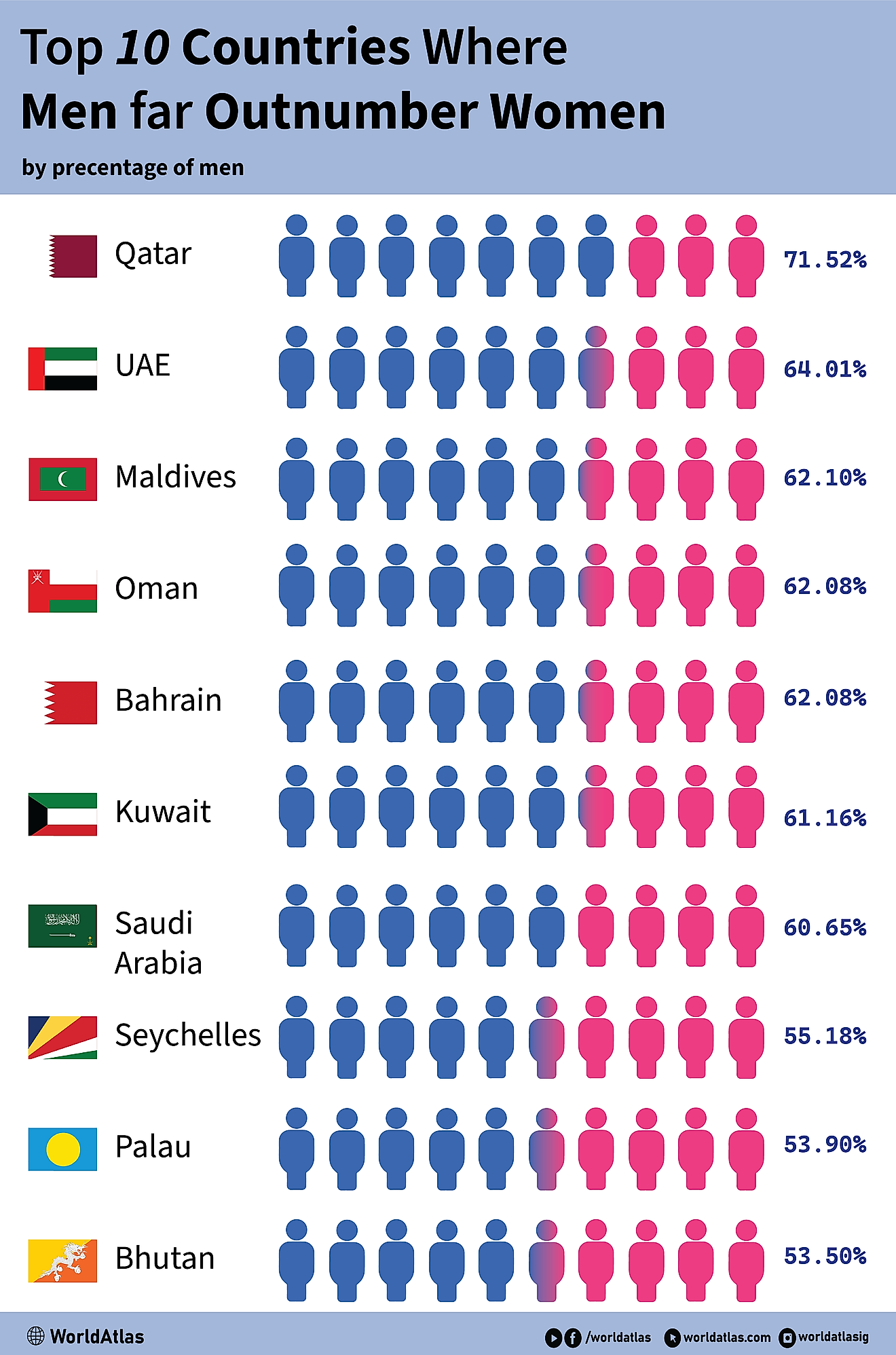
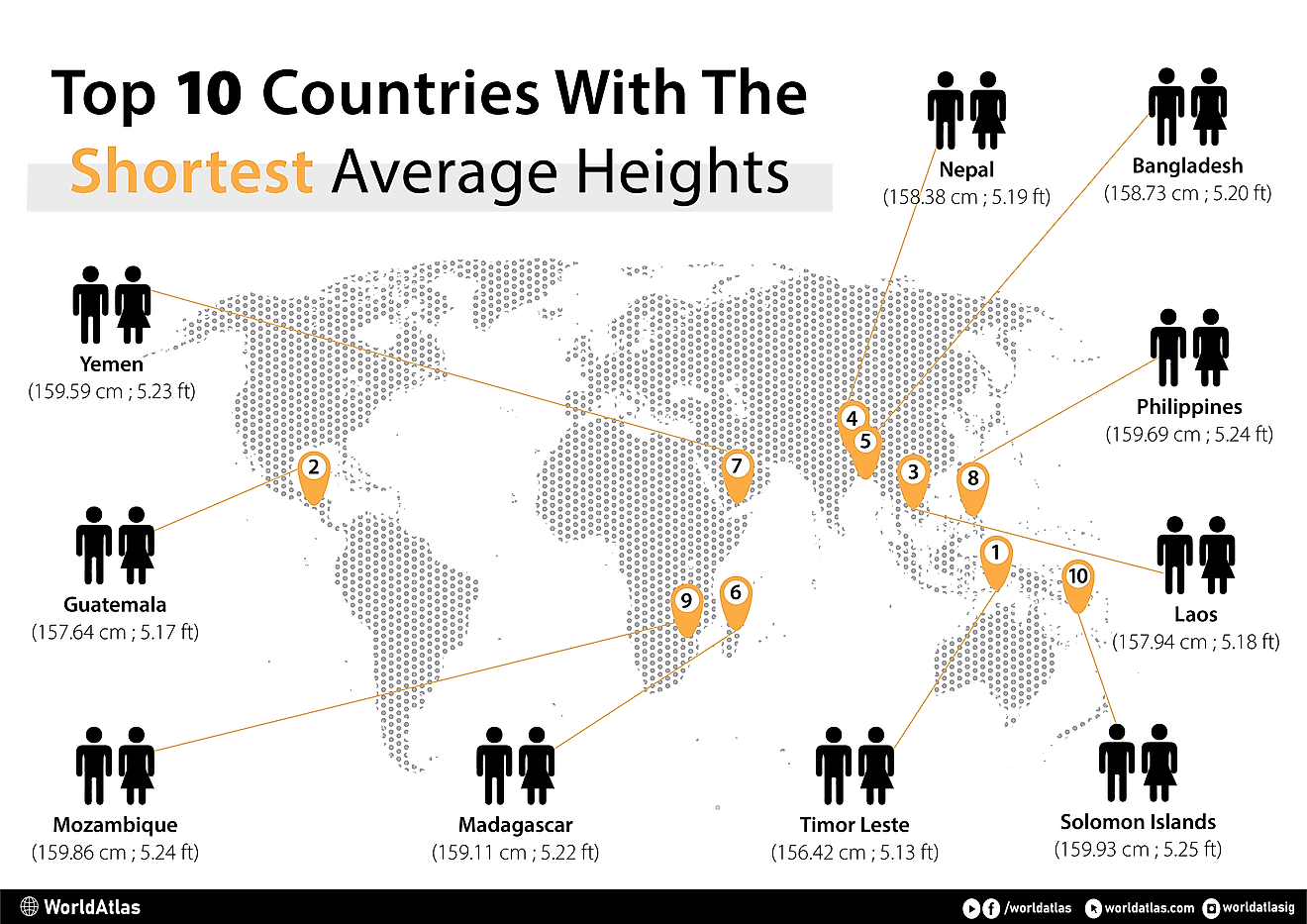
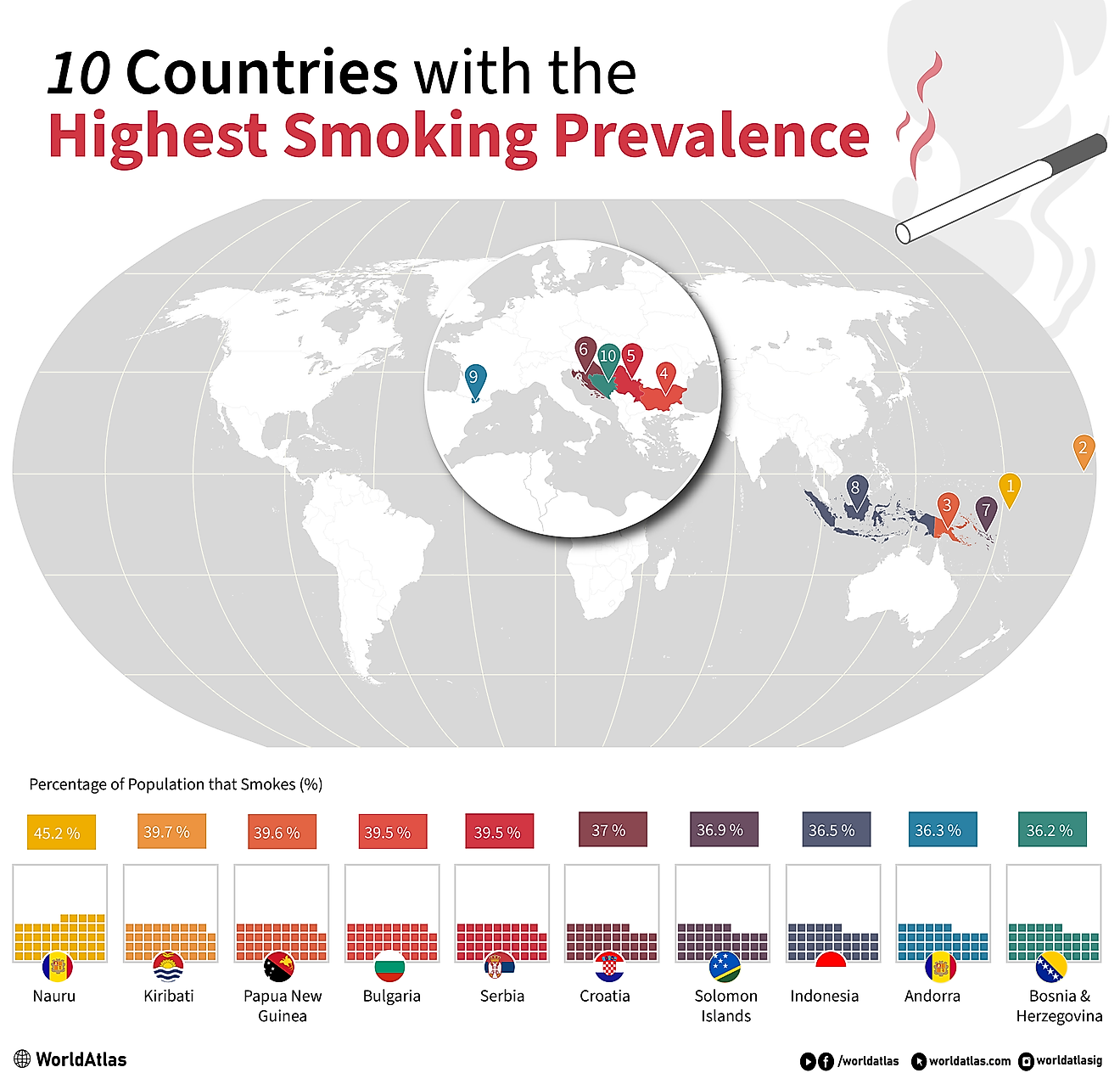
Who are the Luba?
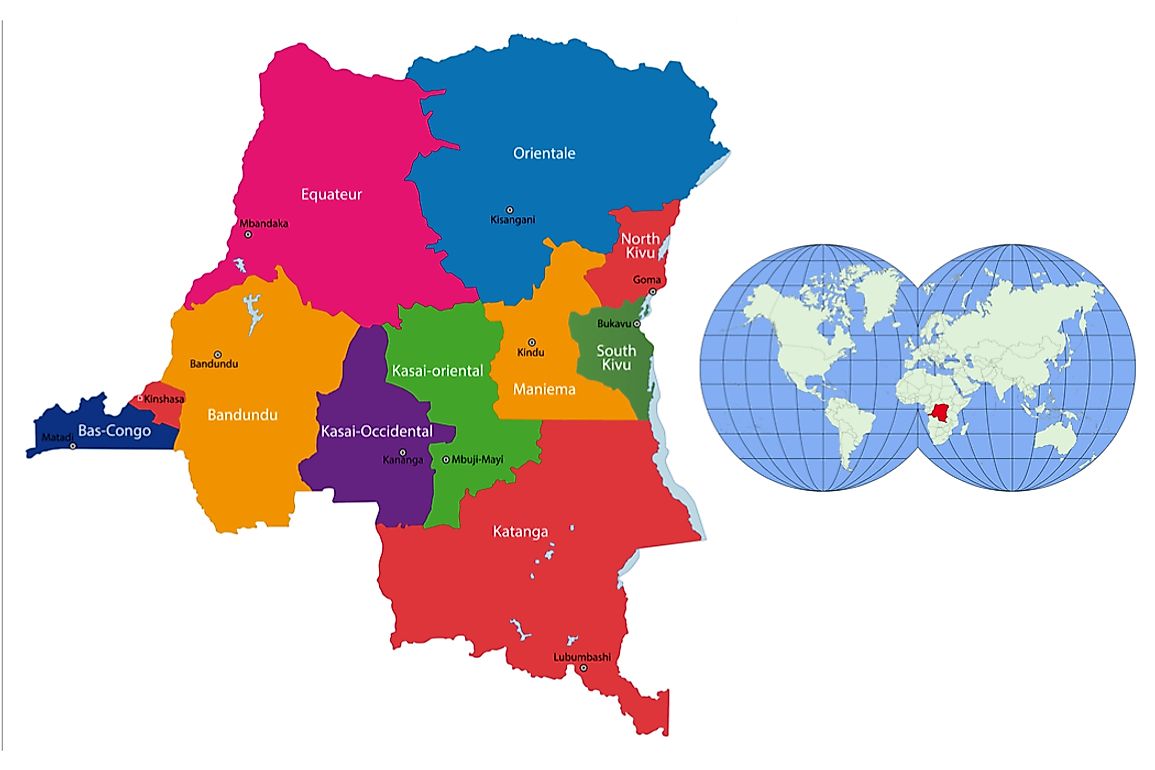
The Luba, also known as Baluba, is the largest group of Bantu Community that lives in the Democratic Republic of Congo. They widely spread in the areas of Katanga, Kasai, and Maniema. They speak the following languages: Luba-Katanga, Luba-Kasai, Luba-Maniema, and Swahili. They live in grasslands and forests where they are mainly hunters, farmers, and traders. The population of the Luba is approximately fourteen million.
People of the Luba
The Luba comprises many people speaking an almost common language. Despite their different origins, they share common cultural characteristics and political activities. The Luba community mainly lives in forests and savanna. They are said to be living in houses made of Reeds and Wattle, which are situated along rivers and lakes. The main area where the Luba lives is Upempa Depression. Due to their creative nature, they build dams for stocking fish dry spell seasons as well as practicing agricultural activities.
History of the Luba
In around 1500, the sub-groups of the Luba community came together to form an empire called The Luba Kingdom. The kings who lead this kingdom were the Black King (Mbidi Kiluwe) and Red King (Nkongolo Mwamba). The empire was very flexible to accommodate the incoming leaders of Lunda community who protected them from Portuguese. Their successful nature granted the significant advantage of overcoming disagreement of succession. The welfare of the people was being put into consideration before the powers of the king. The empire was meant to gather welfare of the community above all. Up to their stable political nature, the succession of the leadership from one generation to the other was successful. The well-developed form of leadership of the Luba creates an eager on the neighboring community regarding their association. It was the powerful kingdom that facilitated the growth of Luba. This mode of operation of the Luba made the Lunda community to emulate them.
Culture of the Luba
The Luba people lived in groups of small villages. Their main activities included hunting, gathering, and farming. They practiced subsistence farming for their survival alongside with hunting since they live close to the forest. They also practiced fruit gathering and planted cassava and maize. Also, they practice livestock farming along the lakes. The farming practices were mainly for their consumption.
Like other communities, the Luba also practiced the religious activities through dancing, offerings, and tides, worshipping, cleansing, and singing. Also, they believe in communicating to the ancestors to ascertain the cause of uncertain circumstance. The Luba people believe in the god called Shakapanga, meaning the Universal creator. Later, the Belgium missionaries introduced Christianity amongst them.
Their economy mainly relied on trading with their high-value metals because of their highly specialized skills in metalwork that gave them great economic background. Their outputs were mostly axes, necklaces, bows, and arrows. Unfortunately, the slave and ivory trade destroyed the kingdom of the Luba. As a result, the community was divided on their succession.