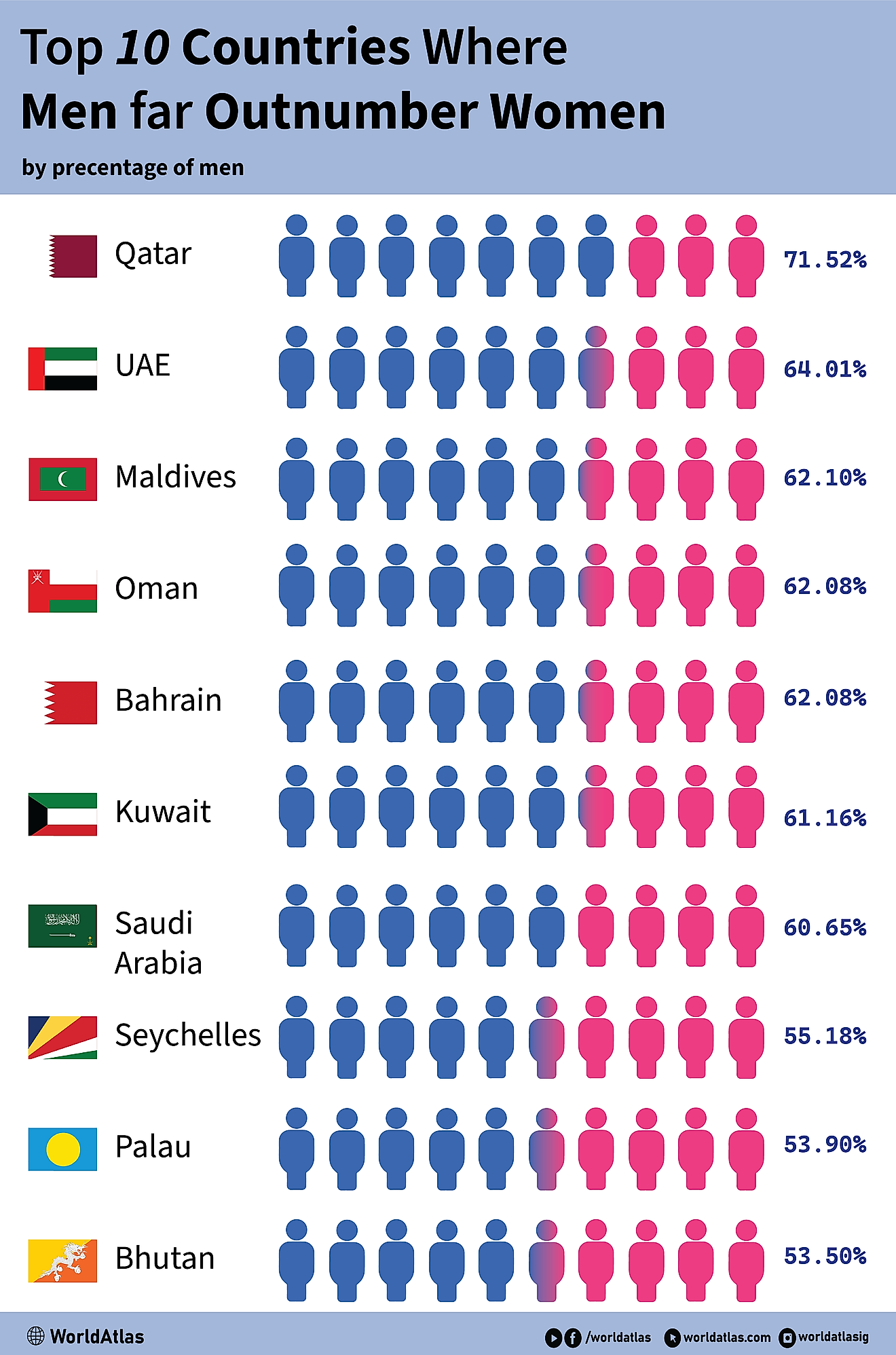
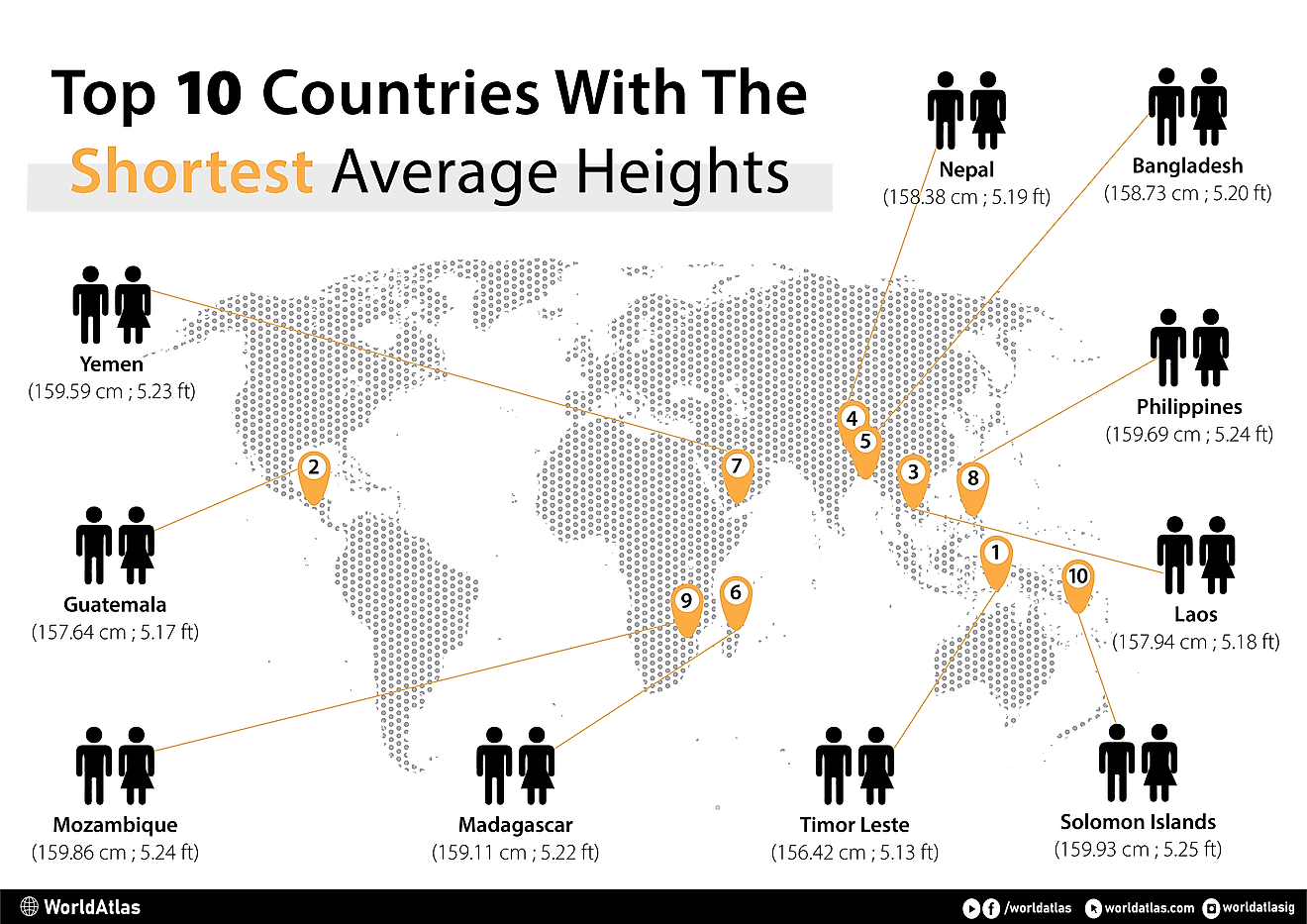
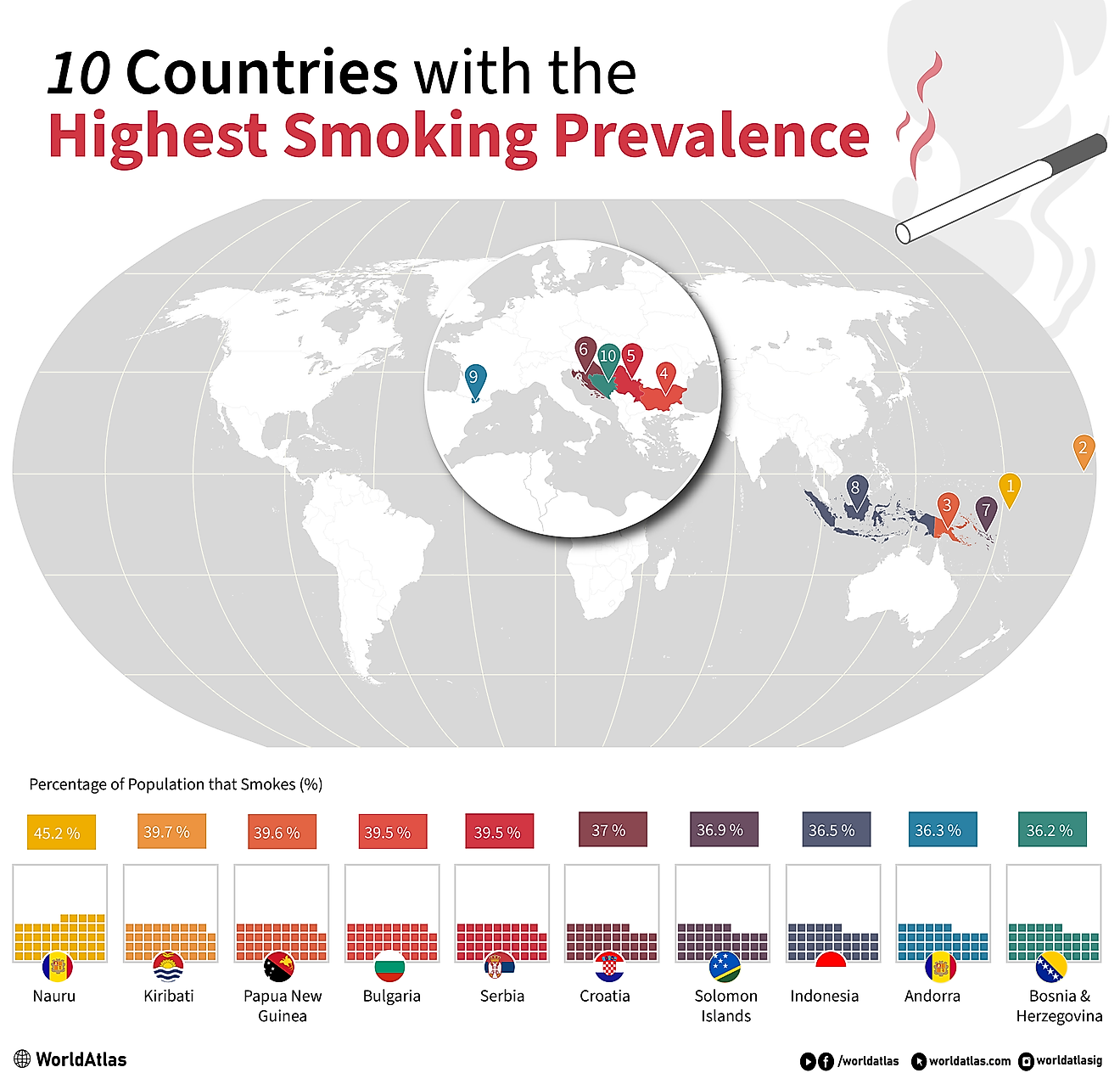
What is Autarky?

Nations all over the world depend on each other for resources. Each country obtains what it does not have by importing and exporting the excess goods to other nations. For example, Arab countries that have plenty of oil export it to other countries and import fruits in exchange. However, some countries have in the past pursued what is called autarky.
What is Autarky?
Autarky is a condition of being self-sufficient in which a country survives without engaging in any international trade. Autarky is not only about an economic occurrence, it can also apply if an entity that function without any external assistance, for example, military autarky is when soldiers defend their country with no outside help. The application of this policy by country has been an attempt to reduce dependence on other nations.
Autarky has been used by a group of individuals particularly the left-wings for instance, Communist, Populist, and Syndicalist. Also, it was adopted by nationalists and conservative in a limited manner.
Autarky can be a policy of either a state or any entity at any time when one seeks to be wholly self-sufficient. Moreover, it can also be restricted to a smaller sector for example when a country works to feed its citizen without importing foodstuffs from outside.
Origin of the Term
Before we look at the extensive history of the term autarky, it is important to trace its origin. Autarky came from the Greek word autarkeria which means “sufficiency in oneself" especially in regards to independence. The term autarkeria is an extension of the word autarkes from auto “self” put together with arkein which means “to ward off” or “keep off.”
Autarky Throughout History
During the earliest societies, palace economists and nomadic pastoralists were perceived to practice a form of autarky, but with time, they moved towards inter-connected society. By the late Bronze Stone Age, most of the self-sufficient palaces were relying so much on trade for their economic survival. This dependence has been attributed to collapse of the Bronze Age governments when all were faced by multiple problems at once and could not been in position to help each other.
Autarkic practices were also seen in communist countries in which the government of those nations pushed for the economic self-sufficiency by establishing common resources and land under the supervision of the state. These lands and resources were used for mutual defense against the predatory attacks of the local. Despite their strict adherence to the policy, most of these communist nations later became the most recognized trading power in the world, for example, Hanseatic League.
Also, some autarkic desires were observed in the backlash from populist towards exploitation of open trade in the nineteen centuries. Some of the mutual societies like Sovereigns of Industry and Grange attempted to establish self-sufficient economies with little success. These societies have wished to create a less dependent economy in what they had perceived to be an exploitative system and to have powerful governments that can advocate for better reforms.
The socialist institutions such as Bourse du Travail used autarkic policies to create their bases. They did this by building their food assistance systems and canteens. Other socialist movements secured the loyalty of their employees, something that enabled them to establish strong institutions, particularly in Europe between 19th and 20th centuries. Through such institutions, employees went to Socialist schools, bought goods from Socialist canteens, and went for a vocation in the Socialist places.
The right-wing autocratic governments that had earlier claimed to pursue autarkic policies chose to engage in a totally different strategy, the same way they claimed to support socialism while at the same time murdering the socialists. Also, the Italian Fascists in 1921 raided the remaining left-wing autarkic developments and destroyed a large proportion of their projects. The same spirit was seen in the Nazi Germany under the guidance of the Hjalmar Schacht who was the then economics minister. The minister claimed to work towards the state of self-sufficient while still pursuing international trade though secretly to avoid conflict with the Treaty of Versailles’ terms. By 1939, Germany was self-sufficient in sugar, potatoes, and bread; however, some foodstuffs were still being imported. To ensure that it was fully self-sufficient, ‘autarky’ in regards to food, Hitler saw the need to conquer other countries for raw materials and food. He set his plan on how to wage war to gain more territories. Despite its effort, Germany lost the few resources it had and the road to defeat began. The German soldiers experienced a shortage of resources occasioned by territory lost.
Currently, few countries still pursue autarkic policies and at the same time trade with those nations they have mutual benefits. An example of these nations is North Korea that based its ideologies on what it is called Juche, “self-sufficiency.” It pertains maintenance of the country's domestic economy. Nevertheless, North Korea engages in extensive trade with other nations such as China, Iran, Russian, and Vietnam among other countries in Africa and Europe.
Recently, there has been a lot of debate on whether or not ‘Brexit’ is a form of autarky. Many leaders around the world have expressed their different opinions.
Is ‘Brexit’ a Form of Autarky?
The debate among the British citizens on whether their country should leave the European block or not gathered the pace during campaigns. Those who were against it saw it as a return of autarky. As the Britain approached the day of voting, many economists had warned about the devastating effects the “Brexit” would have on the country economy. They estimated that at least every household would lose $6,000. Although the negotiation is still on-going, those who had warned have said that the country pound is depreciating, and the overall monetary sector is facing uncertain future.
Criticism of Autarky
A policy like autarky that restricts a country to its domestic economy and locking out other world nations was believed to ultimately lead to economic damage. To outline the criticism, we will look at the application of autarky in North Korea and what critique was said about it.
North Korean once practiced the Juche (self-sufficiency) ideology that the government has called the original and revolutionary idea of Kim II-sung. The ideology advocated for the citizens to be master of their country. Brian Reynolds Myers voiced his criticism that the idea was created to deceive foreign nations and it is just there to be said and not read. It is reported that the move towards socialism, together with international sanctions has impoverished the North Korea citizens and occasioned food shortage.