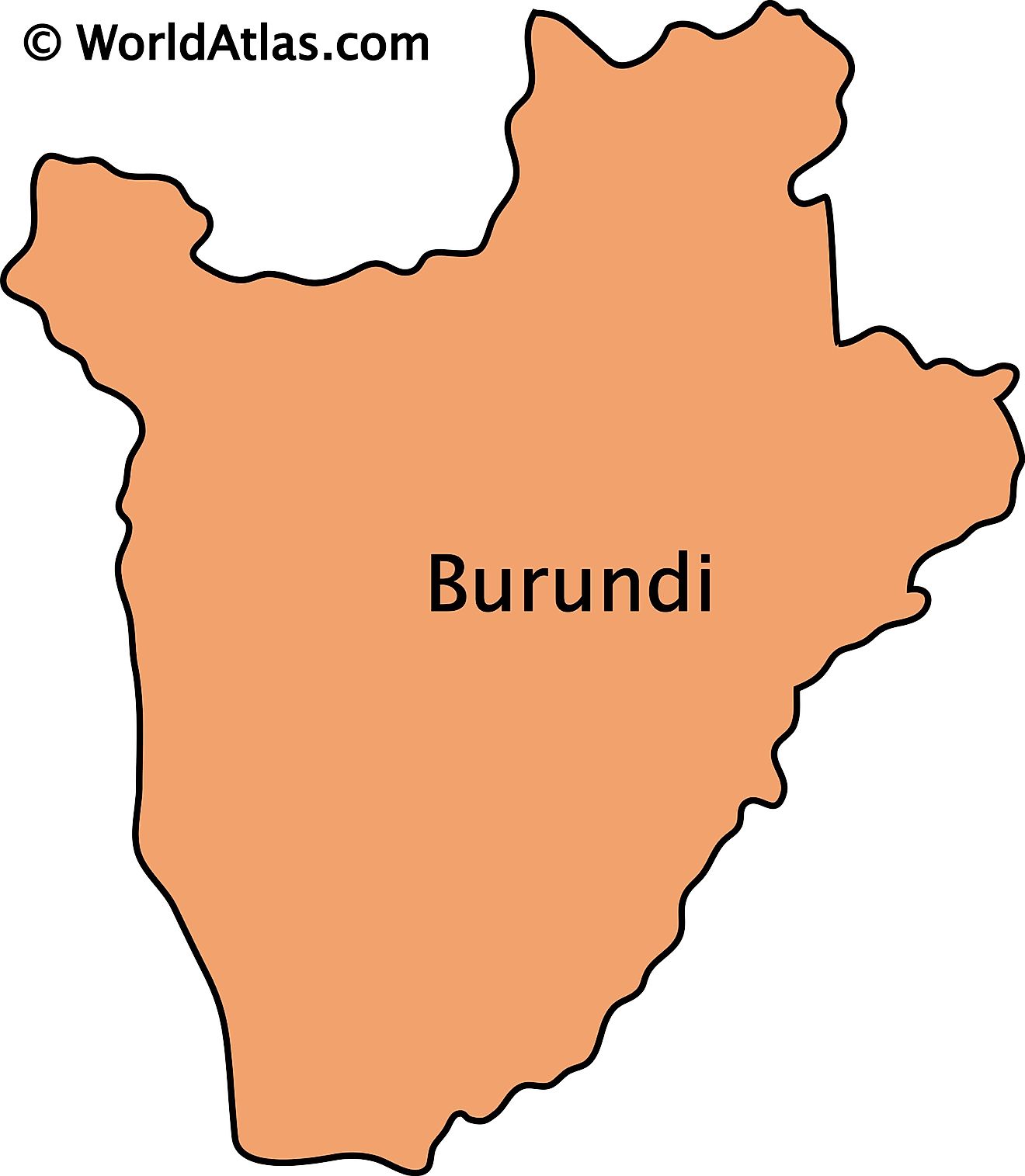
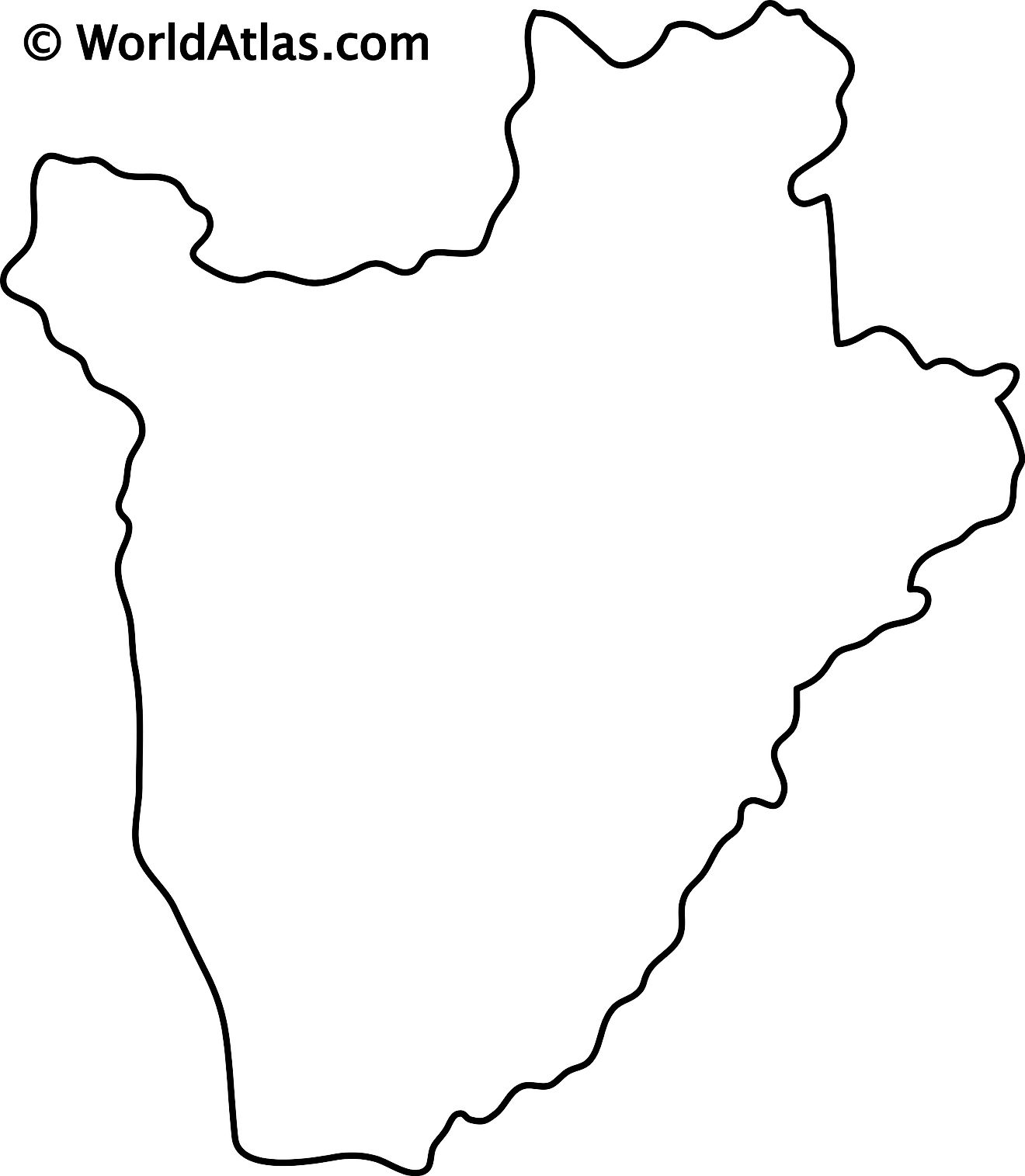
Maps of Burundi
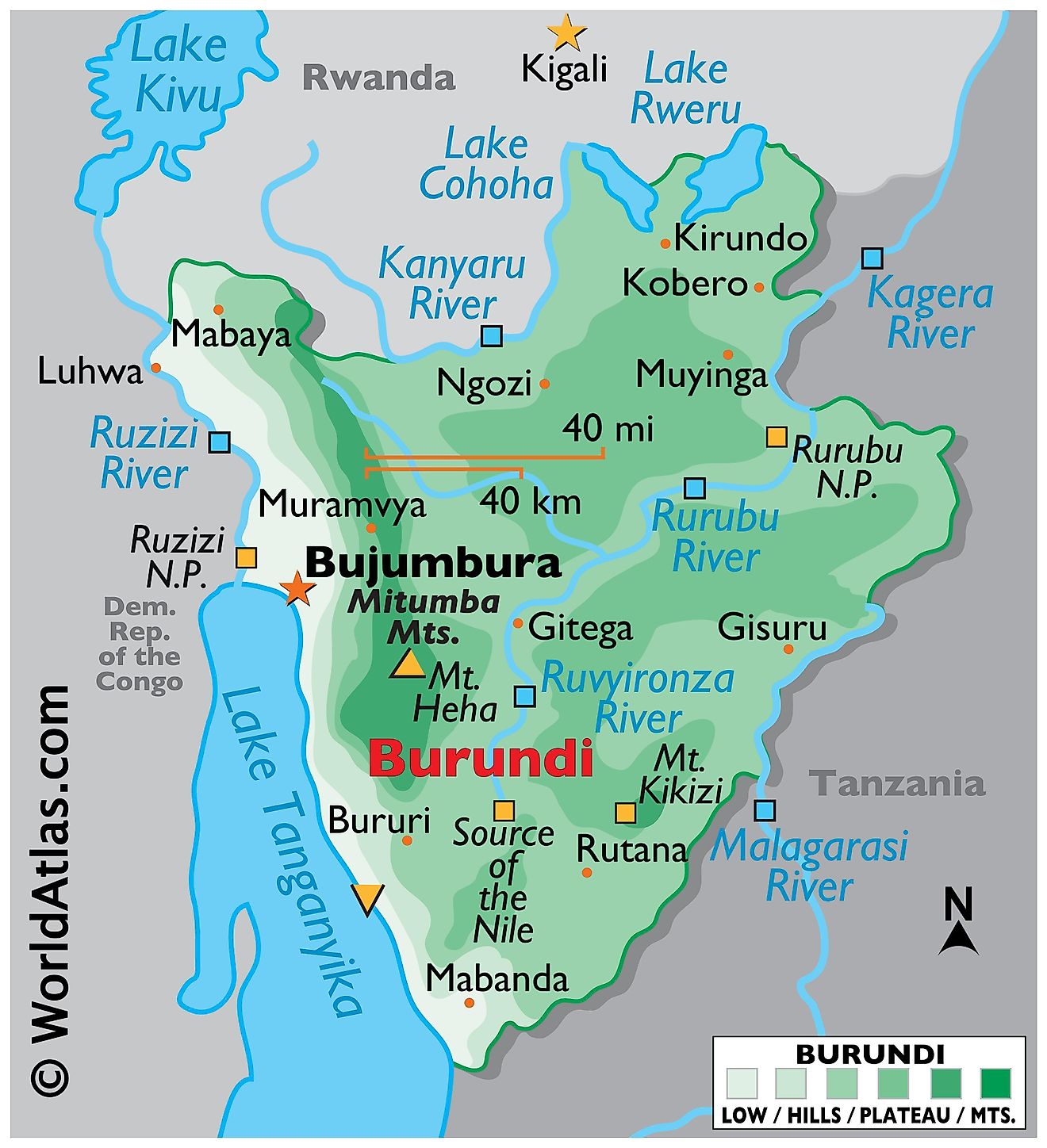
Burundi, a small but geographically diverse country, nestles in East Africa's Great Lakes region. With an area of approximately 10,745 square miles (27,830 square kilometers), it shares its borders with three countries: Rwanda to the north, Tanzania to the east and south, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west. Lake Tanganyika, Africa's deepest and the world's second deepest freshwater lake, marks the southwestern boundary of Burundi.
The geography of Burundi comprises four major regions: the Central Plateau, the Eastern Plateau, the Northern Plateau, and the Western Rift Valley. Each region exhibits distinctive geographical features and biodiversity.
The Central Plateau, covering the heart of the country, constitutes a rolling landscape with elevations averaging around 5,600 feet (1,700 meters). This region serves as a watershed, providing for several rivers, including the Ruvyironza, often considered the most distant source of the Nile.
Adjacent to the Central Plateau, the Eastern Plateau, characterized by its lower elevations, gradually descends towards the Tanzanian border. This region bears less fertile soils and experiences a warmer, drier climate compared to the rest of the country.
North of the Central Plateau, the Northern Plateau exhibits a more mountainous terrain. It features the Kibira National Park, a large tract of mountain rainforest that runs along the ridge of the Congo-Nile Divide. The park, home to diverse wildlife and plant species, including a significant number of primates, is a critical component of Burundi's natural heritage.
The Western Rift Valley, also known as the Albertine Rift, encompasses Lake Tanganyika and its steep, mountainous borders. It showcases breathtaking landscapes with its soaring mountains, some exceeding 8,000 feet (2,440 meters). The region is a part of the East African Rift System, and Lake Tanganyika itself is one of the major bodies of water in this system.
Several significant rivers flow through Burundi, including the Ruvubu, Kagera, and the Malagarasi. The Ruvubu River, the longest river in the country, flows eastward into Tanzania, merging with the Kagera River. Interestingly, the Kagera River, part of the upper headwaters of the Nile, solidifies Burundi's connection to the longest river in the world. The Malagarasi River, on the other hand, is notable for being the longest river flowing into Lake Tanganyika.
The geographical diversity of Burundi directly impacts its climate, which ranges from equatorial in the western Rift Valley to a cooler, more temperate climate in the central and northern plateaus. Despite being located near the Equator, Burundi's high average altitude results in a generally mild climate.
Provinces of Burundi Map
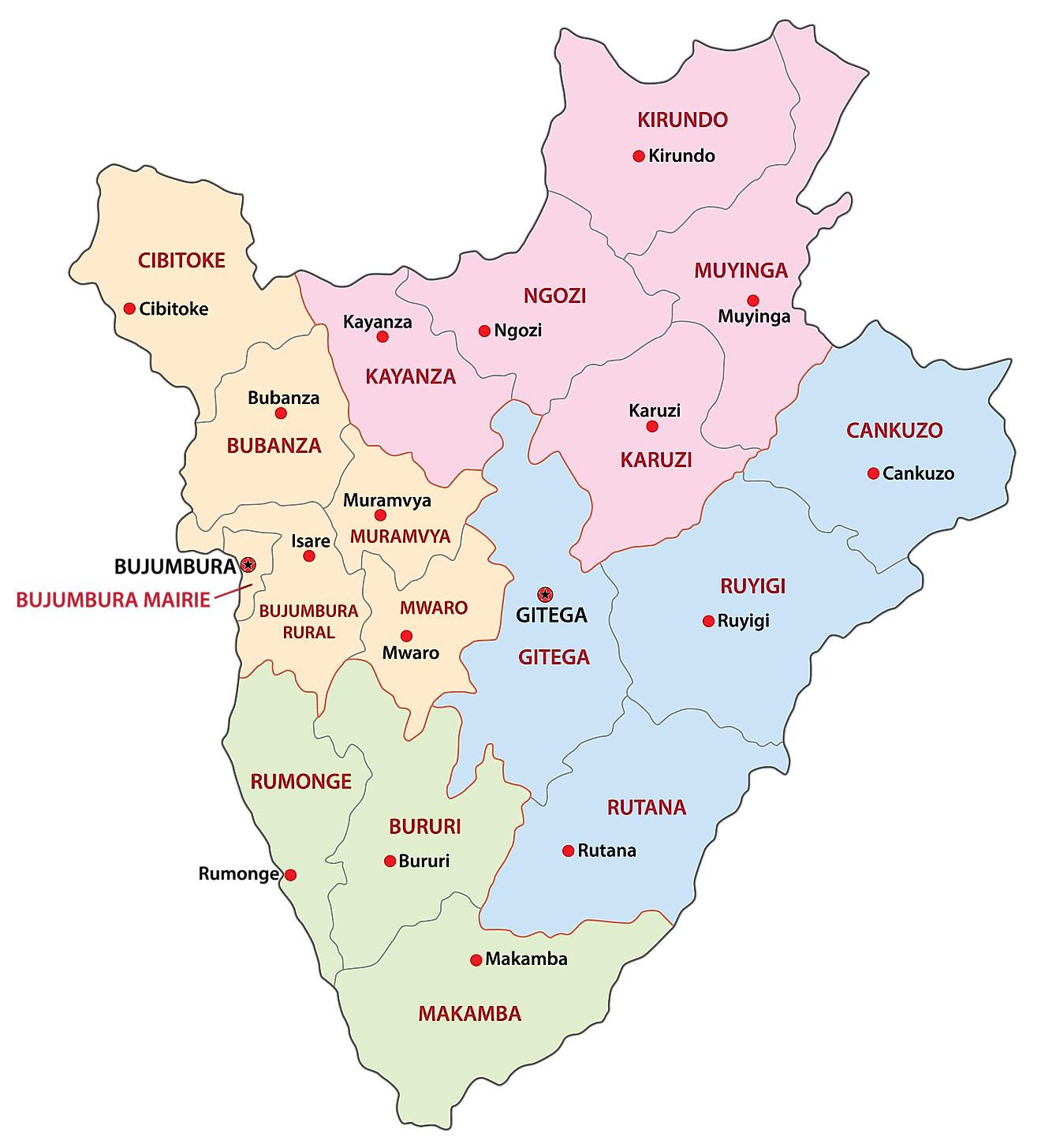
The political map of Burundi shows the 18 provinces and their capital cities. The most populated province is Bubanza with a population of 338,023 people. The largest city of Burundi, and its former capital, is Bujumbura, and its current capital, Gitega, is the second largest city, located in the middle of the country. The largest province by area is Ruyigi, with 2,339 km2.
The provinces of Burundi are: Bubanza, Bujumbura Mairie, Bujumbura Rural, Bururi, Cankuzo, Cibitoke, Gitega, Karuzi, Kayanza, Kirundo, Makamba, Muramvya, Muyinga, Mwaro, Ngozi, Rumonge, Rutana, Ruyigi.
Provinces are divided into 117 communies which are further subdivided into 2,638 collines.
Where is Burundi?
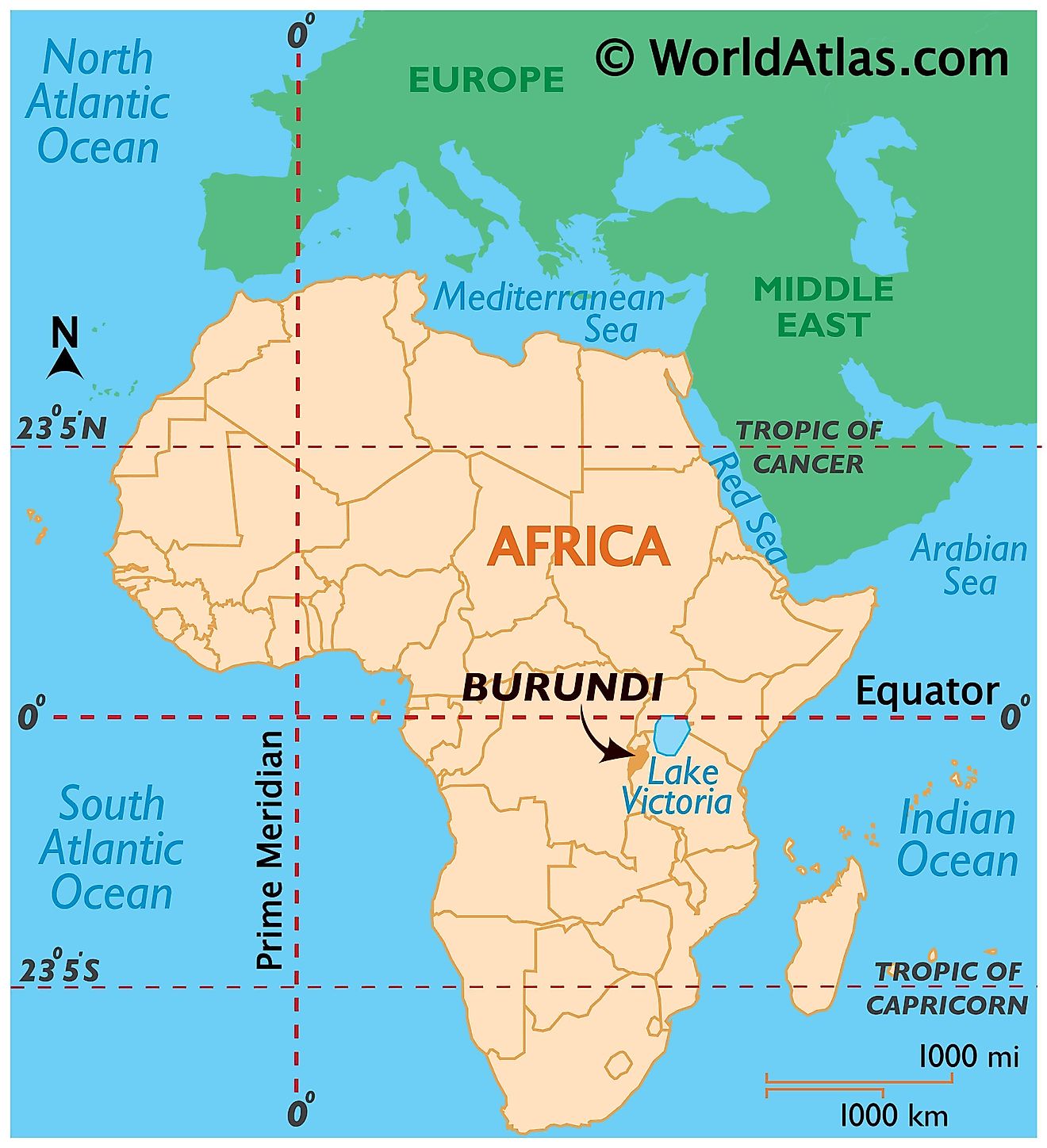
The landlocked country of Burundi is located in the Great Rift Valley in the area of convergence between East Africa and the African Great Lakes region. It lies in the Southern and Eastern Hemispheres of the Earth. Three countries border Burundi. These are Rwanda to the north, the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west, and Tanzania to the southeast and east. The southwestern borders of Burundi feature the world's second deepest lake, Lake Tanganyika.
Burundi Bordering Countries: Rwanda, Tanzania, The Democratic Republic Of The Congo.
Regional Maps: Map of Africa
Outline Map of Burundi
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Republic of Burundi |
|---|---|
| Flag |

|
| Capital City | Gitega (political capital), Bujumbura (commercial capital); note - in January 2019, the Burundian parliament voted to make Gitega the political capital of the country while Bujumbura would remain its economic capital; all branches of the government are ex |
| 3 25 S, 29 55 E | |
| Total Area | 27,830.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 25,680.00 km2 |
| Water Area | 2,150.00 km2 |
| Population | 11,530,580 |
| Largest City |
Bujumbura (1,206,767) |
| Currency | Burundi francs (BIF) |
| GDP | $3.01 Billion |
| GDP Per Capita | $261.25 |
This page was last updated on June 14, 2023