Maps of British Columbia
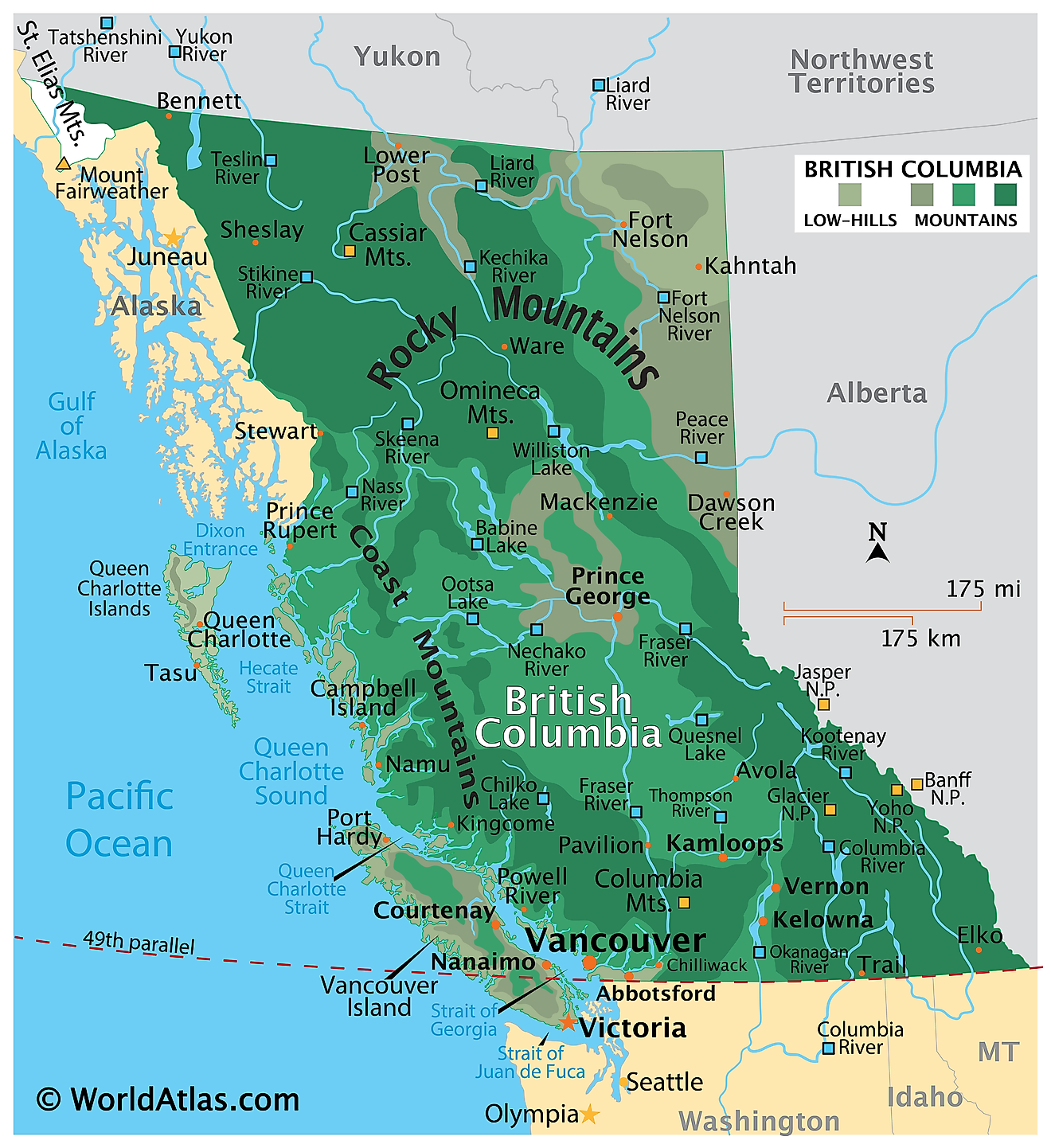
British Columbia, a province in western Canada, stretches over approximately 364,764 square miles. This terrain encompasses rugged coastlines, towering mountain ranges, dense forests, and arid desert landscapes.
British Columbia's coast, stretching over 15,900 miles, features numerous inlets and fjords, providing a natural haven for marine life. Vancouver Island, the largest island in the province, lies off the southwest coast and is home to the vibrant city of Victoria, the provincial capital. Haida Gwaii, an archipelago to the northwest, showcases Indigenous culture and history.
The province's topography features several mountain ranges, including the Canadian Rockies in the east, the Columbia Mountains in the southeast, and the Coast Mountains along the western coastline. These ranges create barriers that contribute to the province's distinct climatic zones.
A ring of volcanic mountains referred to as the Pacific Ring of Fire also features some of the highest mountains in British Columbia. One of these mountains is Mount Waddington - a dormant volcano in the Coast Mountains, which stands at an elevation of 13,186 feet. Mount Fairweather, near to the boundary with Alaska, is the tallest mountain at 15,266 feet.
Climatically, British Columbia divides into three major zones: coastal, interior, and northern. The coastal zone, characterized by a temperate maritime climate, experiences mild winters and cool summers. Precipitation levels remain high, fueling the coastal rainforests. The interior zone, with a continental climate, experiences hotter summers and colder winters, resulting in diverse vegetation, including grasslands, forests, and subalpine ecosystems. The northern zone features a subarctic climate, marked by long, cold winters and short, cool summers, supporting boreal forests and tundra landscapes.
The Fraser River, British Columbia's longest and most important river, spans over 854 miles. It originates in the Canadian Rockies and flows westward, emptying into the Strait of Georgia near Vancouver. The river plays a vital role in the province's economy and ecology, supporting agriculture, hydroelectric power, and salmon spawning.
Some other significant rivers of the province include Columbia, Peace, Skeena, Stikine, Iskut, Nass, and Kootenay. Numerous lakes are scattered across the province’s interior mountain valleys among which the Williston Lake is the largest. The lowest point of the British Columbia province is the Pacific Ocean (0ft).
British Columbia's natural resources, including timber, minerals, and energy sources, play a crucial role in its economy. The province's vast forests provide timber for the thriving forestry industry, while the mountain ranges hold valuable mineral deposits, such as gold, copper, and coal. Additionally, British Columbia benefits from its abundant water resources, utilizing hydroelectric power to meet its energy needs.Notable parks include Pacific Rim National Park Reserve, which protects coastal rainforests and beaches, and Yoho National Park.
Provinces Map
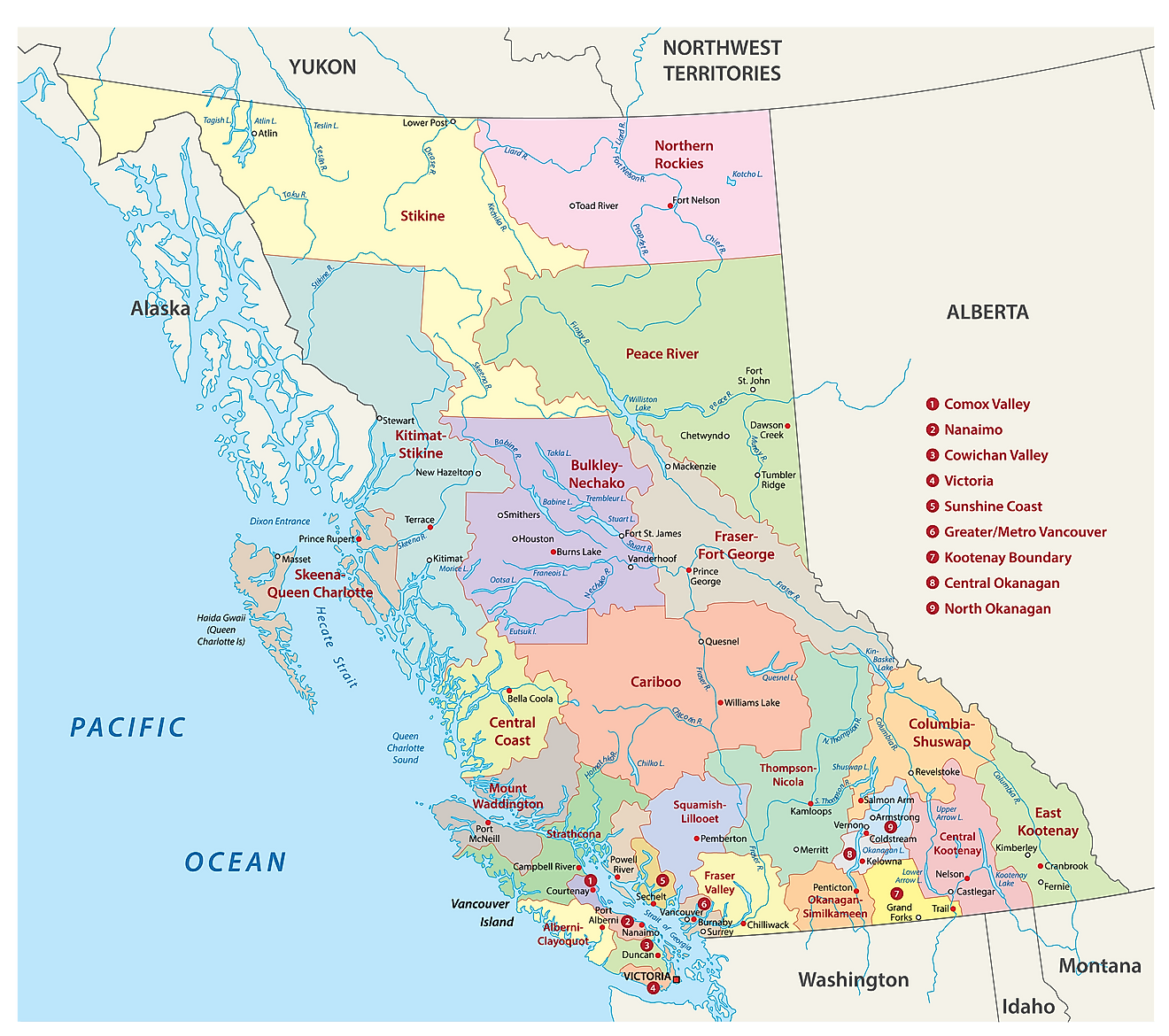
The Canadian Province of British Columbia is administratively divided into 26 regional districts. In alphabetical order, these regional districts are Alberni-Clayoquot, Bulkley-Nechako, Capital, Cariboo, Central Coast, Central Kootenay, Central Okanagan, Columbia-Shuswap, Comox Valley, Cowichan Valley, East Kootenay, Fraser Valley, Fraser-Fort George, Kitimat-Stikine, Kootenay Boundary, Metro Vancouver, Mount Waddington, Nanaimo, North Coast, North Okanagan, Northern Rockies, Okanagan-Similkameen, Peace River, qathet, Squamish-Lillocet, Strathcona, Sunshine Coast, and Thompson-Nicola.
In addition to these regional districts, there are a total of 51 cities, 50 district municipalities, 1 Indian government district, 1 Island municipality, 2 Mountain resort municipalities, 1 resort municipality, 14 towns, and 42 villages.
With an area of 944,735 sq. km, British Columbia is the 5th largest and the 3rd most populous Canadian province. Located on the southeastern edge of Vancouver Island is Victoria – the provincial capital city of British Columbia. The city serves as an administrative and technological center of British Columbia. It is also often referred to as the “Garden City”. Situated in the Lower Mainland region of the Canadian Province of British Columbia is Vancouver – the largest and the most populous city in British Columbia. This coastal seaport city also serves as one of Canada’s most ethnically and linguistically diverse cities.
Where is British Columbia?
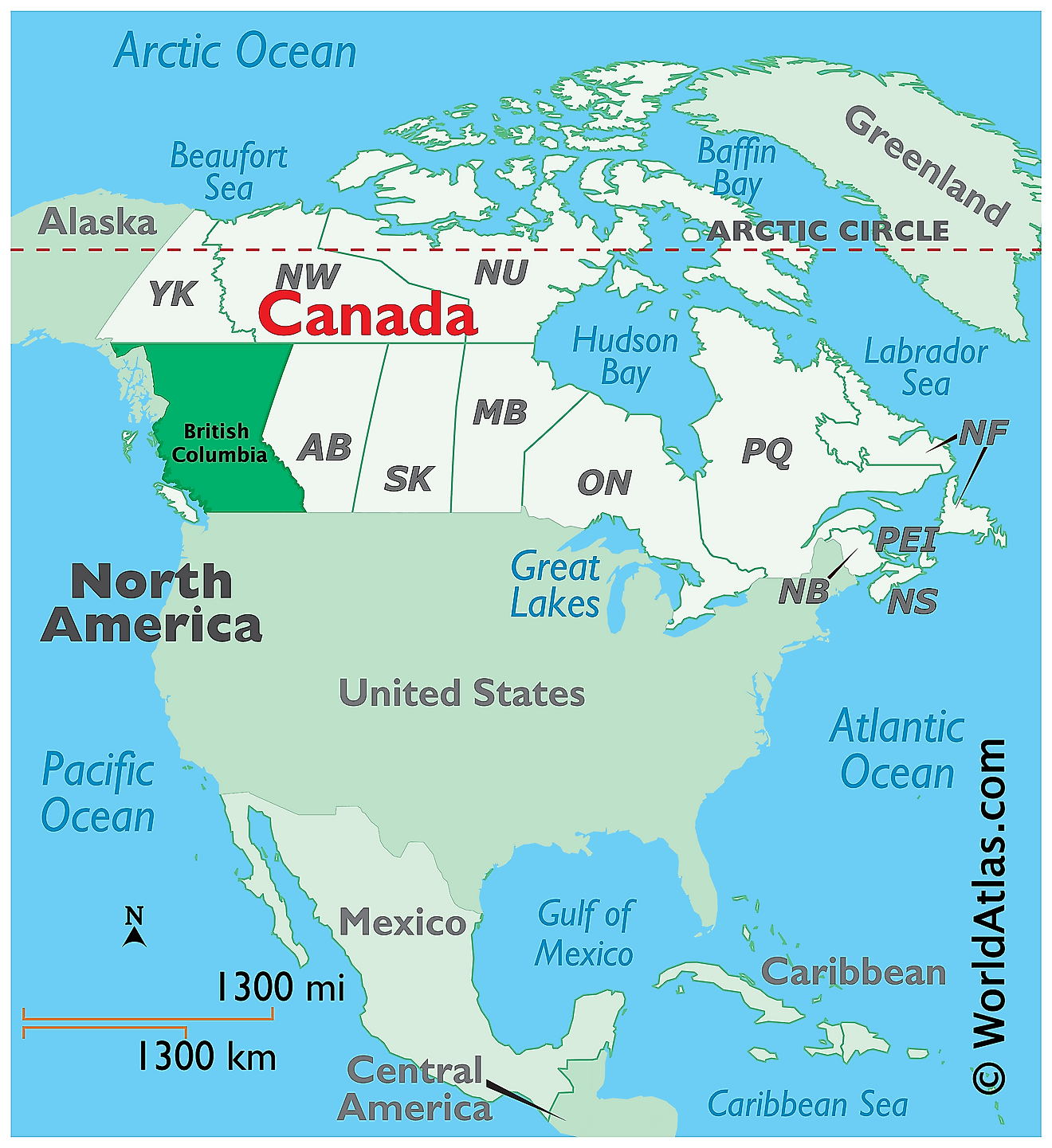
The Province of British Columbia is located in the extreme southwestern part of Canada, in the Continent of North America. It is geographically positioned in the Northern and Western hemispheres of the Earth. British Columbia is Canada’s westernmost province that is sandwiched between the Rocky Mountains and the Pacific Ocean. It is bordered by the Canadian Provinces of Yukon and the Northwest Territories in the north; by Alberta in the east; by the US States of Idaho, Montana, and Washington in the south; and by the Pacific Ocean and the southern part of the US State of Alaska in the west.
Regional Maps: Map of North America
Outline Map of British Columbia
The above blank map represents the Province of British Columbia, located in the extreme southwestern part of Canada. The above map can be downloaded, printed, and used for geography education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.
The above outline map represents the Province of British Columbia, located in the extreme southwestern part of Canada.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Province of British Columbia |
|---|---|
| ISO 3166 Code | CA-bcz |
| Capital City | Victoria |
This page was last updated on March 17, 2023











