Maps of Manitoba
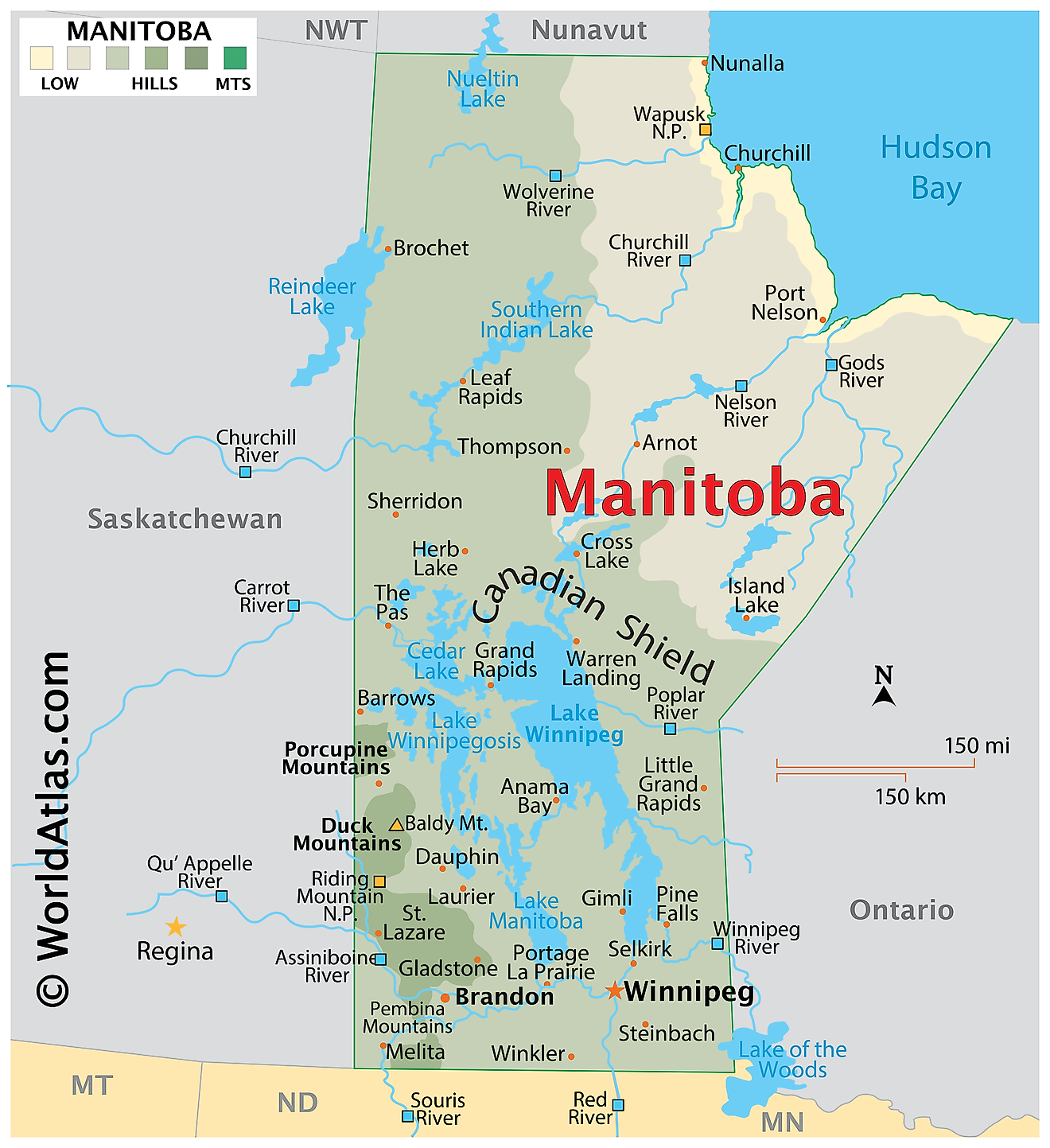
Manitoba, a central Canadian province, boasts a diverse and fascinating geography that warrants further exploration. This comprehensive analysis delves into the province's major geographical features, including its location, climate, landforms, bodies of water, and natural resources.
Manitoba lies in the longitudinal center of Canada, with a total area of approximately 250,116 square miles. It shares borders with Ontario to the east, Saskatchewan to the west, Nunavut to the north, and the United States to the south. The province's geographical location places it within the Central Standard Time Zone.
The climate of Manitoba varies across the province, but it generally experiences a continental climate. The region's climate consists of cold winters and warm summers, with temperature differences becoming more pronounced as one moves northward. The southern areas receive more precipitation, while the north experiences a subarctic climate with longer, colder winters and shorter, cooler summers.
Manitoba's diverse landforms contribute to its unique geography. The province features three main landform regions: the Canadian Shield, the Interior Plains, and the Hudson Bay Lowlands. The Canadian Shield, located in the eastern and northern parts of Manitoba, consists of ancient, hard rock formations with abundant lakes and rivers. The Interior Plains, covering the southwestern and central areas, include flat or gently rolling prairie landscapes. The Hudson Bay Lowlands, in the northeastern part of the province, consist of flat, swampy terrain with numerous bodies of water.
Manitoba boasts an extensive network of rivers, lakes, and wetlands. Lake Winnipeg, the province's largest lake, spans an area of 24,514 square kilometers. Other significant lakes include Lake Manitoba, Lake Winnipegosis, and Cedar Lake. The province also features major rivers, such as the Nelson, Churchill, Red, and Assiniboine Rivers. These waterways serve as critical sources of freshwater, transportation routes, and recreational areas.
Forests cover roughly half of Manitoba's total land area, providing valuable timber resources. Boreal forests dominate the landscape, consisting mainly of coniferous trees like black spruce, white spruce, and jack pine. Deciduous trees, such as trembling aspen and balsam poplar, also thrive in these forests. Manitoba's prairie regions support various grassland ecosystems, home to many plant and animal species.
Manitoba's abundant natural resources play a significant role in its economy. The province boasts rich mineral deposits, including nickel, copper, zinc, and gold. The mining industry contributes significantly to Manitoba's economic growth. Agriculture, another vital sector, relies on the fertile soils of the Red River Valley and the Pembina Valley. Crops such as wheat, canola, and barley flourish in these regions, while livestock production, particularly cattle and hogs, also thrives.
Provinces Map
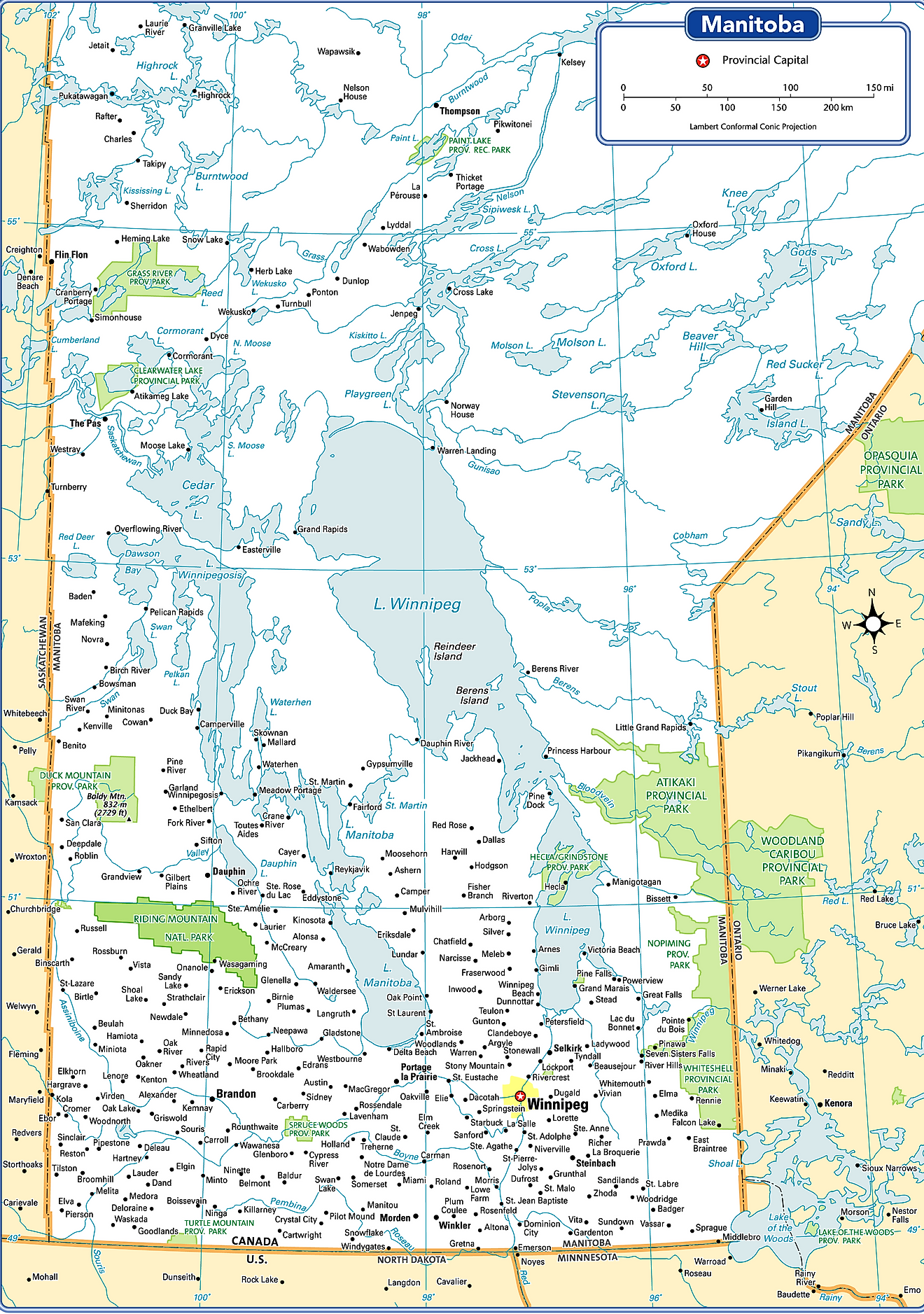
The Canadian Province of Manitoba is administratively divided into a total of 137 municipalities. Of these 137 municipalities in Manitoba, there are 37 urban municipalities, 98 rural municipalities, and 2 local government districts. The 37 urban municipalities are made up of 10 cities, 25 towns, and 2 villages.
With an area of 552,371 sq. km, Manitoba is the 6th largest and the 5th most populous Canadian province. Located at the meeting point of Assiniboine and Red rivers, near the longitudinal center of the North American continent is Winnipeg – the capital and the largest city of Manitoba. The city serves as the administrative, cultural, and transportation hub. The city is also referred to as the “Gateway to the West”. The Canadian Heritage named the city of Winnipeg as Canada’s “Cultural Capital” in 2010.
Where is Manitoba?
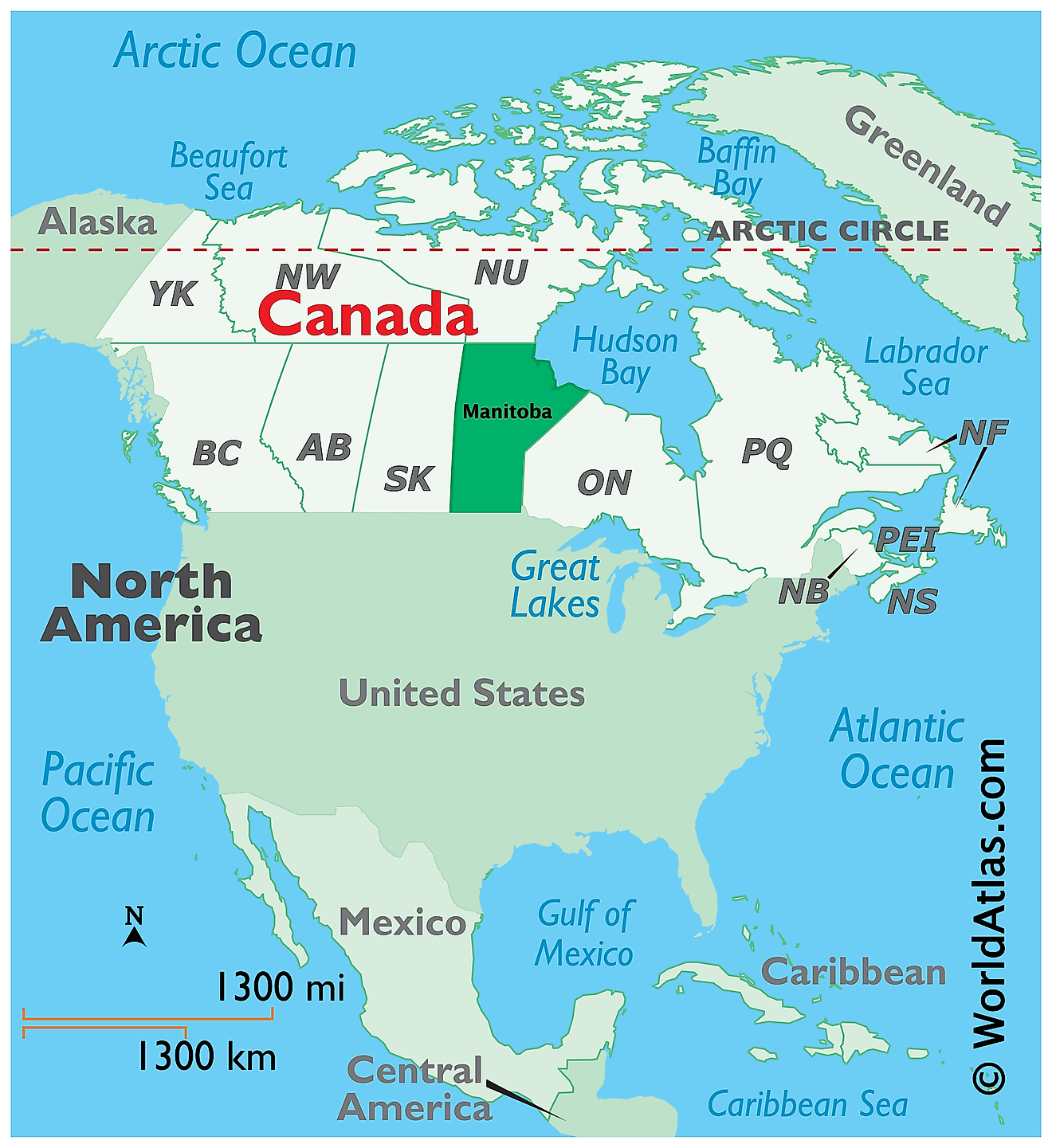
The Province of Manitoba is located at the longitudinal center of Canada, in the Continent of North America. It is geographically positioned in the Northern and Western hemispheres of the Earth. Manitoba is one of the three prairie provinces of Canada and is situated exactly midway between the Pacific and the Atlantic Oceans. It is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan in the west; by the Northwest Territories in the northwest; by Ontario in the east; by the Nunavut Territory in the north; and the US States of North Dakota and Minnesota in the south. It is bounded by the Hudson Bay in the northeast.
Regional Maps: Map of North America
Outline Map of Manitoba
The above blank map represents the Province of Manitoba, located in the central part of Canada. The above map can be downloaded, printed, and used for geography education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.
The above outline map represents the Province of Manitoba, located in the central part of Canada.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Province of Manitoba |
|---|---|
| ISO 3166 Code | CA-mbz |
| Capital City | Winnipeg |
This page was last updated on March 20, 2023











