How Is The Border Between Africa And Asia Defined?

Defining Continents
The concept of defining continents as large land masses dates back to Ancient Greece, when ship navigators named coastal lands along the Black and Aegean Seas and the straits of Bosporus and Dardanelles. The first identified continents were Asia and Europe. The concept of a continent was later expanded to include areas further inland. These first definitions, however, only considered lands that could be reached by navigable waterways.
In modern times, geologists have become involved in defining continents. These scientists tend to utilize the concepts of plate tectonics and continental crusts to determine which land masses may be considered independent continents. Additionally, shared history and culture tend to influence the acceptance of a particular area as a continent in recent times.
Defining Continental Borders
Defining borders serves to create political order and organization in the world. Borders separate nations, states, provinces, regions, municipalities, and even personal property. In most cases, borders are very clearly defined, with the exception of those under international dispute. Continental borders, however, are less clearly identified and agreed upon. In fact, both geologists and geographers often disagree about the number of continents in the world. Classrooms all over the globe learn that the world is divided into as many as 7 continents or as few as 4, depending on the model utilized.
With this inconsistency, how exactly do people come to understand a particular area as an entire continent. This article takes a closer look at this issue, specifically at identifying the border between Africa and Asia.
The Asian Continent
The Asian continent is the largest in the world (when considering the 6 and 7-continent models) and covers a total area of 17.212 million square miles. It has a population size of over 4.46 billion, making it the most populated continent as well. Asia has borders along the Arctic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans. To the west, this continent is bordered by Europe, although this is considered more of a cultural border than geographic in nature. Similarly, its border with Africa is not clearly defined.
The African Continent
The African continent is the second largest in the world (when following the geographic models of 6 and 7 global continents). It covers a total area of 11.7 million square miles and has a total population size of over 1.22 billion, making it the second most populated continent in the world as well. Africa has borders along the Indian and Atlantic Oceans and the Red and Mediterranean Seas. Its border with Asia is often considered to be the Sinai Peninsula.
The Afro-Eurasian Continent
The term Afro-Eurasia, sometimes known as World Island, refers to the largest connected land area on Earth. It covers an area of over 32.81 million square miles and is considered by some geographers to be an important part of the supercontinent cycle. It consists of the regions of Africa, Europe, and Asia (which are commonly considered 3 separate continents) and is home to around 86% of the global population. The border between Africa and Asia effectively separates the Afro-Eurasian continent into Africa and Eurasia.
History of the Border Between Africa and Asia
Ancient Greek and Roman geographers identified a territory known as Marmarica, which was believed to be part of the Asian continent. This area was located between ancient Cyrenaica, which corresponds to the eastern coastal area of modern-day Libya, and ancient Aegyptus, which corresponds to modern-day Egypt and excluded the Sinai Peninsula. Marmarica was divided between east and west by what is known today as the Halfaya Pass, a cliff that stands at 600 feet in altitude.
Everything to the east of the Halfaya Pass was considered to belong to the Asian continent and everything to the west was considered to belong to the African continent. This definition placed Egypt in Asia and Libya in Africa.
Current Border Between Africa and Asia
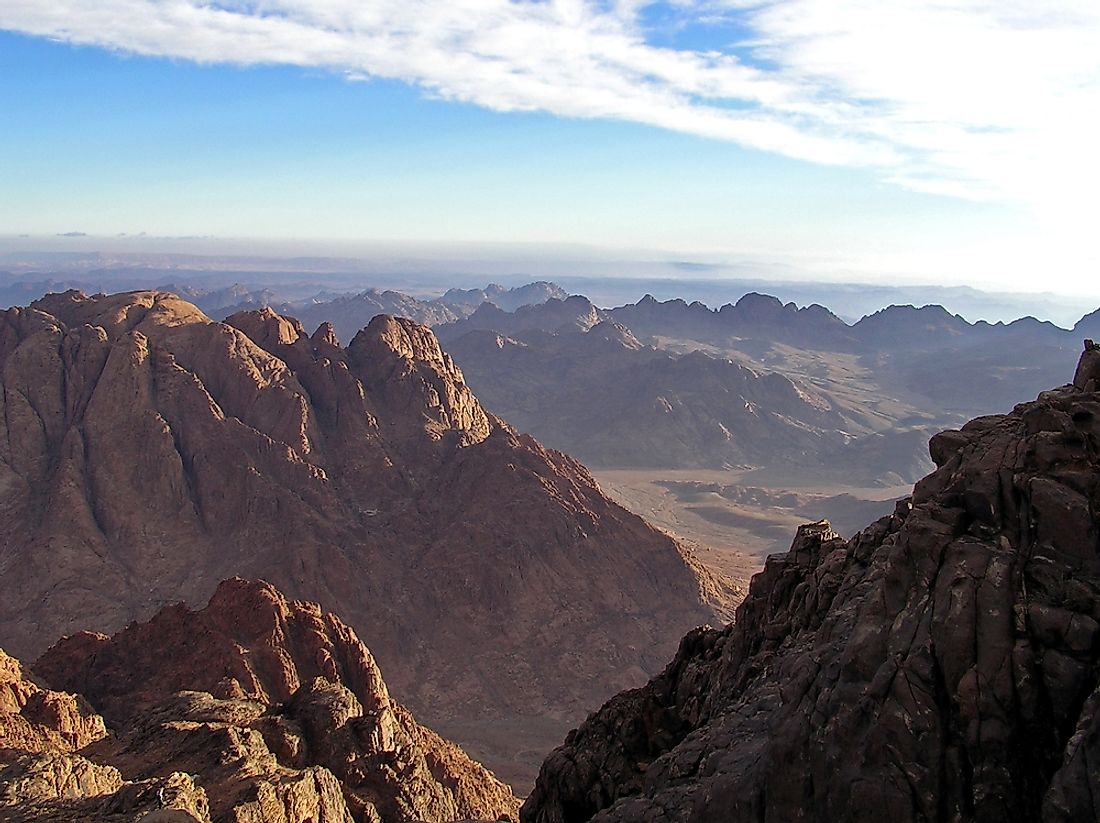
Today, the border between Africa and Asia is centered around the Sinai Peninsula, which is considered part of the territory of Egypt. This triangular-shaped peninsula juts into the Red Sea to the south, with the Gulf of Aqaba along the southeastern coast and the Gulf of Suez along the southwestern coast. To the north, the peninsula has a coastline along the Mediterranean Sea. It covers an area of 23,000 square miles and has a total population of approximately 1.4 million.
The peninsula is connected to both the Asian and African continents by two separate isthmuses of land. To the east, a 120-mile wide strip of land connects the Sinai Peninsula to Asia. The Sinai Peninsula is connected to the African continent by a much smaller area of land known as the Isthmus of Suez, a 78-mile wide section of land that houses the Suez Canal. The Suez Canal allows ships to navigate between the Mediterranean Sea and the Indian Ocean, preventing the need to transport goods around the southern tip of the African continent between Europe and Asia. Additionally, geologists have identified the eastern coast of this peninsula as the division between the Arabian tectonic plate and the African tectonic plate. Despite this geological division based on tectonic plates, the area west of the Isthmus of Suez on the Sinai Peninsula is considered part of the Asian continent.
Egypt - A Transcontinental Country
Because the Sinai Peninsula marks the border between Africa and Asia, Egypt is considered a transcontinental country. This definition is further explained by the fact that the peninsula belongs to both the Asian continent and the mainland area of the country of Egypt, which is considered to be located on the African continent.
One of the reasons that Egypt is considered an African country, rather than an Asian country, is because around 98% of the population lives within the mainland area of the country. This definition displays one of the many factors used to define continental borders. When considering geopolitical factors (like religion and political history), however, Egypt is often grouped with other Middle Eastern countries. When this is the working definition, all of Egypt is considered as part of the Asian continent. In this case, the entire country of Egypt can be used to refer to the border between Africa and Asia as it makes up the southwestern corner of Asia and the northeastern corner of Africa.