Maps of Connecticut
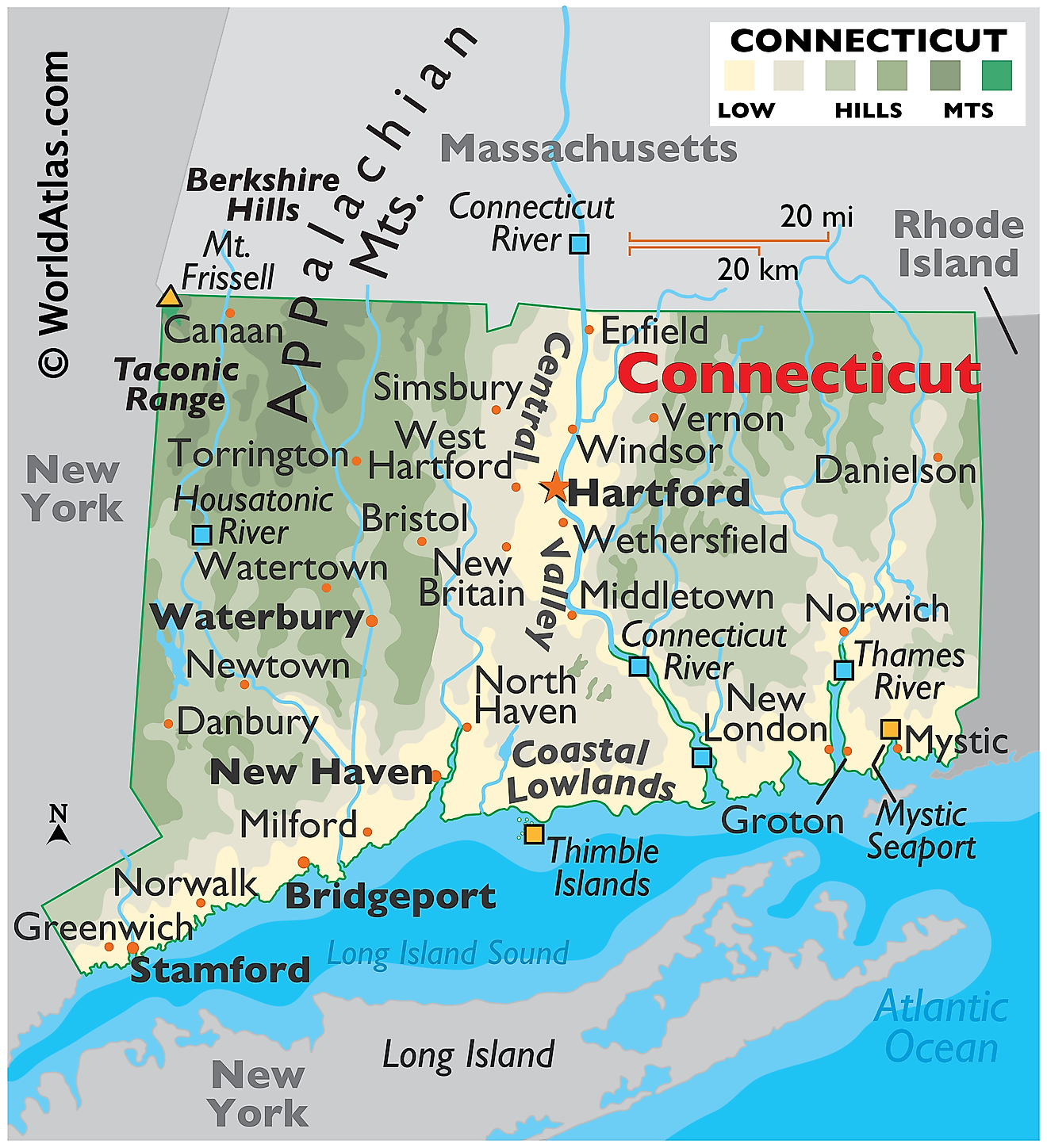
Connecticut, located in the northeastern United States, covers a total area of approximately 5,543 mi2 (14,356 km2). This state shares its borders with New York to the west, Massachusetts to the north, and Rhode Island to the east. Its southern boundary is formed by the Long Island Sound, a tidal estuary of the Atlantic Ocean.
Connecticut, from north to south, is divisible into four primary geographic regions and has additional islands and a number of significant water bodies:
Hudson Highlands: The Hudson Highlands, in the state's northwest corner, encompass the Taconic Mountains and the Berkshire/Vermont Uplands in North central Connecticut. This region is characterized by its rugged terrain and notable elevations, including the state's highest point, Mount Frissell, at 2,380 feet (725 meters) above sea level. The landscape here is marked by steep hills and deep valleys, formed by ancient geological processes. The Taconic Mountains, extending into the Berkshire range, present a series of rolling hills and peaks that provide a distinct contrast to the state's more level regions.
Lower Connecticut River Valley: Flowing through the heart of Connecticut, the Lower Connecticut River Valley cuts a swath through the state. This valley is defined by the Connecticut River, which meanders from the state's northern border to the Long Island Sound. The valley features a mix of forested areas and fertile agricultural lands, benefiting from the rich alluvial soils deposited by the river. This region is also known for its distinctive trap rock ridges, which rise abruptly from the otherwise gently sloping landscape.
Southern New England Coastal Hills and Plains: The Southern New England Coastal Hills and Plains, including the Worcester/Monadnock Plateau in the north-central area, present a varied topography of rolling hills and flat plains. Elevation in this region varies, with higher areas near the Massachusetts border reaching between 500 and 1,100 feet (150 and 335 meters), while the southeastern part ranges from 200 to 500 feet (60 to 150 meters) in elevation. This region's geography contributes to a mix of land uses, including forestry, pastures, and limited agriculture.
Southern New England Coastal Lowland: Along the southern edge of Connecticut lies the Southern New England Coastal Lowland. This narrow strip of land runs parallel to the Long Island Sound, characterized by its relatively flat terrain. The coastline features a series of sandy beaches, rocky bluffs, and saltwater marshes, interspersed with small coves and inlets. The lowland area is predominantly urban and suburban in character, owing to its proximity to the Sound and the ease of transportation and development facilitated by its flat landscape.
Islands of the Long Island Sound: The Long Island Sound hosts several islands which harbor points of interest. For example, the Stewart B. McKinney National Wildlife Refuge sitting on Outer Thimble Island harbors a variety of bird species, with its rocky shores and tidal wetlands. Sheffield Island features a historic lighthouse and a coastline that serves as a nesting area for birds. Faulkner's Island, also home to a historic lighthouse, acts as an important habitat for migrating birds. The Thimble Islands, a group of small islands, display landscapes shaped by glacial activity, combining residential areas with natural environments.
Major Bodies of Water: Connecticut's geography is further defined by its numerous rivers and lakes. Besides the prominent Connecticut River, other significant rivers include the Housatonic, Thames, and Quinnipiac. These waterways have played a crucial role in shaping the state's geography, ecology, and history. Connecticut also boasts several large lakes, such as Candlewood Lake, the largest in the state, and Lake Lillinonah, both contributing to the state's water resources and recreational opportunities.
Counties Map
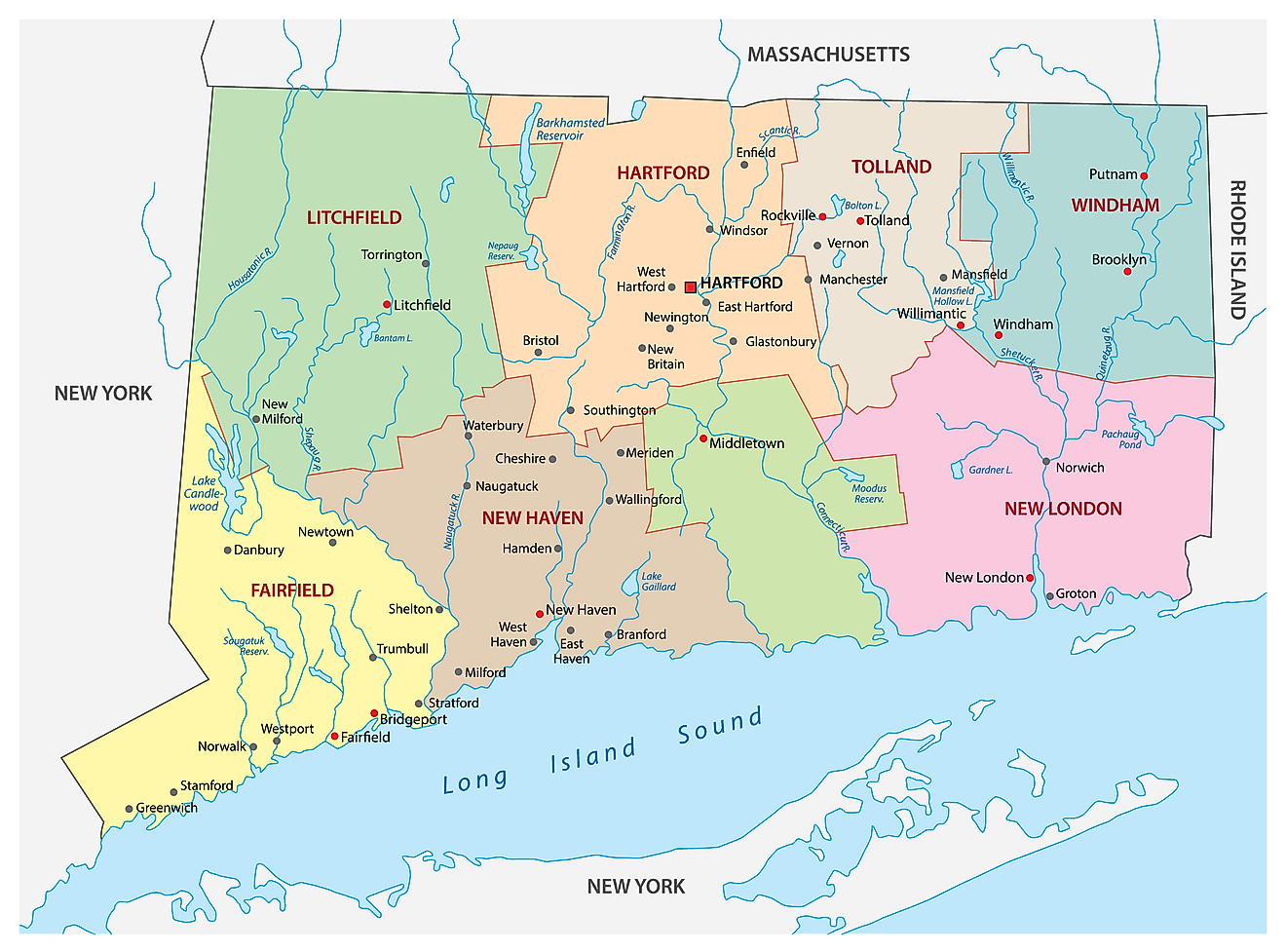
The State of Connecticut is divided into 8 counties. In alphabetical order, these counties are: Fairfield, Hartford, Litchfield, Middlesex, New Haven, New London, Tolland, and Windham.
With an area of 14,357 sq. km, Connecticut is the 3rd smallest, 29th most populous, and the 4th most densely populated state in the USA. Located in the north-central part of the state, on the banks of the Connecticut River is Hartford – the capital and the 4th largest city of Connecticut. It serves as a major port, industrial, financial and commercial center of the state. Due to the presence of numerous insurance company headquarters in Hartford, it is often referred to as the “Insurance Capital of the World”. Situated in the southwestern part of the state, in the Fairfield County is Bridgeport - the largest and the most populous city of Connecticut. Currently, St. Vincent’s Medical Center and the Bridgeport Hospital are the largest employers in Bridgeport.
Where is Connecticut?
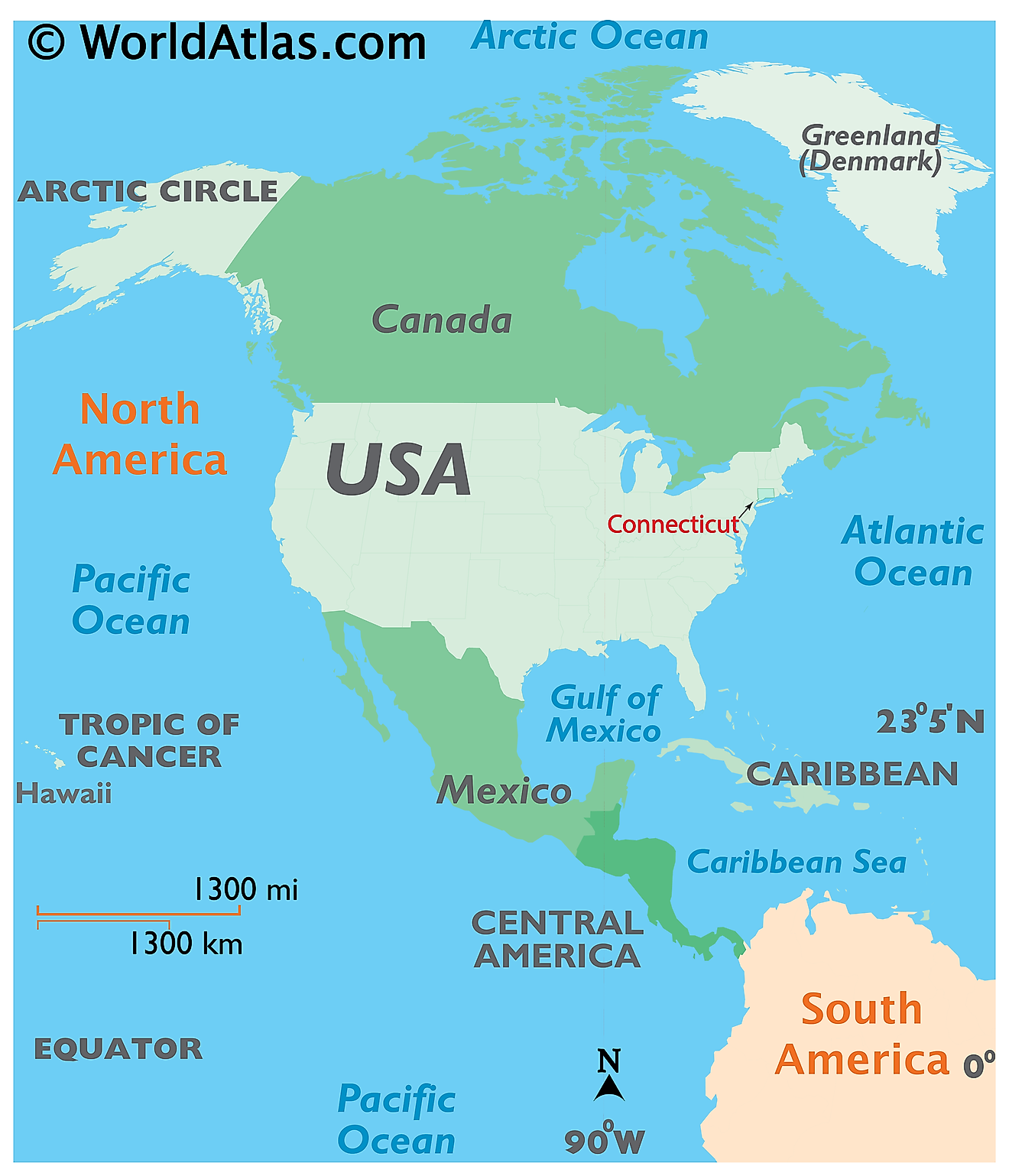
The State of Connecticut is located in the north-eastern (New England) region of the United States. Connecticut is bordered by the state of Massachusetts in the north; by Rhode Island in the east; by New York in the west and by Long Island Sound and the Atlantic Ocean in the south.
Regional Maps: Map of North America
Outline Map of Connecticut
The above blank map represents the State of Connecticut, located in the north-eastern (New England) region of the United States. The above map can be downloaded, printed and used for geography education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.
The above outline map represents the State of Connecticut, located in the north-eastern (New England) region of the United States. Connecticut is roughly rectangular in shape and is colloquially known as the Constitution State, Nutmeg State, the Provisions State and the Land of Steady Habits.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | State of Connecticut |
|---|---|
| ISO 3166 Code | US-CT |
| Capital City | Hartford |
| Major Cities |
|
This page was last updated on January 18, 2024











