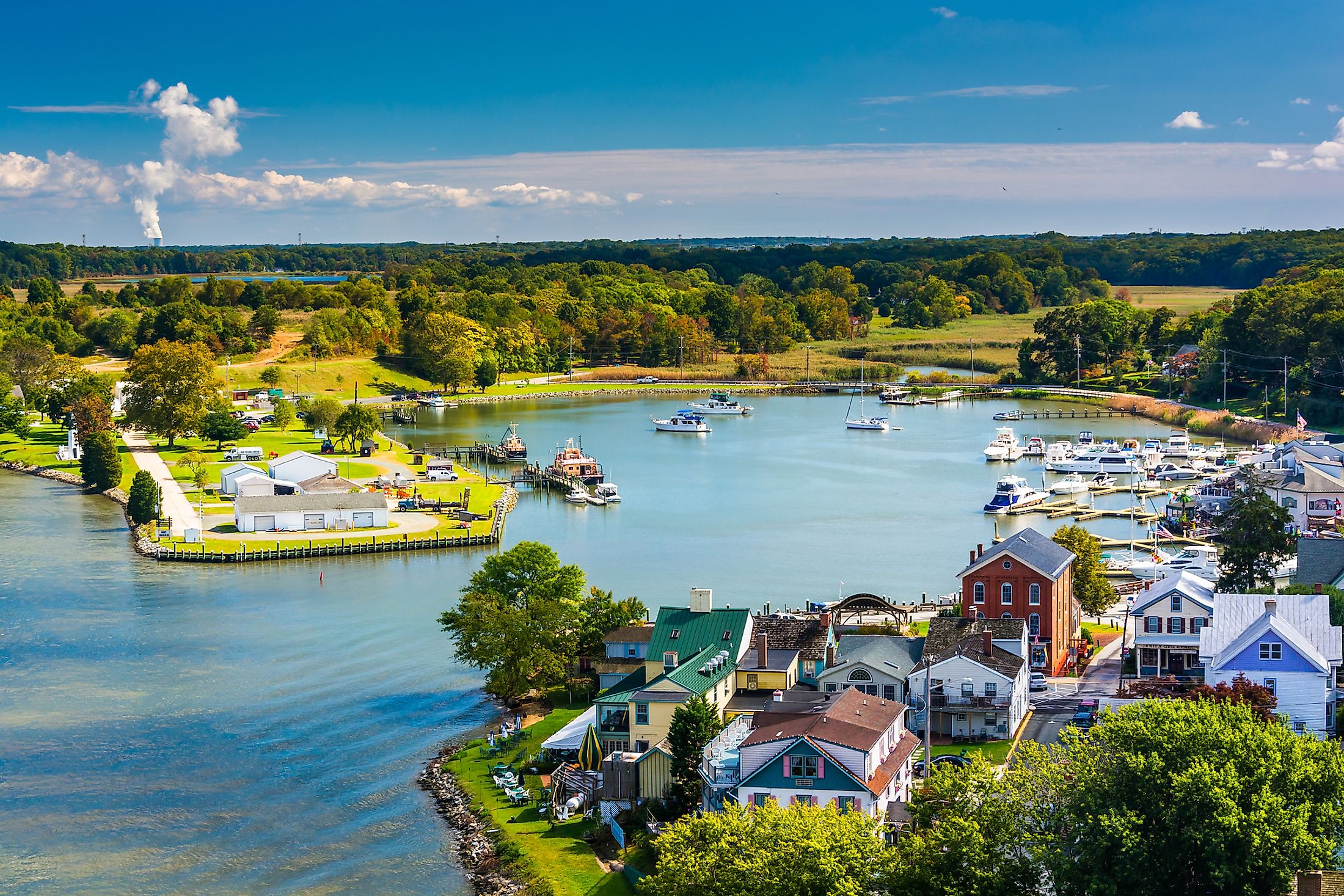
Chesapeake Bay
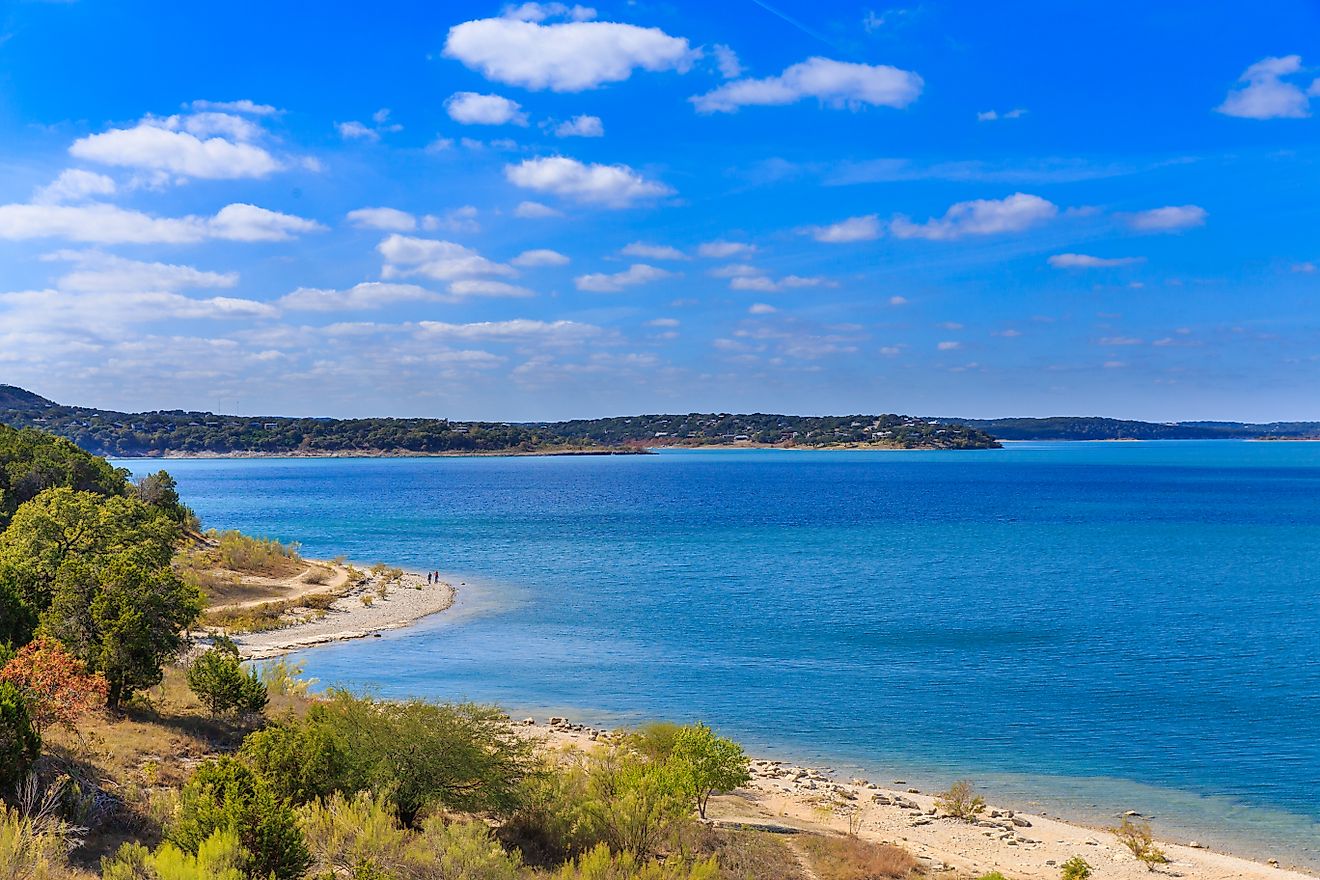
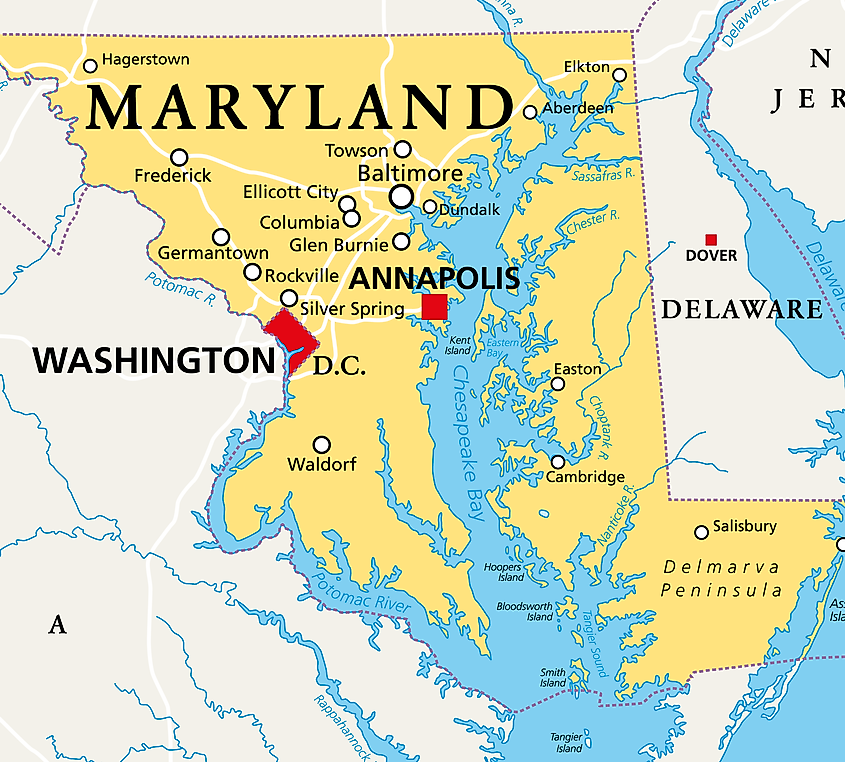
Covering an area of 11,601 km2, the Chesapeake Bay is the world’s third-largest estuary and the largest estuary in the United States. Located in the Mid-Atlantic region, the Chesapeake Bay is one of the largest rias of the Susquehanna River. The Chesapeake Bay is bounded by the North American mainland on the west and by the Delmarva Peninsula on the east. The northern part of the bay is bordered by the US State of Maryland while its southern part is bordered by the US State of Virginia. The bay’s entrance from the Atlantic Ocean is flanked by Cape Henry to the south and Cape Charles to the north.
Geography Of Chesapeake Bay
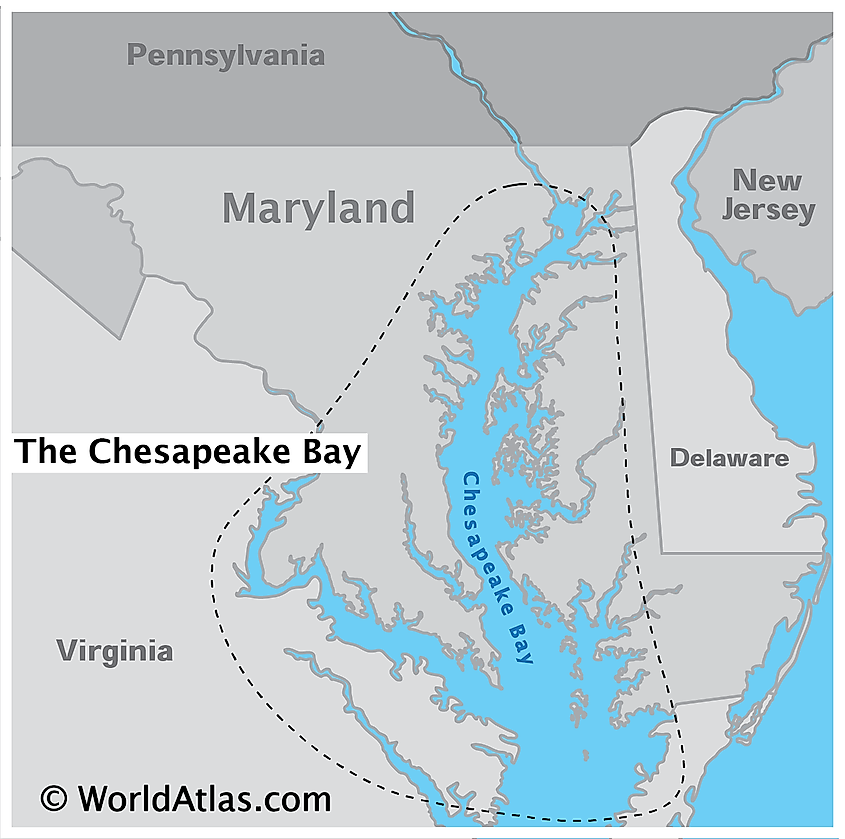
The Chesapeake Bay is about 320km long and stretches from the city of Havre de Grace in Maryland in the north to the city of Norfolk in Virginia in the south. The Bay is about 4.5km wide at its narrowest point and about 48km wide at its widest point. The Chesapeake Bay is quite shallow and has an average depth of 6.4m. The bay reaches a maximum depth of 53m at its deepest point, which is known as “The Hole” and is located to the southeast of Annapolis, close to Bloody Point, on Kent Island, Maryland. The Chesapeake Bay holds more than 15 trillion gallons of water and the total shoreline of the bay including its tributaries is 18,804km. It is estimated that over 150 major rivers and streams flow into the Bay and its 166,534 sq. km drainage basin covers portions of six US states: Maryland, Delaware, Virginia, Pennsylvania, West Virginia, and New York as well as the entire District of Columbia. Over 18 million people live in the Chesapeake Bay watershed.

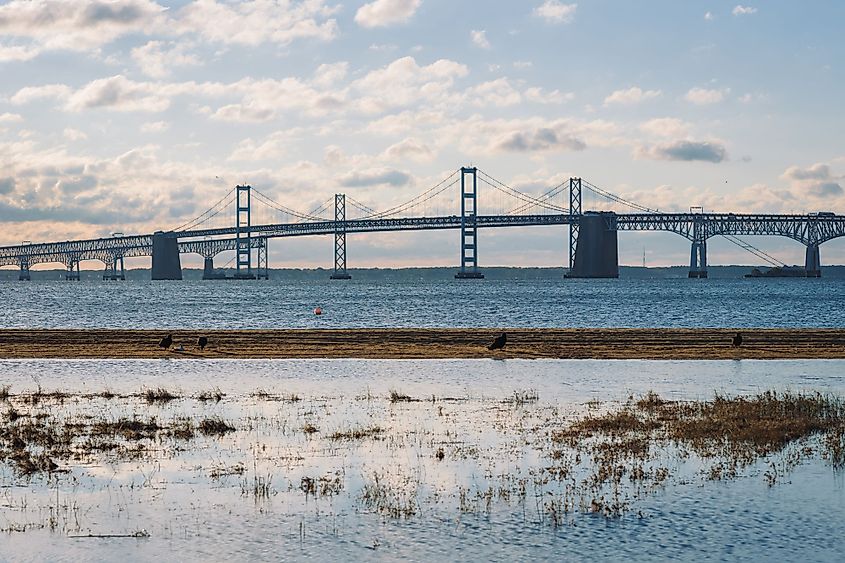
The Chesapeake Bay forms a part of the Atlantic Intracoastal Waterway and is spanned by the Chesapeake Bay Bridge-Tunnel that connects Cape Charles with the Virginia Beach and by the Chesapeake Bay Bridge that connects Sandy Point to Kent Island. The area surrounding the bay experiences a humid subtropical climate with very hot and humid summers and mild to cold winters. The Chesapeake Bay is a major tourist destination and is visited by numerous tourists every year. Fishing, boating, kayaking, crabbing, and sailing are some of the most popular recreational activities that tourists enjoy on the waters of the Chesapeake Bay.

Some of the major rivers that flow into the Chesapeake Bay include the Susquehanna River, Chester River, Potomac River, Rappahannock River, James River, Nanticoke River, Pocomoke River, etc. Since the Chesapeake Bay is an estuary, it contains freshwater, saltwater, and brackish water. The brackish water of the bay has three salinity zones namely oligohaline, mesohaline, and polyhaline. The salinity in the oligohaline zone varies from 0.5ppt to 10ppt while the salinity in the mesohaline zone varies from 1.07% to 1.8%. The polyhaline zone is the saltiest and its salinity varies from 1.87% to 3.6%.
Ecology Of Chesapeake Bay
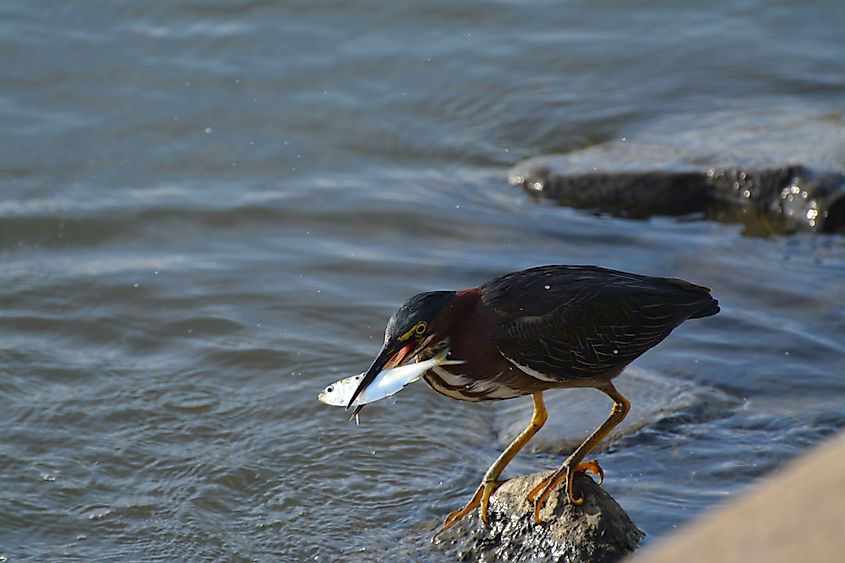

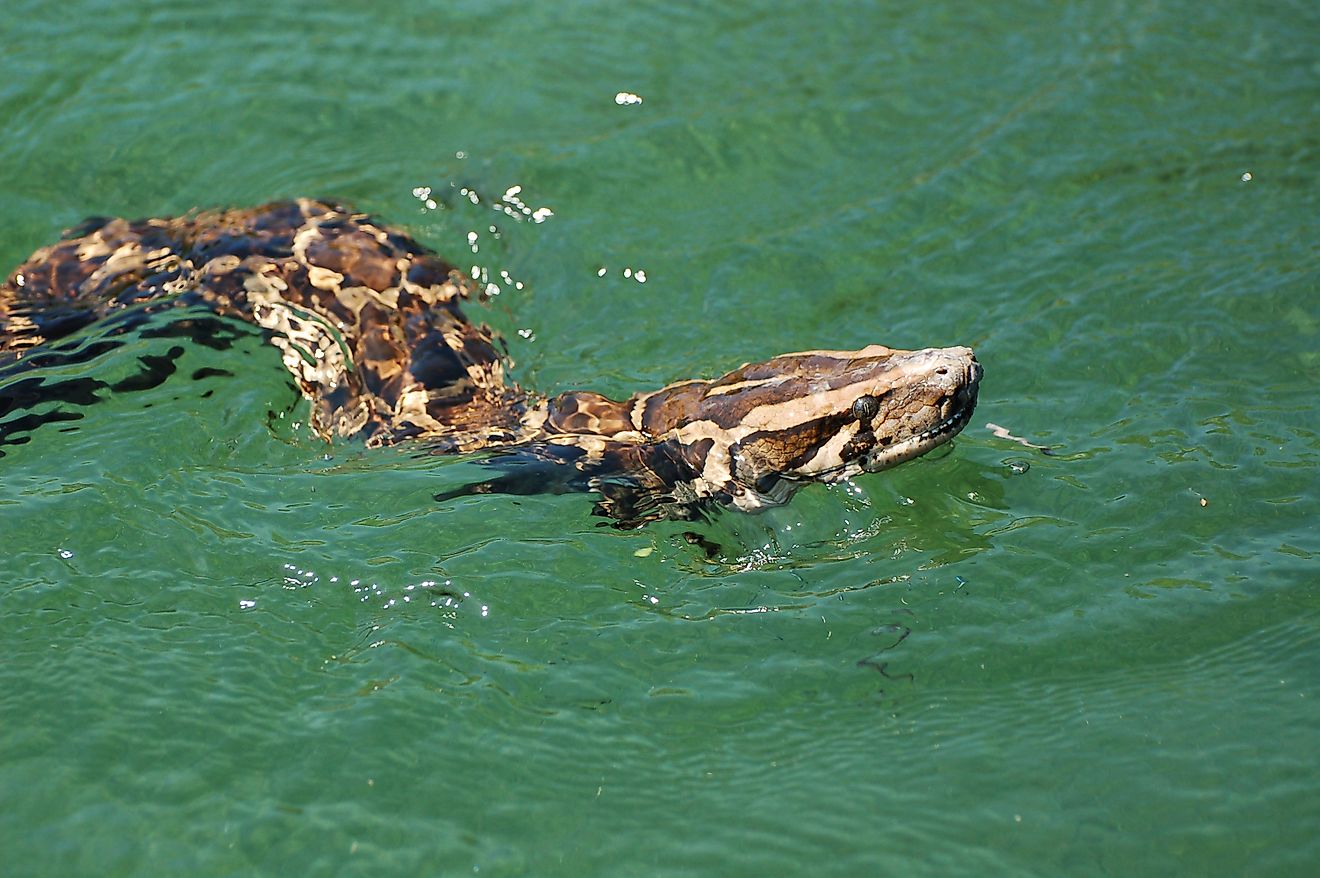
The Chesapeake Bay supports over 3,600 species of flora and fauna which includes 348 species of finfish, 173 species of shellfish, more than 2,700 plant species, and over 16 species of underwater grass. Some of the notable marine species that are found here include Atlantic menhaden, Atlantic horseshoe crab, American eel, eastern oyster, blue crab, etc. Larger fishes like the Atlantic sturgeon, stingrays, and several varieties of sharks like the basking sharks, tiger sharks, scalloped hammerhead sharks visit the Chesapeake Bay. The waters of the Bay serve as one of the most important nursery areas for the sharks along the eastern coast. Numerous other marine species like Bottlenose dolphins, North Atlantic right whale, minke whales, manatee, loggerhead turtles, etc have been recorded visiting the Chesapeake Bay at some point during the year. Different avian species like the bald eagle, ospreys, great blue herons, peregrine falcons, and piping plover have also been observed in the Chesapeake Bay. The Bay produces approximately 500 million pounds of seafood per year.
Brief History Of Chesapeake Bay

It is believed that humans have lived in and around the Chesapeake Bay region for more than 11,500 years. The first humans who lived in the Chesapeake Bay region were the Paleoindians. For several years many North American societies lived in the villages adjacent to the water bodies. The word ‘Chesepiooc’ is an Algonquian word that refers to a village “at a big river”. Over time, the communities living around the Chesapeake Bay formed many confederations like the Nanticoke, Powhatan, and the Piscataway.
In 1524, the Italian explorer Giovanni da Verrazzano sailed past the Chesapeake Bay. In 1525, the Spanish explorer Lucas Vásquez de Ayllón had sent out an expedition from Hispaniola that reached the mouths of Delaware and the Chesapeake Bays. The Spaniards had named the bay “Bahia de Santa Maria”. In the late 16th century, the English colonists first arrived in the bay area to establish a colony. The Bay was mapped and explored by the English Captain John Smith between 1607 and 1609. In 1791, the Chesapeake Bay served as the site for the Battle of the Chesapeake, in which the Royal Navy was defeated by the French fleet. The bay also served as a site of conflict during the War of 1812 and the Oyster Wars in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. By the 1970s, the residential and industrial development in the bay’s surrounding region had led to much pollution of the bay by dumping of untreated sewage, industrial wastes, etc. During this time, commercial fishing and recreational use of the bay also reduced sharply.