The 10 Strangest Philosophical Theories
When you think of famous philosophical theories, Descartes and his Theory of Innate Ideas or the ideas of Ethical Egoism (that morality aligns with self-interest) probably aren't the first that comes to mind. That's because these theories are a little more unconventional by today's standards. However, all ancient philosophies have their time and place. At one time, these theories may not have been strange. Here are some of the strangest philosophies that have existed throughout history.
Idealism

Idealism is a philosophical movement (prominent in the 18th and 19th centuries) that considers reality mental in nature. It is a philosophy that stresses the importance of the ideal in interpreting your experiences. In this view, reality is just a mental construct and there are no fundamental beliefs. Idealism says the existence of anything is dependent on the mind. While this belief doesn't sound too crazy in theory, trying to put it into practice causes a paradox. If reality is just a mental construct, how do multiple people exist together with different ideas of reality?
Hegelianism
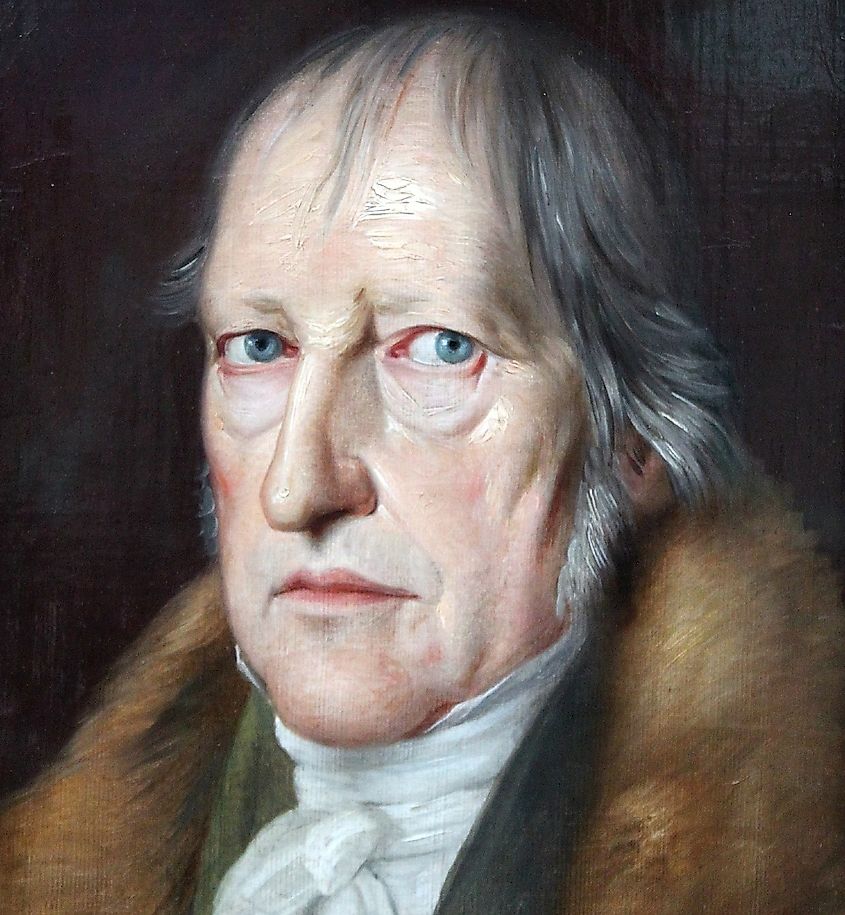

A specific branch of Idealism known for its obscurities is Hegelianism. Invented by the German philosopher Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, Hegelianism is German Idealism. The philosophy is famous for being challenging to understand with obscure phrases and its focus on logic. A dominant idea in Hegelianism is that rationality is the key to reality. This is what Hegel meant when he said, "the rational alone is real." Today, the philosophy isn't particularly popular. After Hegel passed away in 1831, German Idealism also faded away.
Theory of Innate Ideas
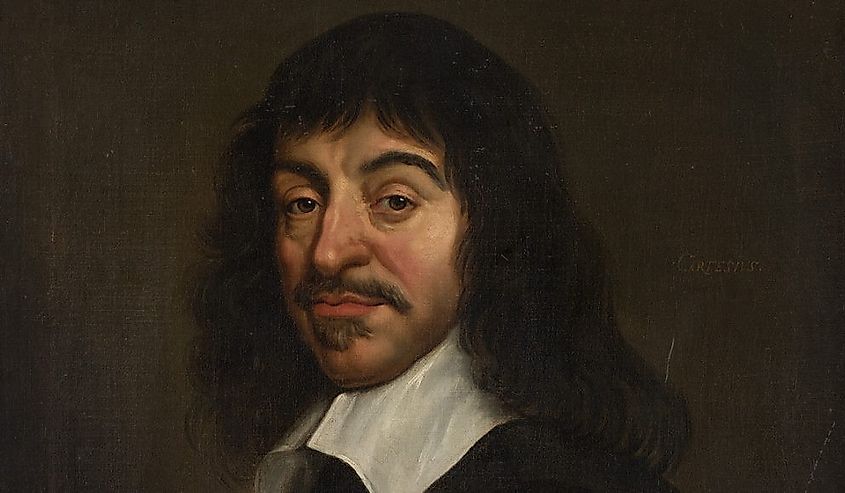

One of the ways we learn is from experience. According to the Theory of Innate Ideas, the human mind is also born with ideas. Innate ideas include the idea of God, infinity, and substance. Some believed these ideas were innate because experience alone cannot explain them. The Theory of Innate Ideas flourished during the 17th century, with Rene Descartes' philosophy. However, this theory raises important questions, such as, if the idea of God is innate, why isn't everyone religious?
Hylozoism

Hylozoism is a philosophy that believes everything, from the stones to the grass, is alive. There are different variations of the philosophy. Some Hylozoists believe everything has a soul or a similar idea. Hylozoism differs from similar philosophies, such as panpsychism, which gives some form of consciousness to all matter. Throughout history, the idea that nature has a soul or spirit has been common. However, many people would find it hard to believe that a rock has a soul today.
Ethical egoism
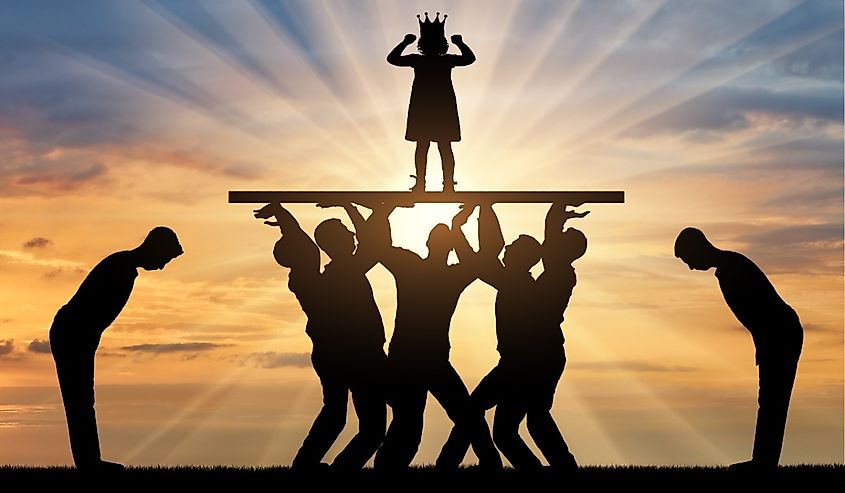

Ethical egoism is a philosophy that says the moral thing to do is the thing that is in your own best interest. In this view, our actions are right as long as they advance our self-interest. This moral philosophy is similar to psychological egoism, which is the idea that self-interest motivates human action. One advantage to ethical egoism is that it avoids the problem of having to choose between self-interest and another morality. However, the theory can result in actions we don't typically associate with a moral choice. For example, according to the theory, it might be okay to steal money since it is serving your own self-interest.
Anarcho-Primitivism
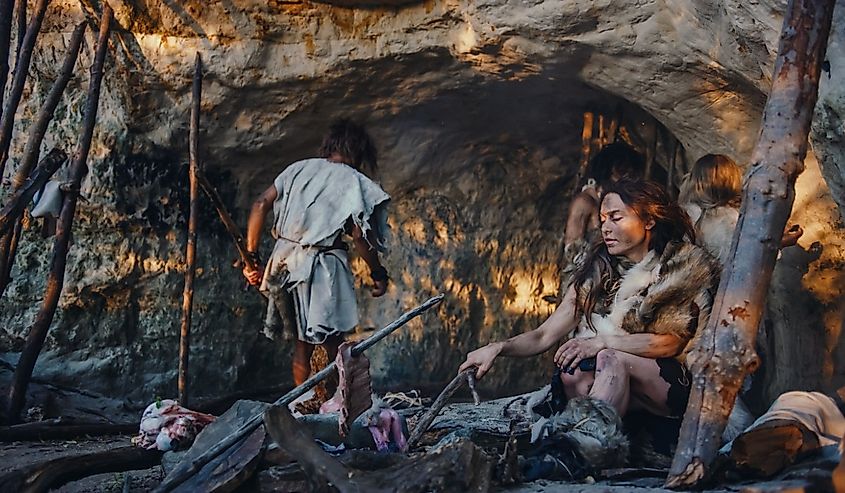

Both a political and ethical movement, Anarcho-Primitivism is a critique contending that civilizations drive us away from each other and nature. This idea advocates a return to the non-civilized way of life, which means going back to hunter-gatherer days. Anarcho-Primitivism also advocates for deindustrialization, getting rid of large-scale technology and moving away from specialized labor. Anarcho-Primitivists usually prefer small-scale, decentralized constructs with minimalist housing where you can live off the land. Living in harmony with nature is one of the core values of Anarcho-Primitivists. This philosophy is similar to primitivism, which challenges modern life.
Trivialism

Trivialism is a theory in logic that says all statements are true and all contradictions are true. Essentially, a trivialist is someone who believes everything is true. The philosophy also emphasizes that everything is uniquely true and assertions can be equally true to each other. This theory is completely opposite to skepticism, which questions the existence of everything. The theory is a paradoxical one since it states all statements, even ones that contradict each other, are true.
Bavarian Illuminati
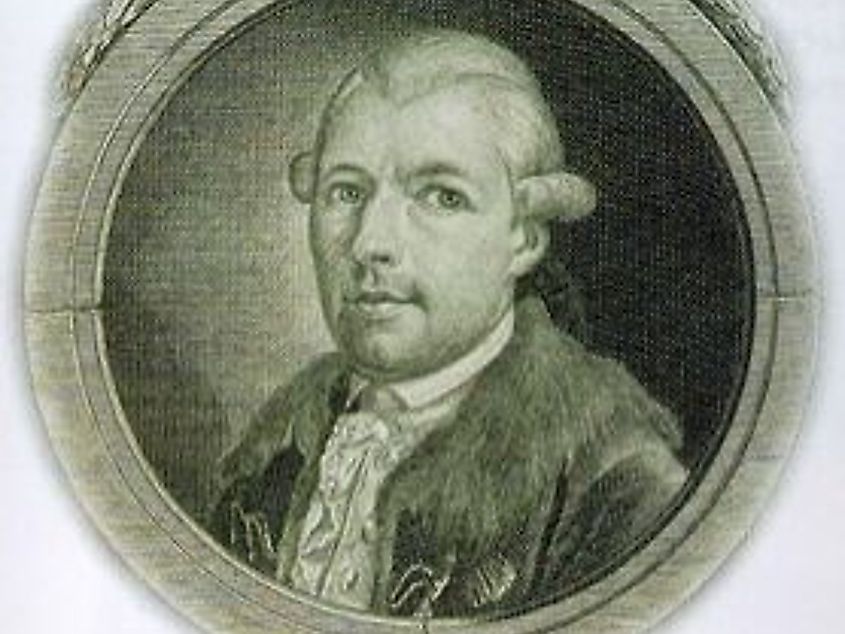

One of the stranger philosophies is the ideas of the Bavarian Illuminati. The Bavarian Illuminati was a philosophical movement founded in 1776 by Adam Weishaupt. The movement was originally called the Covenant of Perfectibility. The leading idea in Bavarian Illuminati philosophy is that human nature is perfectible through a series of specific rituals. Weishaupt and some of his associates developed the rituals needed to achieve the so-called perfection. Another one of the philosophy's ideas was replacing religion with rationalism. While the Illuminati gained an early cult following, this did not last. After internal conflict dissolved the Bavarian Illuminati, Weishaupt spent the rest of his life in exile in Germany.
Pythagoreanism

While there have been many religions throughout human history, worshipping different Gods, few have worshipped numbers. However, the ancient philosophy of Pythagoreanism worships numbers, along with musical harmony. Pythagoreanism is a philosophy dating back to the ancient Greeks. The Greek philosopher and mathematician Pythagoras founded the philosophy. His aim was to solve as many scientific inquiries through philosophy as possible. One of Pythagoras' most famous discoveries was the Pythagorean Theorem. However, beyond his scientific discoveries, Pythagoras also founded the Pythagoreanism Brotherhood. In this philosophy, the pursuit of philosophy itself was for spiritual purification.
Cynicism
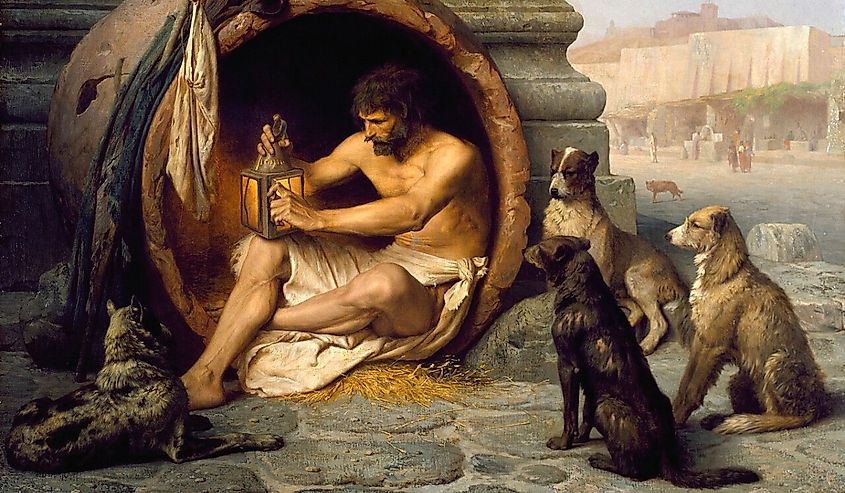

Chances are you have heard the word cynic before. Cynics are members of the school of thought known as Cynicism. The philosophy dates back to the 4th century BCE and is famous for its unconventional beliefs. The philosophy rejects social tradition, comforts, political arrangements, and materialism of the world. Instead, cynics prefer a simple life, usually outside social norms. While Socrates is the founder of the philosophy, Diogenes of Sinope is probably the most well-known cynic. He wanted to destroy all social conventions and return to a natural way of life.
A Note on Strangeness
While these philosophies are all a little strange, take time to think about what it means when something is strange. What are the qualities that make something strange? Are they objective qualities, such as temperature or color? Or are they subjective qualities such as beauty? Usually, when we use the term strange, it is a relative term. Calling something strange means, in comparison to other things, it is out of the ordinary or improbable. However, it's important to remember that calling something strange doesn't change its value. In terms of philosophical theories, even the strange ones are worth learning about. Oftentimes, they are even more interesting to learn than the ordinary theories.