Maps of Tunisia
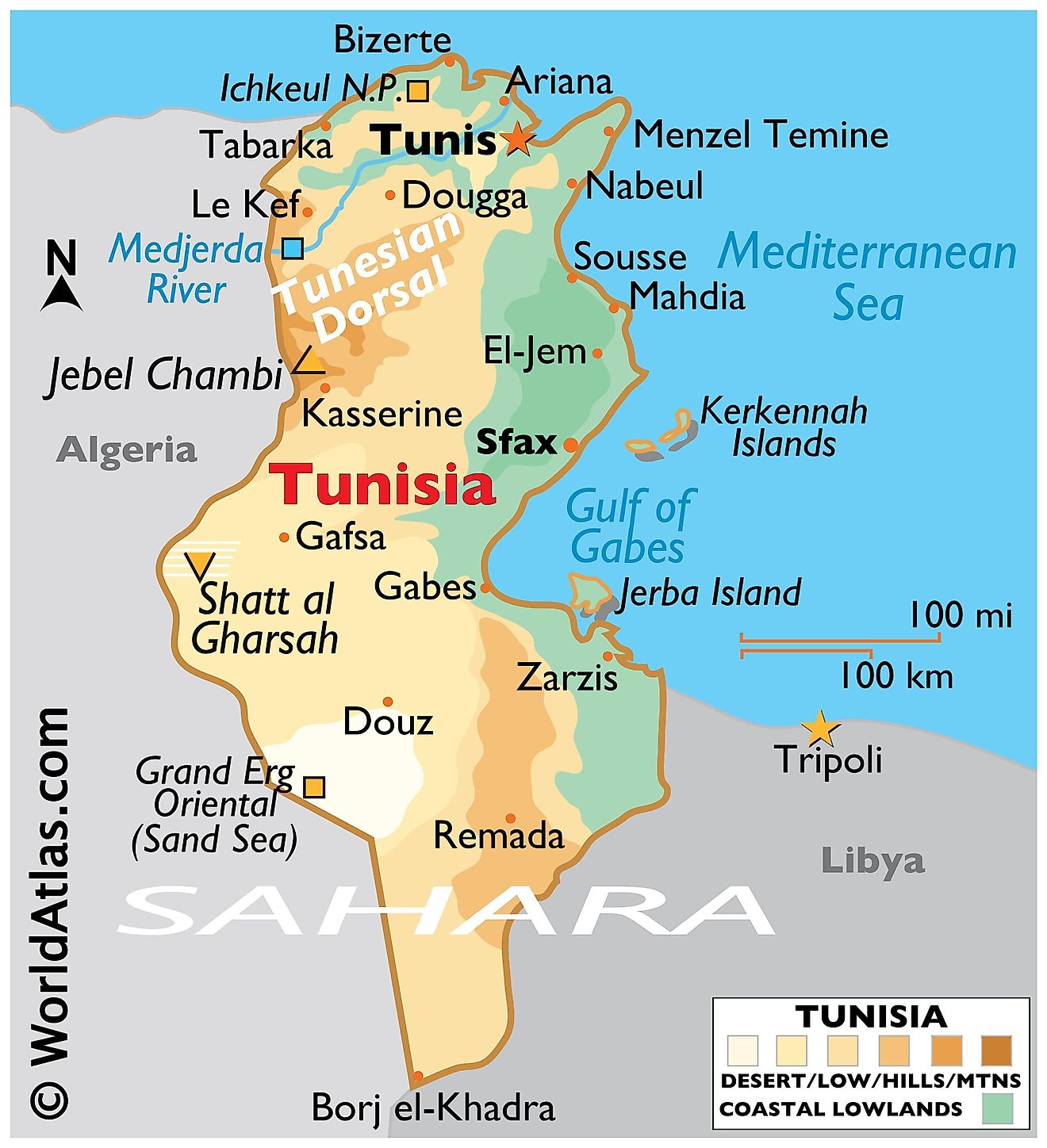
Tunisia is a North African country with a total area of 163,610 sq. km and a coastline of 1,148 km on the Mediterranean Sea to the north. Tunisia sits next to only two other nations. Algeria and Libya. Even though it is not directly connected, Tunisia is only a few hundred kilometers from the Southern European nations of Italy and Malta. Despite being roughly the same size as the state of Wisconsin, Tunisia's north-south extent lends great environmental diversity.
The Tunisian Dorsal is a mountain range that runs in a southwest-northeast direction from Tunisia's border with Algeria in the west to the Cape Bon peninsula in the east. This mountain is an extension of the Saharan Atlas Mountains. Further north of the Tunisian Dorsal, the mountains of the Northern Tell (that include the Kroumirie Mountains in the northwest and the Mogods running along the northern coastline) can be found. The High Steppes (in the west) and Low Steppes (in the east) lie to the south of the Tunisian Dorsale. They are cut by mountains running north to south. Mount Chambi (1,544 M) is the highest point in the country. At 17 m below sea level, Chott el Djerid is Tunisia's lowest point.
The Medjerda River valley lies in between the Tunisian Dorsal and Northern Tell Mountains (shown on the map above). This valley features a series of ancient lake basins and is the country's most fertile grain-producing land. The Medjerda River is the only perennial river in Tunisia and it drains into the Gulf of Tunis. As we go further south, there is a series of depressions called chott. Many intermittent rivers flowing through the country end up in these chotts. Extending inwards from the eastern coastline are large plains called Al-Sāḥil and Al-Jifāra.
The Sahara Desert's Sand Sea, also called the Grand Erg Oriental covers much of the southern portion of Tunisia. Most of the wadis here remain dry all year round and hence, access to water is a major concern here. Tunisia also has several islands. Djerba Island marked on the map above is North Africa's largest island. It is located in the Gulf of Gabès
Governorates of Tunisia Map
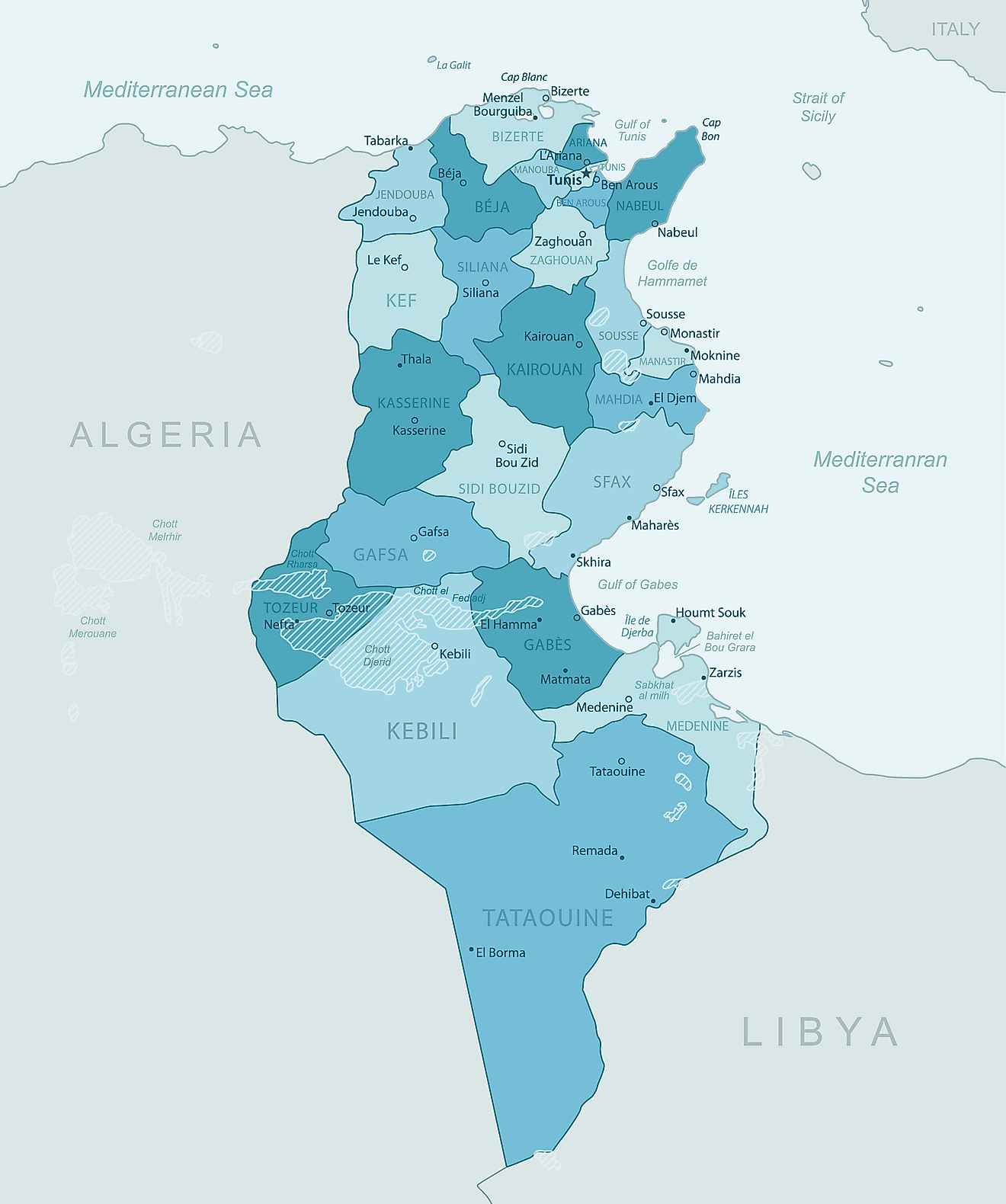
Tunisia has 24 major administrative divisions called governorates. In alphabetical order, they are as follows: Ariana, Beja (Bajah), Ben Arous (Bin 'Arus), Bizerte (Banzart), Gabes (Qabis), Gafsa (Qafsah), Jendouba (Jundubah), Kairouan (Al Qayrawan), Kasserine (Al Qasrayn), Kebili (Qibili), Kef (Al Kaf), L'Ariana (Aryanah), Mahdia (Al Mahdiyah), Manouba (Manubah), Medenine (Madanin), Monastir (Al Munastir), Nabeul (Nabul), Sfax (Safaqis), Sidi Bouzid (Sidi Bu Zayd), Siliana (Silyanah), Sousse (Susah), Tataouine (Tatawin), Tozeur (Tawzar), Tunis, Zaghouan (Zaghwan).
The governorates are further subdivided into 264 districts called mutamadiyat which are further divided into smaller administrative divisions called shaykhats or municipalities and imadats or sectors. Tataouine is Tunisia's largest governorate by area and Tunis is the largest one by population but the smallest by area. The capital of this governorate, Tunis, is also the national capital.
Where is Tunisia?
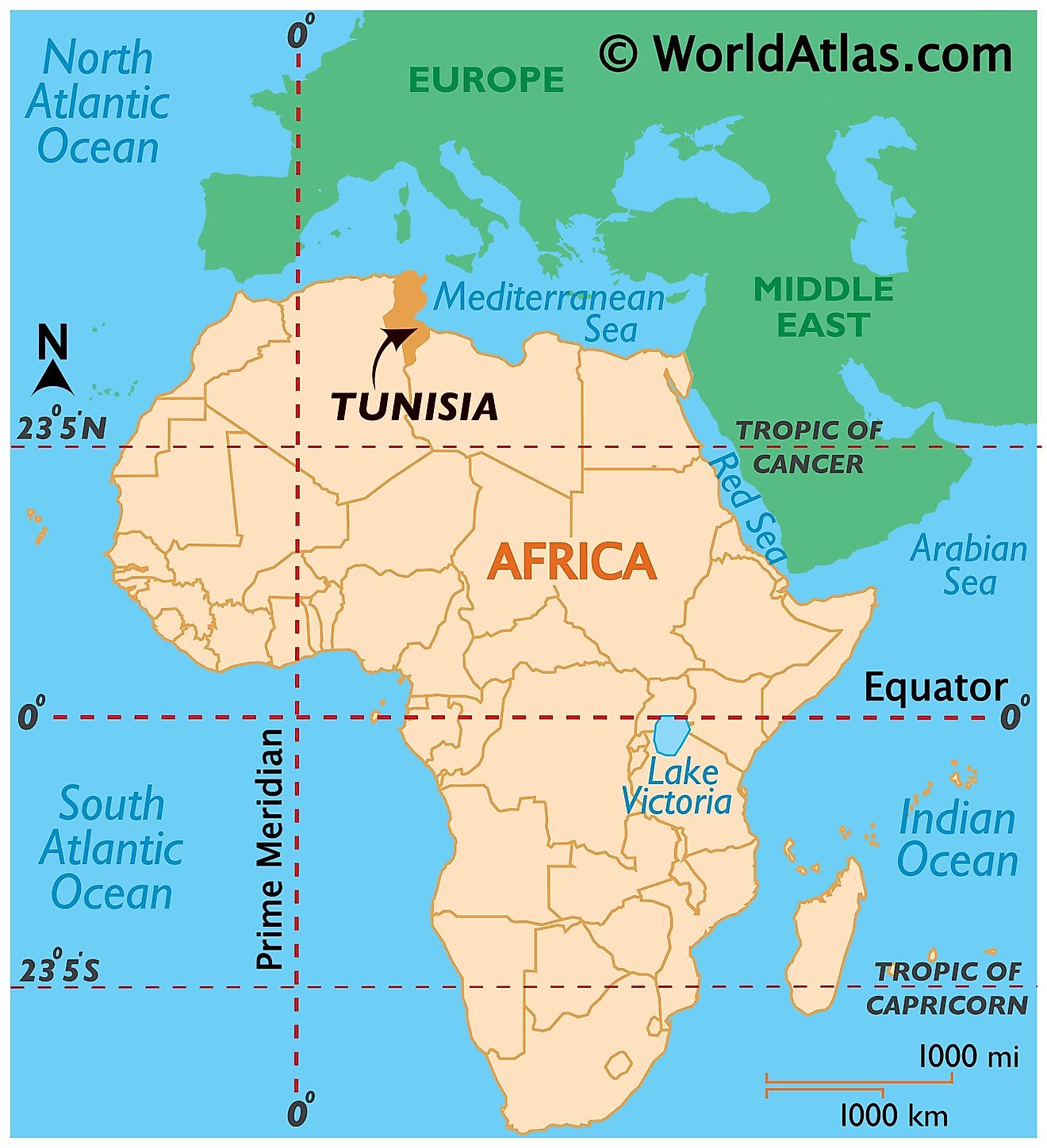
Located in the Maghreb region of North Africa, Tunisia hosts the northernmost point in the African continent called Cape Angela. Tunisia is located in the Northern and Eastern Hemisphere of the Earth. It is bordered by only two neighboring nations. Libya bounds Tunisia to the southeast and Algeria to the west and southwest. The country has a coastline on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east.
Tunisia Bordering Countries: Libya, Algeria.
Regional Maps: Map of Africa
Outline Map of Tunisia
The blank outline map represents mainland Tunisia. The country also has several islands on the Mediterranean Sea which cannot be observed on this map. The above map can be downloaded for free, and used for educational purposes like map-pointing activities.
The above outline map represents mainland Tunisia without its islands on the Indian Ocean. The country extends southwards as a relatively narrow almost vertical band of territory from its coast on the Mediterranean Sea to the north.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Republic of Tunisia |
|---|---|
| Flag |

|
| Capital City | Tunis |
| 36 48 N, 10 11 E | |
| Total Area | 163,610.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 155,360.00 km2 |
| Water Area | 8,250.00 km2 |
| Population | 11,694,719 |
| Major Cities |
|
| Currency | Tunisian dinars (TND) |
| GDP | $38.80 Billion |
| GDP Per Capita | $3,317.54 |
This page was last updated on December 18, 2023