Is Puerto Rico An Island?

- Puerto Rico is an island in the Caribbean Sea.
- Puerto Rico has a population of approximately 2.8 million people.
- Puerto Rico is an unincorporated U.S. territory. Its people are U.S. citizens, but they cannot vote in U.S. elections.
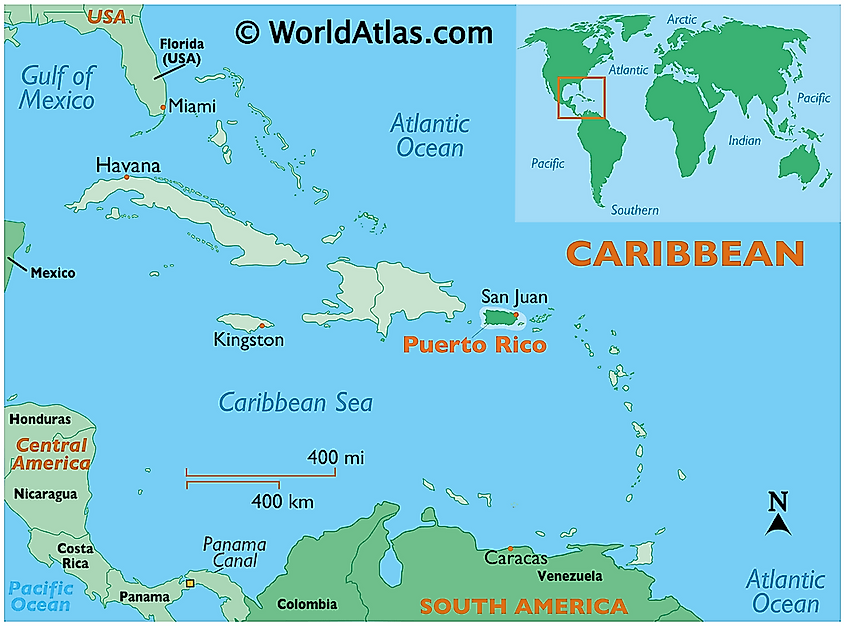
Puerto Rico is a tropical island in the Caribbean Sea. It is part of two island chains, the West Indies and the Greater Antilles. The island sits between the Dominican Republic to the west, and the Virgin Islands to the east.
Geography

The main island of Puerto Rico itself is approximately 110 miles long and 35 miles wide, for a total area of 3,515 sq. miles (9,104 sq. km). The jurisdiction of Puerto Rico also includes several offshore islands, though only two of these islands are permanently inhabited. One of them is Vieques, located about 7 miles off the east coast of the main island. The other is called Culebra, and is located around 9 miles north of Vieques. Another island, Mona, is located about 41 miles west of the main island, and now serves as a protected nature preserve.
Climate
Puerto Rico’s climate is tropical year-round. The average temperature during the year is 79 degrees Fahrenheit (26 degrees Celsius). Rainfall is usually more plentiful during the period of May to October. Puerto Rico is frequently visited by hurricanes. In 2017, Hurricane Maria carved a wide path of destruction in the U.S. territory, cutting off power and communications to the entire island.
Government

Puerto Rico is an unincorporated U.S. territory. It is self-governing, with a government apparatus that resembles that of the 50 U.S. states, including a bicameral legislature, composed of a House of Representatives and a Senate. The Puerto Rican government also has an executive branch headed by a governor. Puerto Ricans are U.S. citizens. However, since Puerto Rico is unincorporated, its citizens cannot vote in U.S. elections, and have no representation in the U.S. government, other than a delegate that sits in the U.S. House of Representatives, but has no voting rights, except in committees. Puerto Rico’s government is based in San Juan, the territory’s capital and largest city.
People
Puerto Rico’s population of approximately 2.8 million is multiracial and multicultural, with a mix of Spanish, Caribbean, African, and indigenous traditions. Both Spanish and English are official languages in the territory. Most Puerto Ricans are adherents of Roman Catholicism.
History

Puerto Rico was originally known as Borikén, which translates as “land of the brave lord”. Its original inhabitants were called the Taino. Christopher Columbus was the first European explorer to visit the island in 1493, during his famed expedition to the so-called New World. The island officially became a Spanish colony 1509. Puerto Rico remained in Spanish hands until the Spanish-American War in 1898, after which it was surrendered to the U.S. Puerto Ricans were given U.S. citizenship in 1917. In 1952, the territory was given the status of commonwealth, giving the island and its people greater autonomy, including control over matters like elections, education, taxes, health, housing, and culture. Since coming under U.S. sovereignty, several referendums have been held asking residents of the territory if Puerto Rico should become a fully-fledged U.S. state. The most recent vote was held during the 2020 Presidential Elections, in which a slight majority voted in favor of U.S. statehood. It will ultimately be up to the U.S. Congress, however, to determine whether Puerto Rico does become a U.S. state.











