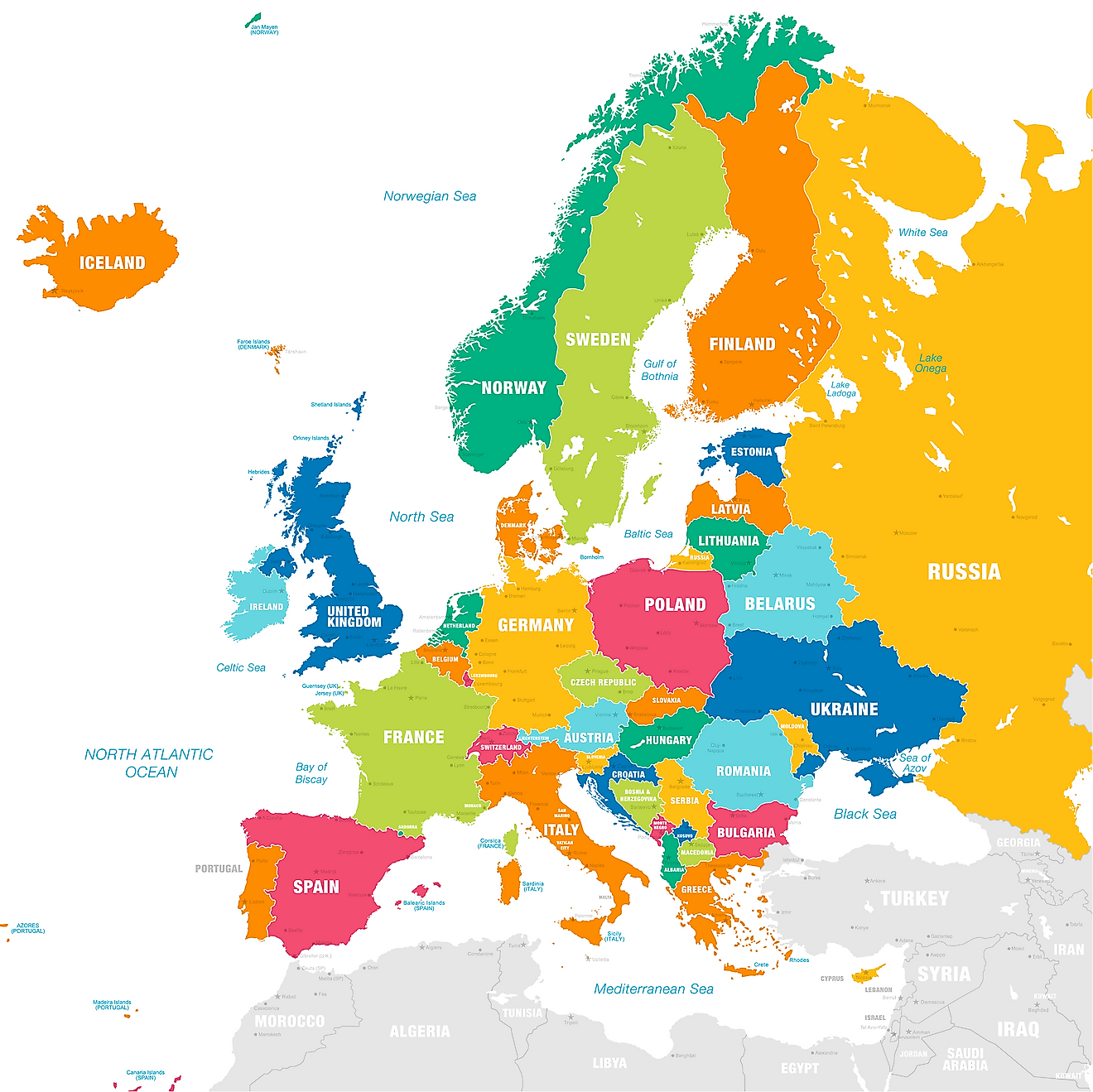
Scandinavian Countries

- Scandinavia is a region in northern Europe. It consists of 3 countries, Denmark, Norway, and Sweden.
- The term "Nordic Countries" includes the countries of Scandinavia, as well as Finland and Iceland.
- All 3 Scandinavian countries are constitutional monarchies and parliamentary democracies.
Scandinavia is a region of northern Europe. It consists of three countries, Denmark, Sweden, and Norway. The Faroe Islands, which lie to the north of the U.K., and Greenland, which is located to the east of northern Canada, are also considered part of Scandinavia from a political perspective, since they are both territories controlled by Denmark. The countries of Scandinavia are also part of the larger group of countries known as the Nordic countries, which includes the region of Scandinavia, Finland, and Iceland.
Contents:
Denmark

The Kingdom of Denmark consists of the Jutland Peninsula, which lies on Germany’s northern border, and an archipelago of 440 islands. The country’s capital, Copenhagen, is situated on the east coast of one of the archipelago’s larger islands, known as Zealand. The coastline of Denmark comprises a total of 7,300 km. Denmark’s total land area is 42,430 sq. km. To the east of Denmark, across the Oresund and Kattegat Straits, is Sweden. To Denmark’s north, across the Skagerrak Strait, is Norway. The North Sea and the Baltic Sea are located west and east of Denmark respectively.

Denmark is a country of approximately 5.8 million people. The largest cities in the country are the capital, Copenhagen, Arhus, which is situated on the east coast of the Jutland Peninsula, and Odense, located on the island of Funen. Around 86% of Denmark’s population is considered ethnically Danish, though this figure also includes people from Greenland, who are mainly Inuit, and Faroese from the Danish-controlled Faroe Islands.
Denmark is a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy. The Danish monarch is the ceremonial head of state. The Danish government is headed by a prime minister and cabinet. The country’s parliament is known as the Folketing. Elections to the Folketing are held at least every four years under an electoral system of proportional representation, where a party’s percentage of votes roughly equals the proportion of that party’s seats in the Folketing. Normally, no one party gets a majority in the Falketing, so coalition governments consisting of two or more parties are often formed.

The Falketing includes two seats each reserved for representatives of Denmark’s overseas territories, the Faroe Islands and Greenland. The Faroe Islands are an archipelago of 18 islands. Its population is approximately 49,000. The people of the islands, known as the Faroese, speak a distinct dialect of Danish, known as Faroese Danish. Most of Greenland’s population of just under 57,000 is of Inuit heritage, and are related to the Inuit of northern Canada. Both the Faroe Islands and Greenland have their own self-governing institutions that manage the territories’ internal affairs, though some in both territories seek outright independence from Denmark.

The Danes have their own unique way of life, which they often call “hygge”. Though there is no specific translation for this term, it generally means being at ease and living life to the fullest. The Danes are also known for their fondness for bicycles. In fact, Copenhagen is often known as the first bike city in the world. In 2016, Copenhagen was voted the best city in the world for cycling. Indeed, cycling is so popular in Denmark that 9 out of 10 Danes own a bicycle.
Sweden

The Kingdom of Sweden is situated between Norway to the west and Finland to the east. Denmark lies across the Oresund and Kattegat Straits to the west and south. The Gulf of Bothnia also separates most of Sweden from Finland. Sweden’s total land area is 410,340 sq. km, making it the largest country in Scandinavia. The total population of Sweden is about 10.1 million, of which around 80% are ethnic Swedes. The largest city in Sweden is its capital, Stockholm, which has about 1.5 million residents. Other large cities include Goeteborg and Malmoe.

Sweden is a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy. The Swedish monarch is the ceremonial head of state, while the government is headed by a prime minister and cabinet. The Swedish parliament, called the Rikstag, consists of 349 members elected to 4 year terms. Like Denmark, Sweden uses a system of proportional representation to elect members of its parliament.

The Swedes have a name for their own way of living, lagom. In fact, this term was created in response to the Danish term, hygge. In the Swedish language, the word lagom means not too much, not too little, just right. In other words, the Swedes prefer to keep a balance in every aspect of their lives. This includes being positive, getting enough exercise, getting enough sleep, living sustainably, living simply, and not being too perfectionist.
Norway

The Kingdom of Norway is situated to the west of Sweden. Denmark lies to Norway’s south, across the Skagerrak Strait, while the aptly named Norwegian Sea lies off Norway’s western coastline. Norway’s total land area is 365,268 sq. km. The country’s total population is about 5.45 million, which makes Norway the least populous country in Scandinavia. Approximately 83% of Norway’s population is ethnic Norwegian. This includes the Sami, another population indigenous to the country. Norway’s largest population center is its capital city, Oslo. Other large Norwegian cities include Bergen, Trondheim, and Stavanger.

Like Denmark and Sweden, Norway is a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy. The Norwegian monarch is the ceremonial head of state, while the government is headed by a prime minister and cabinet. Norway’s parliament is known as the Storting, and is composed of 169 members, elected to 4 year terms. Like Denmark and Sweden, Norway also uses a system of proportional representation for its elections.

The Norwegian lifestyle stresses both hard work and free time. Work settings are generally casual, with no dress code enforced. When they are not working, Norwegians use their free time to the fullest. Indeed, Norwegians get more free time than many other people around the world. This includes afternoons and evenings off, as wells as weekends, religious holidays, and summer holidays. The Norwegians are also sports-loving people. Their national sport is cross-country skiing. In general, the people of Norway are very outdoorsy. Many of them have private cabins in rural settings that they use to relax after a long day of skiing or boating.
Scandinavian Countries
| Rank | Country | Total Area in km2 | Population | GDP per capita (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Denmark | 43,094 | 5,818,550 | 60,170.3 |
| 2 | Sweden | 450,295 | 10,285,450 | 51,615.0 |
| 3 | Norway | 323,802 | 5,347,900 | 75,419.6 |