Maps of Aruba
Aruba, a tiny island nation (that is technically a constituent country within the Netherlands) located in the southern Caribbean Sea, lies just about 18 miles (29 kilometers) north of the coast of Venezuela. This proximity situates Aruba as part of the geographic region known as the Lesser Antilles. Covering a total area of roughly 69.1 square miles (179 square kilometers), the island has no land borders with any other country. To the north and east, Aruba meets the vast expanses of the Caribbean Sea, while the South and West of the island are washed by the waters of the Gulf of Venezuela.
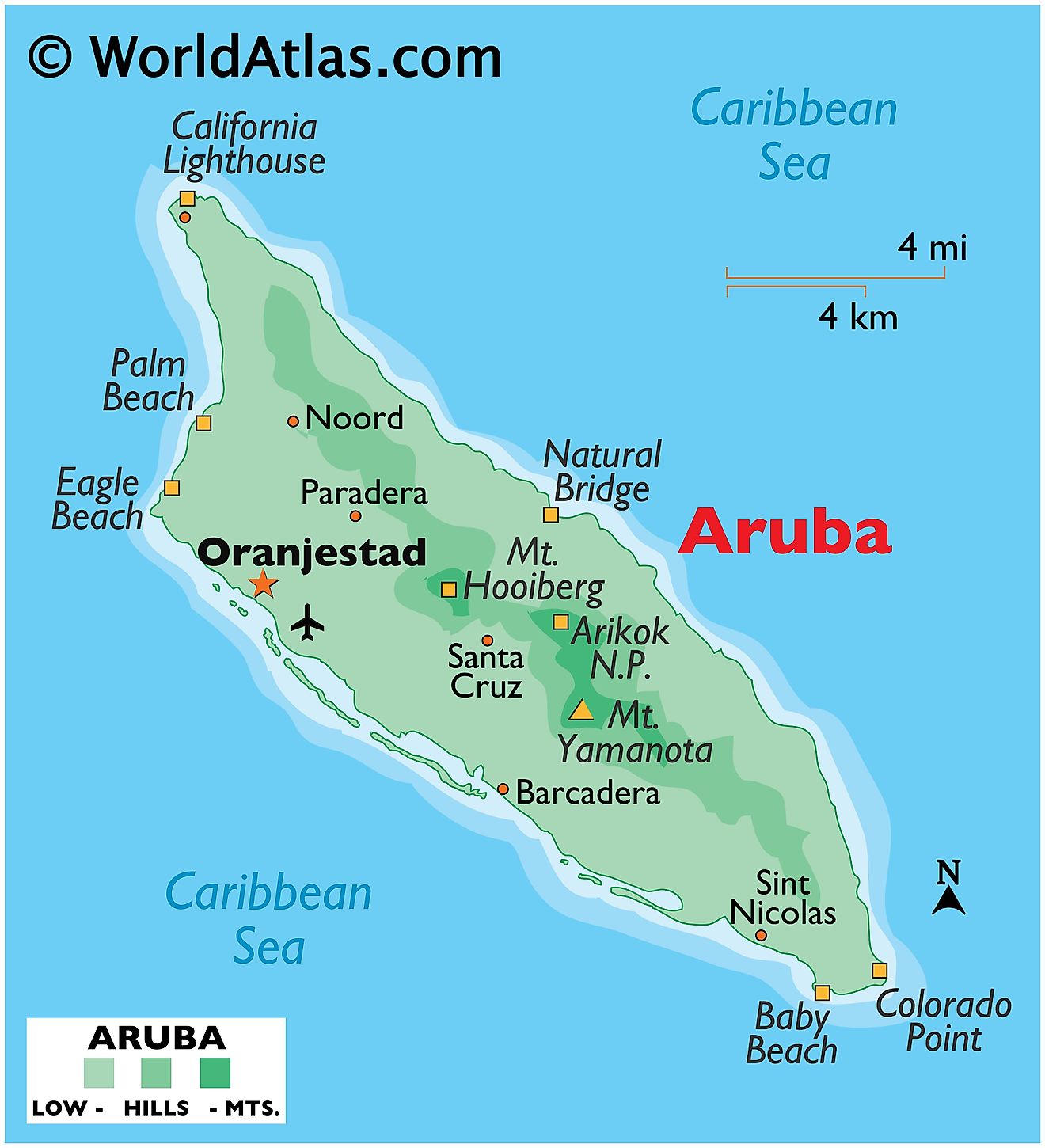
In terms of physical geography, Aruba exhibits a relatively flat landscape characterized by minor variations in elevation. Despite its small size, the island boasts a variety of natural features, from arid deserts to scenic coastlines. Aruba's topography is divided primarily into two geographical regions: the Aruban hills on the northern part of the island, and the coastal plains to the south.
The Aruban hills are home to Aruba's highest point, Mount Jamanota, which stands at 617 feet (188 meters) above sea level. This region showcases Aruba's volcanic origin through its rocky terrain and shallow soils. Here, vegetation is sparse due to the low rainfall and harsh winds that typically whip the northern coast.
South of these hills, Aruba transitions into a wide coastal plain. This region, characterized by its white sandy beaches and turquoise waters, hosts the majority of the island's population and tourist developments. This area provides Aruba's iconic vistas, with its bountiful marine life and coral reefs contributing to the country's reputation as a leading destination for snorkeling and scuba diving.
Aruba's most significant body of water is its surrounding sea, shaping the island's weather, ecology, and economy. Notably, the Spanish Lagoon, located on the southwestern coast of the island, offers a vibrant marine habitat, rich in mangroves and sea grass beds. The lagoon serves as a natural harbor and played a pivotal role in Aruba's history, especially during its colonial era. While Aruba lacks the presence of any major rivers due to its arid climate and relatively flat topography, it does feature a handful of ephemeral streams that appear following periods of heavy rainfall.
Political Map of Aruba
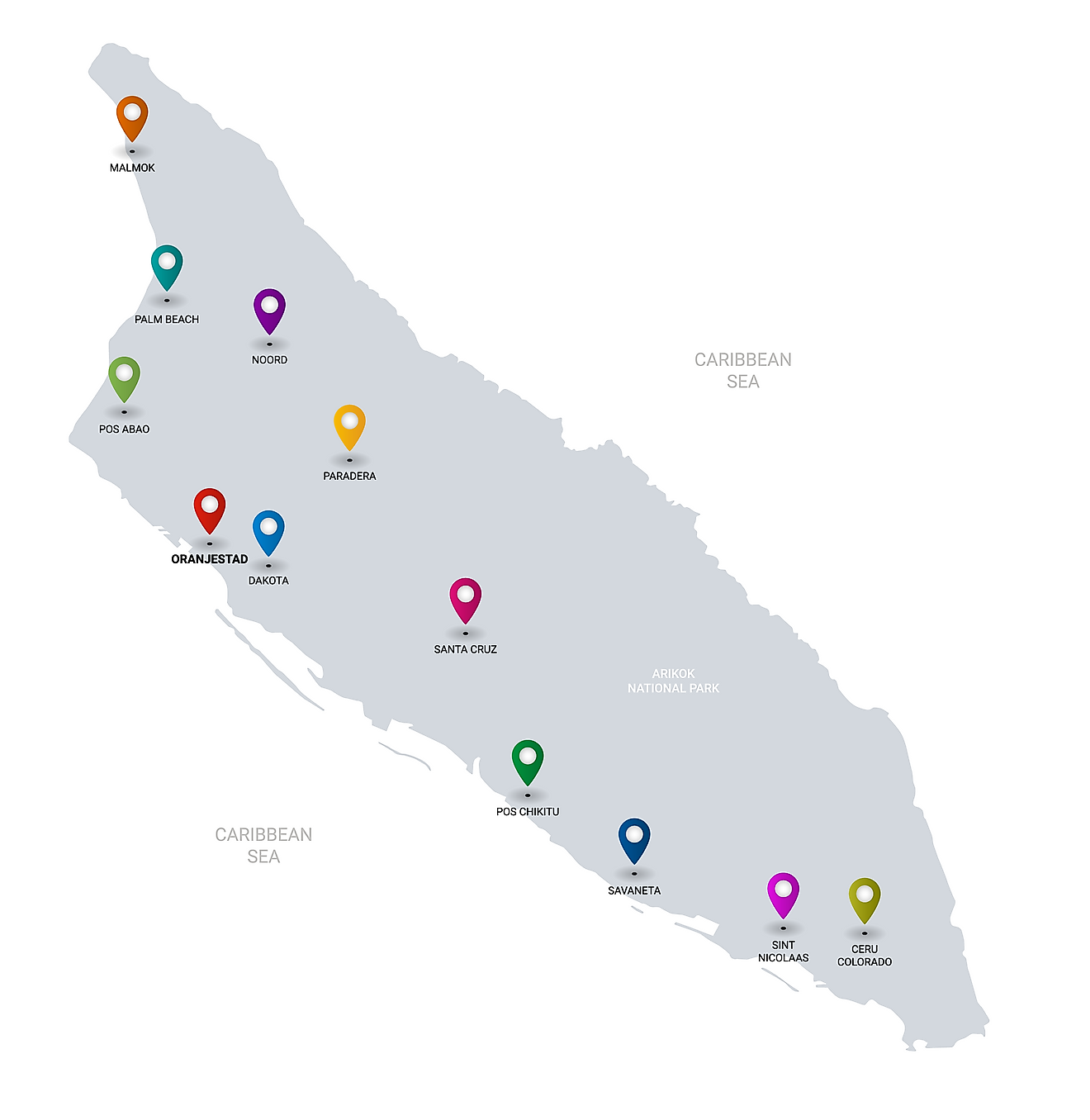
Aruba has no administrative divisions. It is one of the constituent countries of the Kingdom of Netherlands. Situated on the southern coast close to the country’s western island is, Oranjestad – the capital and the largest city of Aruba. It is also the administrative as well as the country’s petroleum processing and shipping center. Oranjestad port serves as the largest port in the island nation.
Where is Aruba?
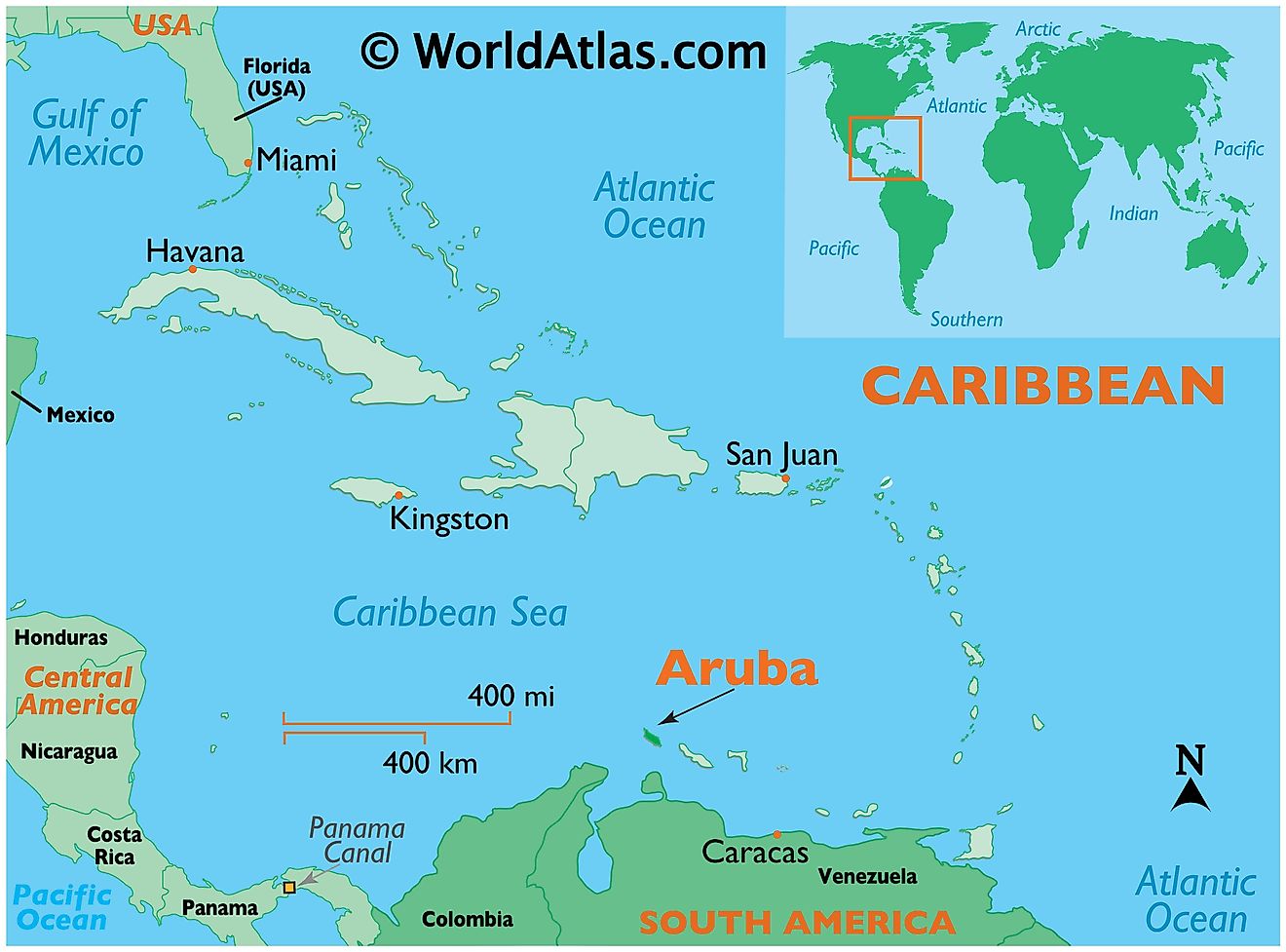
Aruba is an island country located in the south western Caribbean region, off the Venezuelan coast. It is positioned in the Northern and Western hemispheres of the Earth. It is surrounded by the Caribbean Sea.
Regional Maps: Map of North America
Outline Map of Aruba
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Aruba |
|---|---|
| Flag |

|
| Capital City | Oranjestad |
| 12 31 N, 70 02 W | |
| Total Area | 180.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 180.00 km2 |
| Water Area | N/A |
| Population | 106,314 |
| Currency | Aruban guilders/florins |
| GDP | $3.06 Billion |
| GDP Per Capita | $29,007.69 |
This page was last updated on June 14, 2023