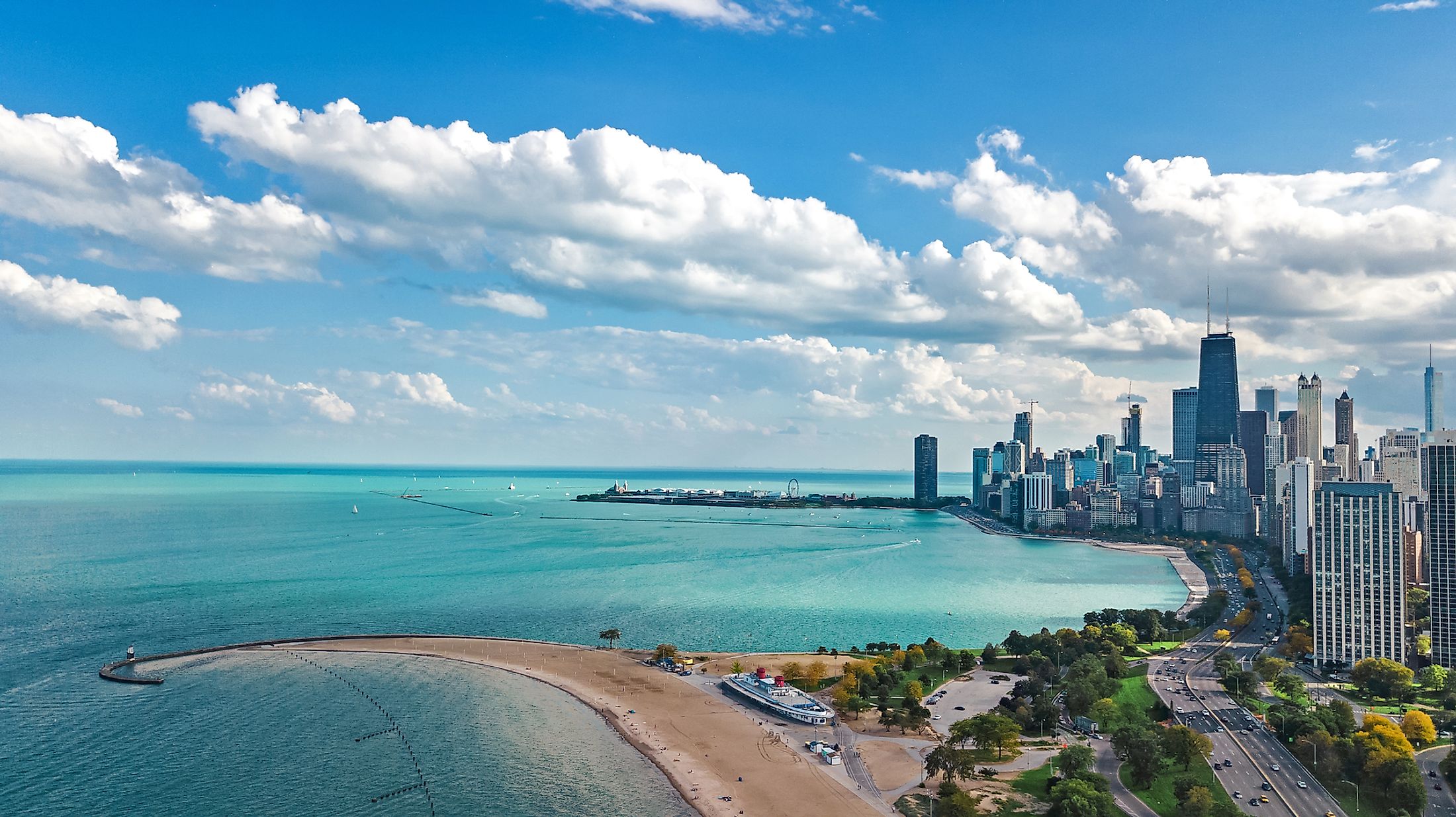
Lake Michigan
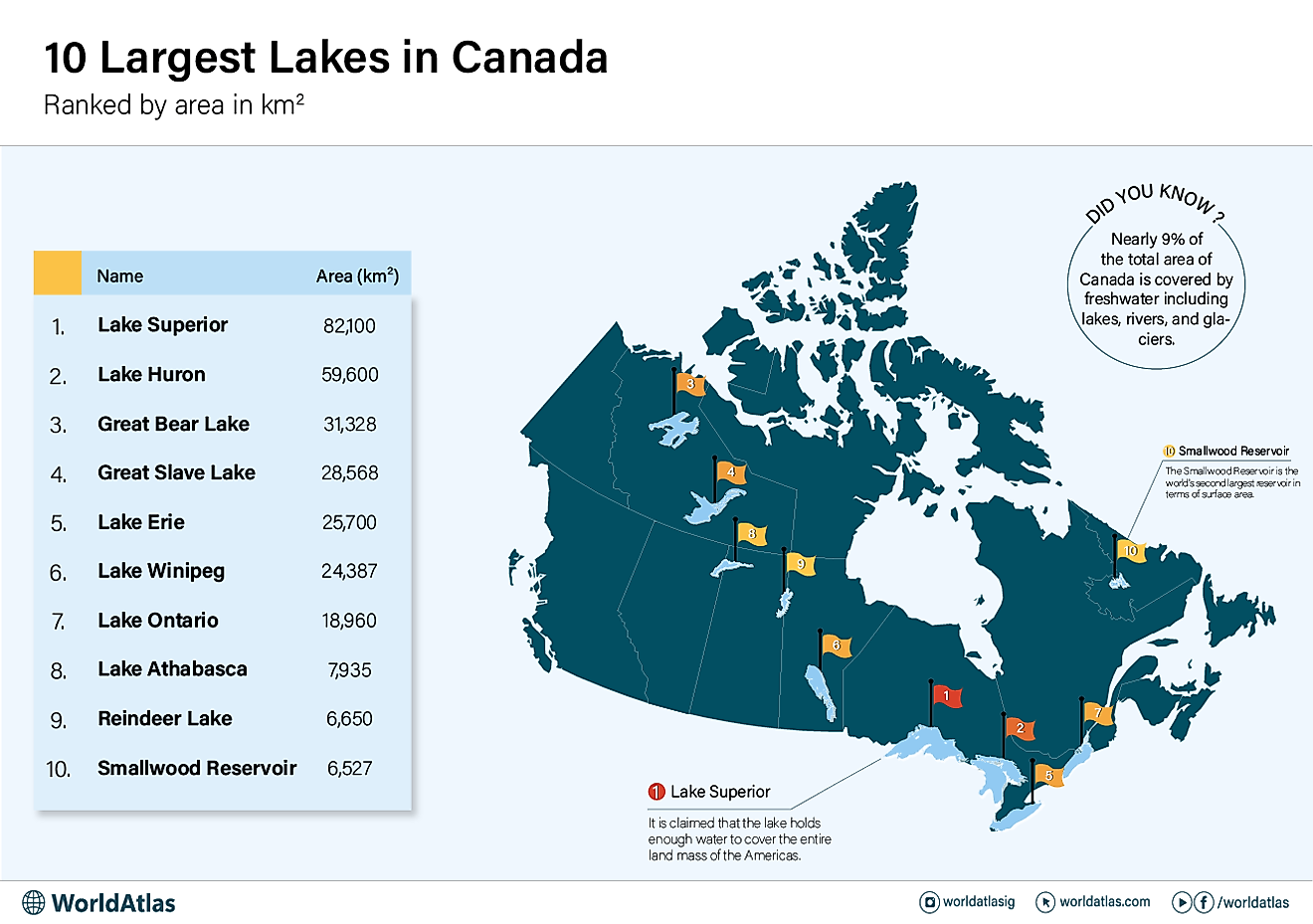
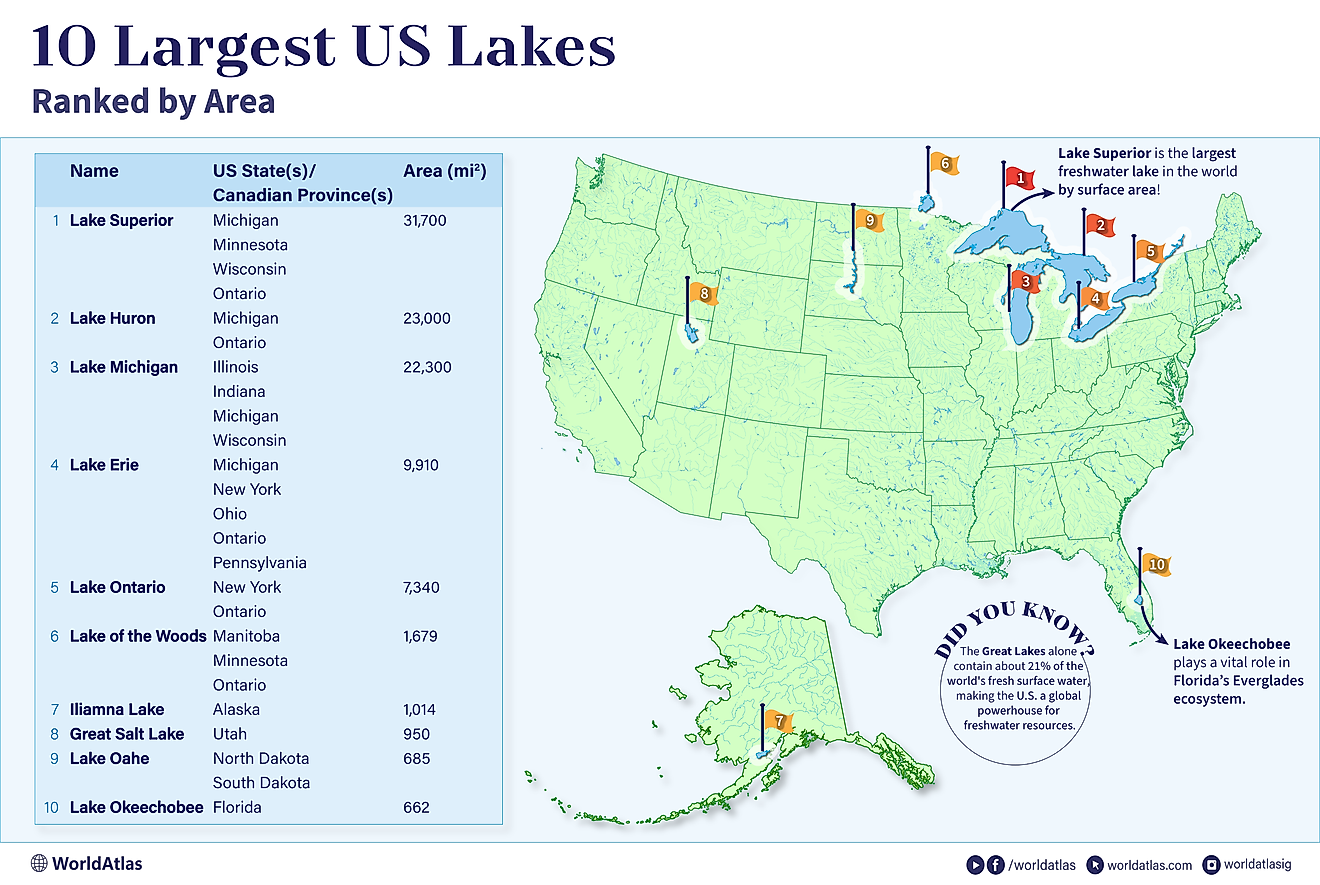
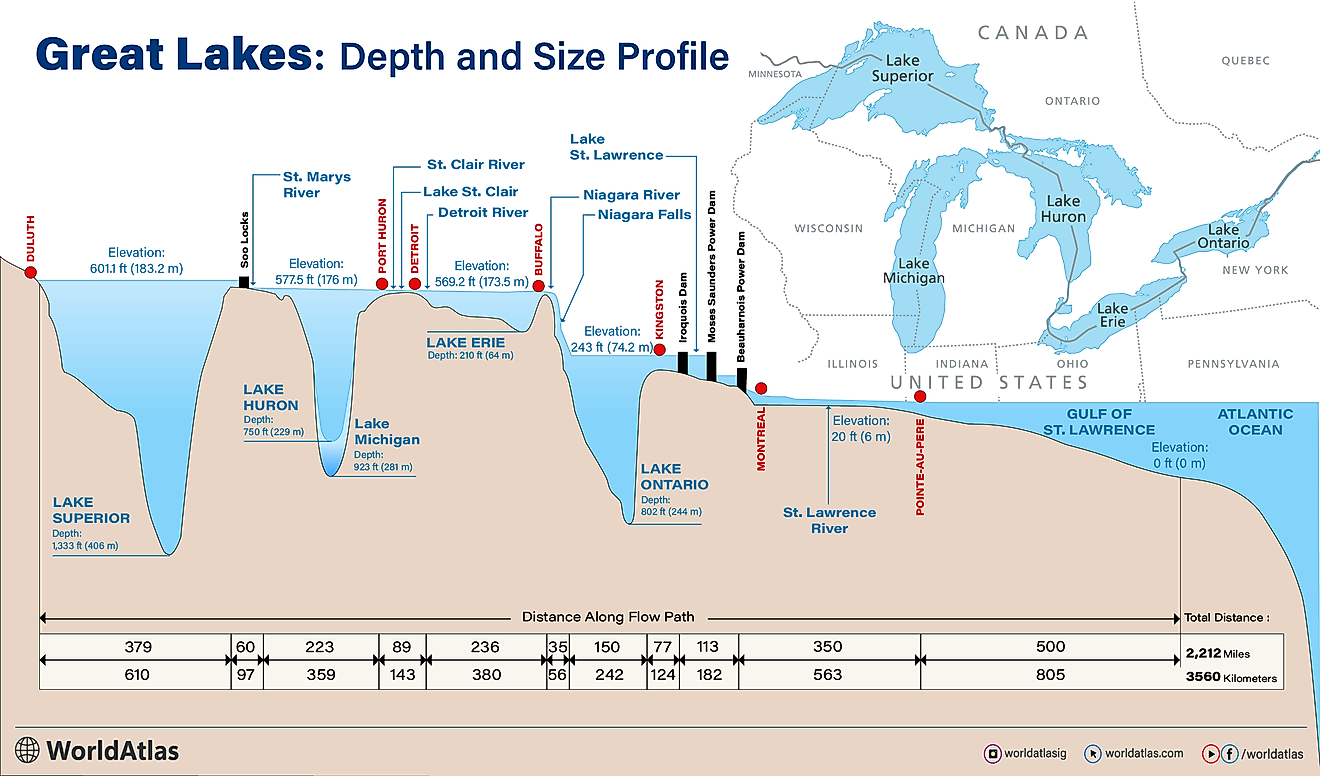
The Great Lakes of North America cover a combined area of 244,106 sq. km and is a series of five interconnected freshwater lakes that are geographically positioned in the east-central part of the continent of North America. The five lakes that span across Canada and United States are Lake Superior, Lake Ontario, Lake Huron, Lake Erie, and Lake Michigan.
Location
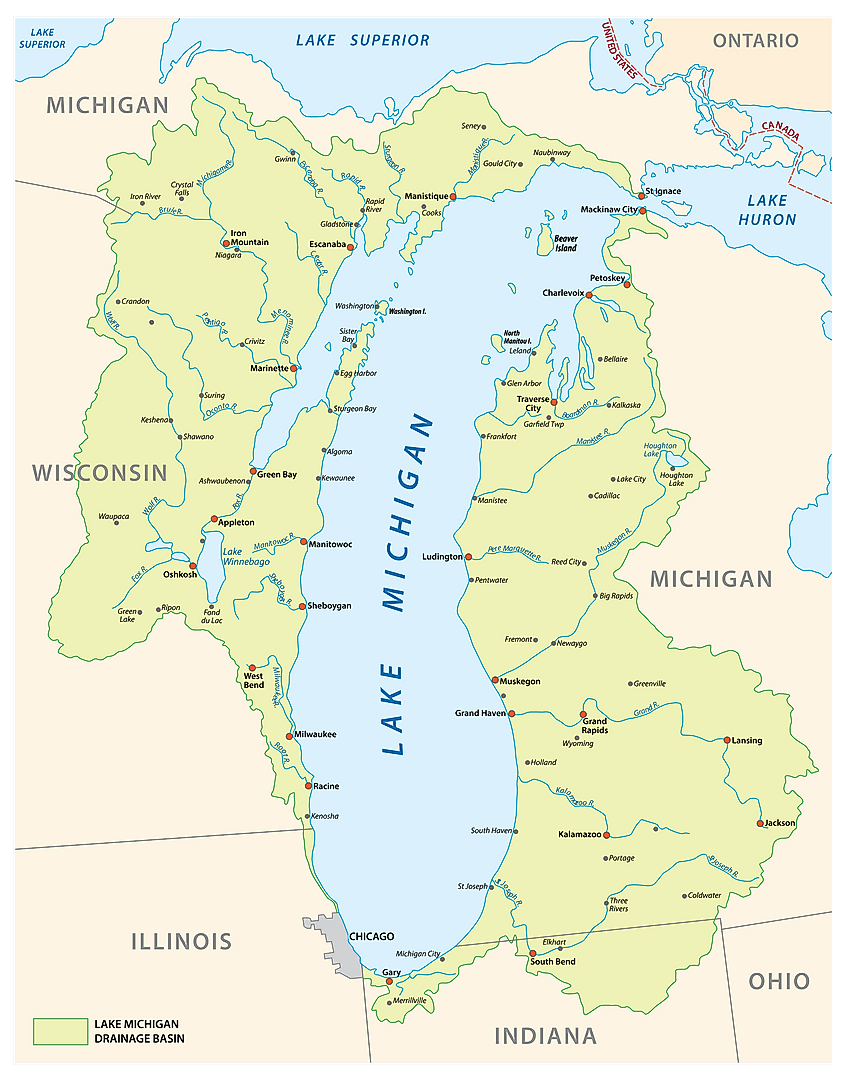
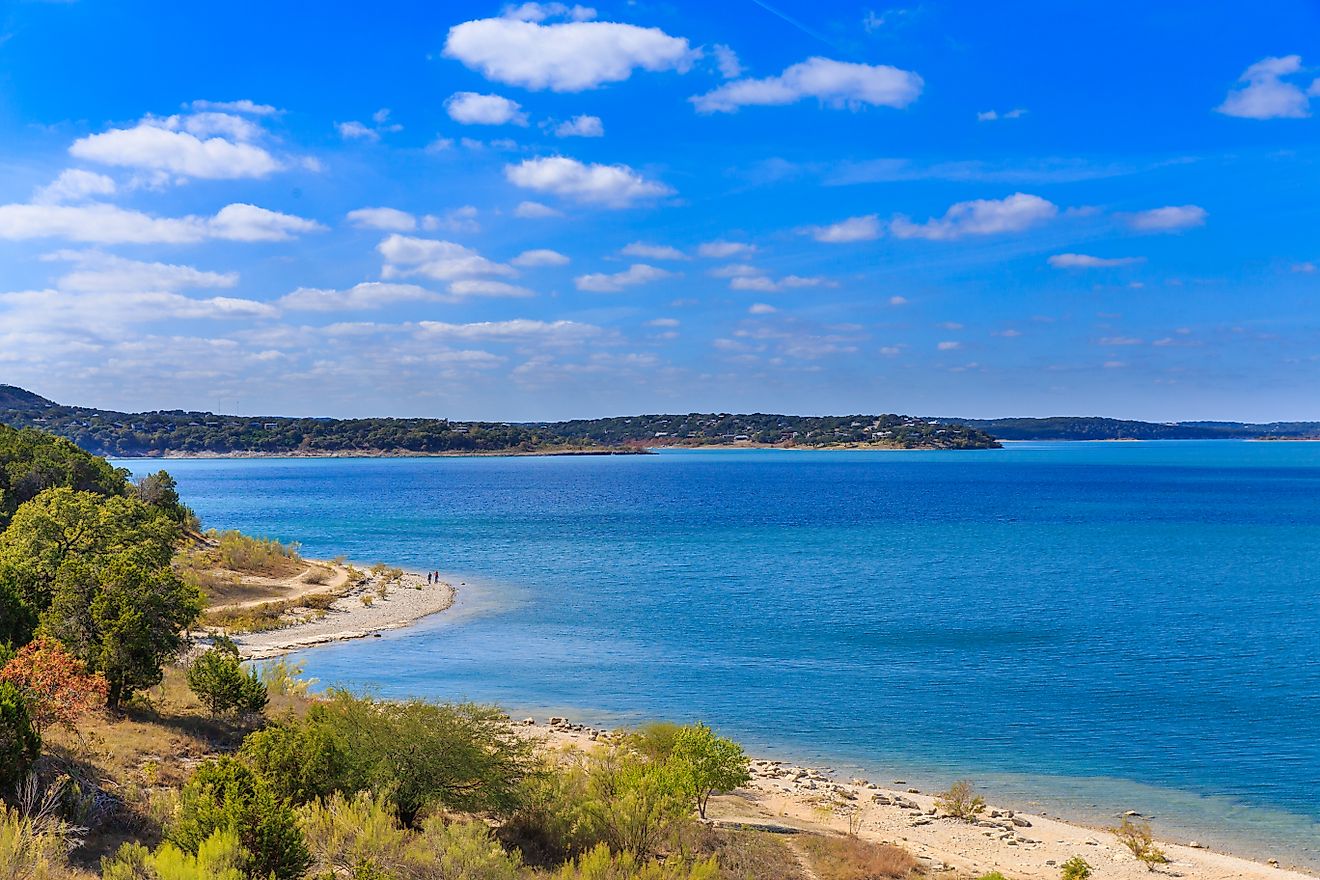
Encompassing an area of 58,030 sq. km, Lake Michigan is the 3rd largest of the Great Lakes by surface area and the 2nd largest by volume. Lake Michigan is the only Great Lake that is situated entirely within the boundaries of the United States and is surrounded by the US States of Michigan in the north and east; Illinois in the southwest; Indiana in the southeast and by Wisconsin in the west. Lake Michigan occupies the western portion of Lake Michigan-Huron and when combined, the Lake Michigan-Huron forms the 4th largest lake by volume and the world’s largest freshwater lake that covers a combined area of 117,000 sq. km.
Geography
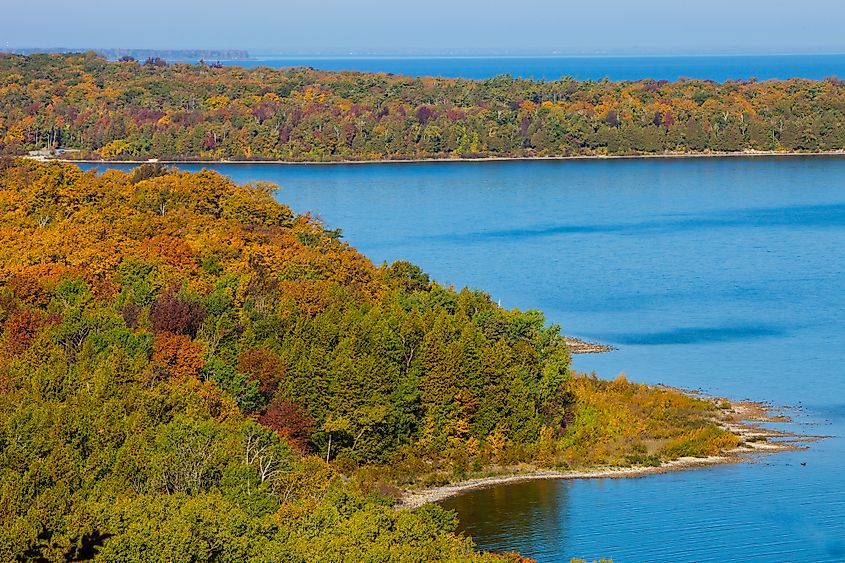

Lake Michigan has a length of about 494 km and a maximum width of 190km. The lake has a mean surface elevation of 176m, which is similar to that of Lake Huron. Lake Michigan has an average depth of 85m and reaches a maximum depth of 281m. The lake holds approximately 4,900 km3 and has a retention time of about 99 years. The 8km wide and 37m deep Straits of Mackinac serves as a connection between Lake Michigan and Lake Huron, while the Illinois Waterway connects Lake Michigan to the Gulf of Mexico. Lake Michigan receives its primary inflows from several rivers and tributaries that flow into the lake. These include the Grand River, Kalamazoo River, St. Joseph River, Fox River, Muskegon River, Milwaukee River, the Menominee River, etc. The primary outflows include the Chicago River, the Calumet River, and the Straits of Mackinac. The large Green Bay forms the northwestern arm of the lake, while the Grand Traverse Bay forms its northeastern arm. Located in the northern part of the lake is its deepest region that is referred to as the Chippewa Basin. The shallow Mid Lake Plateau separates the Chippewa Basin from the South Chippewa Basin.
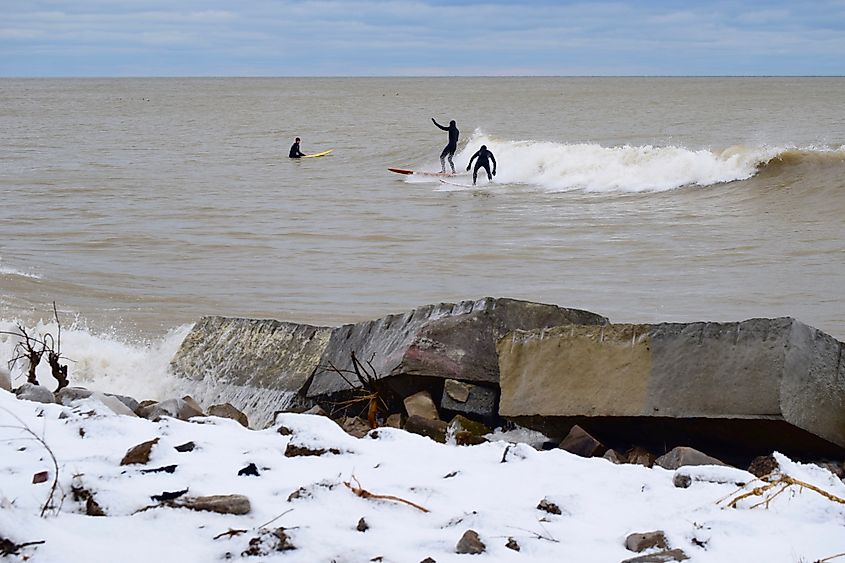

Lake Michigan features several inland beaches and has often been referred to as the “Third Coast” of the US after the Atlantic and the Pacific coasts. The beaches are soft and sandy, while some are covered by sand cherries and green beach grass. The eastern shore of the lake features the largest freshwater dunes in the world that rise to a height of more than 700ft. Several national parks and forests are located along the shoreline of the US States of Indiana and Michigan that features some of the most unique and expansive dunes. The beaches of the western shore and the northern east shore are covered by sands and rocks. Petoskey stone is a pebble-shaped stone that is unique to the lake’s beaches in Northern Michigan.
The northern part of the lake features several islands. Some of these lake islands include Beaver Island, Manitou Island, Fox Islands, Green Island, St. Helena Island, Little Hog Island, etc. Covering an area of 145 sq. km, Beaver Island is the largest island that is located in Lake Michigan.
Flora And Fauna
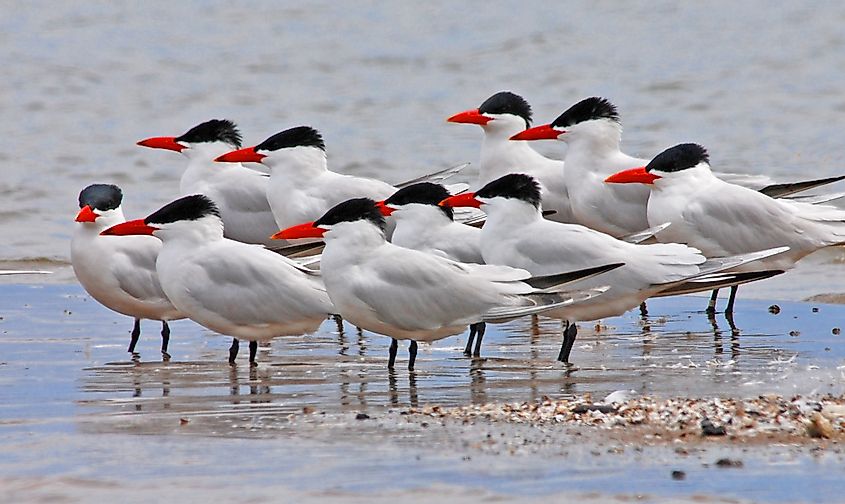

The waters of Lake Michigan support a variety of fish species and other invertebrate fauna. Some of the native fishes that are found here include lake trout, panfish, lake whitefish, yellow perch, bowfin, smallmouth bass, catfish, largemouth bass, etc. Invasive species like sea lampreys, alewife, zebra mussels, round gobies are found in the lake’s waters, which have led to serious declines in the populations of native flora and fauna. Some fishes like brown trout, chinook salmon, coho, and rainbow trout were introduced in the lake’s waters to reduce the number of invasive species. Lake Michigan also supports many water birds like ducks, swans, geese, and predatory birds like bald eagles, hawks, vultures, etc.
Brief History
Geologists believe that Lake Michigan was formed about 1.2 billion years ago due to the splitting of two tectonic plates that resulted in the generation of a Mid-Continent Rift. The Lake Michigan region was originally inhabited by the Hopewell Native Americans and in the later years by the Late Woodland Native Americans. In 1634, the French explorer Jean Nicolet became the first European to explore the Lake Michigan region. During the time of the European exploration, the area was inhabited by the descendants of the Woodland Indians namely the Miami, Chippewa, Ottawa, Sauk, and other Native American tribes. The term “Michigan” has been derived from the native Ojibwe word “michi-gami” which means “great water”. Several European fur trade posts like Fort Michilimackinac and Fort Mackinac were eventually established along the shores and islands of Lake Michigan. During the 19th century, Lake Michigan played a significant role in shaping the economy of the city of Chicago and the other Midwestern US States. Presently, more than 350 shipwrecks have been found buried in the deep waters of Lake Michigan.
Economy
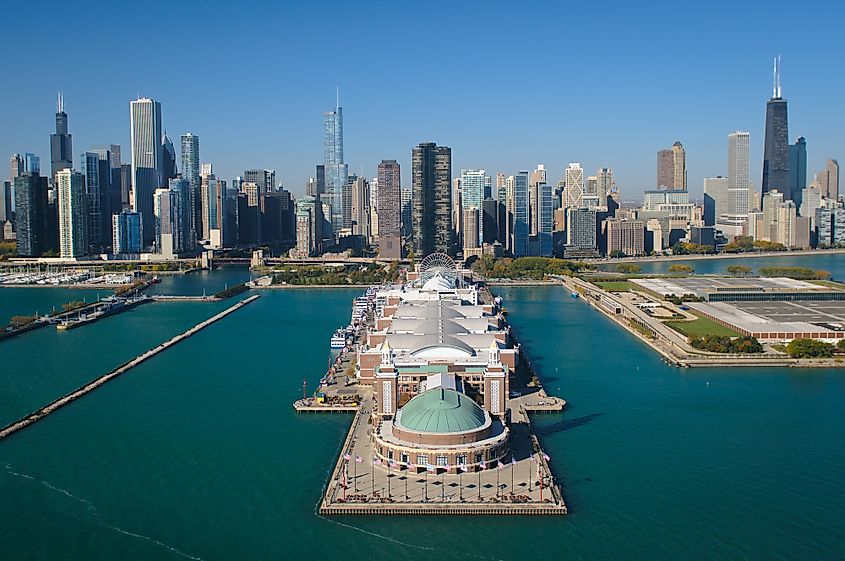

It is estimated that about 12 million people reside along the shores of Lake Michigan and are dependent on the lake for their supply of clean drinking water. As a part of the St. Lawrence Seaway, Lake Michigan serves as a significant navigational route for several commercial cargo ships that carry many economically important materials like iron ore, limestone, coal, etc. Some of the major industrial centers and ports that are located along the shores of the lake include Chicago, Milwaukee, Green Bay City, Gary, and Muskegon. Lake Michigan also serves as an important source for commercial fishing with several commercial fisheries that provide a livelihood for a large number of local American people. The tourism industry around Lake Michigan is also well developed and the habitats of the lake serve as popular tourist destinations attracting lots of tourists.