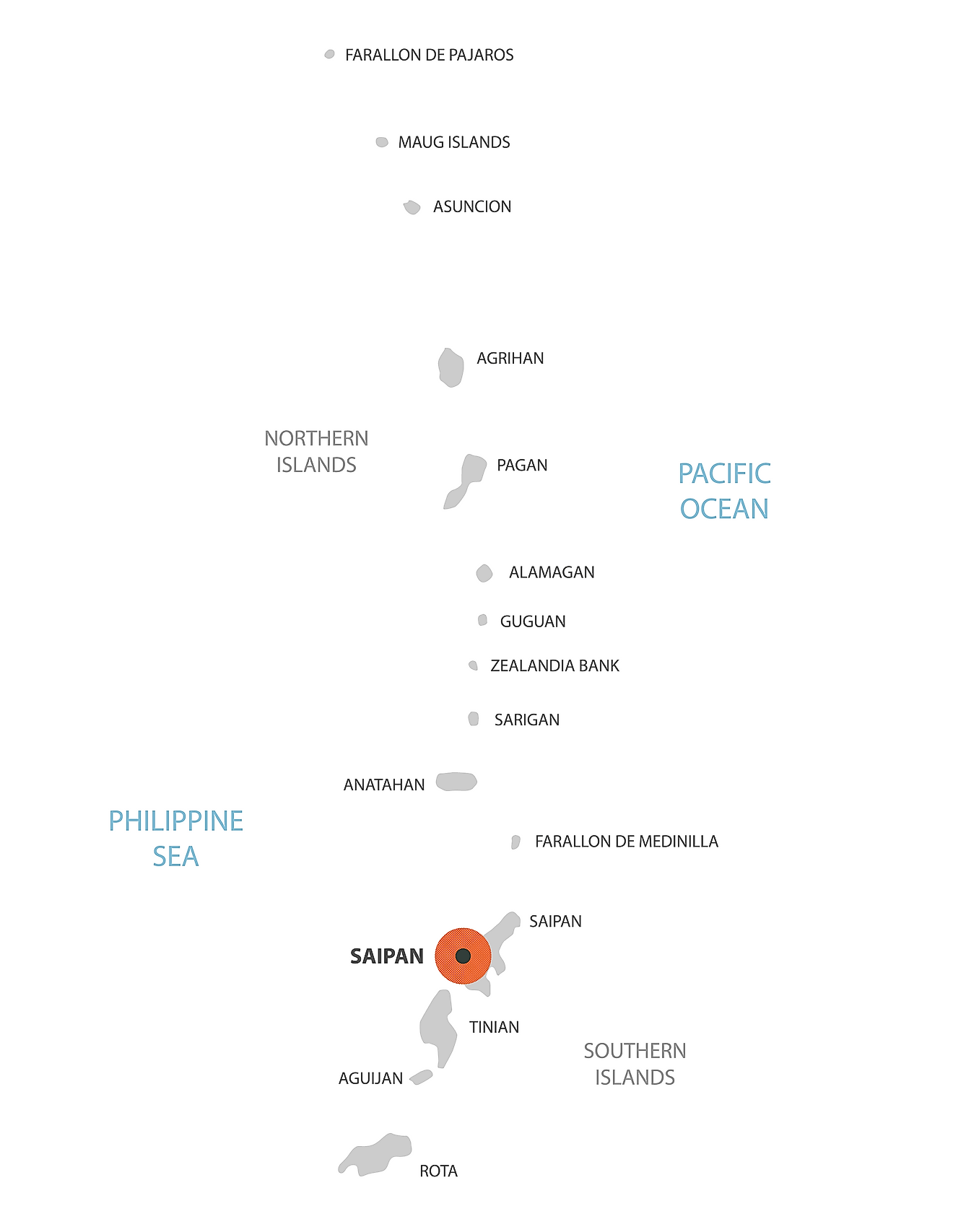
Northern Mariana Islands (officially, the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands [CNMI]) is divided into 4 municipalities. The municipalities are: Northern Islands, Rota, Saipan and Tinian.
Covering a total land area of 475.26 sq.km (179 sq mi), Northern Mariana Islands is an unincorporated and organized territory of the United States and also a U.S. commonwealth. The territory comprises of 15 islands in the Mariana archipelago situated in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.
Situated in the north of Guam island is, Saipan – the capital, the largest and the most populous island of CNMI. The Government of Northern Mariana Islands is located on Saipan, in the village of Capitol Hill. Saipan is also the 2nd largest island by area in the Mariana archipelago, after Guam.
Where is Northern Mariana Islands?
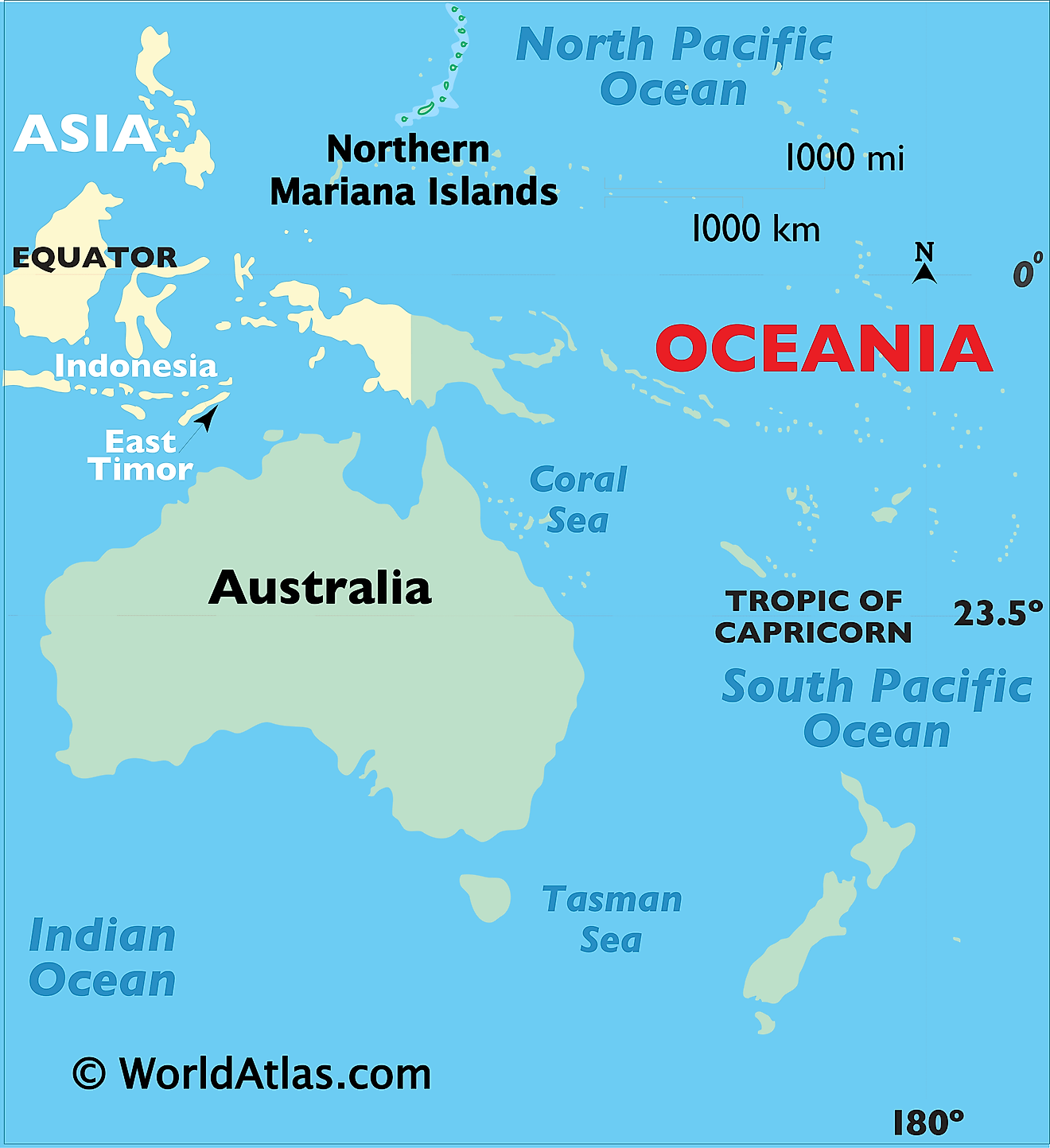
The Northern Mariana Islands is an insular area and commonwealth of the United States consisting of 15 islands of the Mariana archipelago (except Guam), situated in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. These group of islands are geographically positioned in the Southern and Eastern hemispheres of the Earth. The Northern Mariana Islands are located in the North Pacific Ocean and the Philippine Sea, along the Mariana Trench; to the north of Papua New Guinea; to the east of Philippines; to the west of Honolulu and to the northeast of Guam.
Regional Maps: Map of
Outline Map of Northern Mariana Islands

The above blank map represents The Northern Mariana Islands - an insular area and commonwealth of the United States consisting of 15 islands of the Mariana archipelago (except Guam), situated in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. The above map can be downloaded, printed and used for geography education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.
The above outline map represents The Northern Mariana Islands - an insular area and commonwealth of the United States consisting of 15 islands of the Mariana archipelago (except Guam), situated in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. The CNMI is the westernmost territory of the United States.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands |
|---|---|
| Flag |

|
| Capital City | Saipan |
| 15 12 N, 145 45 E | |
| Total Area | 464.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 464.00 km2 |
| Water Area | N/A |
| Population | 57,216 |
| Currency | US Dollar (USD) |
| GDP | $1.32 Billion |
| GDP Per Capita | $23,258.68 |
This page was last updated on November 13, 2023











