Maps of Guyana
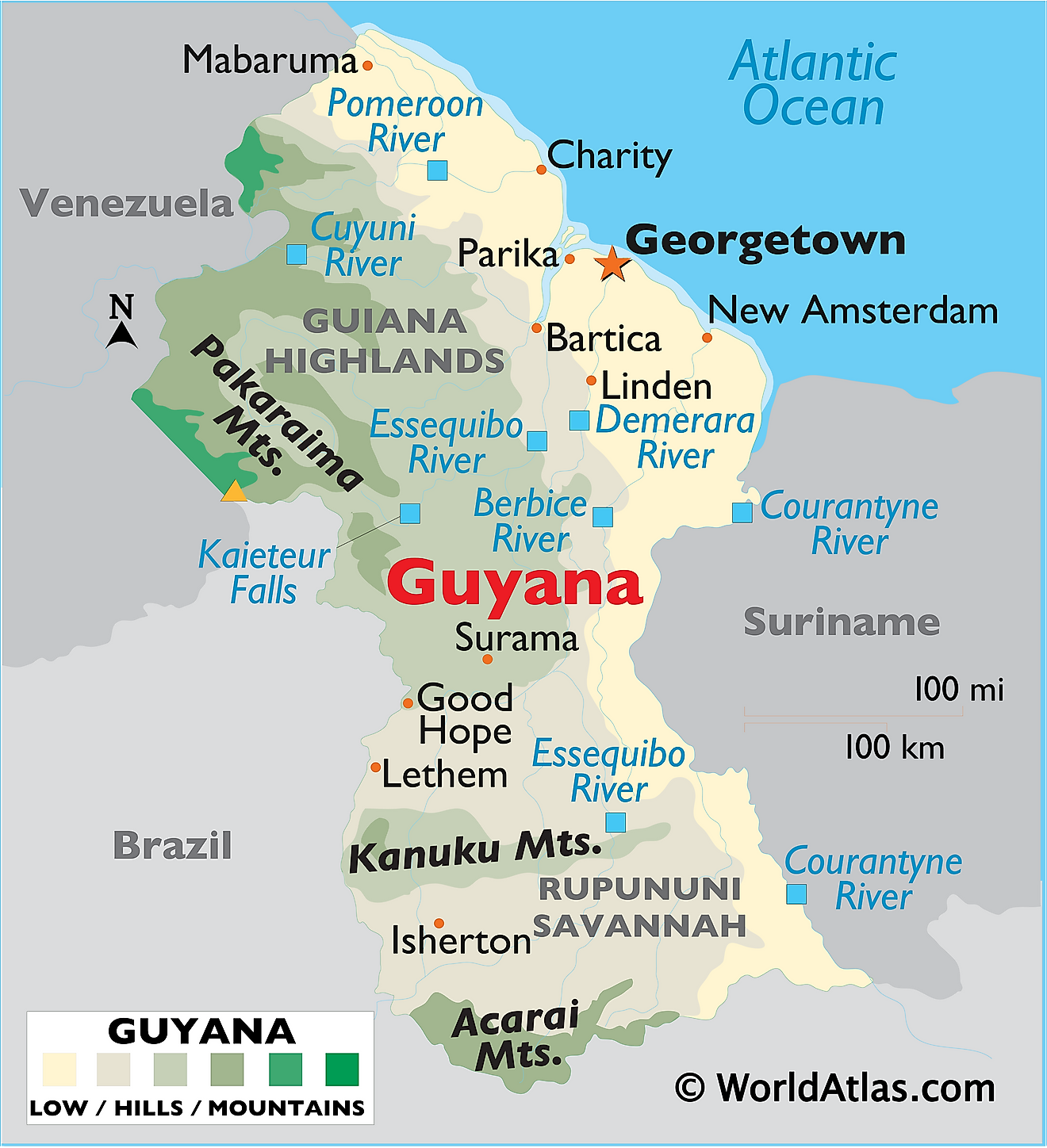
Covering an area of 215,000 sq. km, Guyana is located on the northern edge of South America. Guyana borders three other nations and is the 3rd smallest nation in South America. Suriname sits to the east, Brazil to the south, and Venezuela to the west. Guyana can be divided into four main geographical regions: there's a narrow and swampy coastal plain, a hillier sandy region in the east, the (15,000 sq. km) Rupununi Savannah of the south; and the tropical rain forests and interior highlands - central and west.
The Pakaraima Mountains, Kanuku Mountains, and Acarai Mountains can be observed on the map above. These ranges straddle the southern and western borders of Guyana. Many of these relatively low mountains are fronted by steep cliffs and include several waterfalls. The massive spectacular Kaieteur Falls is 251 meters (822 ft) in height and is one of the most powerful waterfalls in the world. It is about five times higher than Niagara Falls, and about two times the height of Victoria Falls. Situated in the Pakaraima Mountains, at the tripoint border of Brazil-Guyana-Venezuela is - Mount Roraima at 2835m, which is the highest point in Guyana (as marked on the map by an upright yellow triangle). The lowest point is the Atlantic Ocean (0m).
The Essequibo River remains the largest in the nation. The Berbice, Courantyne, and Demerara are also important waterways for Guyana. Some of these rivers flow in a northerly direction and drain into the Atlantic Ocean, while those in the western parts of the country generally flow east into the Essequibo.
The rainforests in Guyana are some of the most remote and hard-to-reach places in the world. These can be found in the western portion of the nation near the Pakaraima Mountains. All manner of exotic animals call this place home. Thanks to its remarkable lack of infrastructure and treacherous environment, little to no humans live here let alone make a trip to this part of Guyana.
Regions of Guyana Map
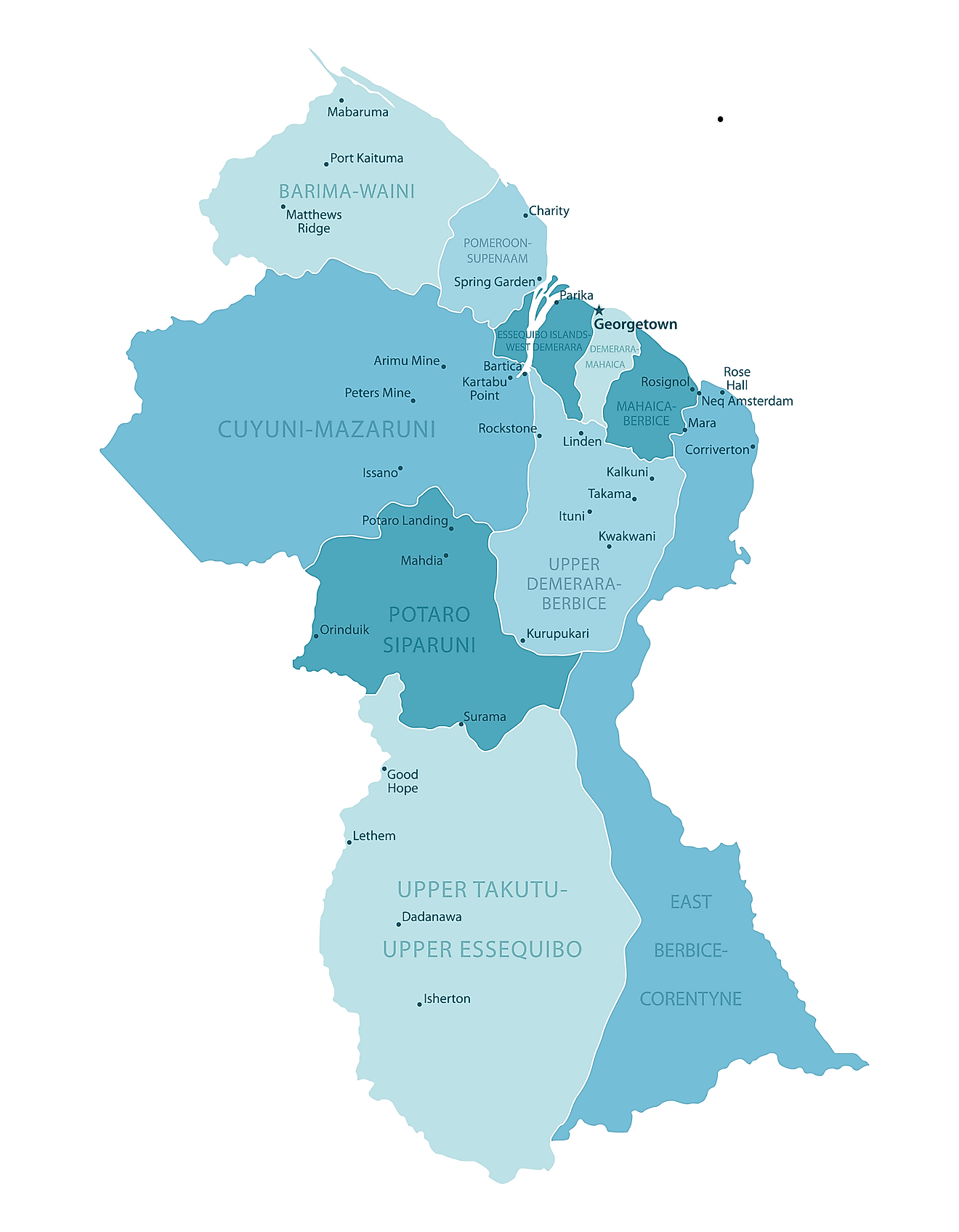
Guyana (Officially, the Co-operative Republic of Guyana) is divided into 10 administrative regions: Barima-Waini, Cuyuni-Mazaruni, Demerara-Mahaica, East Berbice-Corentyne, Essequibo Islands-West Demerara, Mahaica-Berbice, Pomeroon-Supenaam, Potaro-Siparuni, Upper Demerara-Berbice, and Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo. These regions are further subdivided into a total of 27 neighborhood councils.
Covering an area of 215,000 sq. km, Guyana is South America’s 3rd smallest nation. Located in the Demerara-Mahaica region, at the mouth of the Demerara River on the Atlantic coast is Georgetown - the capital and largest city of Guyana. It is the principal administrative center and also serves as the chief seaport and the main commercial and manufacturing centers of Guyana.
Where is Guyana?
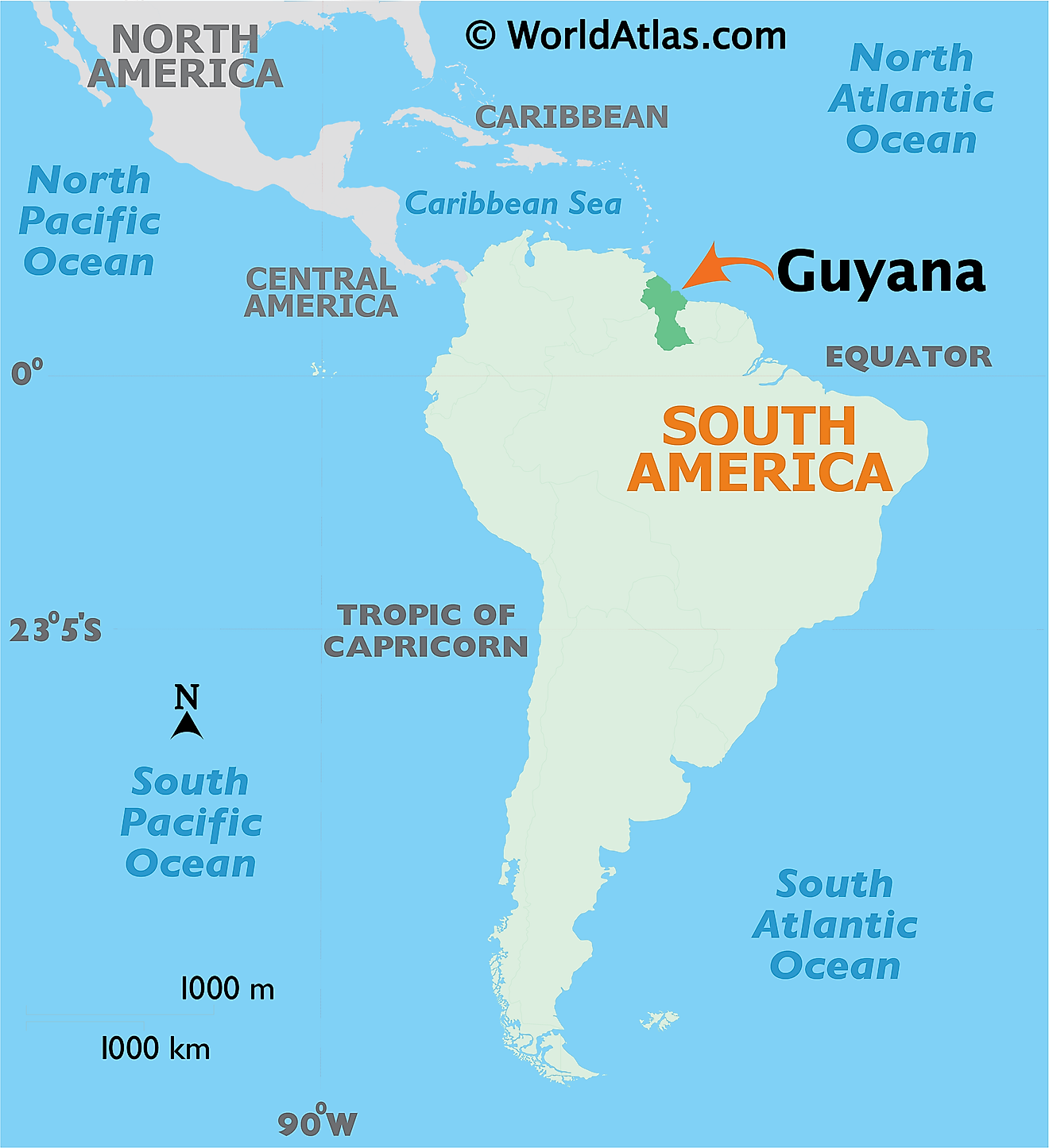
Guyana is a country located on the northern edge of South America. It is geographically positioned both in the Northern and Western hemispheres of the Earth. Guyana is bordered by Suriname to the east; by Venezuela to the west; by Brazil to the south and southwest; and by the Atlantic Ocean to the north. Guyana shares its maritime borders with Barbados and Trinidad and Tobago.
Guyana Bordering Countries: Brazil, Suriname, Venezuela.
Regional Maps: Map of South America
Outline Map of Guyana
The above blank map represents Guyana, a small country located on the northern edge of South America. The above map can be downloaded, printed and used for geography education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.
The above outline map represents Guyana, a small country located on the northern edge of South America. It is also South America’s 3rd smallest nation.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Cooperative Republic of Guyana |
|---|---|
| Flag |

|
| Capital City | Georgetown |
| 6 48 N, 58 09 W | |
| Total Area | 214,969.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 196,849.00 km2 |
| Water Area | 18,120.00 km2 |
| Population | 782,766 |
| Currency | Guyanese dollars (GYD) |
| GDP | $4.28 Billion |
| GDP Per Capita | $5,468.36 |
This page was last updated on December 13, 2023











