Maps of Northwest Territories
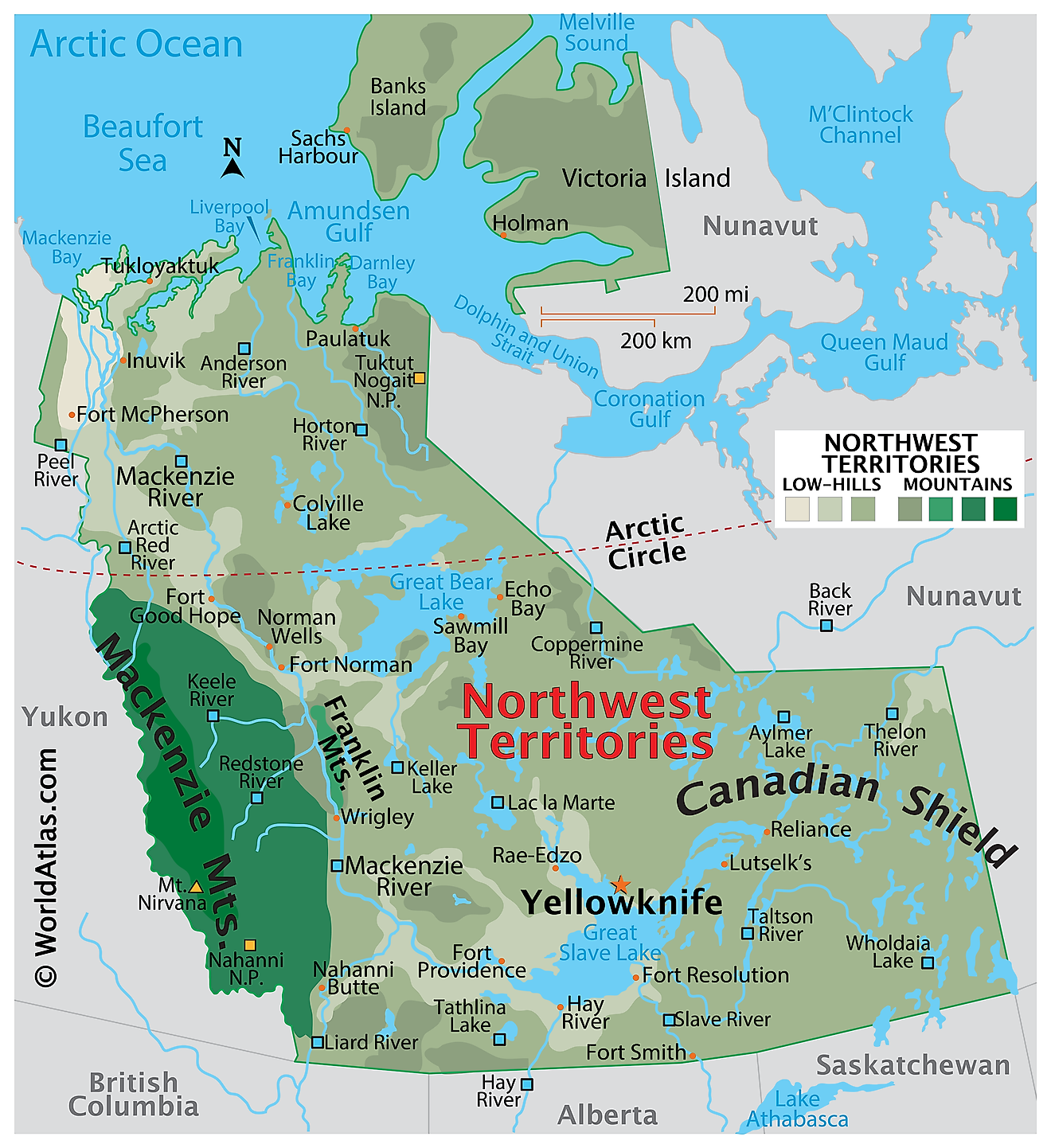
The Northwest Territories, a vast and diverse region in northern Canada, covers an area of approximately 519,735 square miles. It stretches from its border with Alberta to the Arctic Ocean in the north and shares additional borders with Nunavut to the east, Saskatchewan, and British Columbia to the south, and Yukon to the west. The territory boasts a rich geographical landscape characterized by various landforms, climate zones, and ecosystems.
The landforms of the Northwest Territories can be broadly classified into three regions: the Arctic Archipelago, the Canadian Shield, and the Interior Plains. The Arctic Archipelago consists of numerous islands, including Banks Island and Victoria Island, which are the territory's largest. Ice caps and glaciers dominate this region, while the Northwest Passage, a historically significant and seasonally navigable sea route, weaves through these islands.
The Canadian Shield covers the eastern and central parts of the territory, exhibiting ancient, rocky terrain, numerous lakes, and a sparse network of rivers. This region is rich in minerals, including gold, diamonds, and uranium. The Great Slave Lake, the deepest lake in North America, and the Great Bear Lake, the largest lake entirely within Canada, lie within this area. The mighty Mackenzie River, Canada's longest river, originates in the Shield and flows through the territory, ultimately emptying into the Arctic Ocean.
The Interior Plains, situated in the southwestern part of the Northwest Territories, features gently rolling hills, plateaus, and river valleys. This region is part of the larger Western Cordillera and experiences significant petroleum and natural gas deposits.
The territory's climate varies significantly from south to north, with subarctic conditions dominating most areas. Winters are long and cold, while summers are short and cool. In the far north, a polar climate prevails, characterized by persistent ice and snow throughout the year. The treeline marks the boundary between the boreal forest, or taiga, and the treeless tundra. Boreal forests primarily consist of coniferous trees such as spruce, pine, and larch, while the tundra features low-growing vegetation, including mosses, lichens, and small shrubs.
The Northwest Territories is home to a diverse array of wildlife, with species adapted to its extreme conditions. Notable mammals include caribou, muskoxen, moose, and polar bears, while migratory birds such as snow geese, tundra swans, and various species of ducks frequent the area. The territory's lakes and rivers support a thriving fish population, including lake trout, Arctic grayling, and northern pike.
Provinces Map
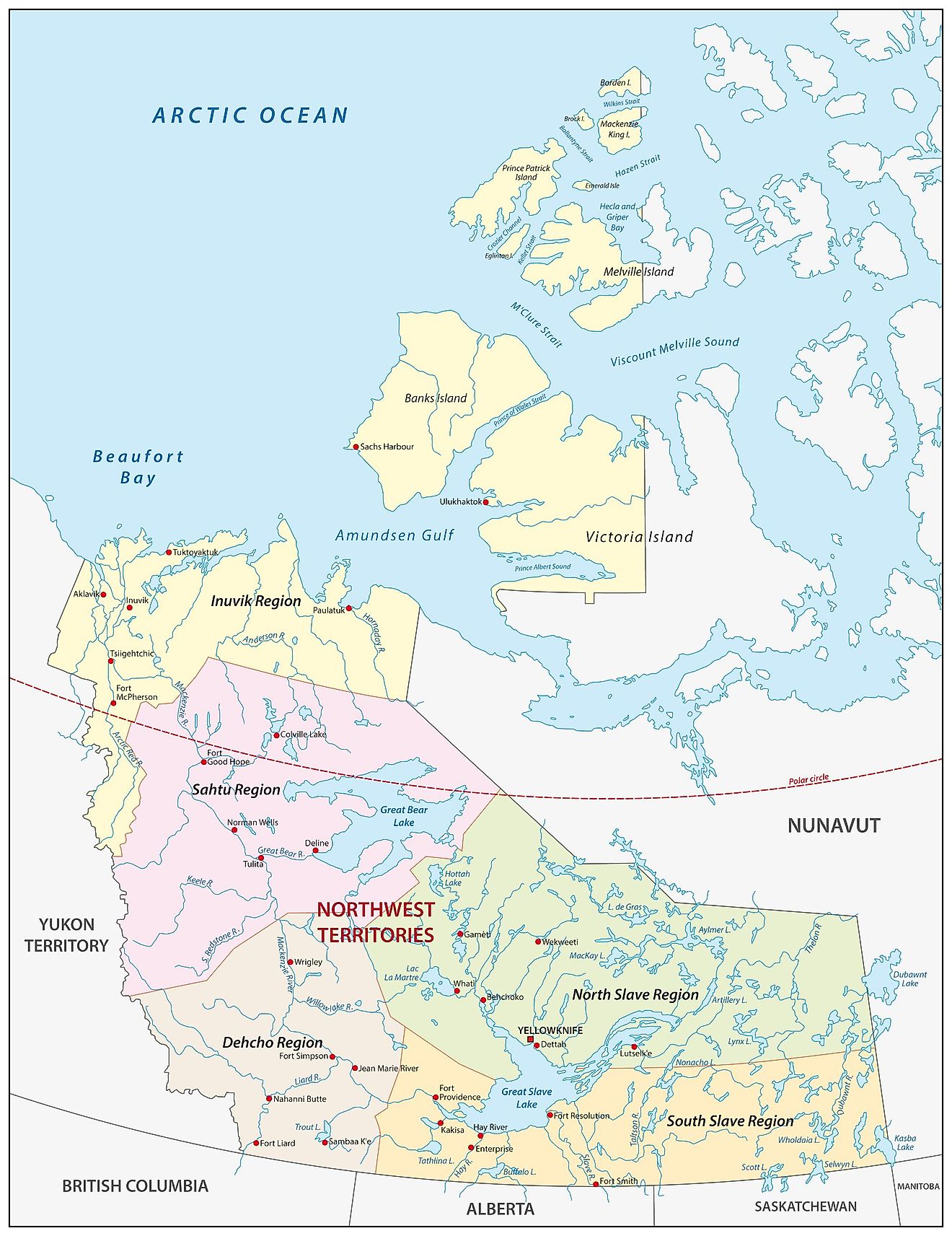
The Northwest Territories is a Canadian federal territory that is divided into 5 administrative regions. In alphabetical order, these regions are Dehcho Region, Inuvik Region, North Slave Region, Sahtu Region, and South Slave Region.
With an area of 1,144,000 sq. km, it is the 2nd largest and the most populous among the three northern territories of Canada. Situated on the northern coast of the Great Slave Lake is Yellowknife – the capital, the largest city, and the most populous community in the Northwest Territories. It serves as a major administrative, educational and commercial center of the Northwest Territories.
Where is Northwest Territories?
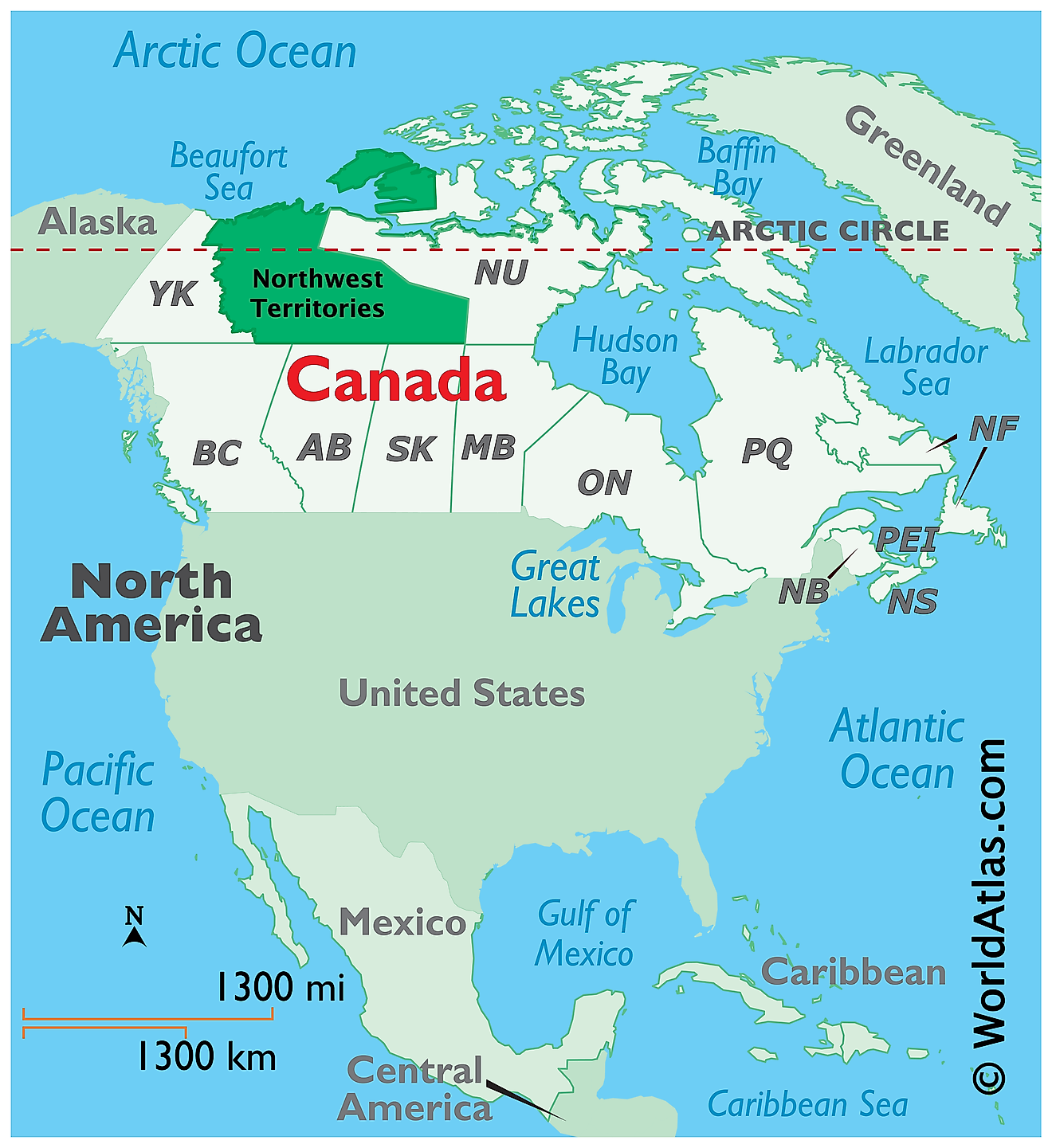
The Northwest Territories is a federal territory located in the northwestern part of Canada, in the Continent of North America. It is geographically positioned in the Northern and Western hemispheres of the Earth. The Northwest Territories is bordered by the Canadian territories of Yukon in the west and Nunavut in the east; and by the Canadian provinces of British Columbia, Alberta, and Saskatchewan in the south. In the north, it is bounded by the Beaufort Sea and the Arctic Ocean.
Regional Maps: Map of North America
Outline Map of Northwest Territories
The above blank map represents the Northwest Territories, located in the northwestern part of Canada. The above map can be downloaded, printed, and used for geography education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.
The above outline map represents the Northwest Territories, located in the northwestern part of Canada.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Province of Northwest Territories |
|---|---|
| ISO 3166 Code | CA-nwtz |
| Capital City | Yellowknife |
This page was last updated on March 24, 2023