Maps of Nova Scotia
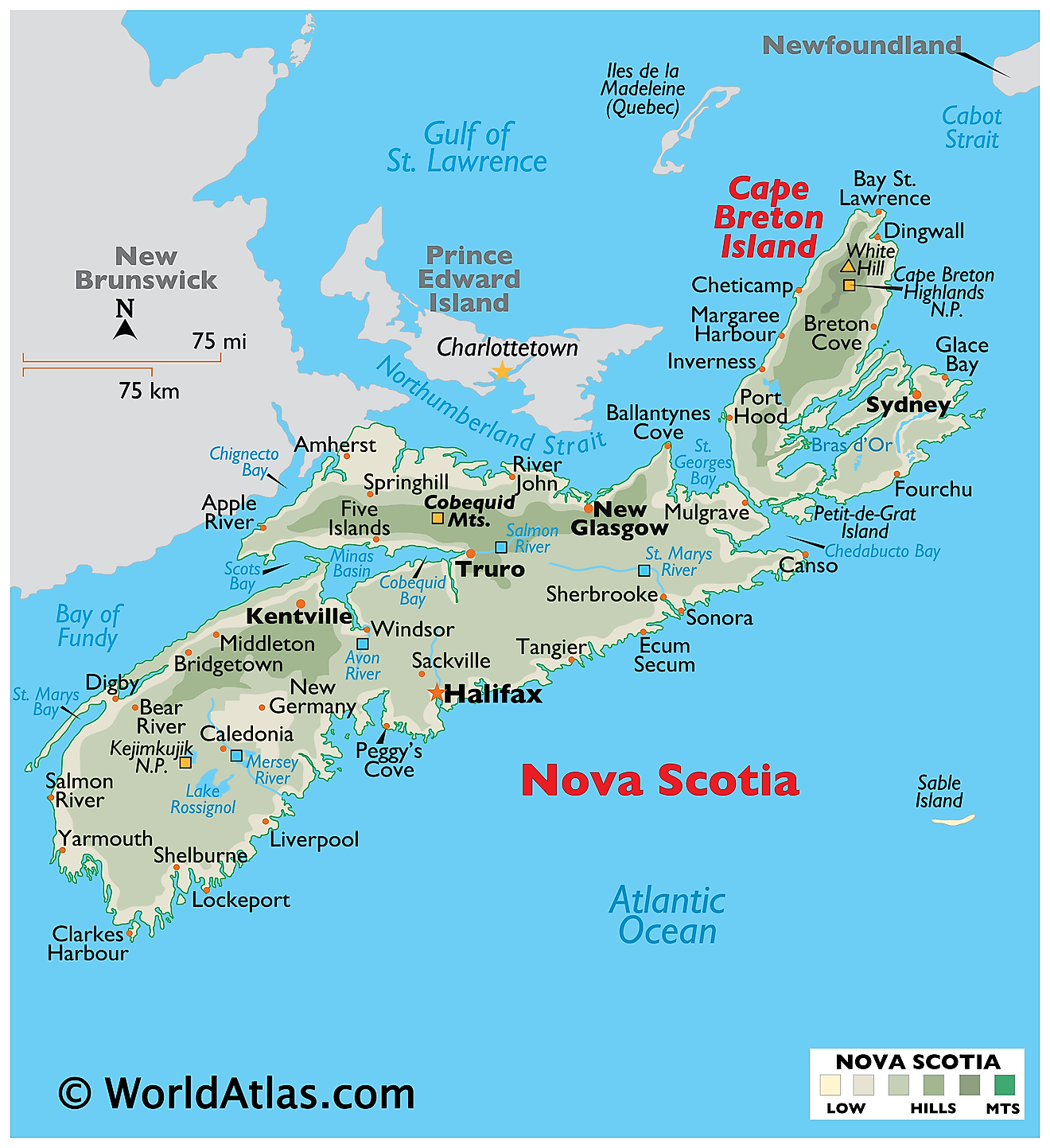
Nova Scotia is a province in eastern Canada and is one of the four Atlantic provinces. It has a total area of approximately 21,345 square miles. Nova Scotia is almost completely surrounded by water. To the east and south, it is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean. To the northwest, it is connected to the province of New Brunswick by the Isthmus of Chignecto, a narrow strip of land that links the Nova Scotia peninsula to mainland North America. Additionally, Nova Scotia includes Cape Breton Island, which is located to the northeast of the mainland and is separated by the Strait of Canso.
Nova Scotia's topography features a predominantly low-lying terrain, with the highest elevation at White Hill, which peaks at 1,745 feet (532 meters). The province comprises three main regions: the Appalachian Uplands, the Central Lowlands, and the Atlantic Coastal Plain. The Appalachian Uplands, extending from the mainland to Cape Breton Island, contain ancient, weathered mountains and deep river valleys. The Central Lowlands, which some refer to as the Nova Scotia Lowlands, consist of rolling hills, fertile valleys, and scattered forests. The Atlantic Coastal Plain, characterized by its sandy beaches, salt marshes, and rocky shores, stretches along the province's eastern and southern coastlines.
Nova Scotia experiences a temperate maritime climate, which results from its proximity to the Atlantic Ocean. The province enjoys relatively mild winters and cool summers, with abundant precipitation throughout the year. Coastal areas often experience fog and cool sea breezes, while inland regions see greater temperature variations. The average annual temperature ranges from 41°F to 46°F, with the warmest months from June to September.
Nova Scotia's diverse geography supports a wide array of plant and animal species. The province's forests, which cover over 75% of the land area, predominantly consist of softwoods such as spruce, balsam fir, and pine, while hardwoods like maple, birch, and oak thrive in some areas. Salt marshes, bogs, and wetlands provide habitats for various plant and bird species in the coastal plain.
Nova Scotia is home to a rich diversity of wildlife, including mammals like white-tailed deer, black bears, and moose, as well as smaller creatures such as squirrels, raccoons, and beavers. The province's coastline and offshore waters support various marine life, including seals, whales, and numerous fish species, like Atlantic cod, haddock, and halibut.
Nova Scotia possesses a wealth of natural resources, with fishing, agriculture, and forestry playing a significant role in its economy. The fertile soil in the Annapolis Valley and the Central Lowlands supports a thriving agricultural industry, with apples, blueberries, and grapes as major crops. The province's extensive forests provide timber for lumber, pulp, and paper production.
Thanks to its abundant marine resources, the fishing industry remains vital to Nova Scotia's economy. Lobsters, scallops, and groundfish contribute significantly to the province's seafood exports. Additionally, Nova Scotia holds potential for offshore oil and gas reserves, and it is exploring opportunities in renewable energy, such as wind and tidal power, to harness its natural resources sustainably.
Provinces Map
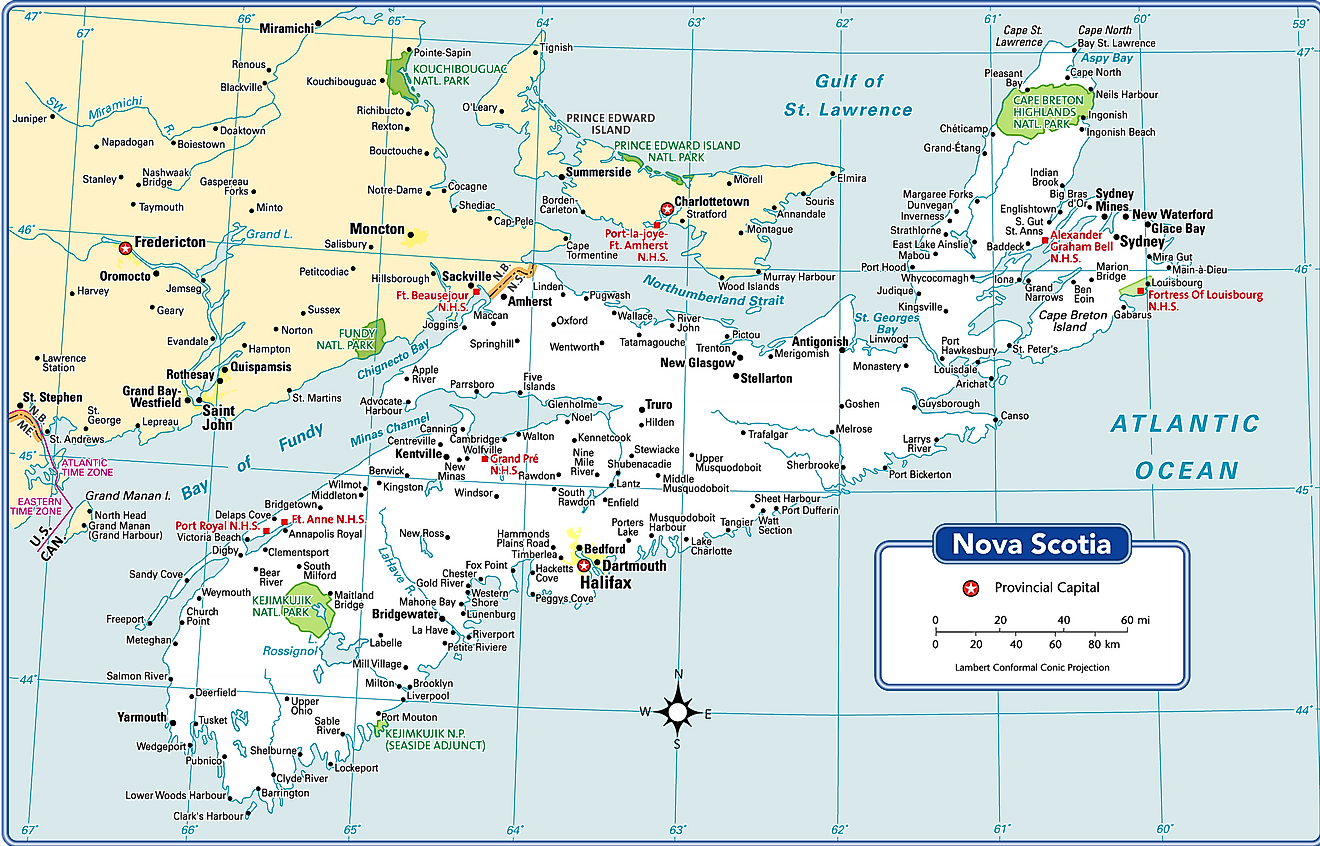
The Canadian Province of Nova Scotia is administratively divided into a total of 50 municipalities. Of these 50 municipalities, there are 3 regional municipalities, 26 towns, 9 county municipalities, and 12 district municipalities.
Nova Scotia also has 18 counties that had appointed court systems for local governance administration prior to 1879. Today, these historical counties are used by Statistics Canada as census divisions but they no longer serve as administrative units.
With an area of 55,284 sq. km, Nova Scotia is the 2nd smallest and the 2nd most densely populated Canadian Province. Located along the Halifax Harbor on the Atlantic coast of the province is Halifax (officially, the Halifax Regional Municipality), - the provincial capital and the largest city of Nova Scotia. After the city of Vancouver, Halifax is the 2nd largest coastal city in Canada. Halifax serves as a major economic center in Atlantic Canada. It also serves as the cultural, financial, and economic center for the Canadian Maritime Region.
Where is Nova Scotia?
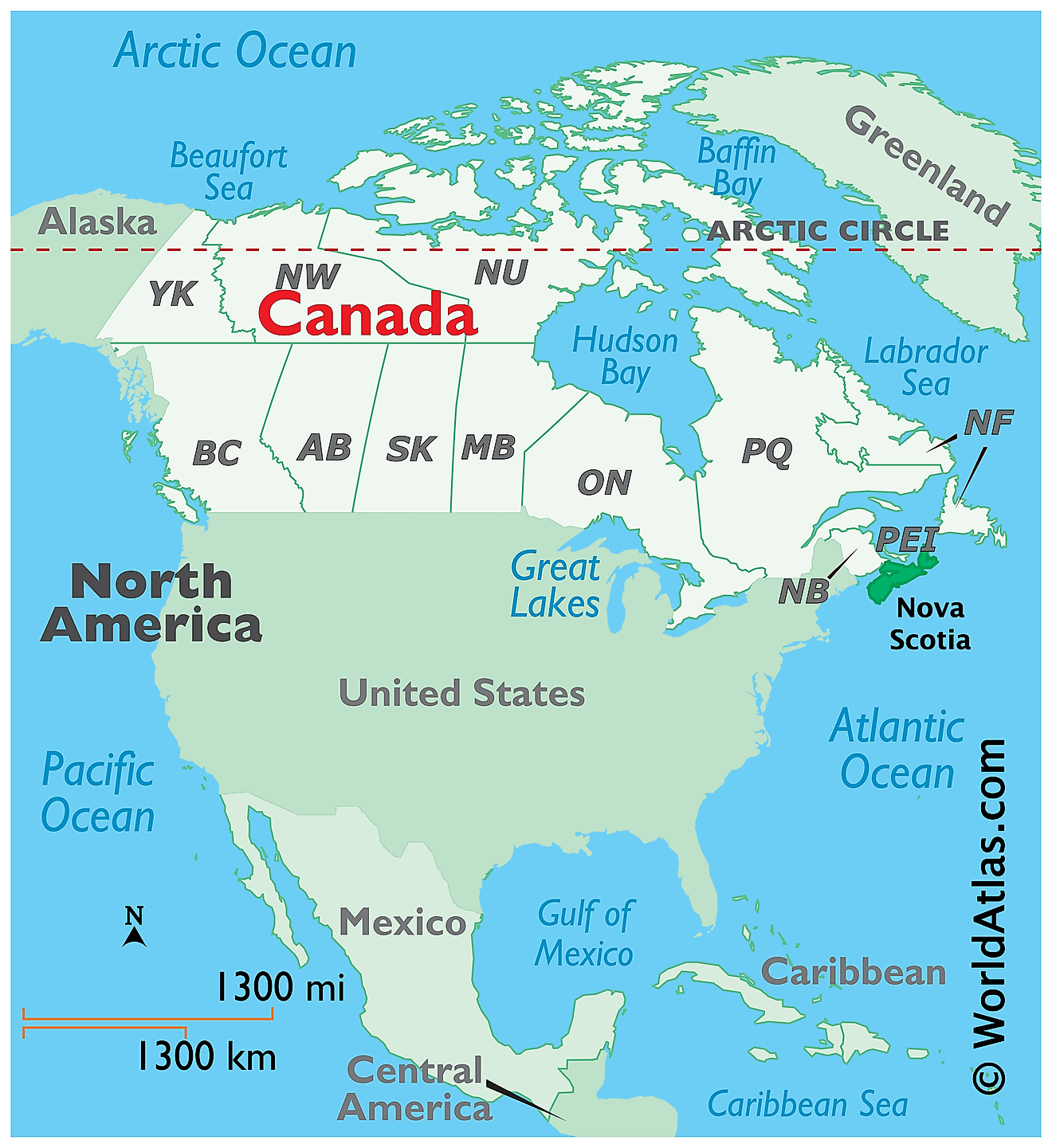
The Province of Nova Scotia is located in the Canadian Maritimes region, in the eastern part of Canada, in the continent of North America. The mainland of Nova Scotia is connected by the Isthmus of Chignecto to the rest of the North American continent. The province’s only land border with the Canadian province of New Brunswick is situated on the Isthmus of Chignecto. The Nova Scotia province is bounded by the Bay of Fundy in the west and by the Atlantic Ocean in the south and east. It is separated from Prince Edward Island in the north by the Northumberland Strait and Newfoundland Island in the northeast by the Cabot Strait.
Regional Maps: Map of North America
Outline Map of Nova Scotia
The above blank map represents the Province of Nova Scotia, located in the Canadian Maritimes region, in the eastern part of Canada. The above map can be downloaded, printed, and used for geography education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.
The above outline map represents the Province of Nova Scotia, located in the Canadian Maritimes region, in the eastern part of Canada.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Province of Nova Scotia |
|---|---|
| ISO 3166 Code | CA-nsz |
| Capital City | Halifax |
This page was last updated on March 27, 2023











