Maps of Quebec
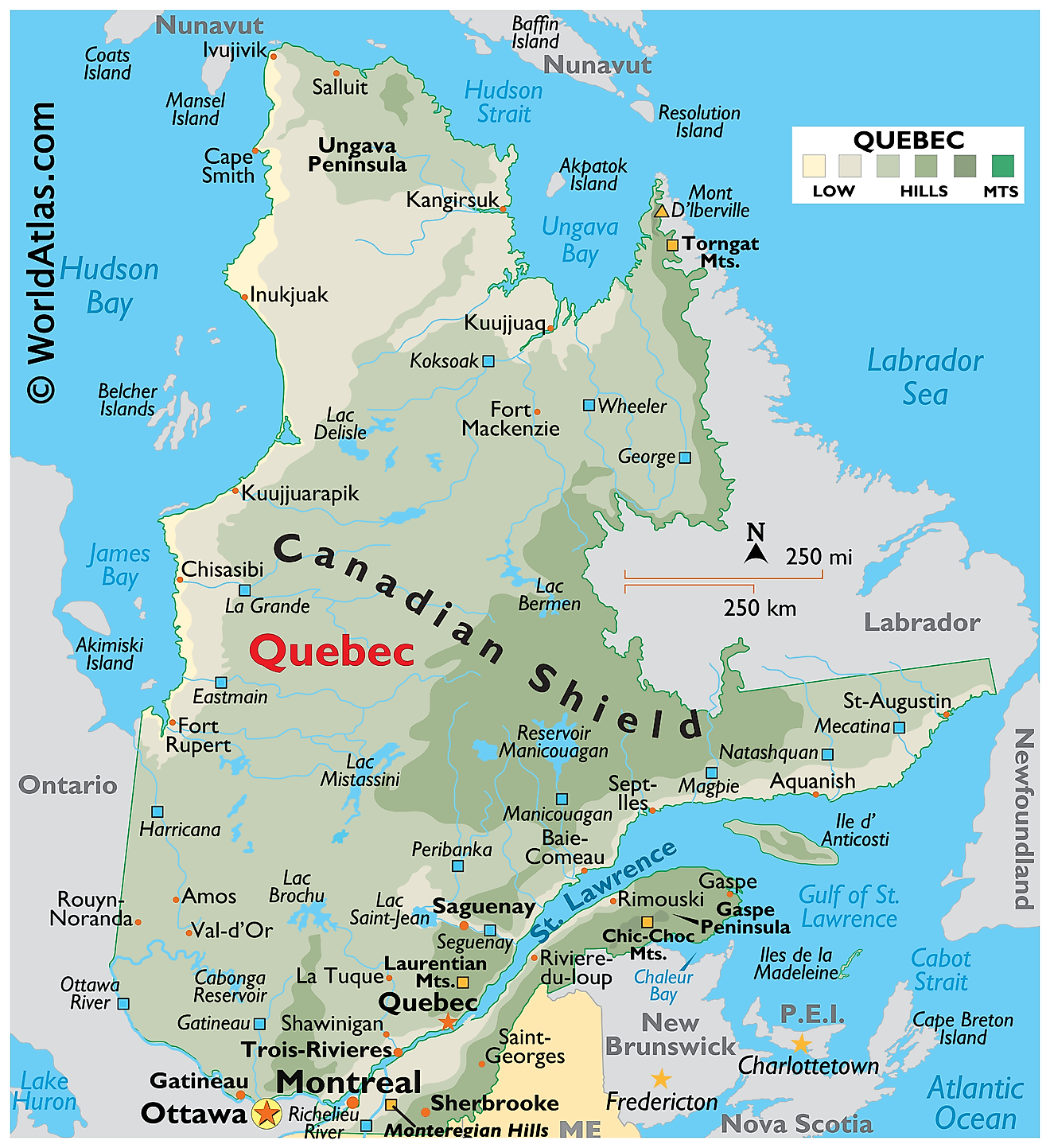
Quebec, the largest Canadian province, encompasses an area of 595,391 square miles. It shares borders with Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, and New Brunswick to the southeast. To the south, Quebec borders the United States, specifically the states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and New York. In the north, the province extends to the Arctic Ocean, while to the east, it meets the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Saint Lawrence.
Quebec's geography divides into four main regions: the Canadian Shield, the Appalachian Mountains, the St. Lawrence Lowlands, and the Ungava Peninsula.
The Canadian Shield, a vast region of ancient rocks and forests, covers the majority of Quebec's landmass. This region, characterized by its rocky terrain, contains numerous lakes and rivers, making it a haven for outdoor enthusiasts. The Shield also boasts some of the world's oldest rock formations, dating back billions of years. Notable rivers in the Canadian Shield include the La Grande River, the Rupert River, and the Eastmain River.
The Appalachian Mountains stretch across the southeastern part of Quebec, extending from the Gaspé Peninsula to the border with the United States. This region, characterized by rolling hills and deep valleys, offers a diverse landscape of forests and farmlands. The Chic-Choc Mountains, a subrange of the Appalachians, provide some of Quebec's most breathtaking scenery and serve as a popular destination for hikers and nature lovers.
The St. Lawrence Lowlands, located between the Canadian Shield and the Appalachian Mountains, consist of flat, fertile plains. The St. Lawrence River, Quebec's most significant waterway, runs through this region, providing vital transportation and trade routes. This river, stretching over 746 miles, serves as the primary drainage system for the Great Lakes and ultimately empties into the Atlantic Ocean. The St. Lawrence Lowlands also host several of Quebec's largest cities, including Montreal and Quebec City.
The Ungava Peninsula, situated in the northeastern part of Quebec, consists of tundra and boreal forest. This remote and rugged region remains largely unpopulated, providing a habitat for various Arctic wildlife species. The peninsula borders the Hudson Strait, which connects the Hudson Bay and the Labrador Sea. The area also features multiple lakes and rivers, including the Caniapiscau River and the Koksoak River.In the far-northern part of the province, the Torngat Mountains dominate the landscape along the province’s border with Newfoundland and Labrador. The treeless Torngat Mountains are highly indented by many fjords and lakes. Located to the northeast of the Torngat Mountains is Mount d’Iberville (Mount Caubvick), which rises to an elevation of 5420 ft and is the highest point in Quebec.
Provinces Map
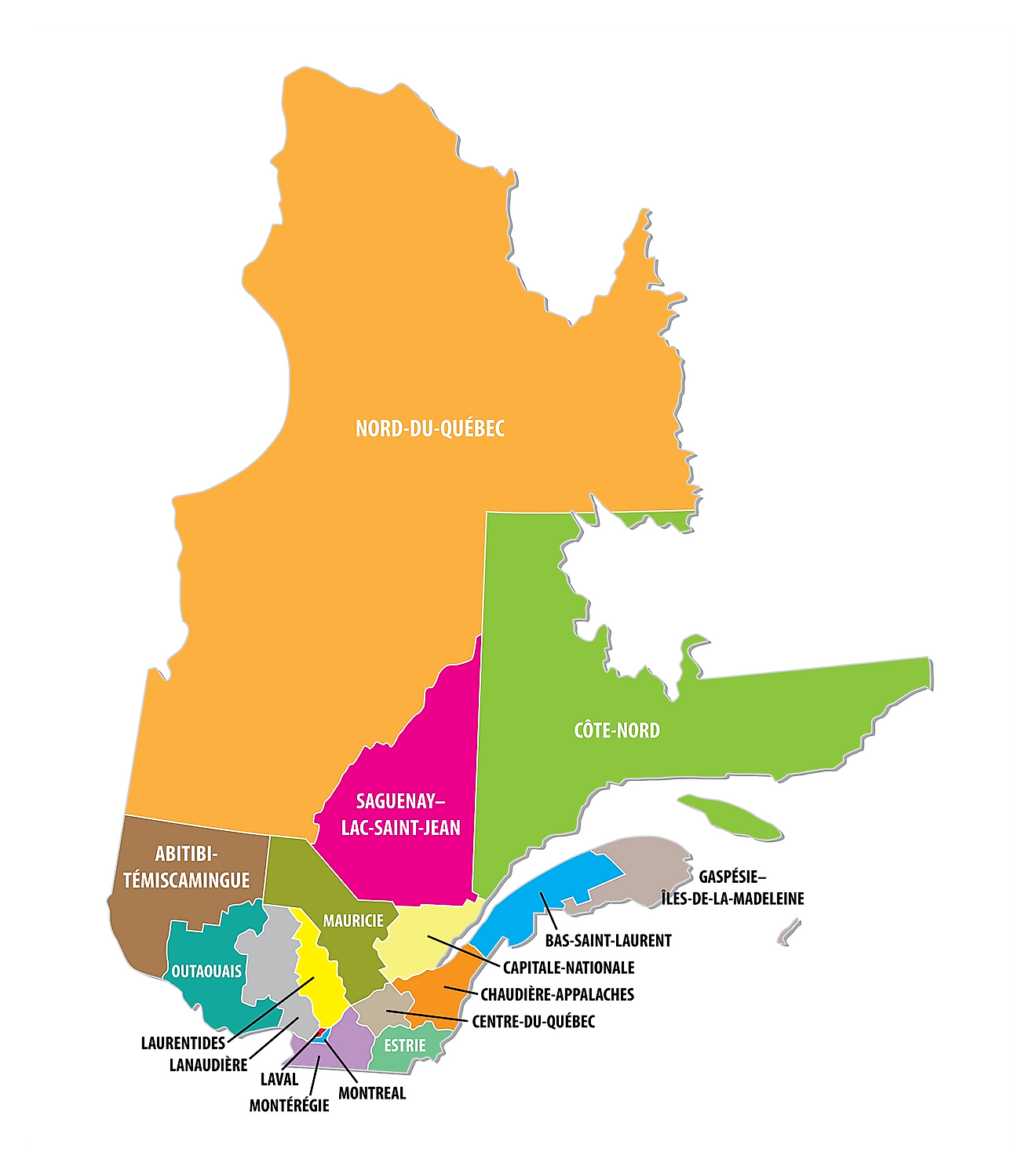
The Canadian Province of Quebec is administratively divided into regional, supralocal and local levels. The province also contains some administrative units that are exclusively reserved for the Aboriginal lands. The Province of Quebec is primarily subdivided into a total of 17 Administrative Regions at the regional level. At the supralocal level, the province is subdivided into 86 Regional County Municipalities and 2 Metropolitan Communities. At the local level, the province comprises a total of 1,117 local municipalities, 11 agglomerations (which includes about 42 local municipalities), and 45 boroughs (that are located within 8 local municipalities).
With an area of 1,542,056 sq. km, Quebec is the largest and the 2nd most populous Canadian Province. Located at the meeting point of St. Lawrence and Saint Charles Rivers, is Quebec City – which serves as the capital and the 2nd largest city of Quebec. It serves as a major port and the provincial administrative center. Situated at the center of Montreal Island in the southwestern part of the province is Montreal – the largest and the most populous city in Quebec.
Where is Quebec?
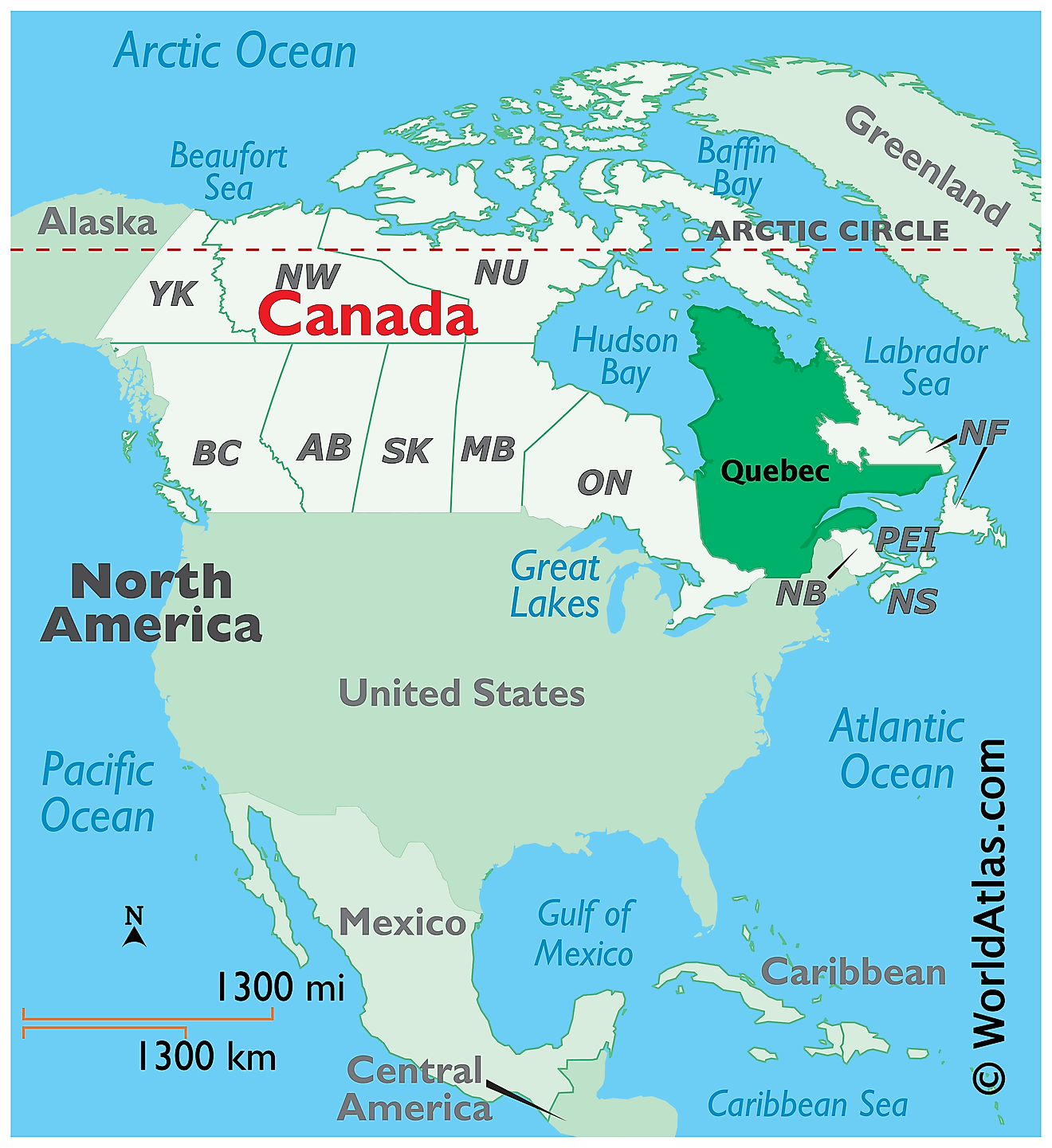
The Province of Quebec is located in the eastern part of Canada, in the Continent of North America. It is geographically positioned in the Northern and Western Hemispheres of the Earth. Quebec is bordered by the Canadian Province of Newfoundland and Labrador in the east; by New Brunswick, the Gulf of St. Lawrence, and the US State of Maine in the southeast; by the US States of New Hampshire, New York, and Vermont in the south; by the Canadian province of Ontario as well as the Hudson Bay and James Bay in the west. It is also bounded by the Hudson Strait and the Ungava Bay in the north.
Regional Maps: Map of North America
Outline Map of Quebec
The above blank map represents the Province of Quebec, located in the eastern part of Canada. The above map can be downloaded, printed, and used for geography education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.
The above outline map represents the Province of Quebec, located in the eastern part of Canada.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Province of Quebec |
|---|---|
| ISO 3166 Code | CA-pqz |
| Capital City | Quebec |
This page was last updated on March 30, 2023







