Gulf Of Aqaba
A gulf is a large inlet of the ocean into the land. These water bodies are usually formed as a result of plate tectonics and are often larger and more deeply indented than the bays. Covering an area of 239 sq. km, the Gulf of Aqaba is the northeastern extension of the Red Sea.
Content:
- Where Is The Gulf of Aqaba?
- Important Geographical Features
- Marine Life
- Important Settlements
- Brief History
- Economy
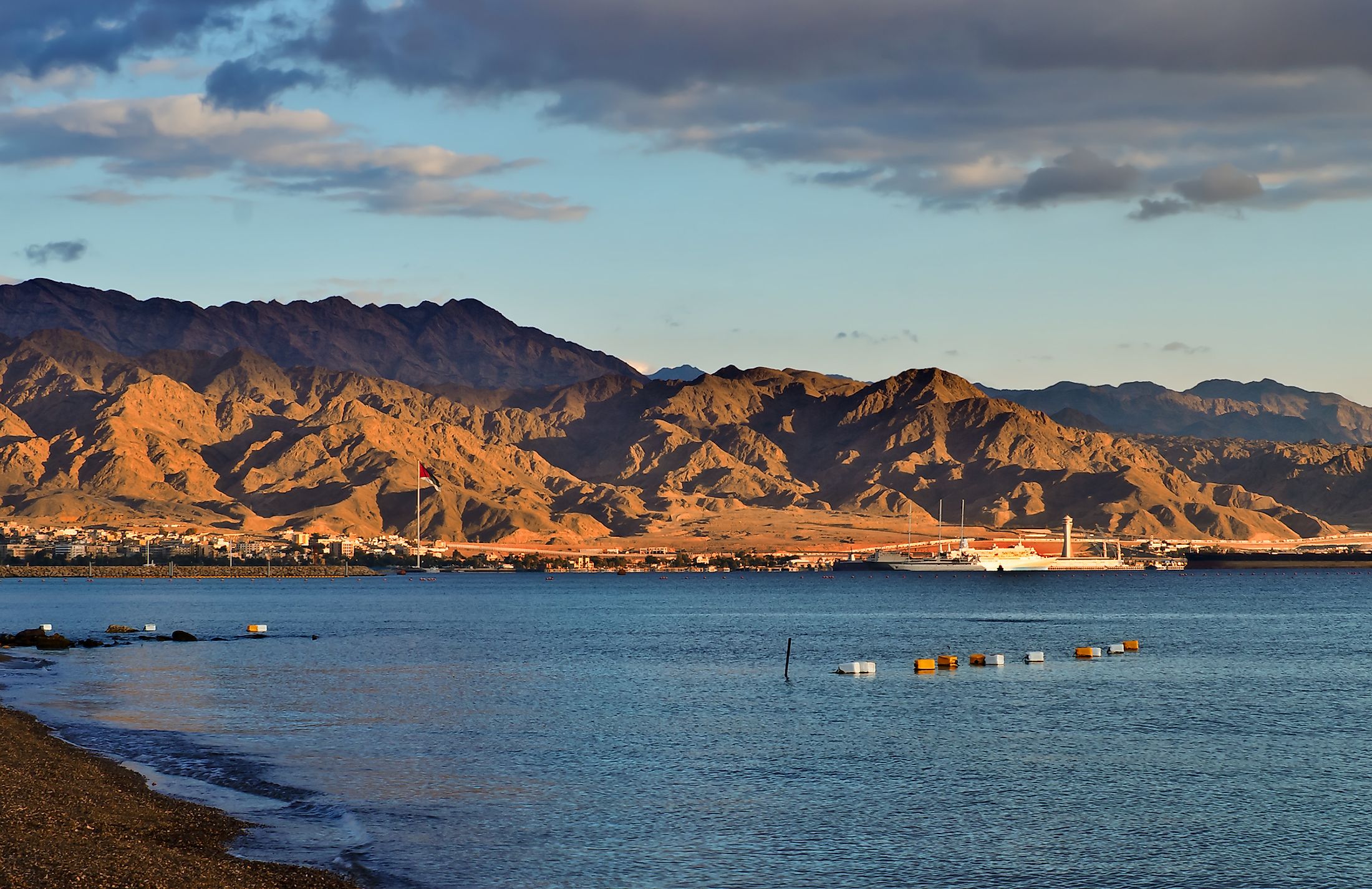
Where Is The Gulf of Aqaba?
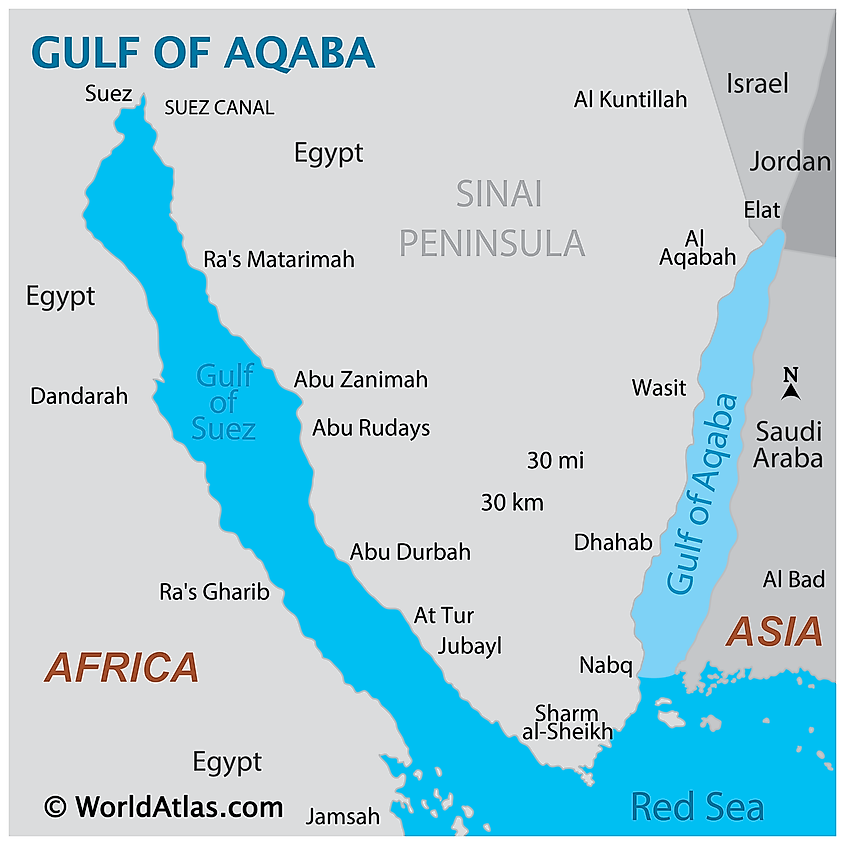
The northern portion of the Red Sea is divided by the Sinai Peninsula into the Gulf of Aqaba in the east and the Gulf of Suez in the west. The Gulf of Aqaba is located along the southeastern edge of the Sinai Peninsula and to the west of the Arabian Peninsula. The Gulf of Aqaba is bordered by the countries of Israel, Jordan, Egypt, and Saudi Arabia.
Important Geographical Features
The Gulf of Aqaba forms an integral part of the East African Rift System and was created by seismic activity along the Afro-Syrian Rift. This semi-enclosed, deep, narrow body of water is approximately 160km long and has a maximum width of 24km and a depth of 1,850m at its deepest point. The Tiran Strait connects the Gulf of Aqaba with the Red Sea. The Gulf of Aqaba also serves as a connecting point between the continents of Asia and Africa.
Marine Life
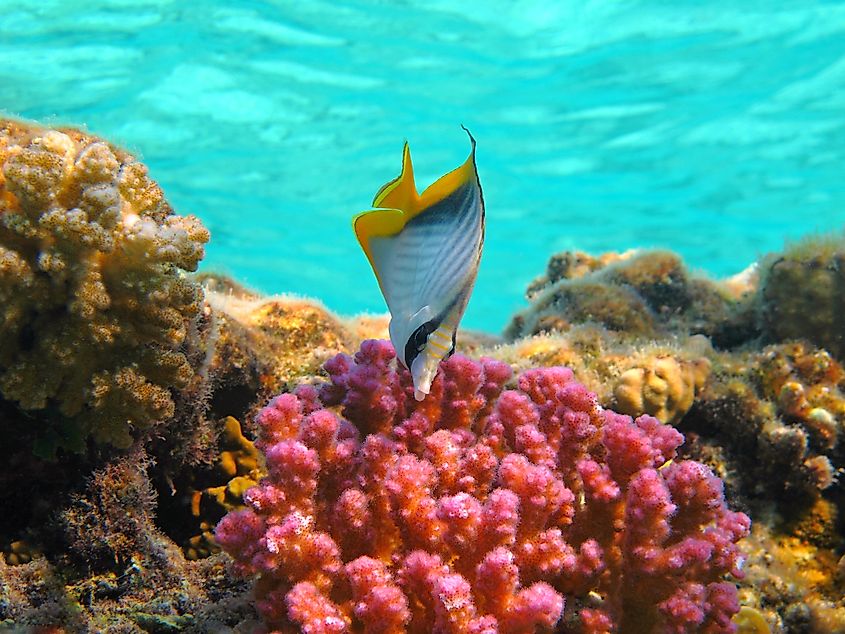

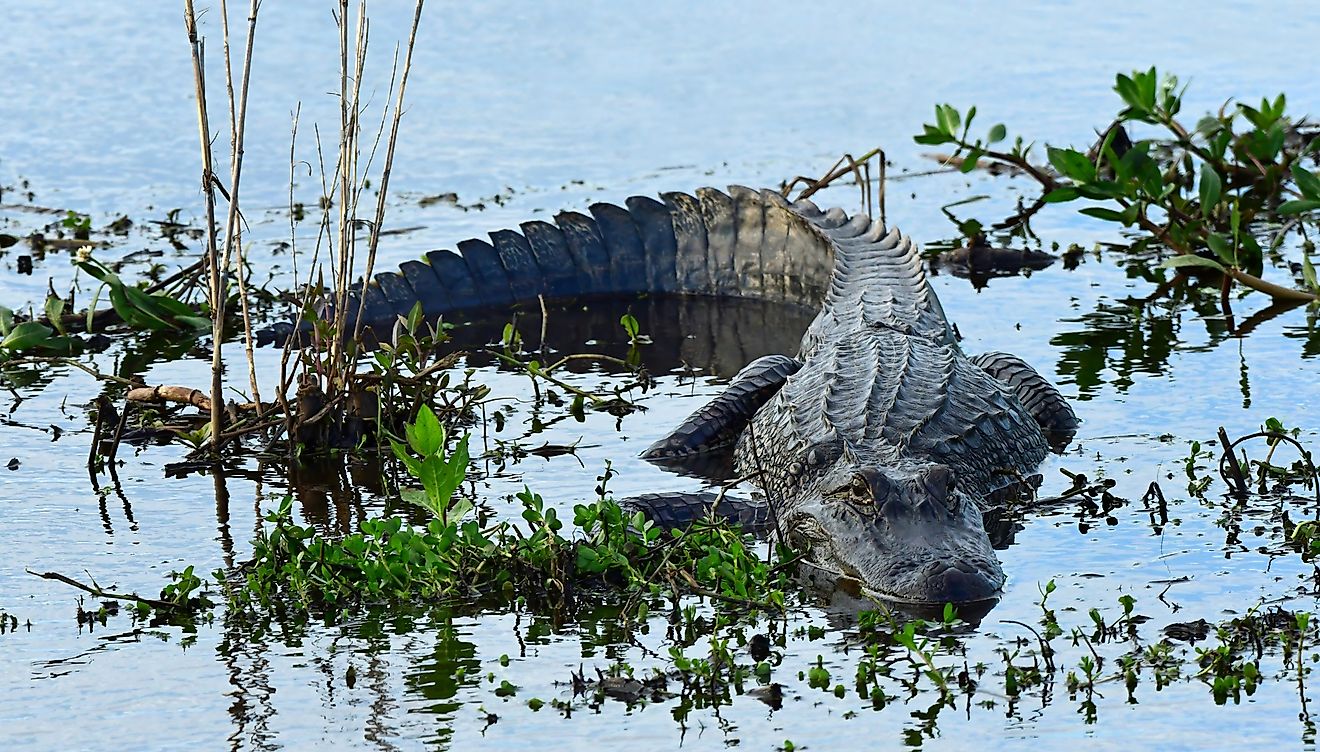
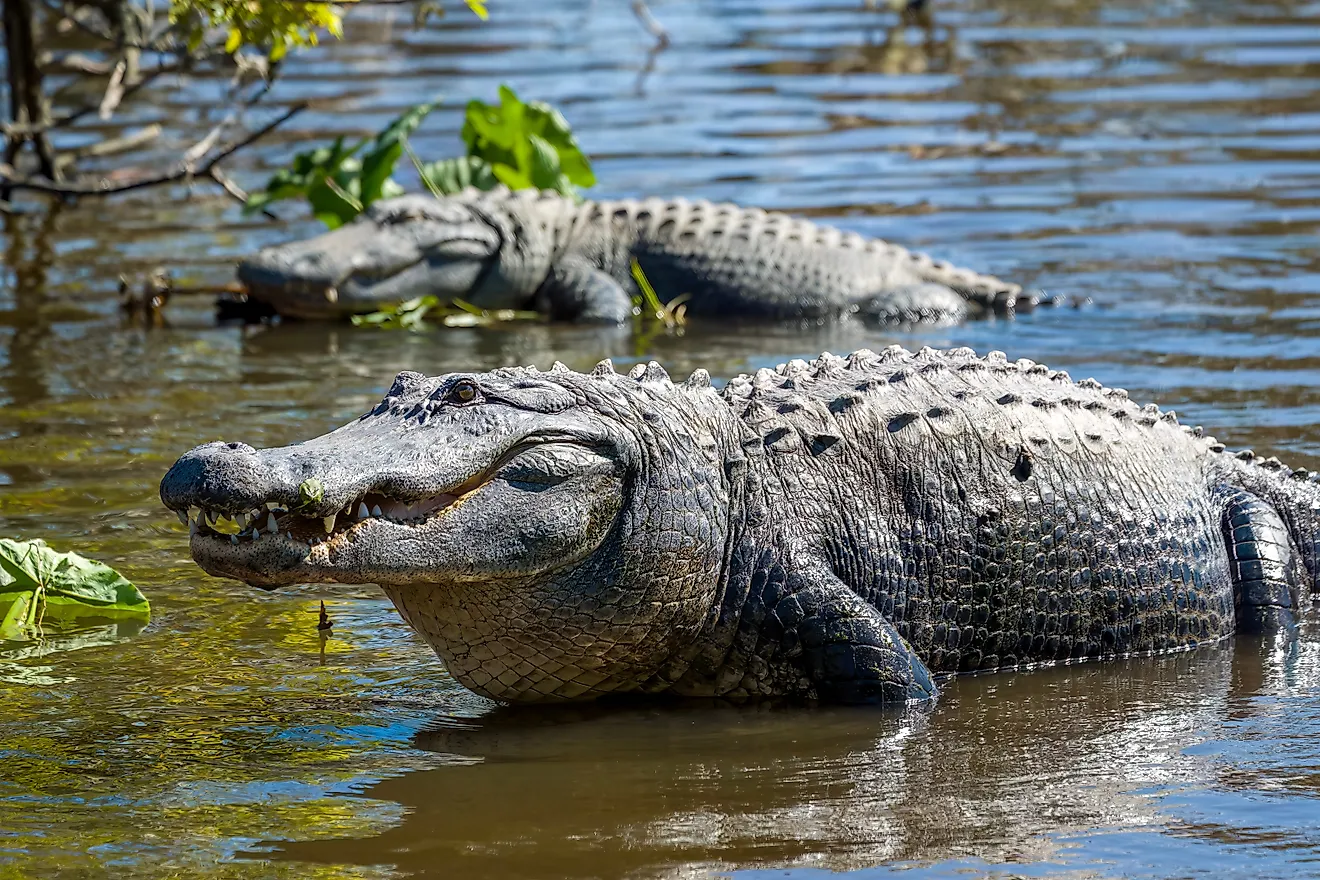
The Gulf of Aqaba supports unique and diverse aquatic ecosystems and serves as a vital habitat for some of the world’s richest coral reefs. The Gulf houses more than 100 coral species, 800 fish species as well as several species of crustaceans and mollusks. Some of the notable fish species that are found in the Gulf of Aqaba include Stonefish, Rusty Parrotfish, Coral grouper, Bluestripe Unicornfish, Royal Angelfish, Crown Butterflyfish, etc. Different types of marine mammals like dolphins, whales, orcas, dugongs, and whale sharks are also found in the Gulf of Aqaba region.
Several marine reserves have been established along the Gulf of Aqaba coast. The ‘Red Sea Marine Peace Park’ has been established by the Government of Jordan, off the shores of the Gulf of Aqaba.
Important Settlements
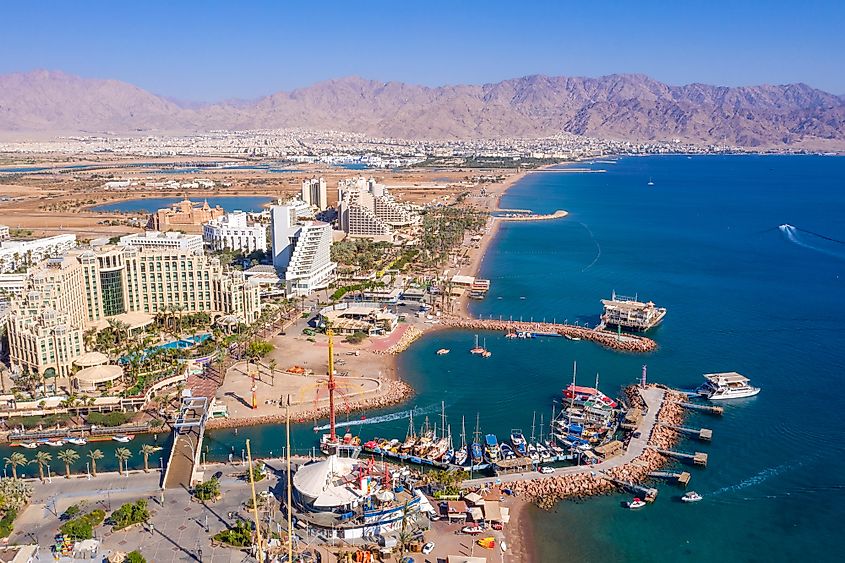

Some of the major cities that are situated on the northern end of the Gulf of Aqaba include Taba (Egypt), Eilat (Israel), and Aqaba (Jordan). All three cities serve as strategically important commercial ports as well as popular tourist destinations. The city of Haql is the largest Saudi Arabian city on the Gulf. Just beyond the southern edges of the Gulf, resorts like Sharm al-Sheikh and others are rapidly transforming into major tourist destinations.
Brief History
Expeditions along the Gulf of Aqaba have been documented during the rule of the fifth, sixth, eleventh, twelfth, and eighteenth Egyptian dynasties. Located at the northern edge of the Gulf was, Ayla – an ancient city and an important commercial hub for the Arab people. The city of Aqaba also served as a major Ottoman port and during WWI, the Battle of Aqaba was an important decisive battle that helped to end the 500-year Ottoman rule over the Greater Syria region.
Economy
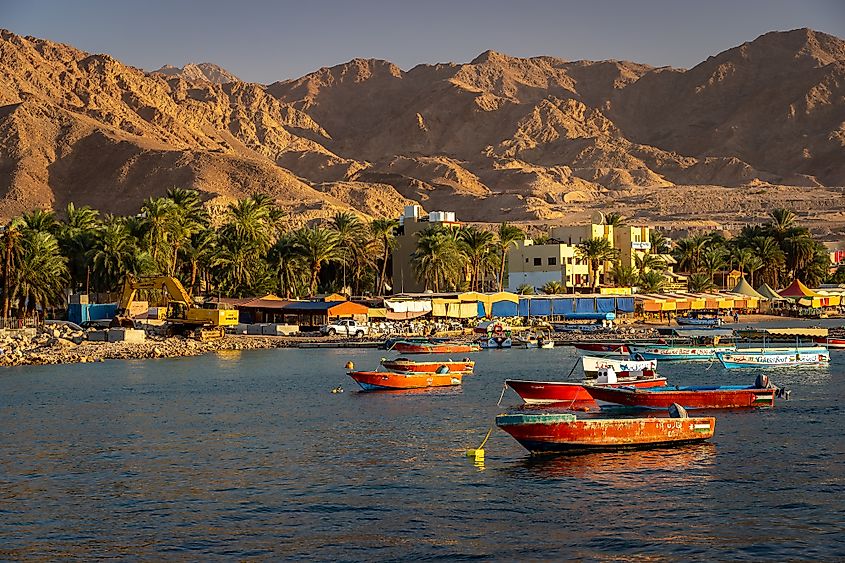

The Gulf of Aqaba serves as one of the world’s most important tourist destinations. About 250,000 dives are performed every year along Eilat’s long coastline. Diving and other recreational activities along the Gulf of Aqaba coast generate income that support livelihoods in the coastal region. Some important ports along the Gulf are Al-Aqabah and Eilat. Dhahab is the only sheltered harbor situated along the Gulf of Aqaba.











