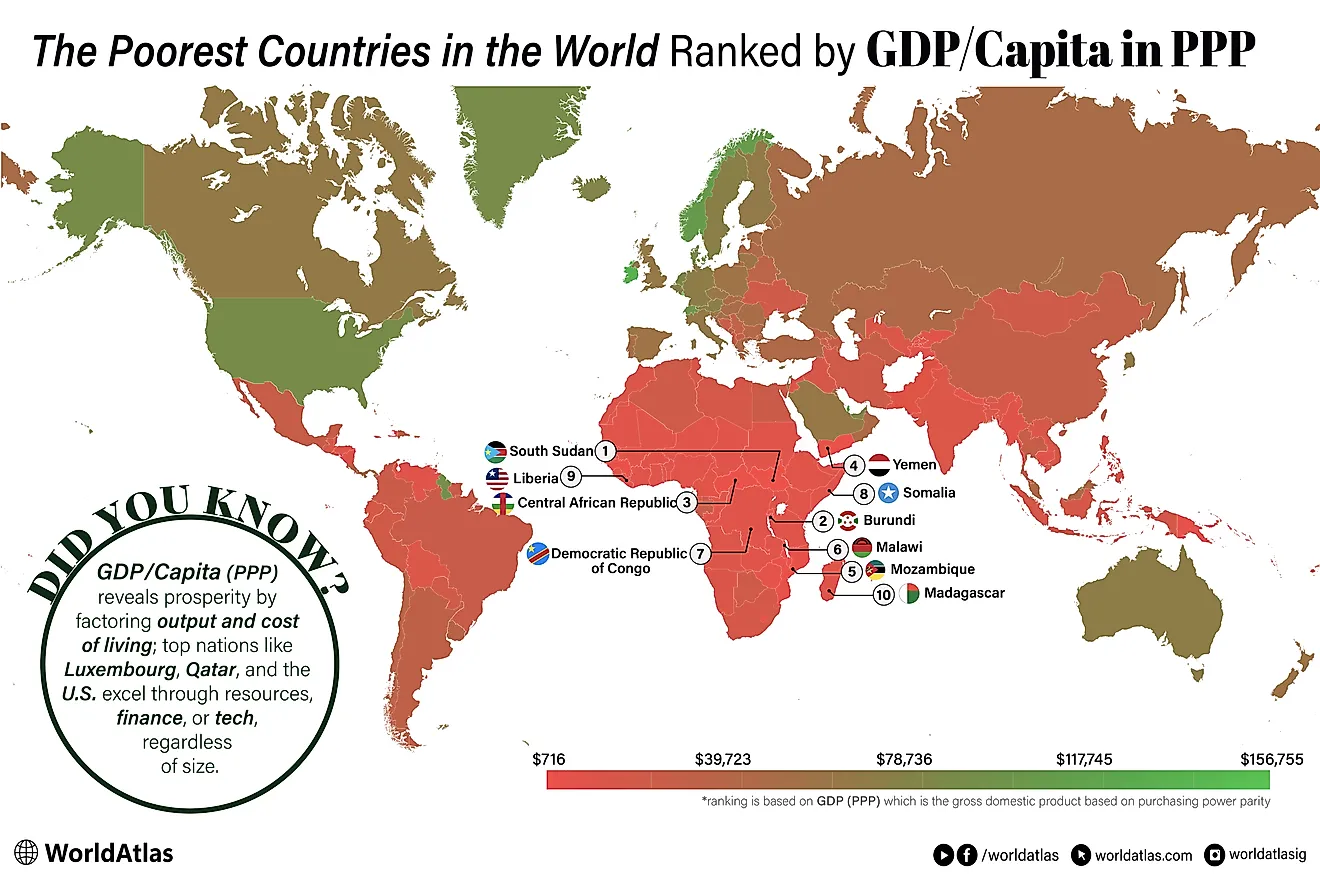
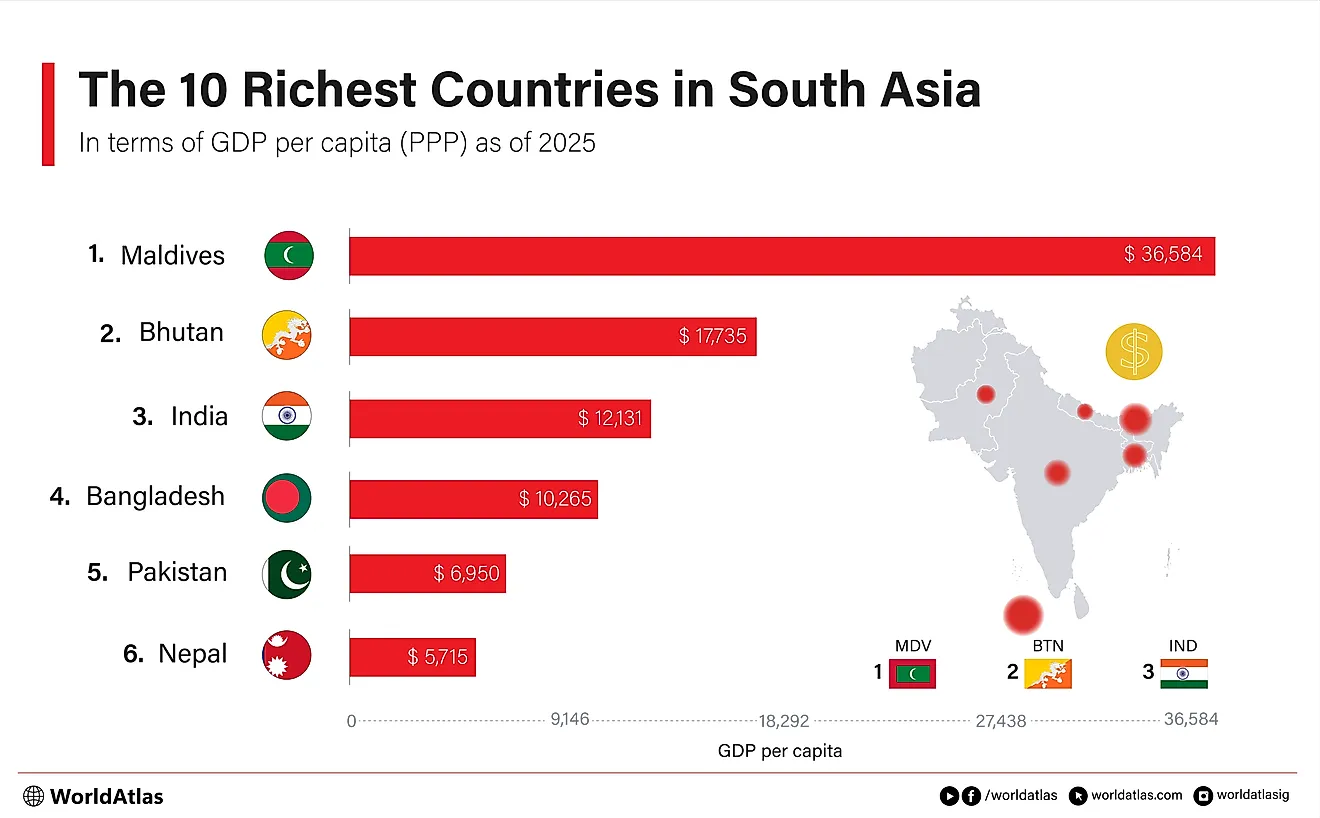
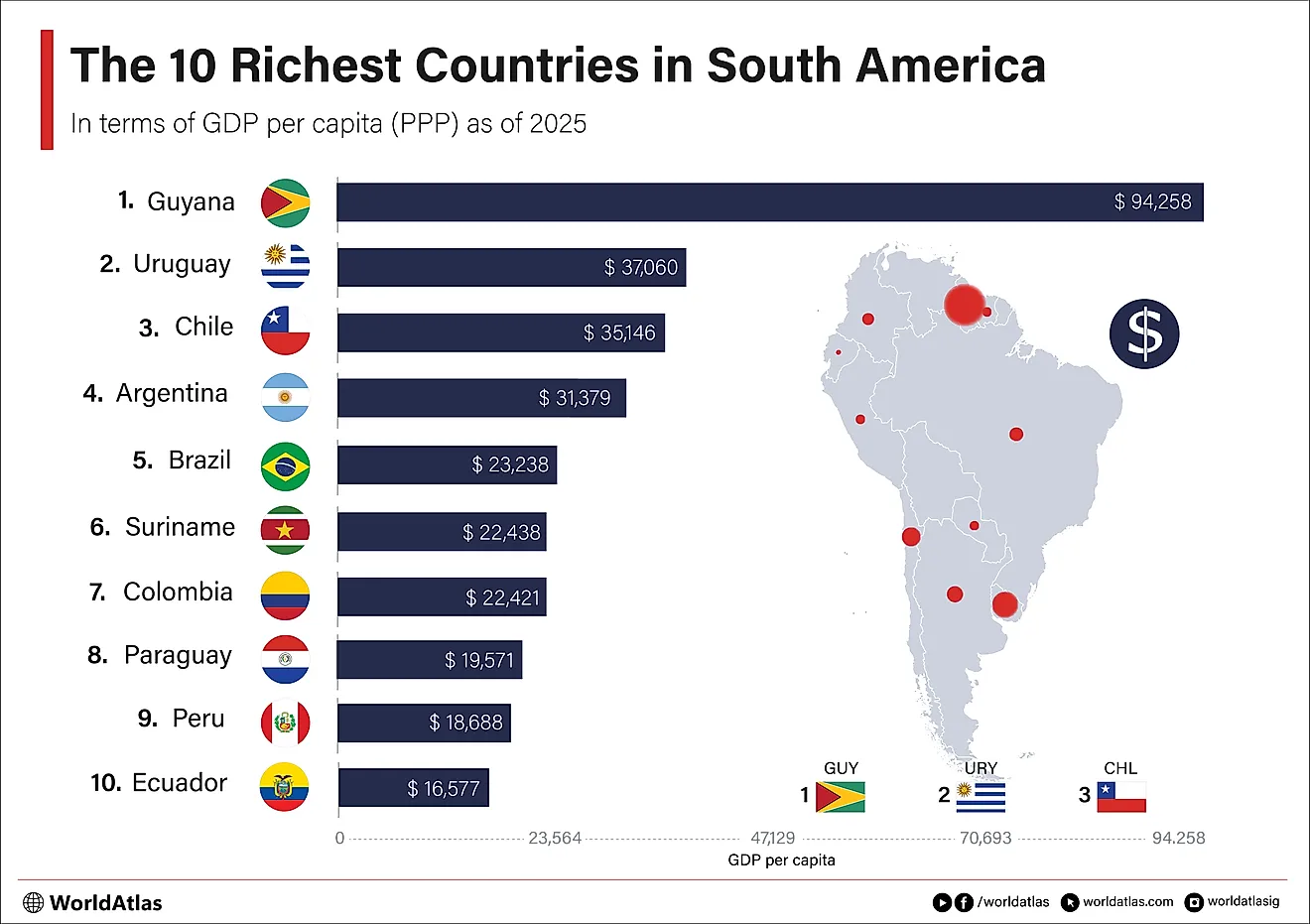
What Are The Biggest Industries In Somalia?

Somalia is an African nation situated on the continent's eastern edge. The Somali economy is considered to be one of the least developed on the continent which is mainly attributed to the violence in the country. The violence in Somalia has made it difficult for international financial organizations to get accurate economic statistics from the country. However, the World Bank estimated that in 2018, the Somali gross domestic product was approximately $6.2 billion which was a 3.1% increase from the 2017 gross domestic product. The Somali economy is reliant on several industries such as agriculture, construction, mining, and telecommunication.
Agriculture
One of the most critical industries in Somalia is agriculture which employes more than 65% of the country's labor force. Like most sectors of the Somali economy, agriculture was significantly affected by the violence that rocked the country. In 2013, the agricultural industry contributed more than 60% of the country's gross domestic product. Farming in Somalia mainly takes place in the country's southern section in areas such as Hiran, Lower Juba, and Gedo that are considered to be the country's most fertile areas. The southern section of Somalia is home to several rivers such as the Juba and Shabelle that make the region more conducive to farming. Some of the crops that Somali farmers grow include sugarcane and bananas, which are sold to other nations, while maize (corn) and sorghum which are mainly grown for local consumption. Despite the presence of a vibrant agricultural industry in Somalia, the country is forced to import most of the food that the citizens consume. To improve the Somali agricultural sector, local farmers partnered with the World Food Program to sell cereals to the organization. Businesspeople in Somalia pledged to help farmers improve the country's agriculture industry.
Livestock keeping
Since ancient times, pastoralism has been one of Somalia's most vital industries. According to the Somali government, more than 80% of the Somali people were involved in pastoralism, and they kept animals such as sheep, camel, cattle, and goats. Most of Somalia's pastoralists move across the country in search of pasture and water for their animals. Apart from keeping animals, some of the pastoralists also gather gums and resins to increase their income. Some unique livestock breeds have been developed in the country such as the Somali sheep and the Somali goat. The Somali goat is mainly kept because it thrives in dry areas. The variety is kept for both meat and milk, and it can produce more than 6.6 pounds of milk during dry seasons. The Somali sheep, on the other hand, is mainly kept for meat. The sheep are also exported to other nations primarily those in the Arabian Peninsula. Apart from sheep, Somali herders also export cattle and camels to countries in the Arabian Peninsula. Some of the countries in the Arabian Peninsula have chosen to invest in Somalia's pastoralism industry to grow the sector.
Fishing
The fishing sector is one of Somalia's most important industries mainly because the country has an exceptionally long coastline. Before 1991, Somalia had several important fishing centers mainly located along the country's coast. During this period, some of the fish species that were often caught included tuna and lobster. Somalia's significant fish reserves attracted investment from other nations mainly those in Europe and Asia. The violence that rocked Somalia significantly affected the country's fishing industry as it discouraged investment in the sector. In the 21st century, the Somali government has attempted to work with the local communities to reestablish the country's fishing sector. In 2012, as part of the efforts to reestablish the country's fishing industry, engineers were employed to assess the renovations at one of the country's most important fishing ports, Las Khorey. The government of the UK assisted in the construction of a fish market at Garowe. Another measure that the Somali government took to improve the fishing sector was opening training schools for fishers.
Mining
Another sector essential to the Somali economy is the mining industry with some of the country's most important minerals being gemstones and salt. Somalia also has limited deposits of other significant minerals such as uranium, tin, and gold. Before 1991, the Somali government was in charge of granting mining rights to companies, however, after the government collapsed, it was difficult for companies to get rights to mine in the country legally. The collapse of the Somali government made it difficult to get accurate data from the country's mining industry. Some of the countries that have been granted the right to mine in Somalia include the East African Mining Corporation and Range Resources Limited from Australia. Industry experts believe that the Somali mining sector has the potential to be one of the country's most important industries.
Telecommunication
The telecommunication industry is one of Somalia's most important sectors. Most of Somalia's telecommunication infrastructure was destroyed during the fighting that took place during the 1991 civil war. By 2010, Somalia's telecommunication industry had experienced resurgence mainly as a result of companies setting up the country's missing infrastructure. Somalia's telecommunication industry attracted investment from foreign nations such as South Korea and China. The telecommunication companies allow the Somali people to bank and send money using their phones. The mobile money system is one of the most vital systems in Somalia as it allows people to pay for services without having to carry large sums of money. The most significant challenge facing the Somali telecommunication industry is the insecurity that plagues the country.
Tourism
Somalia has been blessed with a variety of beautiful sites that attract significant numbers of tourists to the country. The beaches of Somalia are some of its most important tourist attraction sites with the most famous one being the Gezira Beach in Mogadishu and the Baathela Beach in Berbera. The violence in Somalia has dramatically affected the country's tourism industry as it has discouraged tourists from visiting the country.
The Somali economy
The economy of Somalia has been severly affected by the violence that plagued the country. Despite the violence, Somalia has managed to maintain a vibrant informal sector. Various financial experts believe that if Somalia became peaceful, the country's economy would grow exponentially.