Maps of Wyoming
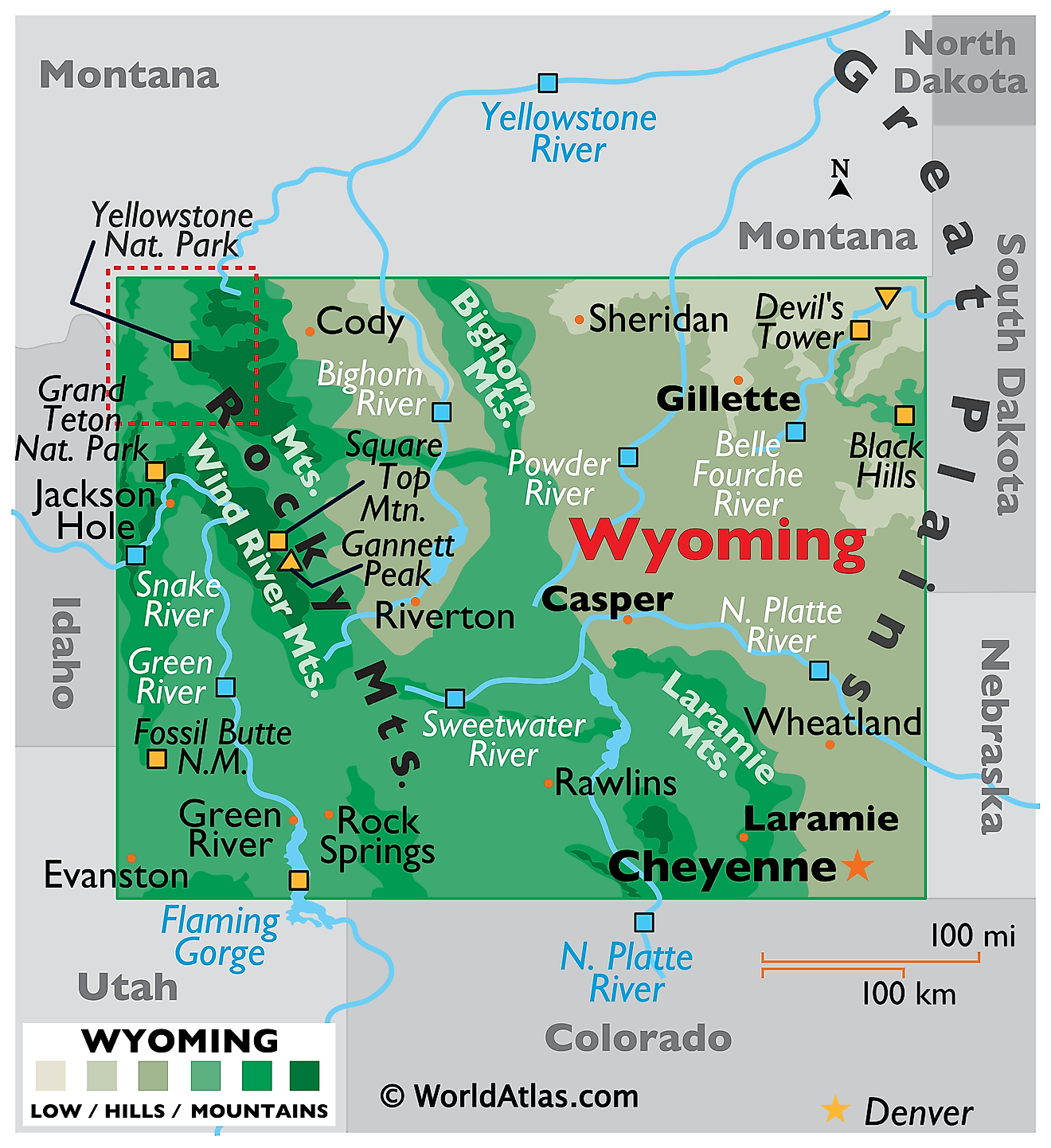
Wyoming is a western US state that shares its northern border with Montana, its eastern border with South Dakota and Nebraska, its southern border with Colorado and Utah, and its western border with Idaho.
Cheyenne is both the state’s capital and most populous city, located in Wyoming’s southeast, with a population of around 65,000 people.
Before the arrival of the Europeans, Indigenous tribes resided on the land that is now Wyoming for thousands of years, just a few including the Arapaho, Cheyenne, Sioux, Shoshone, and Ute tribes. John Colter, part of the Lewis and Clark expedition, was the first recorded American to enter the area of Wyoming in 1807. It would take over 80 more years before it became a state in 1890, joining the Union as the 44th state.
Area
Wyoming has a total area of 97,813 square miles (253,335 square kilometers) making it the tenth-largest state in the country. It is slightly bigger than the United Kingdom and roughly half the size of Spain. Compared to other US states, Wyoming is twice the size of Mississippi and four times bigger than West Virginia.
Bodies of Water
Of Wyoming’s total area, only 720 square miles (1865 square kilometers) are water. It has about 108,767 miles (175,044 kilometers) of river, with some of the most notable rivers including the Snake River, flowing through western Wyoming, the Green River, flowing through Western Wyoming before entering Utah, and the North Platte River, flowing through southeastern Wyoming through the Medicine Bow Mountains. There are over 4,000 lakes and reservoirs in the state. Yellowstone Lake is the largest natural body of water, 20 miles (32 kilometers) long and 14 miles (23 kilometers) wide, and is located in the northwest.
Geographic Regions
Three distinct regions represent Wyoming’s physical geography: The Great Plains, The Rocky Mountains, and The Intermontane Basins.
The Great Plains
The Great Plains represents the eastern portion of Wyoming, predominantly home to shrubs and short grasses. This area is also home to the Black Hills, where Devils Tower National Monument—an igneous rock butte rising to 5,112 feet (1,558 meters)—stands.
The Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, running from north to south, are primarily in the western and central parts of the state. The elevation is much higher here than in other areas, with the state’s highest point, Gannett Peak, at 13,810 feet (4,210 meters) in this section. Both Grand Teton National Park and Yellowstone National Park are in the Rocky Mountains area of Wyoming as well.
The Intermontane Basins
The Intermontane Basin region lies between Wyoming’s mountain ranges, with short grasses, sedimentary rocks, and few trees. The Red Desert, the country’s largest living dune system, is in this area, as well as the Bighorn Basin.
Counties Map
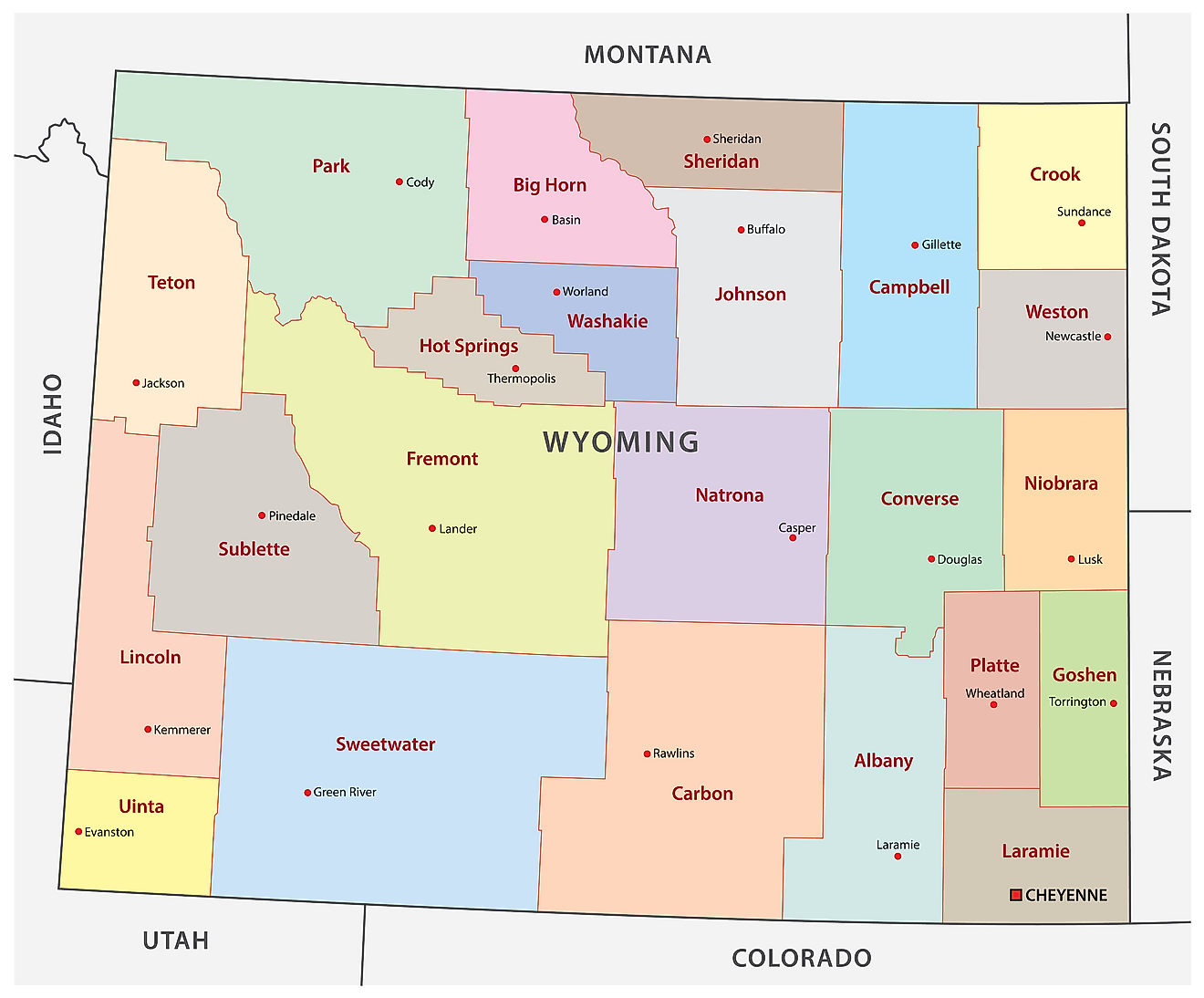
The State of Wyoming is divided into 23 counties. In alphabetical order, these counties are: Albany, Big Horn, Campbell, Carbon, Converse, Crook, Fremont, Goshen, Hot Springs, Johnson, Laramie, Lincoln, Natrona, Niobrara, Park, Platte, Sheridan, Sublette, Sweetwater, Teton, Uinta, Washakie, and Weston.
With an area of 253,600 sq.km, Wyoming is the 10th largest and the least populous state in the USA. Located in the southeastern corner of the state on Crow Creek is, Cheyenne – the capital, the largest and the most populous city of Wyoming. Tourism, government services, transportation and manufacturing industries are the main drivers of the city’s economy. Cheyenne is also one of the country’s least centrally located state capitals.
Where is Wyoming?
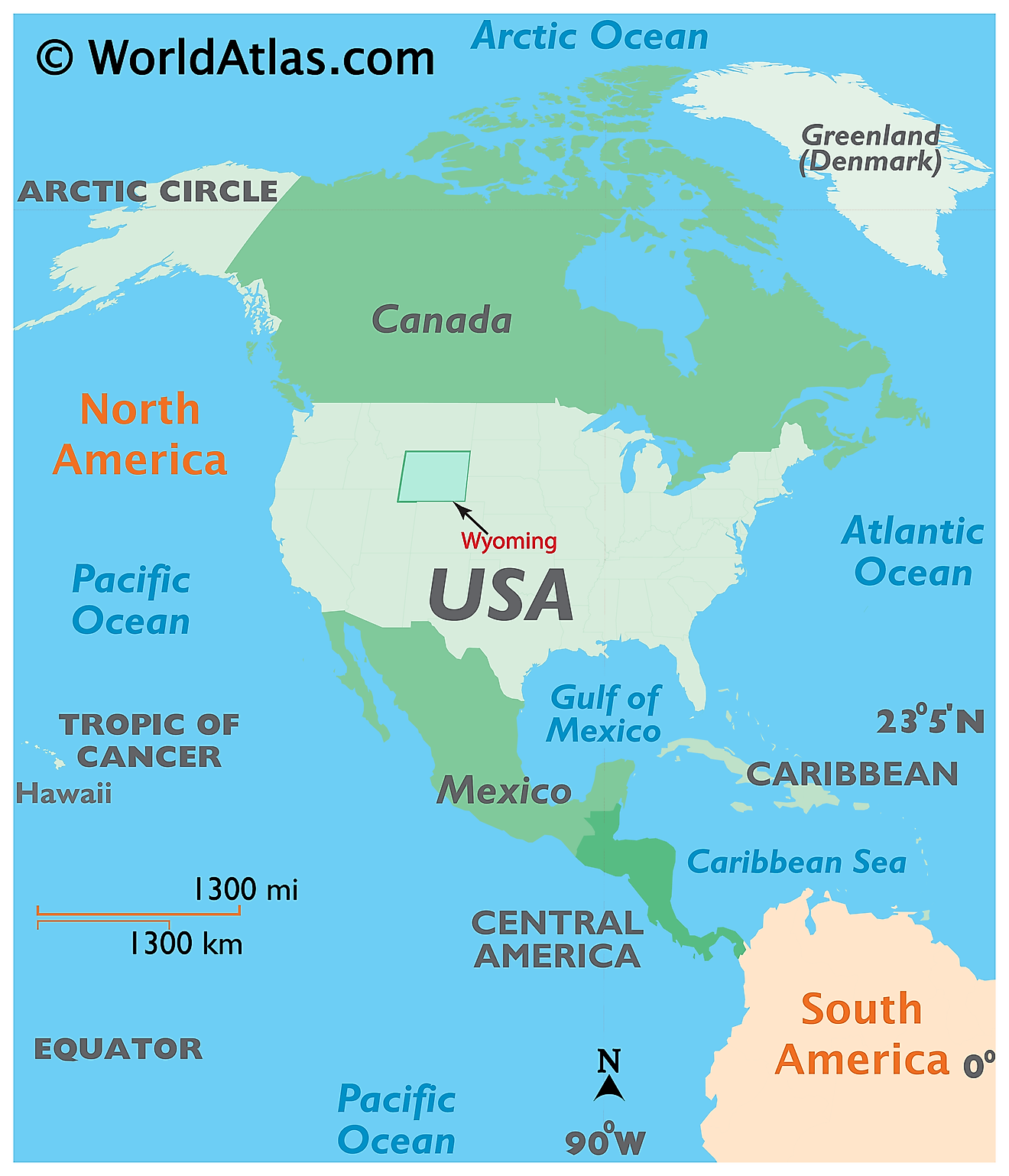
The State of Wyoming is located in the west-central (Mountain States area) region of the United States. The landlocked state of Wyoming is bordered by the states of Utah in the southwest, by Idaho in the west; by Colorado in the south, by South Dakota and Nebraska in the east; and by Montana in the north and northwest.
Regional Maps: Map of North America
Outline Map of Wyoming
The above blank map represents the State of Wyoming, located in the west-central (Mountain States area) region of the United States. The above map can be downloaded, printed and used for geography education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.

The above outline map represents the State of Wyoming, located in the west-central (Mountain States area) region of the United States.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | State of Wyoming |
|---|---|
| ISO 3166 Code | US-WY |
| Capital City | Cheyenne |
This page was last updated on August 29, 2024











