Maps of Antigua and Barbuda
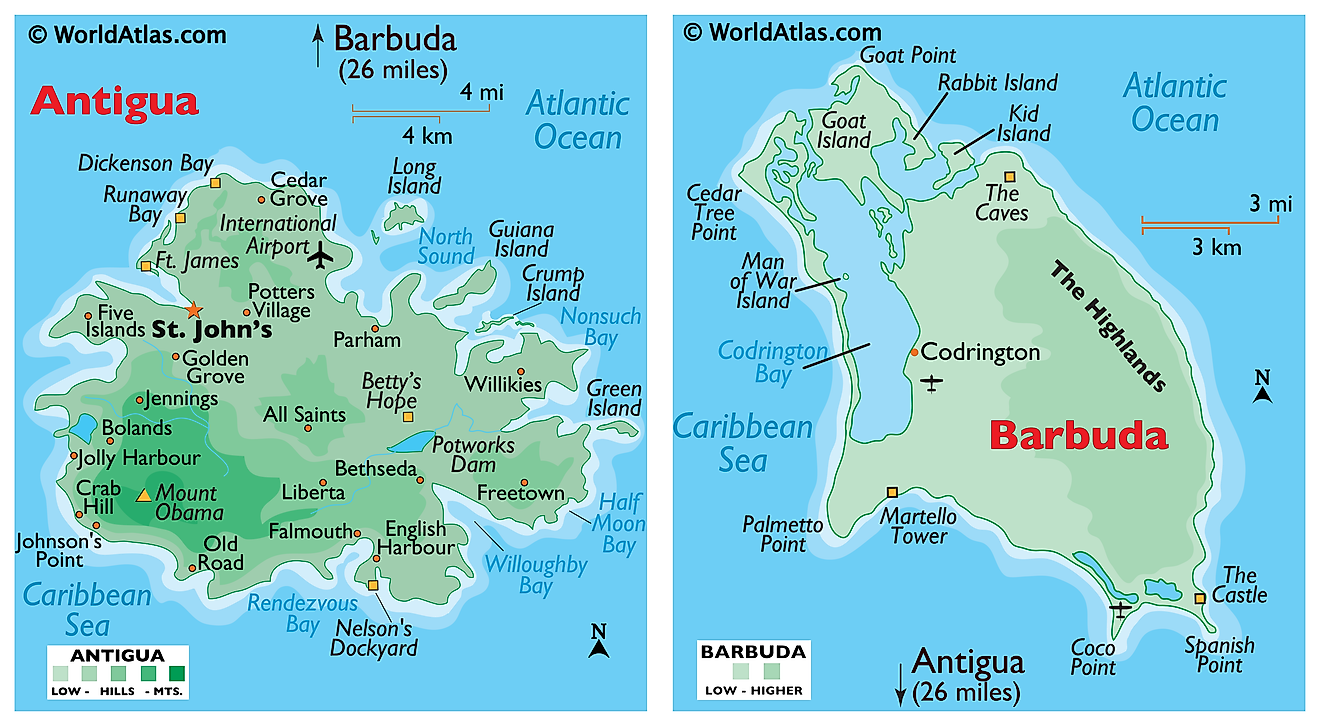
Covering an area of only 440 sq. km, the dual-island nation of Antigua and Barbuda is positioned in the Caribbean's Lesser Antilles and acts as a natural border that helps separate the Atlantic Ocean from the Caribbean Sea. Since Antigua and Barbuda are both islands, they share no borders with other nations. That being said, the closest nation is St Kitts and Nevis. Antigua and Barbuda is also nearby to the British overseas territory of Montserrat, and the French overseas territory of Guadeloupe.
Mountains and hills are hard to come by on both islands. The highest point, as marked on the map, by an upright yellow triangle, is Mount Obama (formerly Boggy Peak), which is located in the hilly region of southwestern Antigua; and is a remnant of a volcanic crater that rises to 405m.
Codrington Bay, an enormous naturally occurring harbor is the largest and most notable geographical feature of Barbuda. The bay allows ships and other watercraft to penetrate deep into the island. As observed on the map, both islands are relatively low-lying limestone formations; and are ringed by reefs and sandbars, and indented by beaches, small lagoons, and natural harbors. There are no rivers of note and only a few streams are present, as rainfall amounts are quite light. The lowest point is the Caribbean Sea (0m)
Beaches are of course one of the stand-out features on both islands. White sand and clear blue water make these two islands a popular destination for tourists traveling from Europe and North America looking to escape harsh winters. Antigua and Barbuda tend to have warm weather all year round with little rainfall aside from the odd tropical storm.
Parishes Map of Antigua and Barbuda
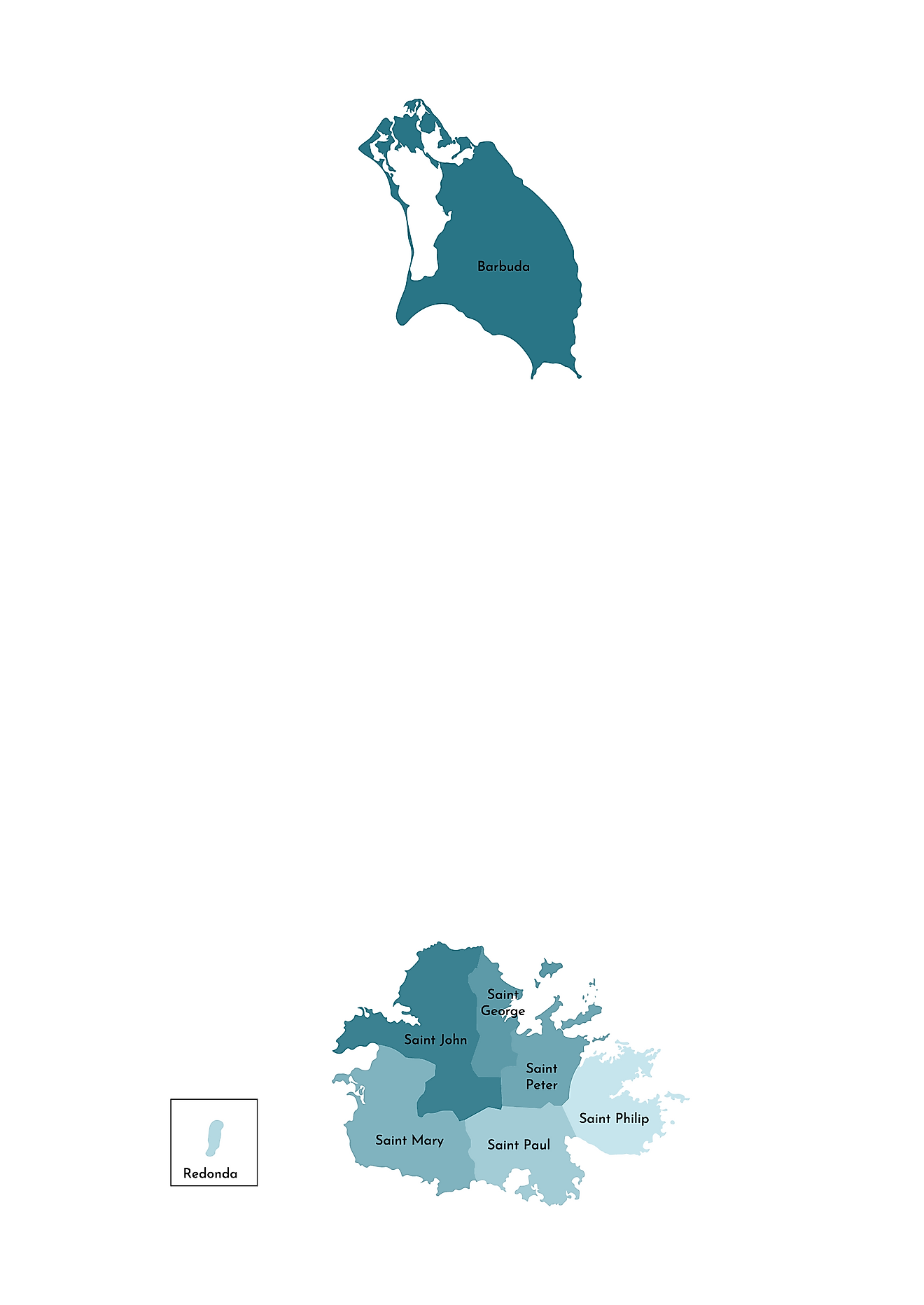
Antigua and Barbuda are divided into 6 parishes and two dependencies. The 6 parishes are Saint George, Saint John, Saint Mary, Saint Paul, Saint Peter, and Saint Philip. The two dependencies are Barbuda and Redonda.
Covering an area of only 440 sq. km, the dual-island nation of Antigua and Barbuda consists of the two principal islands of Antigua and Barbuda which are inhabited; along with several smaller islands and the Redonda island which is still uninhabited. Located on the north-western coast of Antigua Island is St. John’s – the capital and the largest city of Antigua and Barbuda. It is also the chief commercial center of the island nation and the main port of Antigua. Located on Barbuda island is Codrington - which is the largest town of Barbuda.
Where is Antigua and Barbuda?
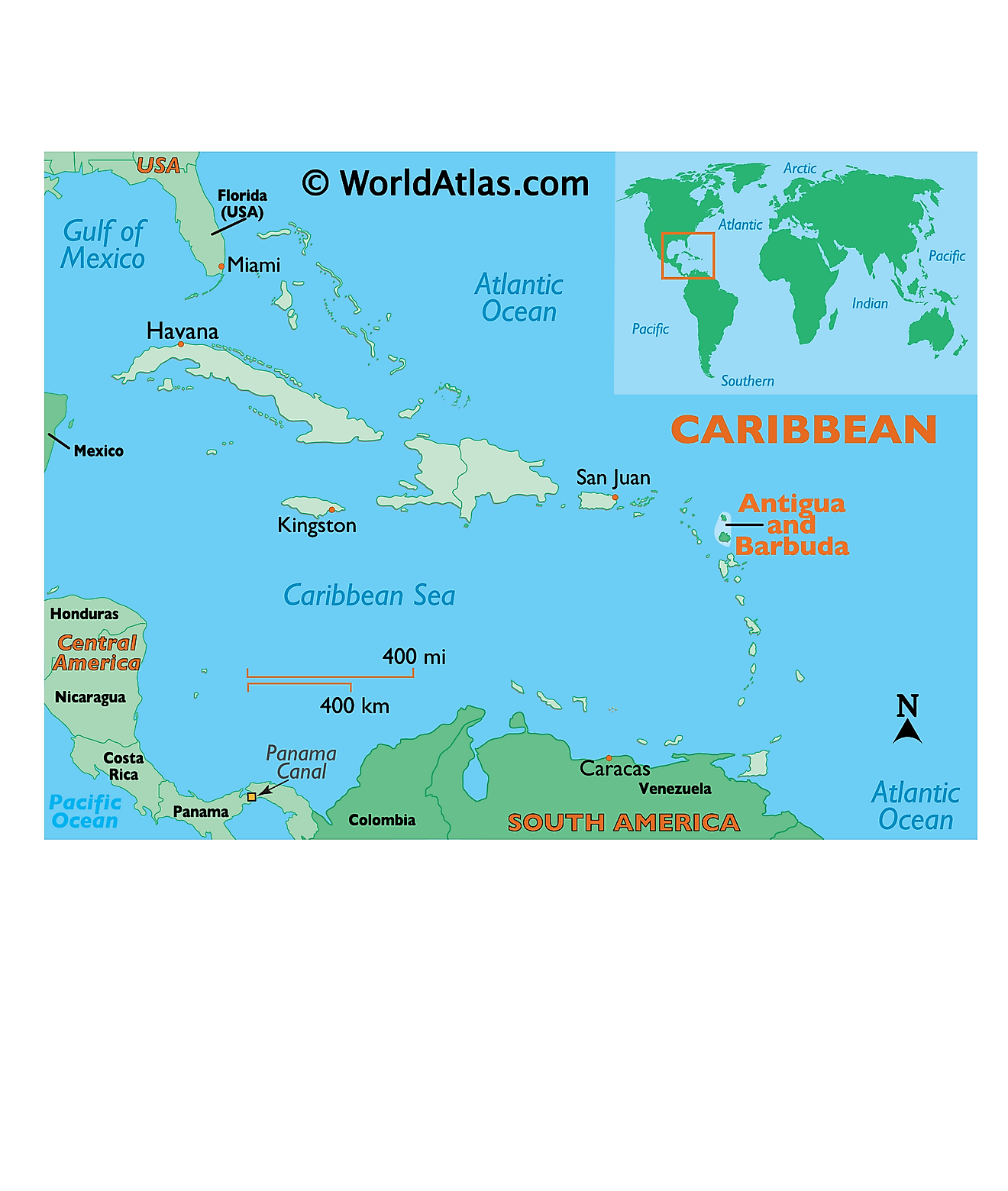
The dual-island nation of Antigua and Barbuda is located in the eastern Caribbean; between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean. The islands are geographically positioned in the Northern and Western hemispheres of the Earth. Antigua and Barbuda Islands are a part of the Lesser Antilles in the southern end of the Leeward Islands chain that are situated to the east-southeast of Puerto Rico and to the north of Guadeloupe. They share maritime borders with Anguilla, Montserrat, Saint Kitts, and Nevis, and Saint Barthélemy.
Regional Maps: Map of North America
Outline Map of Antigua and Barbuda
The above blank map represents Antigua and Barbuda - the dual island nation located in eastern Caribbean which helps to separate the Atlantic Ocean from the Caribbean Sea. The above map can be downloaded, printed and used for geography education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.
The above outline map represents Antigua and Barbuda - the dual island nation located in eastern Caribbean which helps to separate the Atlantic Ocean from the Caribbean Sea.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Antigua and Barbuda |
|---|---|
| Flag |

|
| Capital City | Saint John's |
| 17 07 N, 61 51 W | |
| Total Area | 442.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 442.00 km2 |
| Water Area | N/A |
| Population | 97,118 |
| Currency | East Caribbean dollars (XCD) |
| GDP | $1.73 Billion |
| GDP Per Capita | $17,790.31 |
This page was last updated on December 16, 2023