Maps of Wisconsin
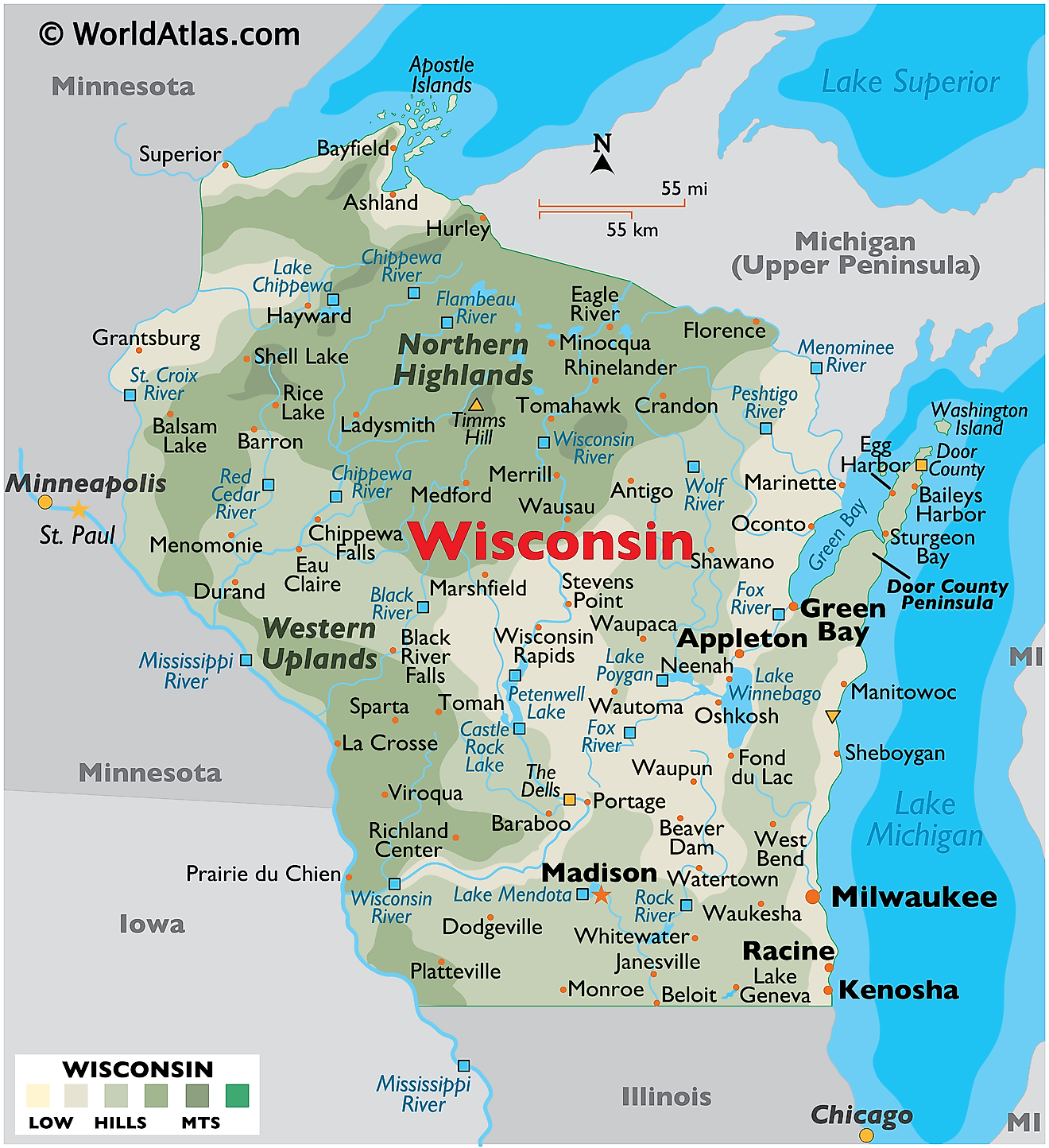
Wisconsin is located in the North Central (also known as the Midwest) region of the United States. Known as "The Badger State" after early prospectors who sheltered in tunnels they mined, it’s also part of the Great Lakes region and is bordered by Lake Superior to the north and Lake Michigan to the east.
The state has over 820 miles (1,320 km) of coastline shared between Lake Michigan and Lake Superior, and over 20% of the state’s land mass lies in the Great Lakes basin. Wisconsin shares borders with four other states: Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Michigan to the northeast, and Minnesota to the west.
Wisconsin’s state capital is Madison, a city with 268,516 residents, and its most populous city is Milwaukee, with a population of 561,385.
The state is home to many tourist attractions, such as the Wisconsin Dells, The House on the Rock, Lambeau Field, Milwaukee Art Museum, and the Apostle Islands National Lakeshore. It became part of the United States on May 29, 1848, as the 30th state.
Wisconsin falls entirely within the Central Time Zone.
Size
Wisconsin covers a total area of 65,496 mi2 (169,640 km2), ranking 23rd in size among the U.S. states. Its land area is approximately 54,167 mi2 (140,291 km2), while its water area covers around 11,329 mi2 (29,349 km2).
By comparison, this makes Wisconsin roughly equal in size to countries like Tunisia or the U.S. state of Georgia. The state spans approximately 310 miles (499 km) from north to south and about 260 miles (418 km) from east to west.
Bodies of Water
Wisconsin contains over 15,000 lakes and more than 84,000 miles (135,184 km) of streams and rivers. Of its many rivers, 13,500 miles (21,726 km) are navigable. The longest of these is the Wisconsin River (a tributary of the Mississippi River), which spans 430 miles (692 km). The Mississippi River also runs along the state’s western border.
The largest lake within the state is Lake Winnebago, covering 137,700 acres. Other significant lakes include Green Lake, Lake Mendota, and Lake Monona.
Notable bodies of water include Lake Superior and Lake Michigan, both forming natural borders. Wisconsin has 19 harbor towns on its Great Lakes shorelines, and more than 1.6 million residents get their drinking water from these two lakes.
Climate
Wisconsin experiences a humid continental climate. The northern region has cold winters and warm summers, while the southern region enjoys slightly milder winters. The average temperature in January is around 15°F (-10°C), and in July, it reaches approximately 70°F (21°C).
While the annual rainfall in Wisconsin averages 34 inches (863 mm), this figure does vary from region to region. The same is true for snow, with annual snowfall levels ranging from 40 to 50 in (101 to 127 cm) depending on the region. Some areas, such as the Vilas County snowbelt, can get up to 125 inches (318 cm).
While hurricanes do not affect Wisconsin, the state can experience thunderstorms, tornadoes, and blizzards. Severe weather events are most common in spring and summer.
Topography
Wisconsin's terrain is diverse and consists of extensive plains, densely forested areas, and rolling hills. The highest point is Timms Hill at 1,951 ft (595 m), located in Price County. The lowest point is along Lake Michigan at 581 feet (177 meters).
While Wisconsin does not have significant mountain ranges or canyons, it does possess interesting topographic features such as the Baraboo Range, a 25-mile long stretch of mountain-like Precambrian rock. The Driftless Area, a plateau untouched by the last glacial period, is characterized by rugged hills, deep river valleys, and karst topography.
Geology
The geology of Wisconsin features ancient rock formations, such as Precambrian crystalline basement rock, which includes granite and quartzite, which are nearly three billion years old. A widespread marine environment during the Paleozoic period 250 to 540 million years ago flooded the region, depositing sedimentary rocks such as limestone and sandstone which now cover most of the central and southern parts of the state.
The state is rich in minerals, notably lead, zinc, copper, and iron ore, the latter especially abundant in the Penokee Range in northern Wisconsin.
Earthquakes are rare and typically minor, with the state lying outside major seismic zones. The glacial activity that started around 100,000 years ago and ended approximately 10,000 years ago significantly shaped the state's landscape, leaving behind an abundance of glacial features such as moraines, drumlins, and kettle lakes.
Natural Environment
Wisconsin hosts a significant diversity of flora and fauna. Prominent tree species include sugar maple, white pine, and birch, which, together with other varieties, cover about 46% of its land area with forests.
Important animal species include white-tailed deer, black bears, and gray wolves. The state is also home to bald eagles, sandhill cranes, and numerous freshwater fish species such as walleye, muskie, and northern pike. Wisconsin's ecosystems range from northern forests to prairie grasslands, wetlands, and shoreline habitats.
The state’s official symbols feature a variety of wildlife, including the American badger (state animal), the robin (state bird), muskellunge (state fish), as well as plants including the wood violet (state flower) and sugar maple (state tree).
Natural Attractions
Wisconsin’s most important natural attractions include Devil's Lake State Park, the most visited with a 360-acre lake and 500 ft quartzite bluffs; Apostle Islands National Lakeshore on the state’s northern tip and overlooking Lake Superior, popular for its sea caves and old-growth forests; and Kettle Moraine State Forest, a heavily glaciated region with over 100 miles of hiking and biking trails.
Other natural attractions include Horicon Marsh; known for its birdwatching, it is home to species including a large population of nesting redhead ducks, American white pelicans, northern harriers, and red-tailed and rough-legged hawks. Copper Falls State Park, which features waterfalls and ancient lava flows, is another notable natural attraction.
Tourist Attractions
Roughly 113 million tourists visit Wisconsin every year, injecting an estimated $25 billion into the state’s economy. Notable tourist attractions include the Harley-Davidson Museum in Milwaukee, home to the legendary motorcycle brand; Frank Lloyd Wright's architectural masterpiece, Taliesin, located in Spring Green; and the historic Circus World Museum in Baraboo.
Other popular sites include the Milwaukee Public Market, the Wisconsin State Capitol in Madison, and the Green Bay Packers Hall of Fame at Lambeau Field. The Wisconsin Dells, known for its waterparks and scenic river tours, attracts millions of visitors annually, while Door County offers quaint villages, cherry orchards, and scenic coastal views.
Geographical Regions
The state of Wisconsin features five distinct geographical regions. These are:
Northern Highland: This region occupies much of northern Wisconsin and is dominated by forests, rolling hills, and thousands of glacial lakes. It is part of the Canadian Shield and includes large tracts of public lands, such as the Chequamegon-Nicolet National Forest. The economy here revolves around forestry, tourism, and outdoor recreation, including hiking, fishing, hunting, and snowmobiling in the winter months. The Northern Highland region is home to the scenic Turtle-Flambeau Flowage and the Vilas County lakes region.
Central Plain: The Central Plain features a mix of agricultural land, forests, and unique sandstone formations. It is well known for its cranberry production, particularly in the Wisconsin Rapids and Warrens areas. The Wisconsin Dells, famous for its dramatic rock formations carved by the Wisconsin River, is one of the state's major tourist attractions. The region is also home to the Necedah National Wildlife Refuge, a significant habitat for migratory birds. The land is relatively flat, making it ideal for farming, with corn, soybeans, and potatoes being the most cultivated crops.
Western Upland: This region is defined by rugged hills, deep river valleys, and limestone bluffs along the Mississippi River. The Driftless Area, a unique unglaciated part of Wisconsin, features dramatic topography that contrasts with the rest of the state. This area is known for its small farms, organic agriculture, and dairy production. Cities like La Crosse and Prairie du Chien sit along the Mississippi River, offering historic attractions and river tourism. The region is a popular destination for hiking, birdwatching, and scenic drives along the Great River Road.
Eastern Ridges and Lowlands: This region stretches along the eastern part of the state and is home to Wisconsin’s largest cities, including Milwaukee, Madison, and Green Bay. The landscape consists of rolling hills and fertile farmland, making it a center for dairy farming and other agricultural industries. Lake Michigan plays a crucial role in moderating the climate of this area. Major cultural and economic centers are located here, including manufacturing, universities, and historic attractions like Old World Wisconsin and the Milwaukee Public Museum.
Lake Superior Lowland: A narrow strip of land bordering Lake Superior, this region has a cool climate and is heavily forested. It is home to the Apostle Islands, known for their sea caves and wilderness areas. The region has historically been important for mining and logging, though today, tourism and outdoor recreation dominate the economy. The city of Superior serves as a gateway to the Great Lakes shipping industry. The area receives heavy snowfall in winter, making it a destination for cross-country skiing and snowshoeing.
Counties Map
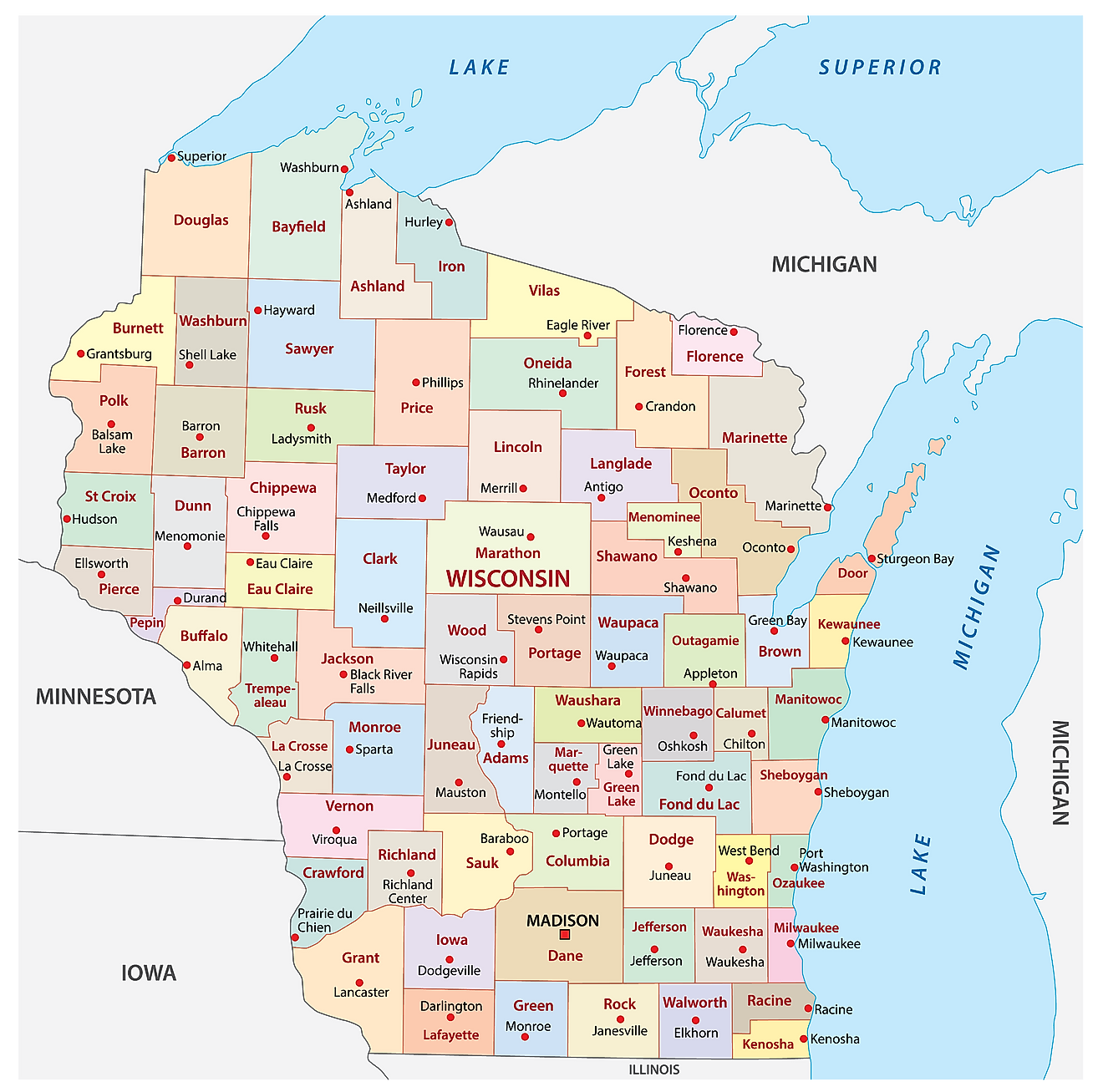
The State of Wisconsin is divided into 72 counties. In alphabetical order, these counties are: Adams, Ashland, Barron, Bayfield, Brown, Buffalo, Burnett, Calumet, Chippewa, Clark, Columbia, Crawford, Dane, Dodge, Door, Douglas, Dunn, Eau Claire, Florence, Fond du Lac, Forest, Grant, Green, Green Lake, Iowa, Iron, Jackson, Jefferson, Juneau, Kenosha, Kewaunee, La Crosse, Lafayette, Langlade, Lincoln, Manitowoc, Marathon, Marinette, Marquette, Menominee, Milwaukee, Monroe, Oconto, Oneida, Outagamie, Ozaukee, Pepin, Pierce, Polk, Portage, Price, Racine, Richland, Rock, Rusk, Saint Croix, Sauk, Sawyer, Shawano, Sheboygan, Taylor, Trempealeau, Vernon, Vilas, Walworth, Washburn, Washington, Waukesha, Waupaca, Waushara, Winnebago, are Wood.
With an area of 169,640 sq.km, Wisconsin is the 23rd largest and the 20th most populous state in the USA. Located in the central region of the southern part of the state is Madison – is the capital city of Wisconsin. It serves as an administrative, educational, commercial, cultural, industrial, and technological center of the state. Situated on the western shores of Lake Michigan is Milwaukee – the largest city in Wisconsin. It serves as the major cultural and economic center of the Milwaukee Metropolitan Area. In 2018, it was named “The Coolest City in the Midwest” by the Vogue Magazine.
Where is Wisconsin?
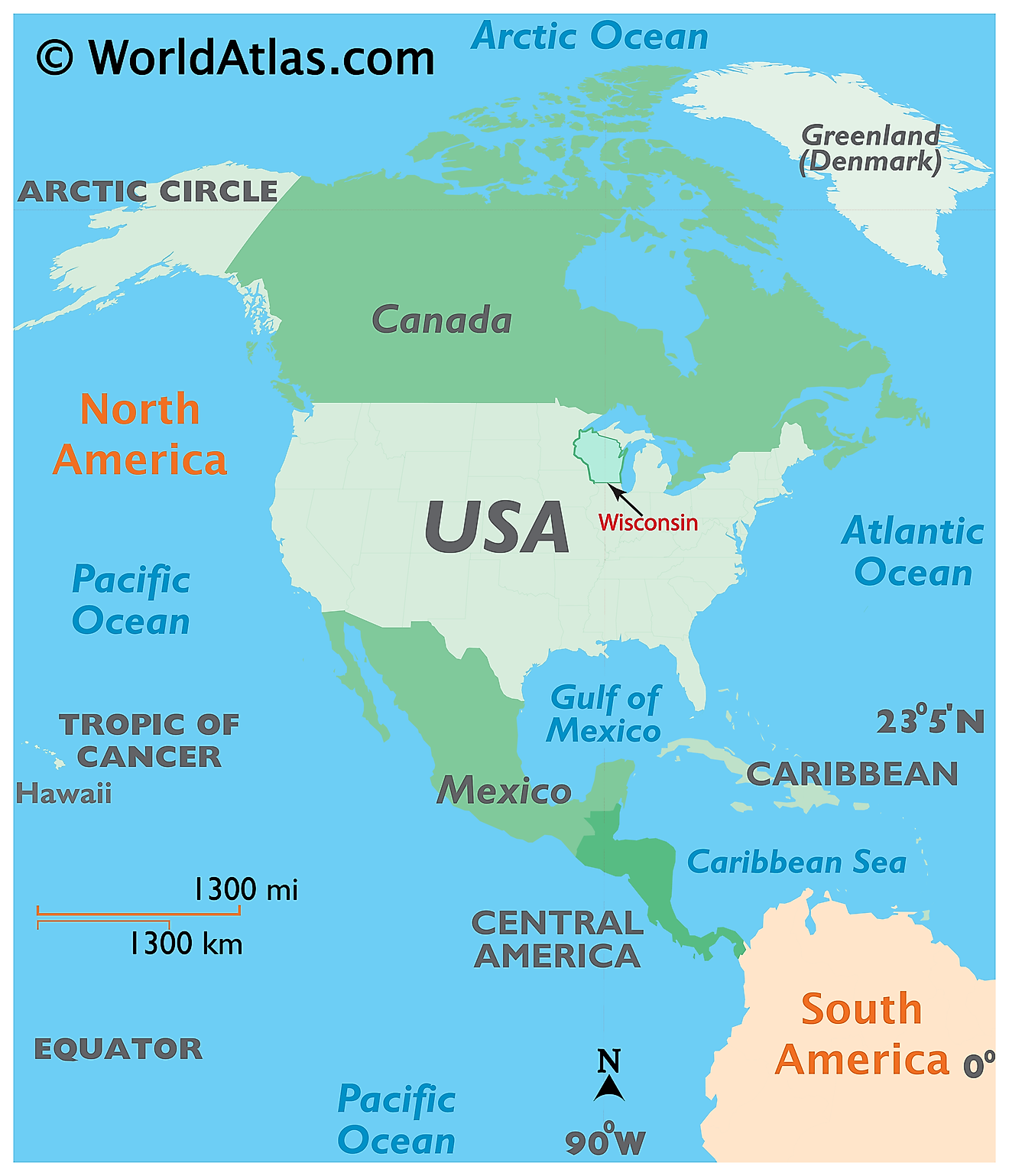
The State of Wisconsin is located in the East North Central (Great Lakes and Midwestern) region of the United States. Wisconsin is bordered by the state of Illinois in the south; by Iowa in the southwest; by Minnesota in the west and by Michigan in the northeast. It is also bounded by Lake Superior in the north.
Regional Maps: Map of North America
Outline Map of Wisconsin
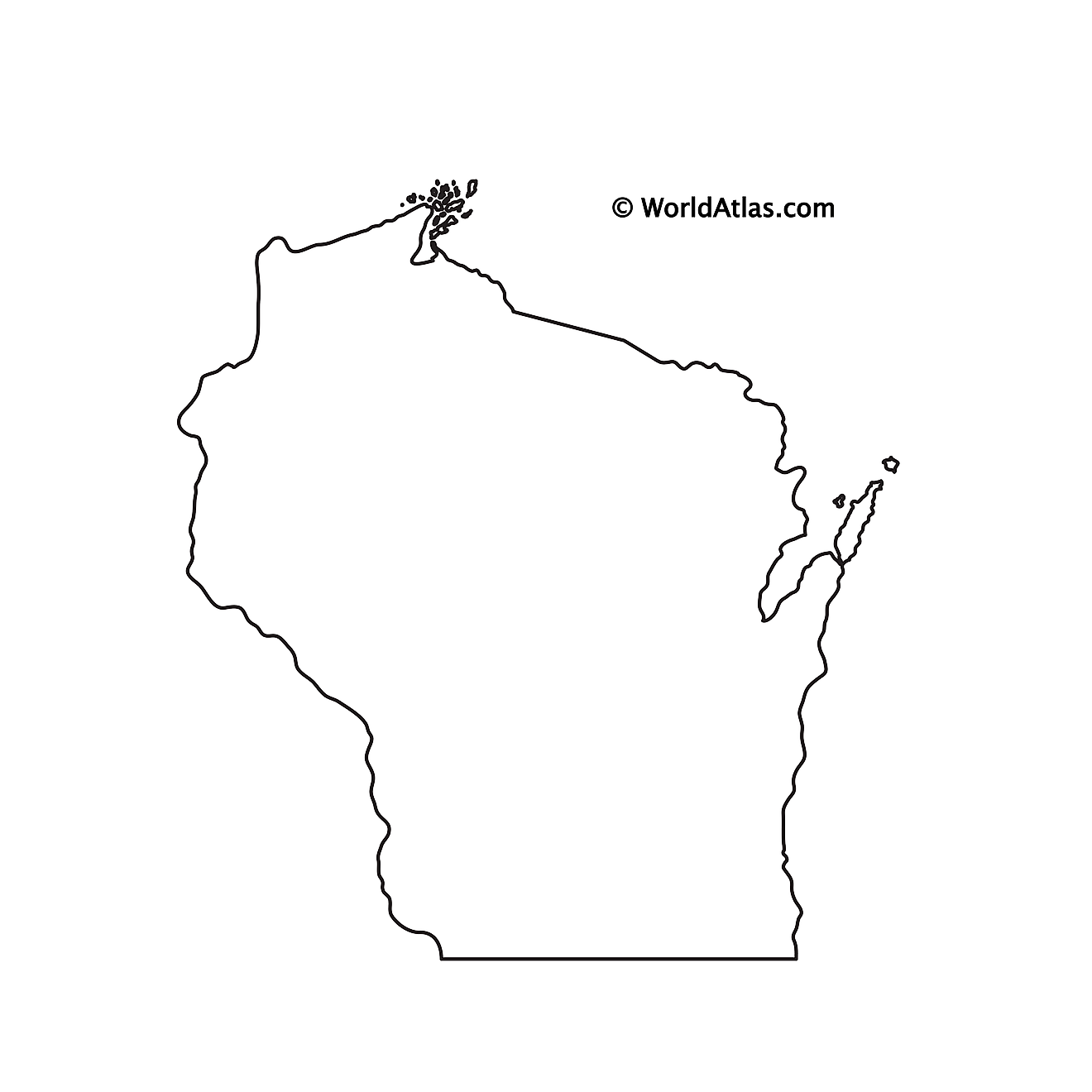
The above blank map represents the State of Wisconsin, located in the East North Central (Great Lakes and Midwestern) region of the United States. The map can be downloaded, printed and used for geography education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.
The above outline map represents the State of Wisconsin, located in the East North Central (Great Lakes and Midwestern) region of the United States. The state has been nicknamed "America’s Dairyland" – as it is one of the nation’s leading producers of dairy products.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | State of Wisconsin |
|---|---|
| ISO 3166 Code | US-WI |
| Capital City | Madison |
| Major Cities |
|
This page was last updated on February 18, 2025











