Tomb of Agamemnon
The Tomb of Agamemnon, located in the historic landscape of the Greece Peloponnese, is more than just an archaeological site; it's a bridge connecting the mystical world of Homer's epics to the concrete evidence of the Mycenaean civilization. This majestic tomb not only encapsulates the grandeur of ancient Greek history but also highlights the intricate blend of myth and reality. Its discovery in the late 19th century marked a significant milestone, reigniting global interest in Greek antiquity and opening new chapters in the study of the Mycenaean Age. Delve deep into the rich tapestry of legends, historical revelations, and the enduring impact of this iconic site on our understanding of ancient Greece.
The Legendary King And His Tomb

Agamemnon, a pivotal figure in ancient Greek mythology and literature, stands as one of the most significant characters in the epic tales of Homer. Recognized widely as the king of Mycenae, Agamemnon plays a central role in both the "Iliad" and the "Odyssey." He is depicted as the commander of the Greek forces during the legendary Trojan War, a position that underscores his importance and influence in Greek heroics and mythology. His character is often associated with the themes of power, leadership, and the tragic consequences of pride and hubris.
Agamemnon's story is not just limited to his role in the Trojan War; it also extends to the complex familial dynamics and the cycle of revenge and tragedy in his homecoming, as portrayed in Aeschylus's Oresteia. His tale, interwoven with the fates of other illustrious characters such as Achilles, Odysseus, and his wife Clytemnestra, offers a rich tapestry of heroism, betrayal, and the inexorable nature of fate, making him a quintessential figure in Greek mythology and a subject of extensive study in the classical literature and history of Greece.

The Tomb of Agamemnon stands as a testament to the legendary King Agamemnon. Mycenae, the ancient city associated with Agamemnon, retains its grandeur as one of the most significant archaeological sites in Greece. The late 19th century brought Mycenae back into the limelight when Heinrich Schliemann, a pioneering archaeologist, claimed to have discovered Agamemnon's tomb, replete with golden treasures. This discovery was monumental, propelling Mycenae into the headlines and reigniting interest in Greek history and archaeology.
Despite controversies surrounding Schliemann's methods and the authenticity of his findings, his work undeniably played a crucial role in enhancing the understanding of the Mycenaean Age. The site, now a haunting and impressive ruin, continues to attract hundreds of thousands of tourists each year, serving as a vivid reminder of Greece's rich ancient heritage and its enduring influence on the Western imagination.
Sect Of The Hero And Mycenaean Legacy
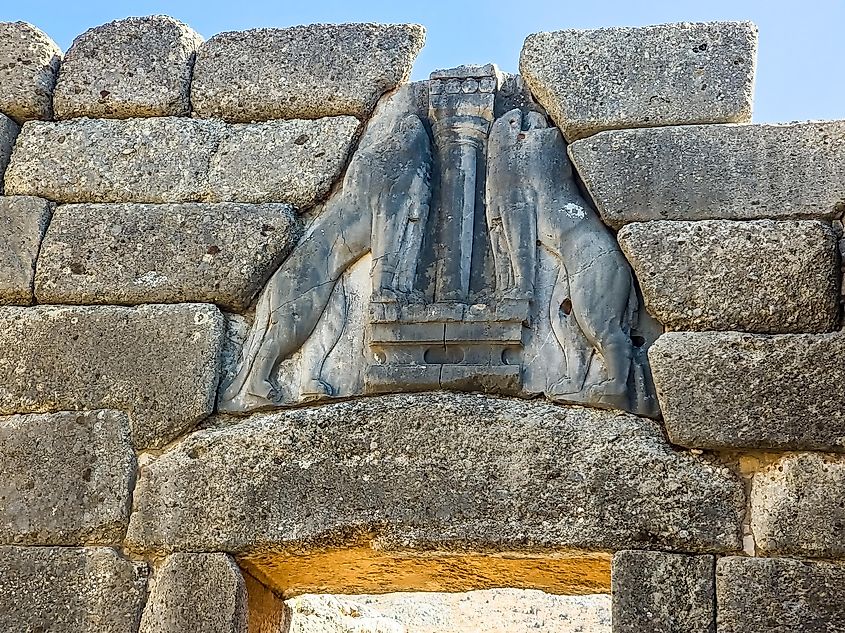

Interestingly, the worship of Agamemnon did not emerge during the zenith of Mycenae's Late Bronze Age but rather surfaced approximately four centuries later. This delay highlights the enduring impact of Agamemnon's legacy, transcending the boundaries of time.
During this later era, the once-mighty citadel of Mycenae lay in ruins, its towering walls serving as silent witnesses to a glorious past. Despite the decline of Bronze Age Mycenae, the legendary stature of Agamemnon and his city never waned. The site, steeped in a rich tapestry of myth and history, continued to captivate the imagination of successive generations. It stood as a poignant symbol of war, heroism, and the human condition, reflecting the complex interplay of historical reality and mythological narrative.
The enduring fascination with Agamemnon's story, woven into the fabric of Greek cultural and literary traditions, attests to the profound influence that the Mycenaean civilization and its legendary figures have had on the development of Western thought and storytelling. This lasting legacy underscores the timeless appeal of Mycenaean culture and its capacity to inspire and intrigue long after its decline.
Mycenae Rediscovered And Reimagined

The resurgence of interest in Mycenae commenced around the 18th century, marking a pivotal chapter in the rediscovery of ancient Greek civilization. This period saw European treasure hunters and archaeologists, captivated by the allure of Greece's storied past, converging on Mycenae to excavate and explore its ruins. Their endeavors unearthed the remnants of a civilization that had once dominated the Aegean, reigniting global fascination with Mycenae's historical and cultural significance.
This renewed interest in Mycenae was particularly pronounced in post-Ottoman Europe, where the site transcended its archaeological value, becoming a symbol of various political ideologies. During this era, Mycenae's legendary status intertwined with the romantic-nationalist sentiments sweeping across Europe.

Furthermore, the excavations and studies conducted during this period played a critical role in shaping modern understanding of the Mycenaean Age. Scholars and archaeologists, through their meticulous work, pieced together the fragmented history of this ancient civilization, offering insights into its societal structure, cultural practices, and interactions with other contemporary civilizations. This awakening of interest in Mycenae not only enriched historical knowledge but also stimulated a broader appreciation for the complexities and achievements of ancient Greek civilization. As a result, Mycenae's influence extended beyond the confines of academia, capturing the public imagination and reinforcing Greece's pivotal role in the tapestry of human history.
In Summary
The Tomb of Agamemnon, embodying millennia of history, myths, and cultural transformations, stands as a testament to Greece's enduring legacy. From its legendary origins to its rediscovery and the controversies it sparked, this site offers a fascinating glimpse into the complexities of history, mythology, and human endeavor. Share this journey through time with friends and family and explore how the past continually shapes our understanding of the present.