Laos Culture – the Culture of Laos

Laos is Southeast Asia’s only landlocked nation. The small country is home to around 6,758,353 individuals. Despite its size, Laos has great cultural diversity due to a large number of ethnic groups residing in the country. The government of the country officially recognizes 49 of the about 200 ethnic groups living in Laos. The ethnic Lao people are the largest group accounting for about 53.2% of the population. Buddhism is the religion of the majority in Laos.
Cuisine
The ethnic diversity of Laos is reflected in the country’s cuisine. Strong regional variations exist among the dishes. Sticky rice is the staple food of Laos. Common meals in the country include sticky rice served with a spicy minced chicken or fish dish. Most Laotian dishes are spicy. The green papaya salad called tam mak hung is a popular dish. Tropical fruits are often served as dessert. Lao cuisine uses generous volumes of fermented fresh water, fish sauce, chilies, and galangal. Insects are also sometimes consumed.
Clothing
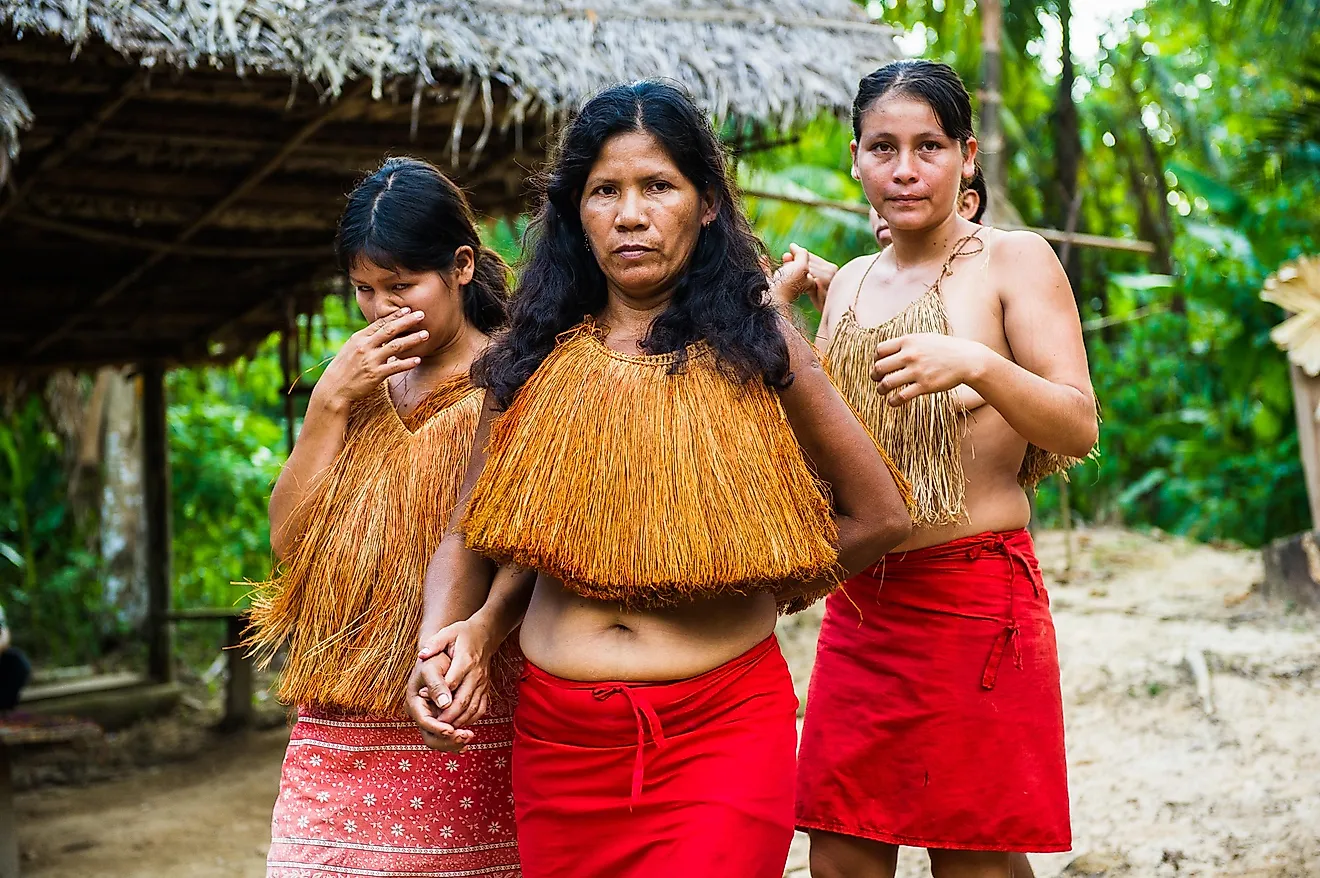
Although fashion in Laotian cities are influenced by Western culture, traditional clothing is worn during special occasions or in rural areas. Clothing often helps distinguish among the ethnic groups in the country. Traditional clothing for Lao women features a long skirt and a matching shawl. French inspired blouses are usually worn with the skirt. Lao Men wear the traditional sampot or billowed trouser with an Indochinese shirt or a Mandarin collar jacket. They also wear a traditional shawl. Silk is extensively used to make clothing. Gold and silver jewelry is usually worn with the traditional dresses. Similar to the Lao people, other ethnic groups in Laos have their distinct styles of clothing.
Sports
Football is the most popular sports played in Laos. Muay Lao, a martial arts form and Ka-taw or kick-volleyball, boat races, etc., are some of the traditional sports played in the country.
Literature
Traditional literature in Laos is influenced by Hindu and Buddhist cultures. Hindu mythological stories and epics have helped shape the literary scene in Laos. The Lan Xang kingdom’s rule in the 16th and 17th centuries witnessed an increase in its literary wealth. Epic poetry like the Sang Sinxay and the Thao Hung Thao Cheuang is the most valued literature from this period. The country also has a rich folklore tradition.
Arts and Crafts
Weaving is an important cultural expression in Laos and is popular among most ethnic groups. Weaving skills are passed from mothers to daughters in Laos households. Silk weaving is most valued and often silkworms are raised at home on a diet of mulberry leaves. Traditional Laotian clothing is usually heavily embroidered with stunning motifs of elephants, temples, and other Khmer influenced patterns and designs. Bronze sculptures of Buddha are present throughout the country. Buddha is represented in different forms in these sculptures.
Laotian craftsmen are also famous for their woodworking skills. Richly carved furniture produced by them are very attractive in appearance. Lao metalwork in silver and gold is also appreciated globally. Bamboo handicrafts and basketry are also quite common.
Music and Dance
The lam is regarded as the national music of Laos. It involves a singer singing improvised poetry to quick tempo music. This form of music traces its origin to the animist traditions that involved chanting during religious ceremonies. Lam can also be used in story-telling. The khaen is an important Laotian musical instrument. It is a mouth organ made of bamboo. Other musical instruments used in the country include drums, gongs, flutes, cymbals, zithers, etc.
The lam vong is the national folk dance of the country. The dance is influenced by Buddhist traditions. It begins with an individual performing Buddhist mudras with the hands and the head. The performer is soon joined by other dancers. The ethnic groups of the country have their distinct dance forms. Most involve dressing up in colorful, elaborate costumes and elegant movements.
Social Life in Laos
The gender gap in Laos is less pronounced. Lao Women are generally treated with respect and enjoy considerable cultural and social status. However, the status of women belonging to some of the other ethnic groups is not always high.
Gender discrimination at work is not permitted in the country. However, in traditional households, there is a natural tendency for women to manage household chores and children. In the religious scene in Laos, men dominate as religious leaders. Although women play an important part in religious practices, it is the men who have the top positions.
Ethnic Lao usually have a considerable degree of freedom in selecting their life partners. Marriages are usually hosted in the bride’s home. Divorce can be initiated by either of the partners if the marriage fails. In some of the patrilineal groups living in Laos, however, marriages are usually fixed by the parents. Some of the highland groups also practice polygyny although it is an illegal practice in the country.
The families living in lowland Laos have a tendency toward matrilocality. Here families consist of a group of related women. Usually, the older daughter leaves with her husband when the younger one marries and moves in with her mother and father. The youngest daughter of the family usually inherits the house and is responsible for taking care of her aging parents. In highland patrilineal groups, brothers usually live together with their parents and their own families under one roof. Here, the sons usually inherit their parents’ property.
The people of Laos are of peaceful nature and try to avoid conflicts with others. Social hierarchy is considered important. People are expected to greet each other with politeness.