Time Zones In Australia
Australia is, by far, the largest country in Oceania, covering about 7.7 million km2. It comprises the mainland Australian continent, Tasmania Island, and numerous other smaller islands. Although Oceania has 16 time zones (UTC+9 to UTC-6), only three are used in Australia. However, the individual states in the country regulate the time, some of which use Daylight Saving Time. Australia’s three time zones are Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST), Australian Central Standard Time (ACST), and Australian Western Standard Time (AWST). Besides, Australia also has offshore external territories which observe different time zones. All states except Queensland, Western Australia, and Northern Territory use Daylight Saving Time.
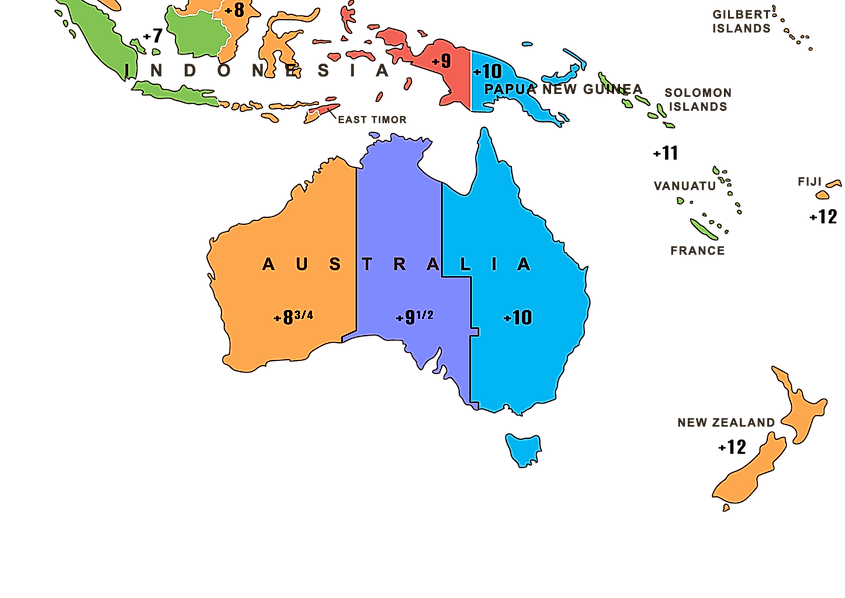
Australian Western Standard Time Zone
Australian Western Standard Time (AWST), also known as Western Standard Time is eight hours ahead of the UTC (UTC+8) and is often used during standard time. It is observed all year round in Western Australia, which includes cities such as Perth, Albany, Broome, Busselton, and Bunbury. AWST has the same offset time as Malaysia Time, Hong Kong Time, and Hotel Time Zone.
Australian Eastern Standard Time Zone
Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST) is known by other names, including Eastern Standard Time (EST). It adds ten hours to the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC+10, meaning that it is two hours ahead of Western Standard Time. This time zone is observed using AEST in winter and Australian Eastern Daylight Time (AEDT) in the summer. AEST is used in several states and territories, including the Australian Capital Territory, Victoria, Tasmania, and New South Wales (except Broken Hill that observes Australian Central Standard Time). Queensland observes AEST all year, meaning it does not use DST.
Australian Central Standard Time Zone
Australian Central Standard Time or Central Standard Time is a half-hour time zone, meaning that the local time differs by half an hour rather than the usual whole hour. ACST is offset at 9 hours and 30 minutes ahead of UTC (UTC+09:30). It is observed as ACST during standard time and as ACDST during DST. ACST is used in South Australia, Northern Territory, and New South Wales (only in Broken Hill).
Daylight Saving Time
The governments of individual Australian states and territories determine whether to use DST within their areas. After the world wars, Tasmania became the first to adopt DST in 1968, followed by Victoria, New South Wales, Queensland, Australian Capital Territory, and South Australia in 1971. However, Queensland dropped its use the following year. Northern Territory and Western Australia did not adopt daylight saving. However, Western Australia and Queensland have used DST severally in the last four decades but on a trial basis. Officially, DST is observed from 2 am on the first Sunday in October to 3 am on the first Sunday in April.