Flags, Symbols & Currency of United Kingdom
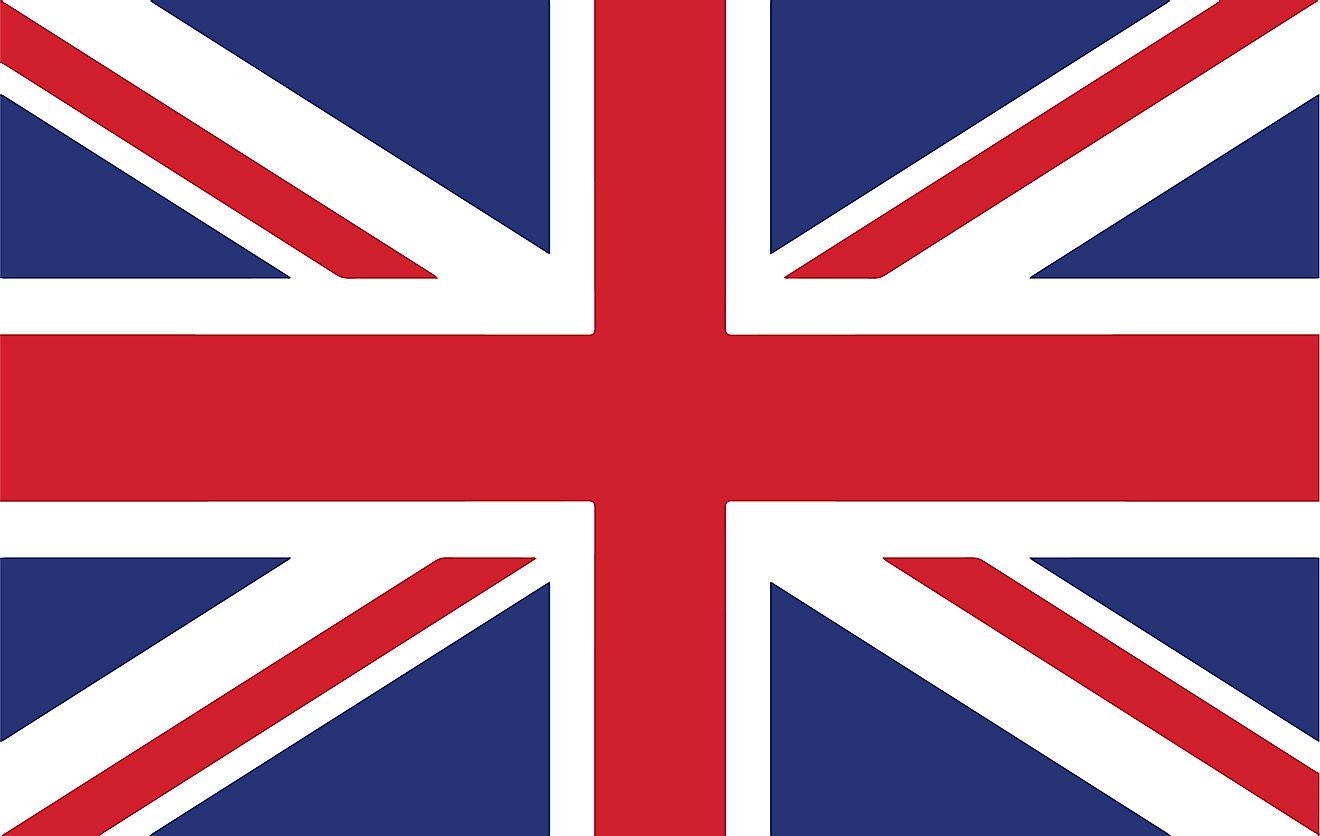

The National Flag of the United Kingdom was officially adopted on January 1, 1801.
The National Flag of the United Kingdom (Union Jack) features a blue background with the centered red cross edged in white. This is superimposed on the diagonal white cross on the blue background; which is again further superimposed on the diagonal x-shaped red saltire. In short, the Union Flag is a composite of St. George's Cross of England (the centered red cross bordered in white); St. Andrew's Cross of Scotland (the diagonal white cross on the blue field), and Saint Patrick’s Cross of Ireland (diagonal x-shaped red saltire). The flag has a width-to-length proportion ratio of 1:2.
History of the flag of the UK
The Scottish and the English crowns were united on March 24, 1603, when James VI of Scotland became the King of Britain and was renamed James I. In 1606, it was decreed by a royal proclamation by James I, that a single flag would be used to represent the whole United Kingdom. The first flags of Great Britain were hence flown during the rule of James I and Charles I during 1603-1649. The flag used during this period displayed the red cross of England (St. George’s Cross) that was superimposed on the white cross of Scotland (St. Andrew’s Cross) on a blue background. From 1649-1660, during the Commonwealth and the Protectorate period, the Irish harp was inducted into the flag. However, this flag was modified and subsequently, the original flag was restored in 1660, during the restoration of Charles II on the throne. The Act of the Union in 1800 enabled the two kingdoms of Great Britain and Ireland to join together. In 1801, the St. Patrick’s Cross was incorporated into the flag and the modern Union Jack was officially adopted as the Flag of the United Kingdom on January 1, 1801. The Union Jack has been the basis for several other flags including the flags of other Commonwealth countries and their constituent states or provinces, and the flags of British Overseas Territories.
Symbols of United Kingdom
United Kingdom Royal Coat of Arms

The Coat of Arms is used by the Queen or King in their official capacity as monarch, and are officially known as the Arms of Dominion.The United Kingdom Royal Coat of Arms consists of a shield divided into four quadrants. One of the quadrants contains the guardant lions of England. Two of the quadrants contain the rampant lion of Scotland. The final quadrant contains a harp which represents Northern Ireland. The shield is surrounded by a garter bearing the motto: Honi soit qui mal y pense (“Evil to him who evil thinks”). The garter symbolizes the Order of Garter that is an ancient order of knighthood of which the Queen is the sovereign. Supporting the shield are a crowned lion and a unicorn. The crowned lion represents England and the unicorn represents Scotland. The crowned lion also crowns the Coat of Arms that is surmounted by the Royal Crown. Below the crown is displayed the national motto: Dieu et mon Droit (“God and my right”). Displayed beneath the shield are rose, thistle, and shamrock – the plant badges of the United Kingdom.
National Motto
"Dieu et mon droit" ("God and my right").
National Anthem
- Anthem Title: "God Save the Queen"
- Music Composer: Unknown
- Lyricist: Unknown
- Date of Adoption: September 1745
"God Save the Queen" is the official national anthem of the United Kingdom. It also serves as the national and royal anthems in all Commnowealth realms, overseas territories of UK and the British Crown dependencies. The music composer and lyricist of the anthem are however unknown. The anthem has been in use since September 1745. The first verse out of the two verses are generally sung for official occasions.
"God Save the Queen"
1.
God save our gracious Queen!
Long live our noble Queen!
God save the Queen!
Send her victorious,
Happy and glorious,
Long to reign over us,
God save the Queen.
2.
Thy choicest gifts in store
On her be pleased to pour,
Long may she reign.
May she defend our laws,
And ever give us cause,
To sing with heart and voice,
God save the Queen.
The Currency of United Kingdom is the Pound sterling
The current official currency of the United Kingdom is the pound sterling (£, GBP). GBP is an abbreviation of "Great Britain Pound." It is the world's oldest currency which is still in use.
The pound sterling is a decimal currency, meaning its sub-units are based on a factor of 10. One-pound Sterling has 100 pence (symbol: p).
Coins
The common coin denominations are 1p, 2p, 5p, 10p, 20p, 50p, £1, and £2. Britons tend to speak “pee” instead of pence, like "20 pee" for a 20p coin. A pound is also referred to as a “quid”. A five-pound note is colloquially called a “fiver,” while the ten-pound note is known as a “tenner”. £1 and £2 coins feature different portraits of Queen Elizabeth II.
Banknotes
The common denominations of UK’s banknotes are £5, £10, £20, and £50. The current £5 banknote features an image of Sir Winston Churchill, a Nobel laureate and the UK’s prime minister during World War II. It also features Queen Elizabeth II – the reigning monarch on the other side. The £20 note has Adam Smith, and the £50 note features Matthew Boulton and James Watt. Charles Darwin is featured on the £10 note which has been withdrawn from circulation in March 2008.
The Bank of England is the central bank of the UK. It is also known as the “Old Lady” of Threadneedle Street. The bank is responsible for designing and printing the banknotes. It has started switching from traditional paper notes to polymer banknotes. On September 13, 2016, the Bank of England issued its first £5 note made of a polymer substance. The polymer £5 note features Sir Winston Churchill. The polymer £10 note is planned to be released on September 14, 2017, and will feature novelist Jane Austen. The new polymer £20 notes are planned to be issued in 2020 that features JMW Turner.
The Bank of England has two very large denomination notes called “Giant” and “Titan”. They are worth £1 million and £100 million, respectively. These notes are not in circulation, instead, their purpose is to enable authorized banks in Scotland and Northern Ireland to hold equivalent values in Bank of England notes.
Historical Currencies of the United Kingdom
Different historic sources indicate that the pound was already in circulation during the Anglo-Saxon period. The Tealby penny was circulated during the medieval period and was used as the standard currency unit until most of the 20th century. The sterling silver coins were introduced in 1552. The gold coins were introduced in 1663 and were used to export goods, making Britain a gold standard country. The establishment of the bank of England led to the issuance of the first paper money in 1694. The gold standard was adopted again in 1861. During WWI, the gold standard was abandoned and the treasury paper notes were used as the official currency. The Pound was then pegged to US Dollar and in the latter part of the 1940s, it became a part of the Bretton Woods System. Before decimalization in February 1971, the pound sterling had sub-units of shillings and pence (12 pence = 1 shilling and 20 shillings = 1 pound). The penny also had subdivisions named “halfpennies” and “farthings,” which were worth half and a quarter of the penny, respectively.