Maps of Alberta
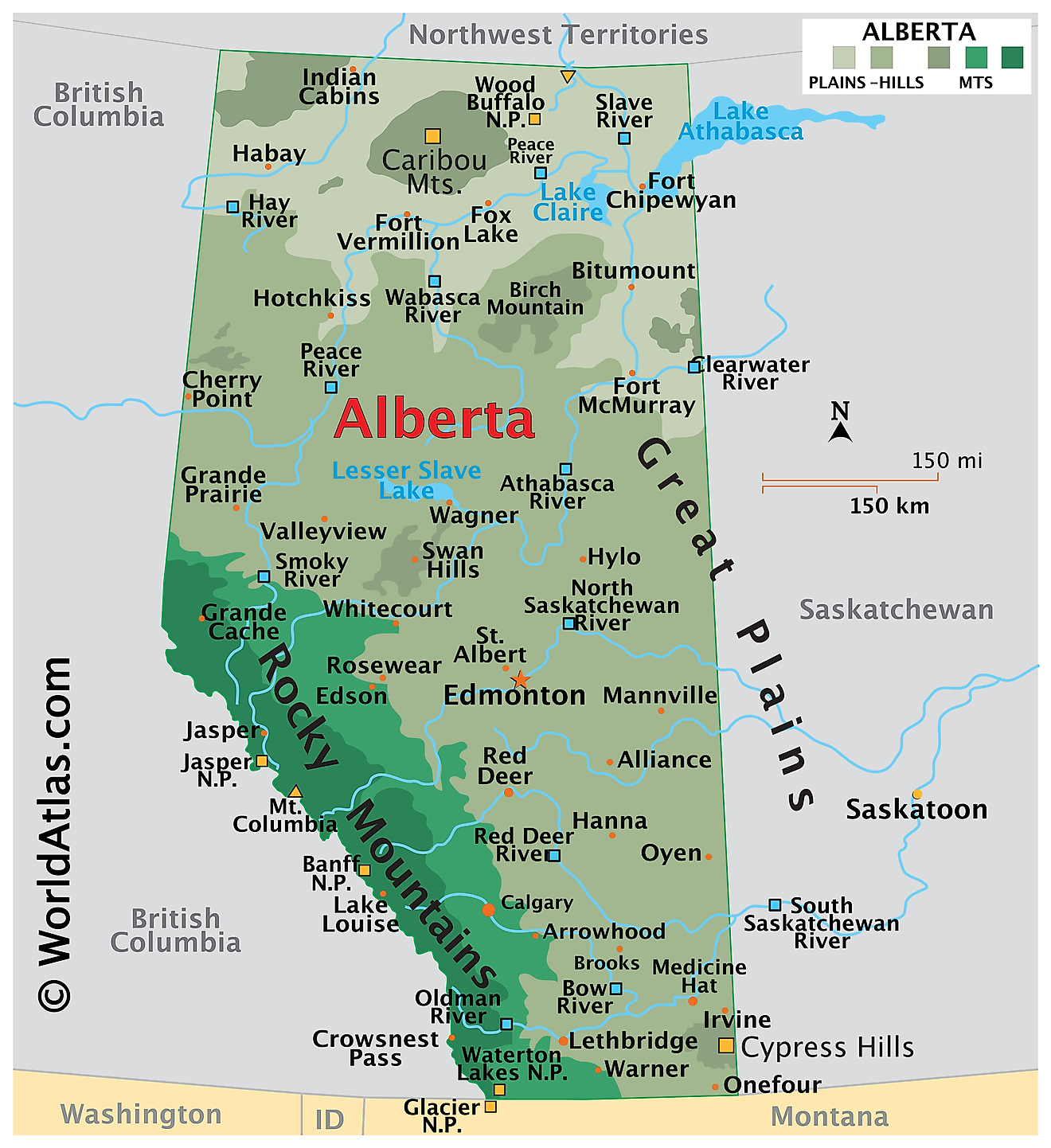
The Province of Alberta, located in Western Canada, encompasses diverse geographical features that contribute to its unique character. Bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Territories to the north, and the U.S. state of Montana to the south, Alberta's geography spans an area of approximately 255,541 square miles. This vast region comprises several distinct landscapes, such as the Rocky Mountains, prairies, boreal forests, and parklands, each with ecological significance.
In the western part of Alberta, the Canadian Rocky Mountains dominate the landscape, forming a dramatic backdrop to the province. These mountains contain some of the highest peaks in Canada, such as Mount Columbia, which rises to 12,293 feet. The Rockies are a major attraction for tourists and adventurers, offering hiking, skiing, and mountain climbing opportunities. In addition, the region holds five national parks, including Banff and Jasper, which protect the pristine alpine environment and provide a haven for diverse wildlife.
To the east of the Rockies, the Foothills region transitions from the mountains to the flatlands. This area features a mix of forests, rolling hills, and grasslands, providing essential habitats for many species. The Foothills also contain rich natural resources, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, significantly contributing to Alberta's economy.
Moving further east, the Alberta Prairies dominate the landscape, characterized by vast expanses of grasslands and fertile agricultural lands. The province's prairies, part of the larger Great Plains ecoregion, support a diverse array of plant and animal life. This area experiences a semi-arid climate, with long, cold winters and short, warm summers, making it suitable for the cultivation of cereal crops, such as wheat and barley. The Prairies also host numerous wetlands, which serve as vital nesting grounds for migratory birds and play a crucial role in maintaining the region's ecological balance.
The Boreal Forest, stretching across northern Alberta, constitutes one of the largest contiguous areas of this unique ecosystem in the world. This vast expanse of forest, characterized by coniferous trees, such as spruce, pine, and fir, and interspersed with wetlands and lakes, supports an incredible variety of plant and animal species. This region plays a critical role in carbon storage and acts as a buffer against climate change.
The Parkland region, located in central Alberta, serves as a transition zone between the Boreal Forest and the Prairies. This area contains a mix of aspen forests, grasslands, and wetlands, providing habitats for a diverse range of flora and fauna. The Parkland region supports extensive agriculture, particularly livestock farming, and is home to several of Alberta's major cities, including Edmonton, the provincial capital.
In terms of hydrography, Alberta contains numerous rivers and lakes that shape its landscape and ecology. The province's two major rivers, the North Saskatchewan River and the South Saskatchewan River, flow eastward from the Rockies, eventually joining to form the Saskatchewan River. These rivers play an essential role in providing water for agriculture, industry, and domestic use, as well as supporting a rich array of aquatic life.
Provinces Map
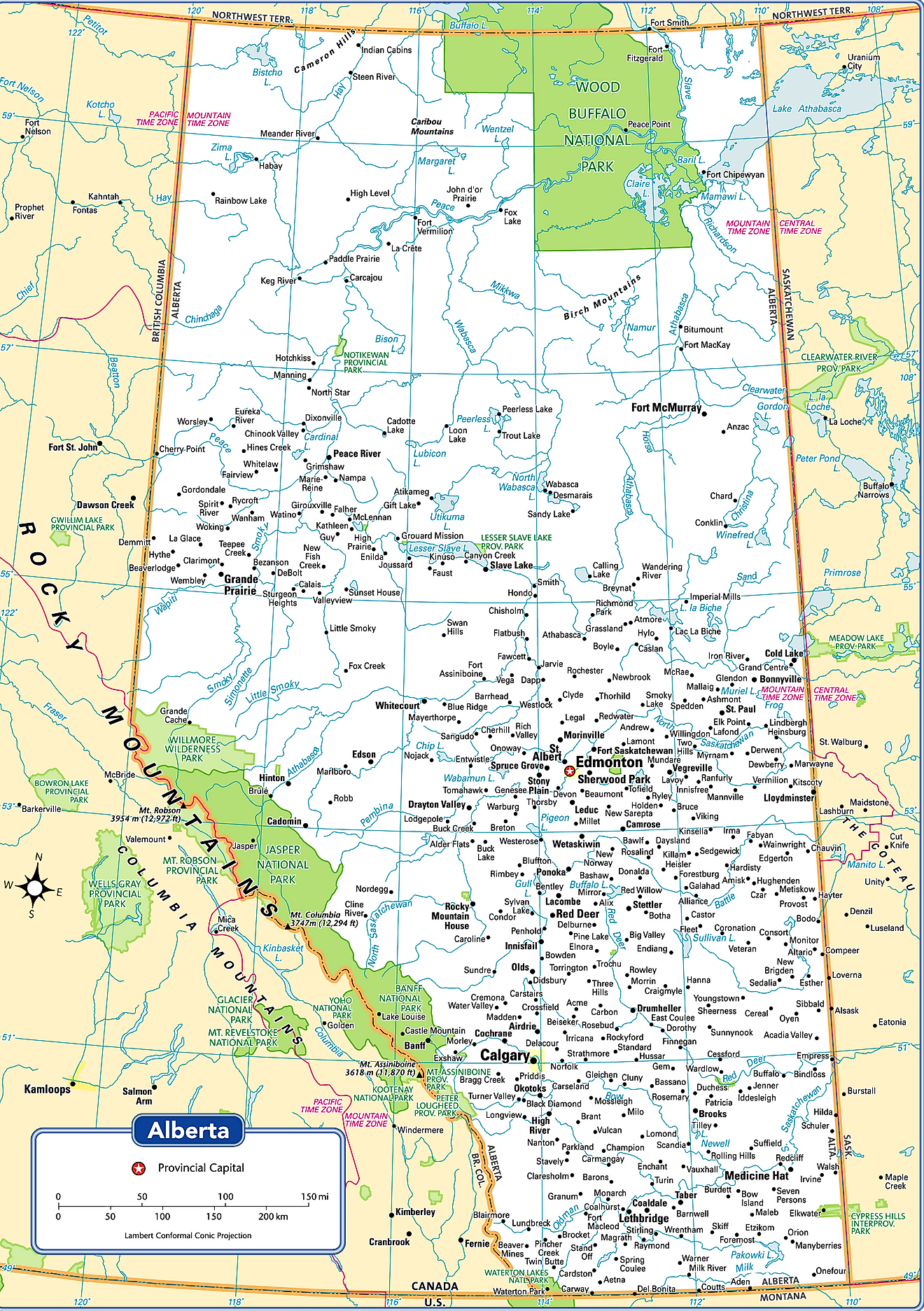
The Canadian Province of Alberta is administratively divided into several different types of local governments such as, the urban municipalities (which includes cities, villages, towns, and summer villages); rural municipalities (which include counties/municipal districts, special areas, and improvement districts); specialized municipalities; Métis settlements, Indian reserves and many unincorporated communities (which include hamlets, a townsite and urban service areas).
Currently, Alberta consists of 19 cities, 107 towns, 81 villages, 51 summer villages, 6 specialized municipalities, 63 municipal districts, 7 improvement districts, 3 special areas, 389 hamlets, 2 urban service areas, and 1 townsite. In addition to these, there are a total of 8 Métis settlements – which are rural areas that are currently inhabited by Alberta’s indigenous Métis people. About, 6,566.6 sq. km of total land area in Alberta is occupied by Indian reserves.
With an area of 661,848 sq. km, Alberta is the 6th largest and the 4th most populous Canadian province. Located in the heart of the Edmonton Capital Region and on the North Saskatchewan River, is Edmonton – the capital and the 2nd largest city of Alberta. It serves as the administrative, cultural, economic, and educational center of Alberta. The city hosts various year-round festivals and has therefore been nicknamed “Canada’s Festival City”. The city of Edmonton is the northernmost among all the major Canadian cities and is often referred to as the “Gateway to the North”. Situated in the southern part of Alberta near the confluence of Bow and Elbow rivers is Calgary – which serves as the largest and the most populous city of Alberta.
Where is Alberta?
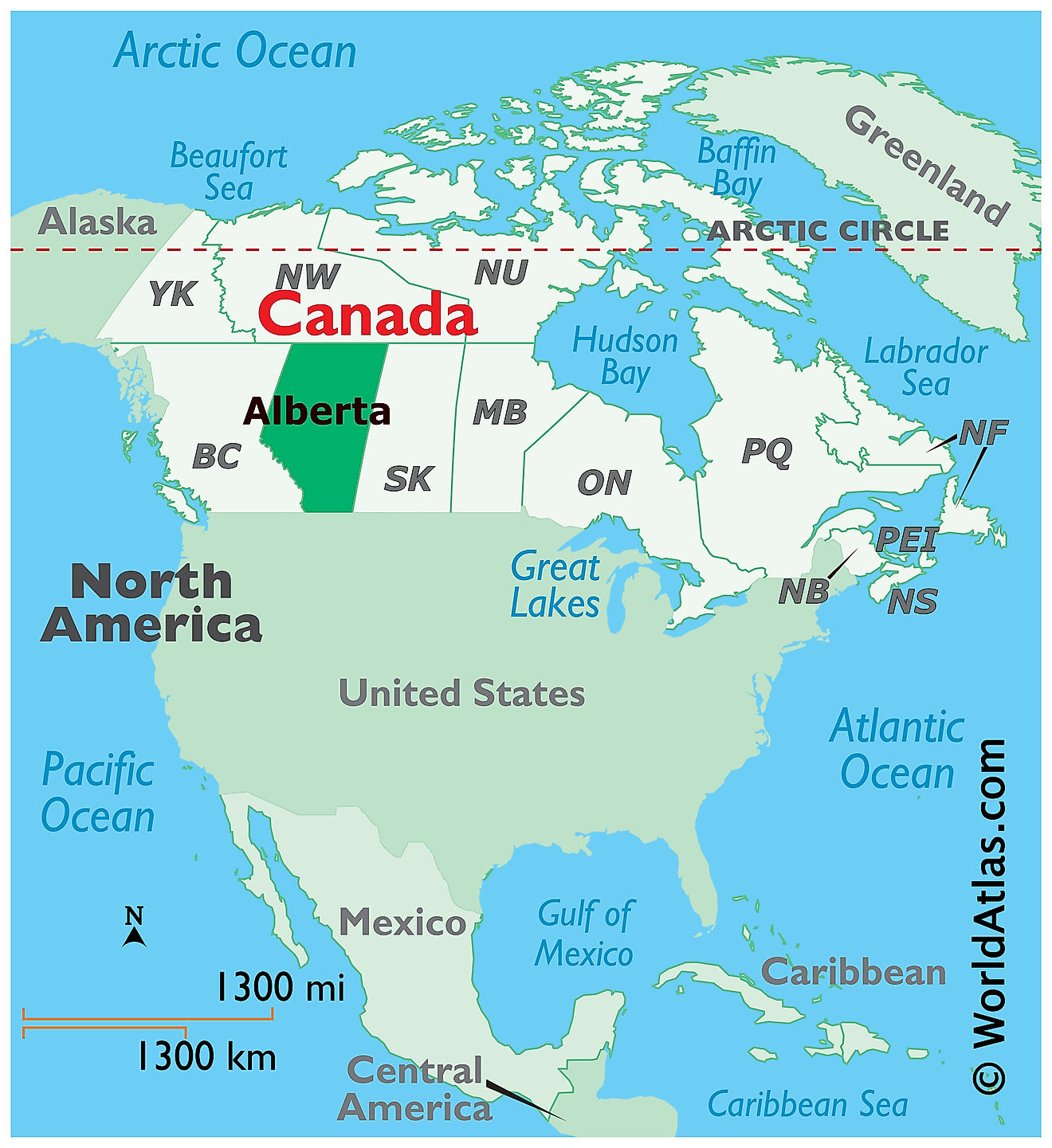
The Province of Alberta is located in the west-central part of Canada, in the Continent of North America. It is geographically positioned in the Northern and Western hemispheres of the Earth. Alberta is a landlocked province that is situated in the Prairies region of Canada. It is bordered by the other Canadian Provinces of British Columbia in the west; by the Northwest Territories in the north; and by Saskatchewan in the east. In the south, the 49th parallel north latitude forms Alberta’s international boundary with the US State of Montana.
Regional Maps: Map of North America
Outline Map of Alberta
The above blank map represents the Province of Alberta, located in the west-central part of Canada. The above map can be downloaded, printed, and used for geography education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.
The above outline map represents the Province of Alberta, located in the west-central part of Canada.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Province of Alberta |
|---|---|
| ISO 3166 Code | CA-abz |
| Capital City | Edmonton |
This page was last updated on March 16, 2023











