Maps of Zambia
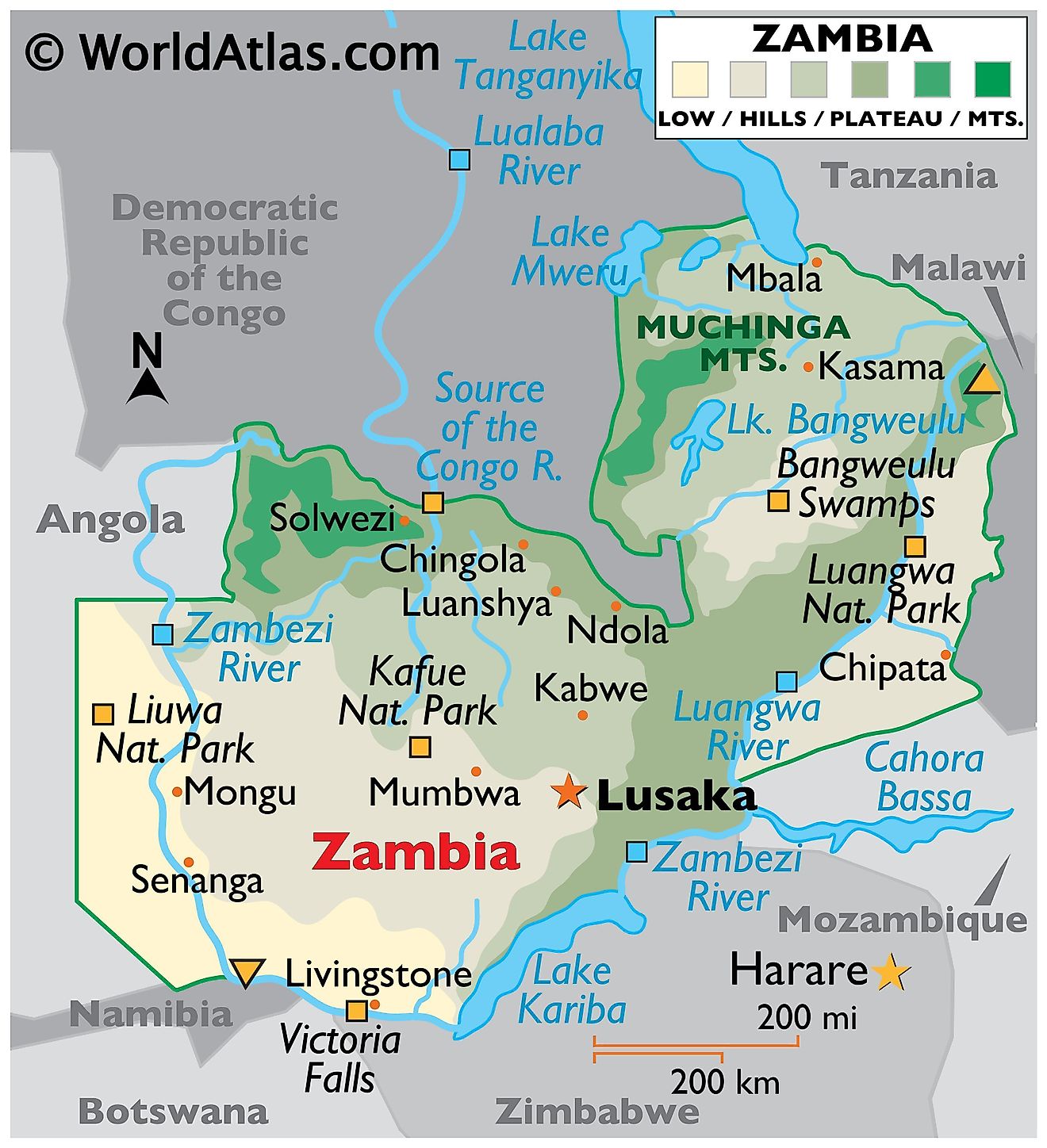
Zambia, a landlocked country in the southern region of Africa, covers a total area of approximately 752,618 km2 (290,587 mi2). It shares its borders with eight countries, namely Tanzania to the northeast, Malawi to the east, Mozambique to the southeast, Zimbabwe to the south, Botswana and Namibia to the southwest, Angola to the west, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north.
Zambia possesses four distinct geographical regions: the central plateau, the major valleys, the eastern highlands, and the western sandy plains.
The Central Plateau, an area of roughly 1,000 to 1,600 meters above sea level, extends over a large portion of Zambia. This region mainly features undulating flat lands interspersed with gently sloping hills. This region plays a crucial role in the country's agriculture, supporting vast swathes of crops including maize, tobacco, and various types of vegetables due to the relatively fertile soil and moderate climate.
The Valleys: Adjacent to the central plateau, Zambia features two major valleys: the Zambezi Valley in the south and the Luangwa Valley to the east. The Zambezi Valley, formed by the mighty Zambezi River, constitutes a significant portion of Zambia's southern border. Its lower altitudes and higher temperatures allow it to sustain a variety of wildlife and flora. The Luangwa Valley, carved by the Luangwa River, also boasts an abundant wildlife population, and it is considered one of the greatest wildlife sanctuaries in the world.
The Muchinga Escarpment: To the northeast rise eastern highlands rise, which mark a stark contrast to the central plateau and the valleys. Also known as the Muchinga escarpment, these highlands offer a more rugged terrain with altitudes reaching up to 1,800 meters. The region sees more rainfall than the rest of the country, resulting in the growth of lush forests and several endemic species of flora and fauna. The cooler climate also supports the cultivation of coffee, a significant export product of Zambia. Last, Zambia's highest point is an unnamed elevation within the Mafinga Mountains at 2,339 meters (7,674 feet); the lowest point of the country is the Zambezi River at 329 meters (1,079 feet) above sea level.
The Western Sandy Plains lie in the western parts of Zambia, adjacent to the border with Angola. This region incoporates parts of the Kalahari Basin and displays vast expanses of sandy soil unsuitable for most forms of agriculture. However, Western Zambia is largely covered by the Barotse Floodplain and the Miombo Woodlands which support a range of vegetation including grasslands, woodlands, and scrublands.
Lakes: Lake Tanganyika, the world's second deepest freshwater lake, marks Zambia's northern border with Tanzania. Lake Bangweulu, one of the country's most significant internal bodies of water, is located in the northern part of the central plateau. These lakes, along with several others such as Lake Mweru and Lake Kariba, contribute to the country's fishing industry and play essential roles in transportation and tourism.
Rivers: The most significant river in Zambia is the Zambezi River, which originates in Zambia and flows through several countries before emptying into the Indian Ocean. Other major rivers include the Kafue and the Luangwa, both crucial for their contribution to Zambia's hydropower generation, irrigation, and as water sources for the local wildlife.
Provinces of Zambia Map
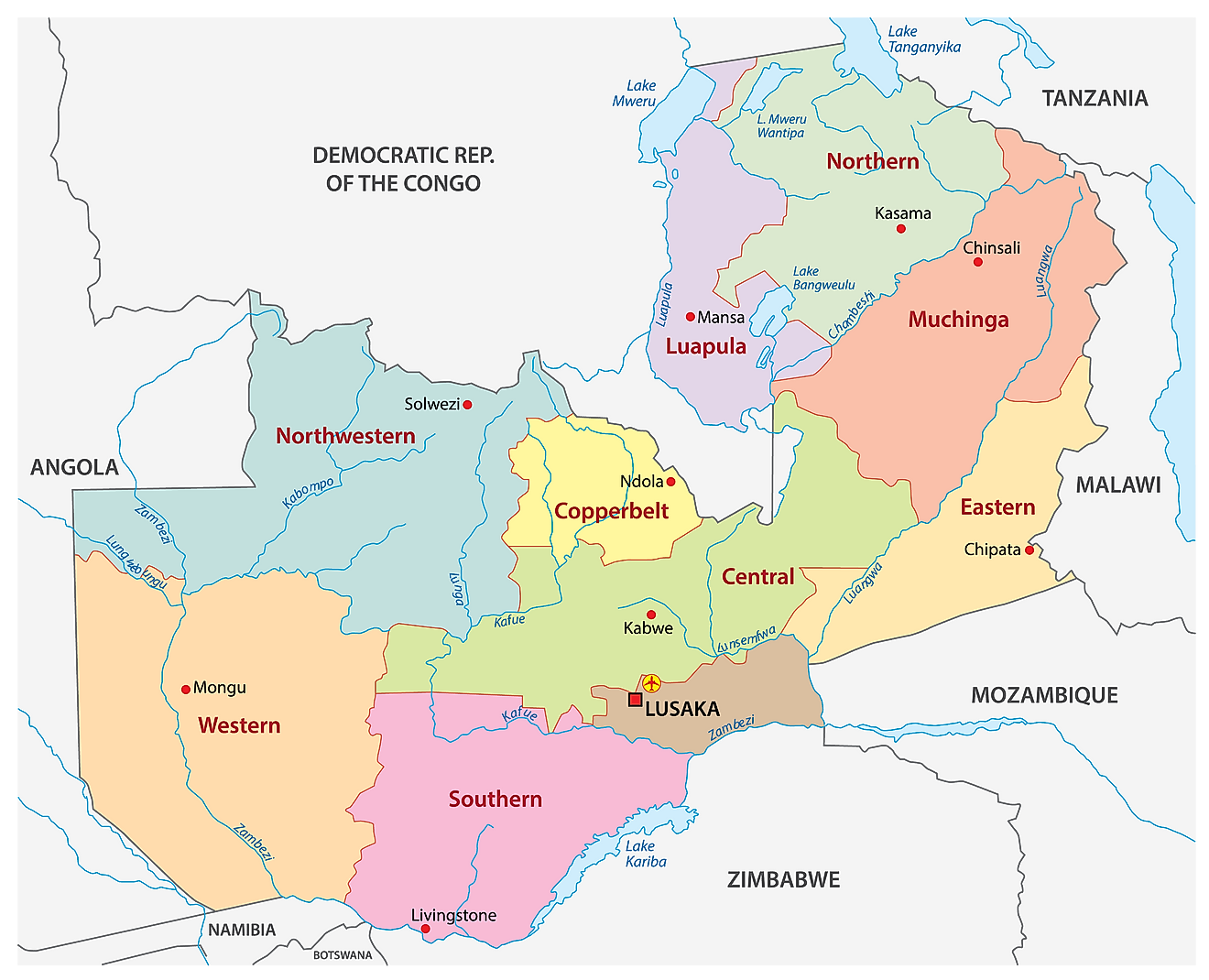
Zambia is divided into 10 provinces. These are Central, Copperbelt, Eastern, Luapula, Lusaka, Muchinga, Northern, North-Western, Southern, and Western. These provinces are further subdivided into districts. With an area of 126,386 sq. km Western Province is the largest by area. Lusaka, which is the smallest province with an area of 21,896 sq. km, hosts the national capital city of Lusaka. It is also the most populous and the most densely populated province in the country.
Where is Zambia?
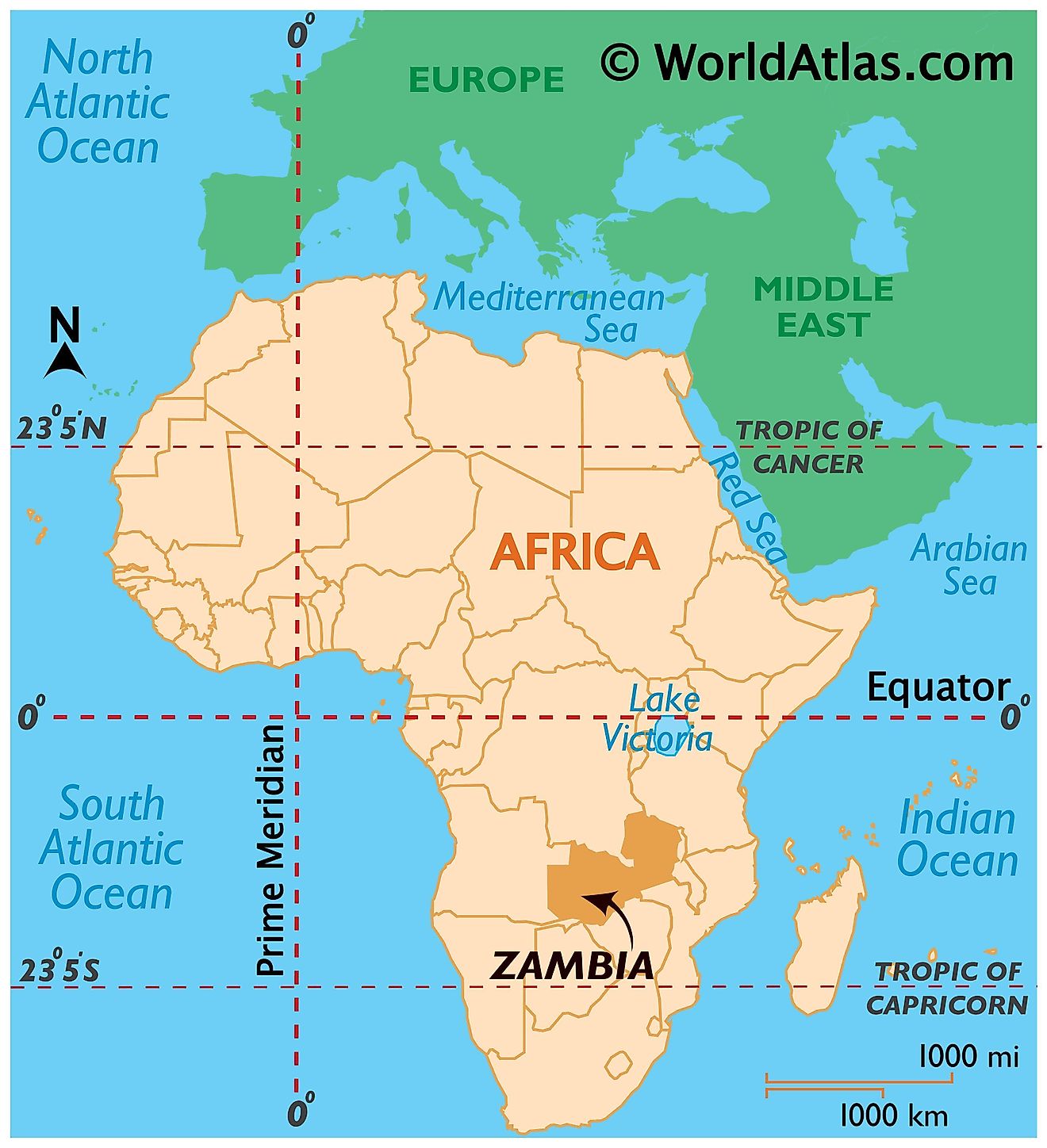
Zambia is a Southern-Central African landlocked country. It is located nearly midway between the Equator and the Tropic of Capricorn in the Southern Hemisphere. Longitudinally, it is located in the Eastern Hemisphere of the world. Zambia is bordered by seven countries. It is bounded to the north by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and to the south by Zimbabwe and Botswana. Tanzania borders the country to the north-east, Malawi to the west and Mozambique to the southeast. Angola borders Zambia to the west and Namibia to the southwest.
Zambia Bordering Countries: Namibia, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Angola, Botswana, Tanzania, The Democratic Republic Of The Congo, Malawi.
Regional Maps: Map of Africa
Outline Map of Zambia
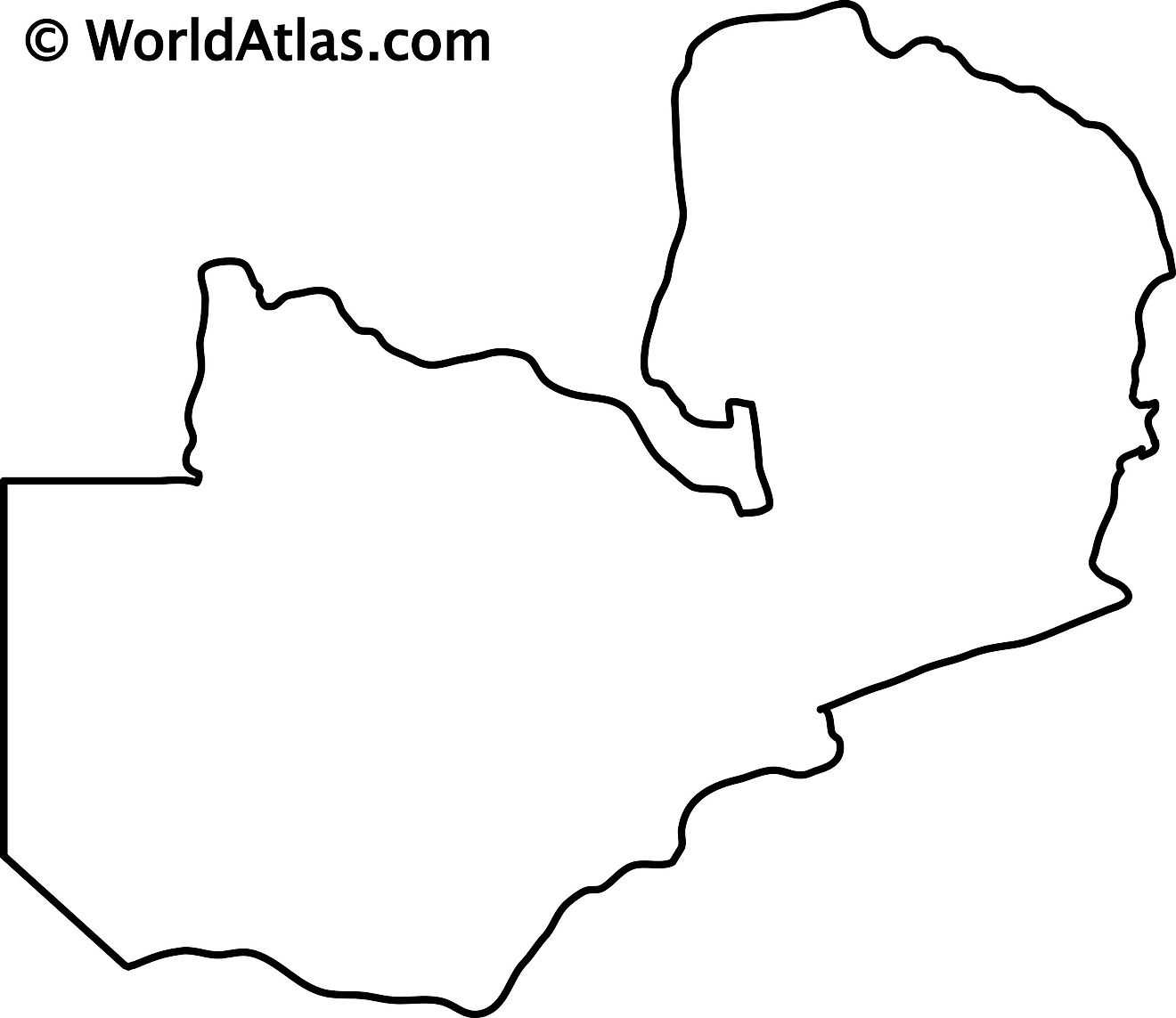
The blank outline map of Zambia can be downloaded for free and printed to be used for academic purpose or coloring.
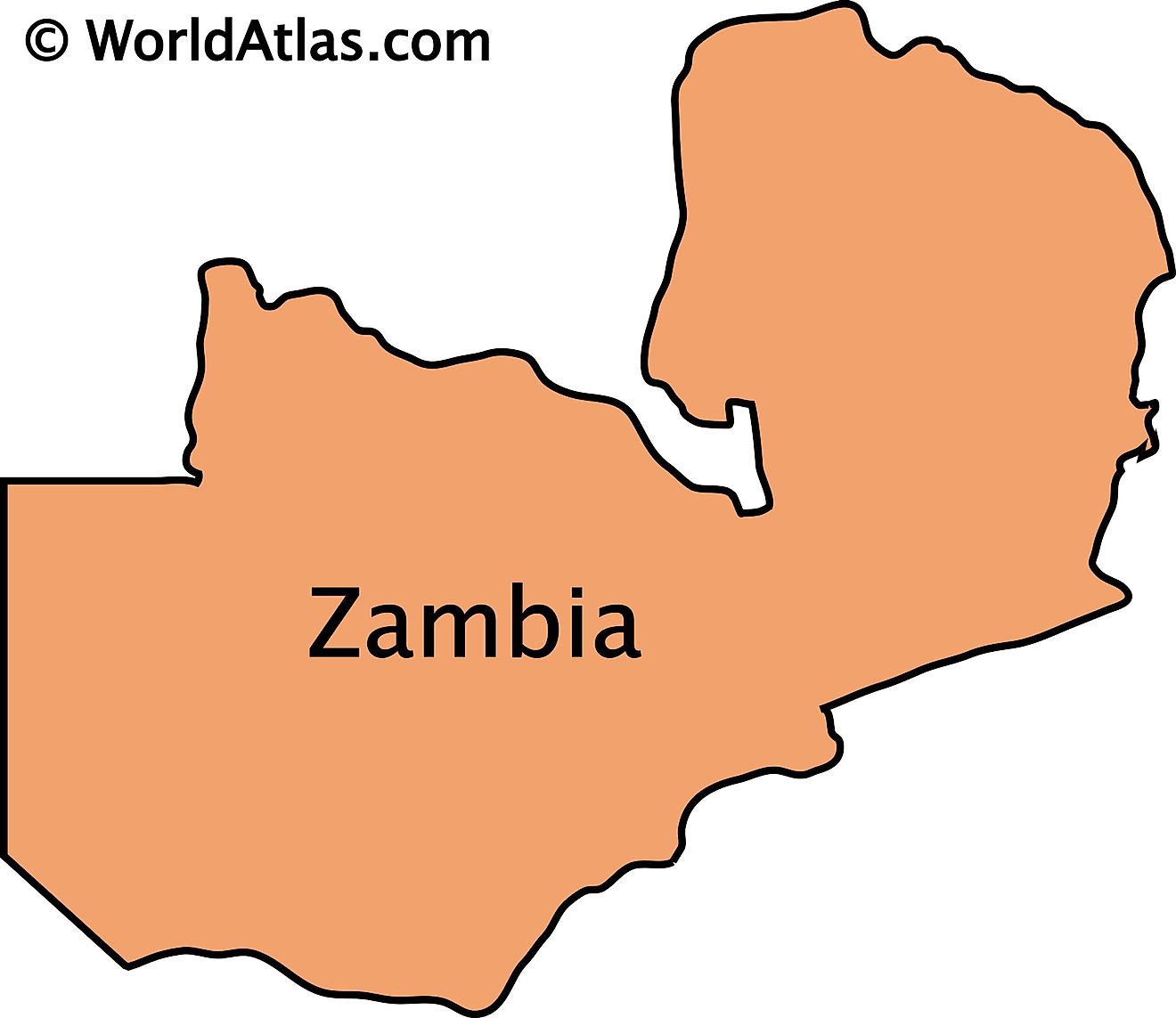
The outline map of Zambia exhibits the unique butterfly shape of the country. This shape is caused by the Congo Pedicle (pedicle or little foot) which is the DRC's southeast salient that divides Zambia into two lobes like the two wings of a butterfly.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Republic of Zambia |
|---|---|
| Flag |

|
| Capital City | Lusaka; note - a proposal to build a new capital city in Ngabwe was announced in May 2017 |
| 15 25 S, 28 17 E | |
| Total Area | 752,618.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 743,398.00 km2 |
| Water Area | 9,220.00 km2 |
| Population | 17,861,030 |
| Major Cities |
|
| Currency | Zambian kwacha (ZMK) |
| GDP | $23.06 Billion |
| GDP Per Capita | $1,291.34 |
This page was last updated on August 3, 2023











