Maps of Eritrea
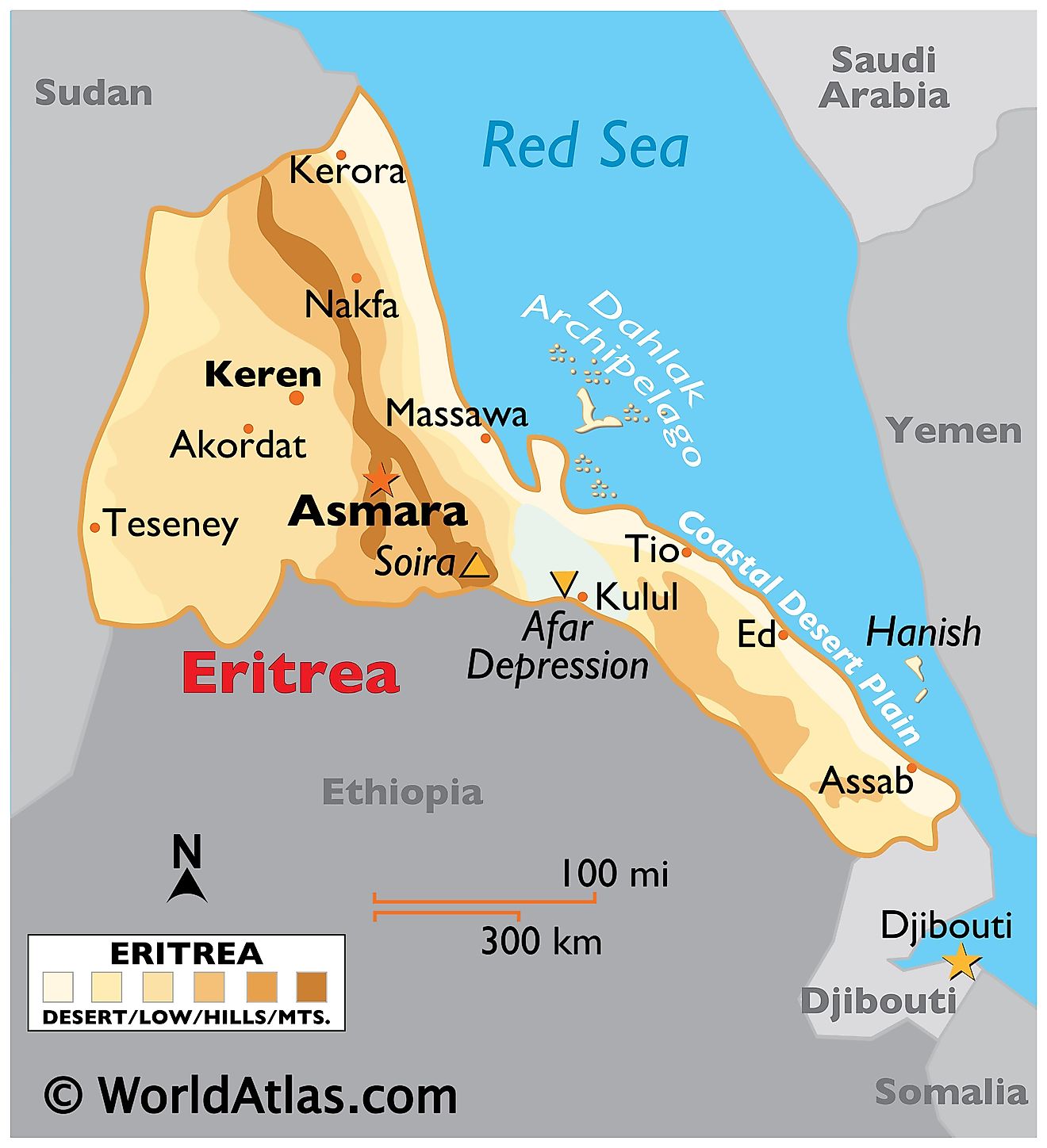
Eritrea, a country in the Horn of Africa, spans an area of about 121,100 km2 (46,757 mi2). It shares its borders with Sudan to the west, Ethiopia to the south, and Djibouti to the southeast. Its eastern and northeastern coastline lies along the Red Sea.
The country is divisible into roughly four distinct geographical regions, which are primarily highlands and lowlands.The Central Highlands, or Kebessa, form the backbone of Eritrea. This region, characterized by a cooler, more temperate climate, contrasts sharply with the surrounding areas. The highlands gradually rise to their apex at Emba Soira, Eritrea's highest point, reaching an elevation of 3,018 meters (9,902 feet).
The Eastern Lowlands, also known as the Danakil Depression, lie east of the Central Highlands. This region extends into the arid and hot coastal desert along the Red Sea. The Danakil Depression descends to Eritrea's lowest point at Lake Kulul, which is about 75 meters (246 feet) below sea level. This area is one of the hottest and most inhospitable places on Earth, marked by salt flats and volcanic formations.
The Western Lowlands consist of fertile plains and rolling hills in the northwest, gradually sloping towards the Sudanese border. This region benefits from the seasonal rivers that originate in the highlands, making it more suitable for agriculture than the Eastern Lowlands.
Gash-Barka, in the southwest, blends aspects of the highlands and western lowlands. It features undulating plains and occasional hills, with a climate that supports a variety of agricultural activities.
Major bodies of water include the Red Sea coast, known for its extensive coral reefs and islands. The country's coastline extends for about 1,155 kilometers (717 miles). Notable rivers in Eritrea include the Tekezé, Mereb, and Barka, all of which play a crucial role in the country's agriculture and ecosystems. These rivers are predominantly seasonal, with flows varying dramatically between the dry and wet seasons.
Regions of Eritrea Map
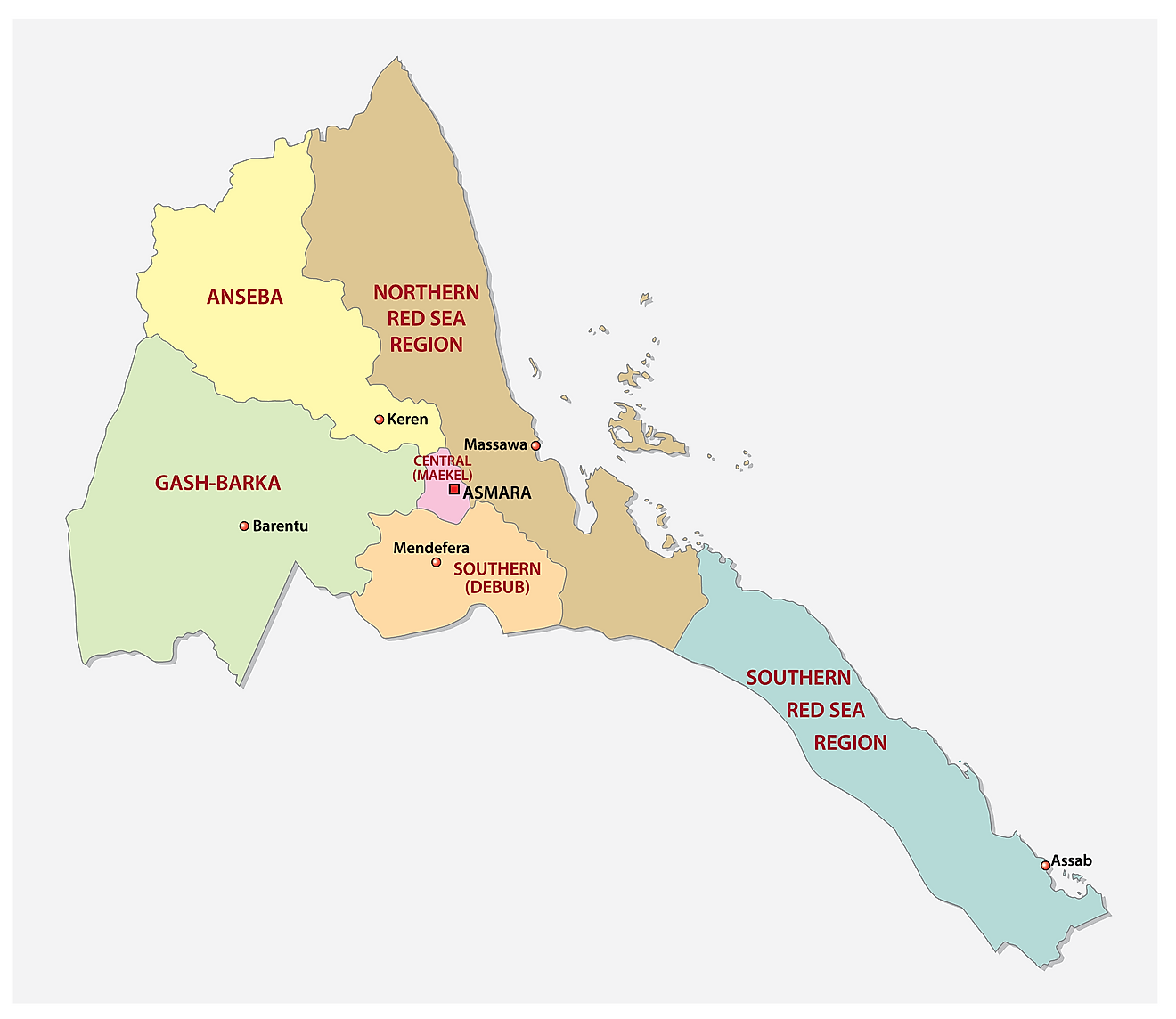
Eritrea is divided into six administrative divisions called regions. These are: Anseba, Debub (South), Debubawi K'eyih Bahri (Southern Red Sea), Gash Barka, Ma'akel (Central), and Semenawi K'eyih Bahri (Northern Red Sea). They are further subdivided into sub-regions.
Debub is the most populous of these regions of Eritrea. The national capital of Asmara is located in the Ma'akel (Central) Region.
Where is Eritrea?
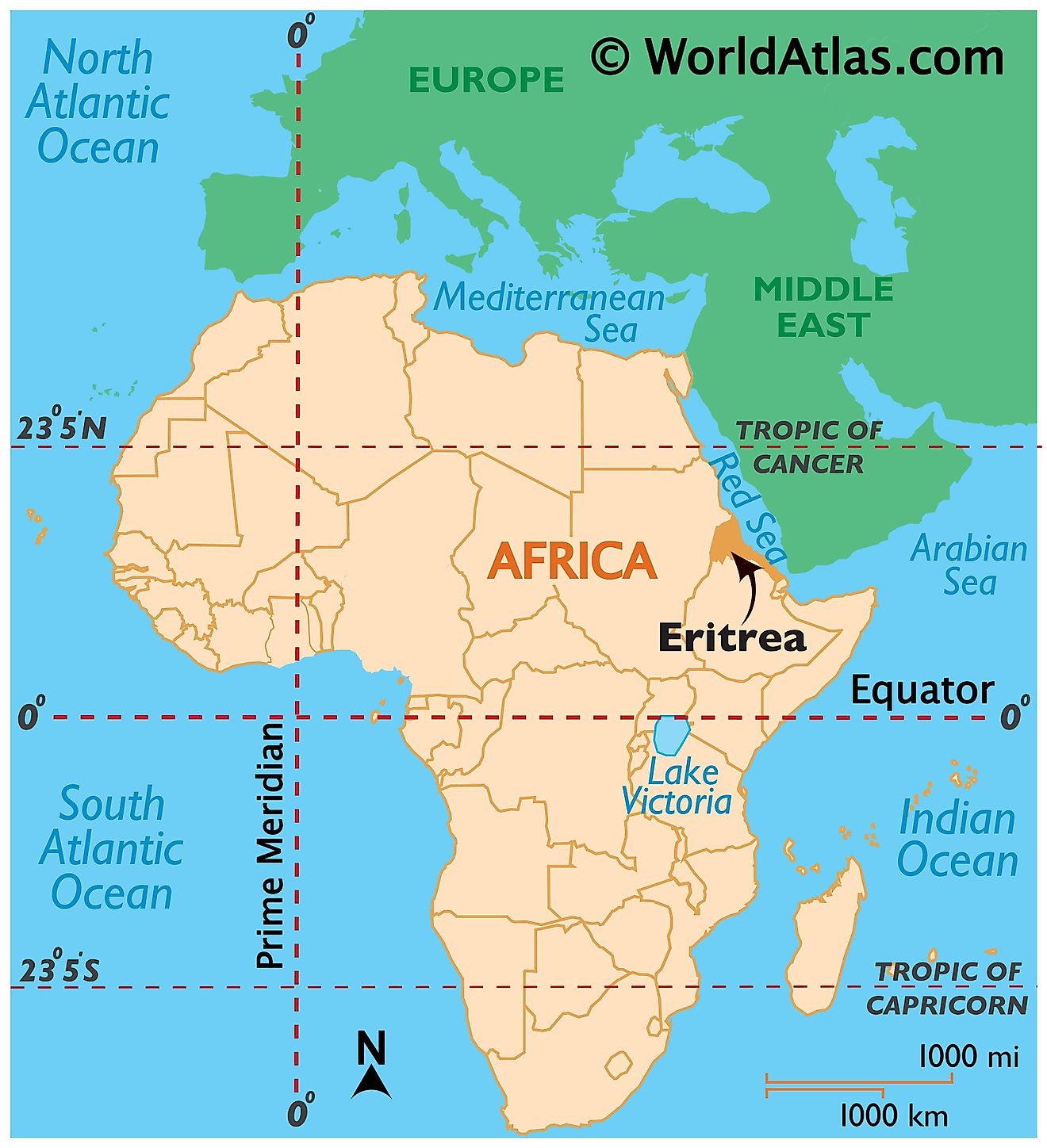
Eritrea is an Eastern African country located in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres of the Earth. Three countries border Eritrea. These are Ethiopia, Sudan, and Djibouti to the south, west, and southeast respectively. Eritrea has an extensive coastline on the Red Sea to the north and east.
Eritrea Bordering Countries: Ethiopia, The Sudan, Djibouti.
Regional Maps: Map of Africa
Outline Map of Eritrea
Key Facts
| Legal Name | State of Eritrea |
|---|---|
| Flag |

|
| Capital City | Asmara (Asmera) |
| 15 20 N, 38 56 E | |
| Total Area | 117,600.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 101,000.00 km2 |
| Water Area | 16,600.00 km2 |
| Population | 3,213,972 |
| Largest City |
Asmara (1,072,666) |
| Currency | Nakfa (ERN) |
| GDP | $2.07 Billion |
| GDP Per Capita | $642.51 |
This page was last updated on November 13, 2023