Is A Ban On Animal Testing For Cosmetics The Need Of The Day?

- Animal testing became mandatory in the United States in 1938, after the government passed the Food, Drugs, and cosmetics Act.
- The FDA still endorses animal testing for cosmetics to date.
- The EU banned cosmetics-related animal tests in 2009.
Cosmetic animal testing is a kind of animals-testing that is used to confirm the hypoallergenic properties and safety of cosmetics before being introduced in the market. A cosmetic is a product that helps cleanse the body or improve its appearance. Using animal testing in cosmetics development might involve testing all the ingredients of the finished commodity or the finished product on the animals, often rats, mice, or rabbits, among others. Cosmetic testing on animals can be very harmful to the test subjects; therefore, it is banned in Norway, Israel, India, and the European Union.
History
Before 1937, cosmetic testing on animals was not mandatory; however, everything changed after a pharmaceutical company introduced Elixir sulfanilamide into the market without any scientific research. Elixir sulfanilamide was meant to heal streptococcal infections, but instead, it ended up poisoning people. The medicine ended up causing a considerable poisoning outbreak that resulted in the death of over 100people. The epidemic forced the American government to introduce the Food-Drugs-and-Cosmetic Act in 1938 that enforced more thorough guidelines on cosmetic products. The new law forced companies to start testing their products on animals.
Methods
The different methods of testing cosmetics include several tests that are classified differently based on the purpose of the product. Most experiments start at the initial development stage of the product, and the effects of all the ingredients are tested separately before the finished product is tested. Every single ingredient used to create cosmetics can cause the death of over 1,400animals. Some of the most common methods include acute toxicity, skin sensitization, dermal penetration, skin irritation, and Draize test.
Scientists use Skin-sensitization tests to confirm if the cosmetic’s ingredients can cause any allergic reaction. Skin sensitization tests were initially applied to the shaved part of a guinea pig. Dermal penetration tests are usually done on rats, and they are used to help researchers understand how the chemical will penetrate the skin into the bloodstream. Acute toxicity tests are usually done on mice and rats. Draize tests causes irritation of the eye or skin, endocrine disruption, airway-sensitization, and dermal-sensitization. Skin irritation or corrosivity tests assess the possibility of cosmetic products causing irreversible skin damages. Acute toxicity tests help the researchers determine the effects of exposing people to these chemicals. Acute toxicity tests can cause animal seizures and convulsions.
Which Animals Are Used For Cosmetic Testing?
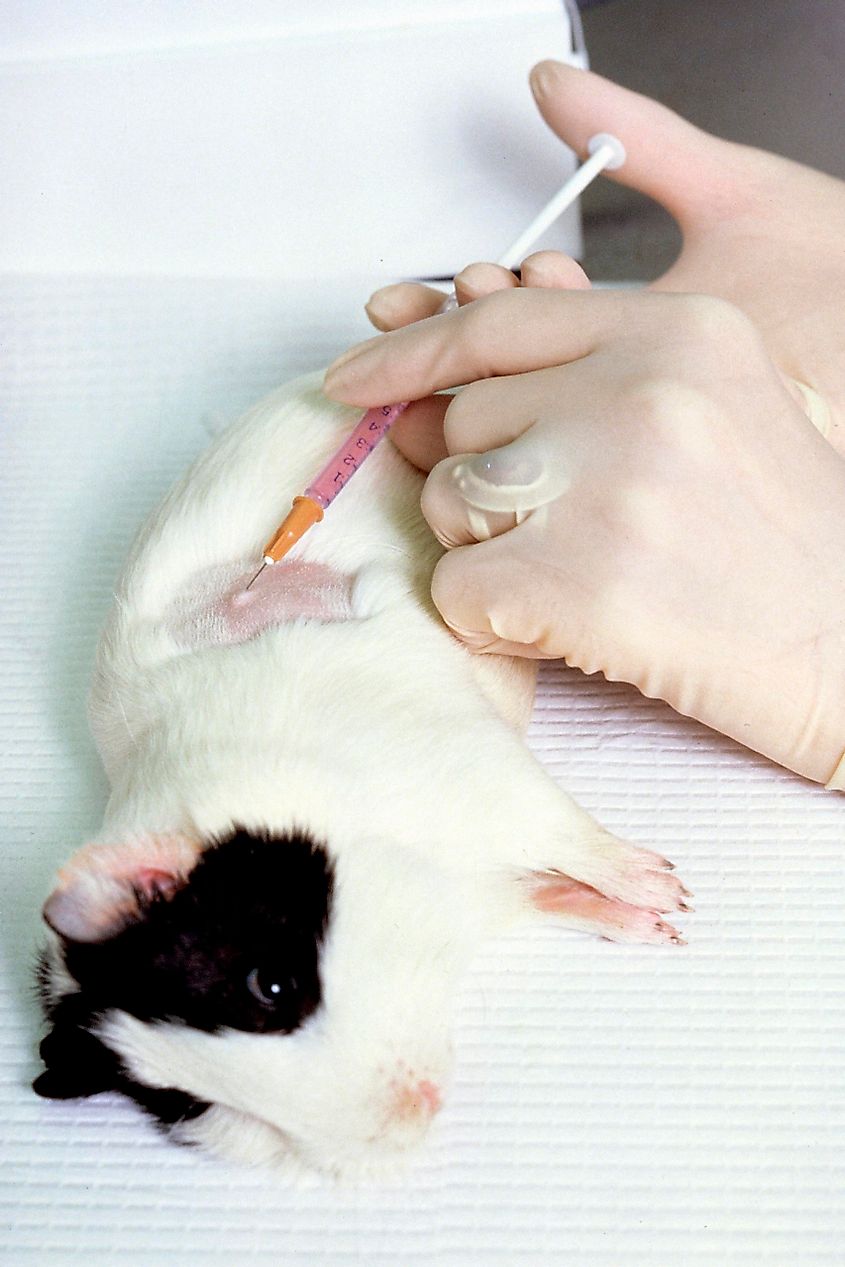
Over 500,000 animals around the world are used to test different cosmetics annually, that is over 1,369animals per day. Cosmetic companies use several animals when testing the safety of their products. Some of the most common animals include mice, rats, rabbits, dogs, guinea pigs, and in some cases, human beings. Rats are usually forced to inhale or consume specific cosmetic or have it rubbed on a shaved part of their skin daily for about 90days and then killed. In some cases, pregnant rabbits and rats are force-fed cosmetic ingredients for over 3 weeks and then killed together with their unborn offspring after the tests are done. Some cruelty-free firms carry out tests on human beings. The human test involves people rubbing a small portion of the products on their skin to confirm if the cosmetic is effective and safe. Human testing is usually done in the final stages of testing a new product.
Is Testing Cosmetics On Animals Legal?

Animal testing for cosmetics has been legal in most countries like the United States since 1938, when they introduced the Food-Drug-and-cosmetics Act. However, over the years, many animal rights groups have come up and fought against animal testing. The public outcry on the harsh tests that are done on these animals forced some governments to ban animal testing within their jurisdictions. Several manufacturers say that they don’t do animal testing; however, they are required to prove that their products are safe in some countries. These companies can prove that their cosmetics are safe without animal testing in some jurisdictions, but in other nations, they will have to do animal testing. Anima testing for cosmetics is banned in several jurisdictions including the EU, Sao Paulo (Brazil), the European-Free-Trade Association, India, Israel, the U.K., Turkey, New Zealand, and Guatemala.
Arguments For A Ban
Animal testing harms and even causes the death of several animals
One of the most common dangerous tests done on animals is the Lethal-dose 50% test (LD50), where the test subjects are given test chemicals until 50% of them die. Even though the process of this test has never been validated, the LD50 test is used to determine the toxicity level of cosmetics for human use. The animals in the high-dosage group can endure forced inhalation, bleeding, rashes, and suffer from convulsion, seizures, and even paralysis. The LD50 test is 65% accurate with cosmetics as compared to human cell-line tests that are 80% accurate. While some tests can be painless, the test animals are not always left alive after the tests are done.
During some animal tests like the Draize test, the animals endure inhumane treatments. The Draize Test involves a researcher applying the test substance to the skin or eye of a conscious, restrained animal and leaving it there for a few minutes before rinsing it out. The test is controversial and is considered to be unscientific and cruel by the critics because of the subjective nature of the test and the difference between the human and rabbit eyes.
Most of the products tested are never used
Unfortunately, most animal tests in this industry don’t always result in the release of a new product. The development process of most cosmetics is abandoned if the ingredients being used harm the animals. These animals suffer and die after being exposed to dangerous tests that don’t have direct human benefits. The failure rates in this industry are over 90%. The FDA suggests the failure rate of the animal tests could be over 96%. The U.S. is the only developed country without major bans on animal-tested products.
Exemptions from the animals testing laws
All the current animal testing acts, including the AWA (Animals welfare Act) of 1966, don’t cover birds, fishes, mice, and rats, which make up over 95% of the animals used in cosmetic testing. The Animals Welfare Act covered 820,812 animals that are used in animal tests by 2016, leaving about 25million other species uncovered. These animals are vulnerable and can be abused and mistreated without being protected by the AWA. Even though most facilities govern themselves with animal testing compliance, they can apply for exemptions from the animal testing laws if they can prove that their cosmetics can help people in some ways.
Arguments Against A Ban
Animal testing aids research
The most effective way of confirming the safety of cosmetics in organic tissues before being used by human beings is through animal testing. Animal testing also helps cosmetic companies confirm if their new product is working. An educated guess wouldn’t be good enough for firms that deal with legal-liabilities when their products harm the users. Even though cosmetics are not like drugs that are immediately harmful to human beings or animals during the initial testing stages, unplanned results on animals don’t bear the same legal responsibilities with animals as they would with human beings.
However, with animal testing, cosmetic firms can conduct trial and error experiments on animals and learn more about their products before introducing them to the market. A huge percentage of all breakthroughs in drugs and cosmetics in the last century have resulted from direct research involving animals. Testing the viability and effects of the ingredients used to produce cosmetics and the end product on animals before trying on human beings, help manufacturers produce safe products. With animal testing, people are guaranteed never being exposed to dangerous chemicals or toxins that would affect their health. Animal testing is the only viable method of determining how chemicals react when used in a certain way.
Animals testing provide an opportunity for research lifespan-applications
Even though the composition of animals is not similar to that of humans, it is sufficient enough for researchers to determine how cosmetic products would work on human beings. The average lifespan of human beings in some nations is over 80years, while that of a mouse is 3years. Therefore, with animal testing, scientists can research the effects of cosmetics during different stages of an animal’s life. The effect of some cosmetics can be studied on multiple generations. The information obtained from animal testing can be used to make the product safer for all users irrespective of their age.
There are no adequate alternatives
Living systems are very complex; therefore, the only way you can be sure if a cosmetic is effective is by testing it on animals. Studying cell-cultures can be useful, but they don’t provide opportunities for exploring the interrelated processes that occur in the immune system, endocrine system, and the central nervous systems. Scientists can run computer-simulations, but the information will not be enough to replace actual testing. Computer simulations can be reliable if accurate data obtained from animal research is used to create the model.











