What Is A Citadel?
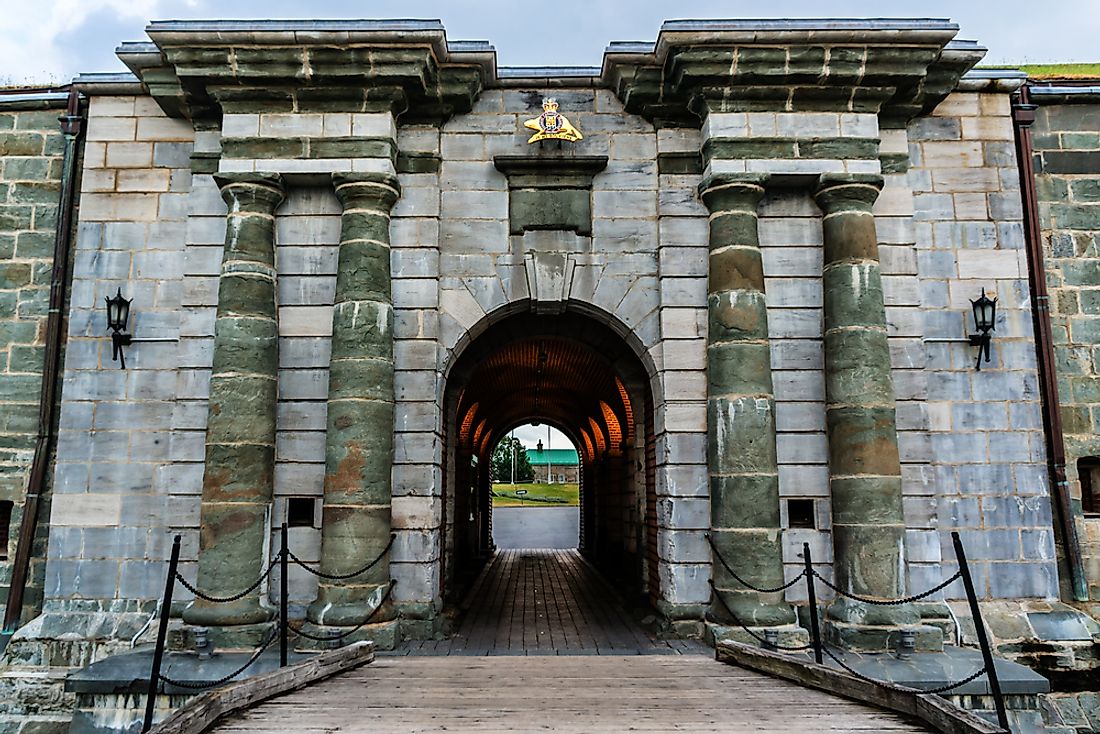

A citadel is a castle or fortified structure built on higher ground that protects a city or town. It is a defensive core that can be described as "little city" since it is a smaller part of a city or town. Fortresses form the most substantial part of the system and sometimes form part of the outer wall. In the modern day, fortifications are used to secure military command and control centers unlike the previous years between the fifteenth to nineteenth centuries.
The History of Citadels
3300 BCE to 1300 BCE
The oldest form of citadels represented a centralized form of authority among the inhabitants. Civilization at the Indus Valley brought about the construction of the oldest known 12 meters tall citadel. The main purpose of this citadel remains unknown with many believing that it served the defensive purposes in the valley.
8000 BCE to 600 CE
A citadel in Ancient Greece was a place of refuge and strength. It gave the inhabitants a sense of belonging and served as a store for food and military supplies. It also acted as a sacred place for worship and a palace.
500 CE to 1500 CE
During the middle ages, citadels had their fortifications, and it did not entirely depend on the city walls when attacked. Fortresses were considered the last defense option of a city under siege.
1600 CE to 1820 CE
The principal purpose of citadels during this period in history was to protect the governing power from the inhabitants. Fortifications served the purpose of subjecting the inhabitants to loyalty for the governing political rulers. The people living around or next to these citadels had a sense of protection. For instance, the King of England, King Charles II constructed a Royal fortress at a place called Plymouth. The Citadel had the capacity of holding guns that could fire the town and sea. On the other hand, Barcelona, under the Spanish government, constructed a premier citadel in 1714 to hold down the Catalans who were rebels of the mid-seventeenth and early eighteenth centuries. In the nineteenth century, the inhabitants destroyed the castle after rebellions calmed down. In North America, a citadel named, Citadelle of Quebec is a gigantic citadel, constructed from 1673 to 1820, which serves as the home for the Canadian Royal 22nd Regiment.
Modern Uses of Citadels
In modern day, citadels are mostly used to protect military commands and control points not cities and towns or at strategic locations on boundaries of a country. These modern-day citadels can protect the command and control points of military firms, from nuclear to aerial bombing. Examples of such strongholds are the Cheyenne Mountain nuclear bunker that is in the United States, and another one is present in London, United Kingdom. Fortifications are, therefore, crucial in the day-to-day protection of people, firms, and companies.