How Many Countries Are In The Middle East?
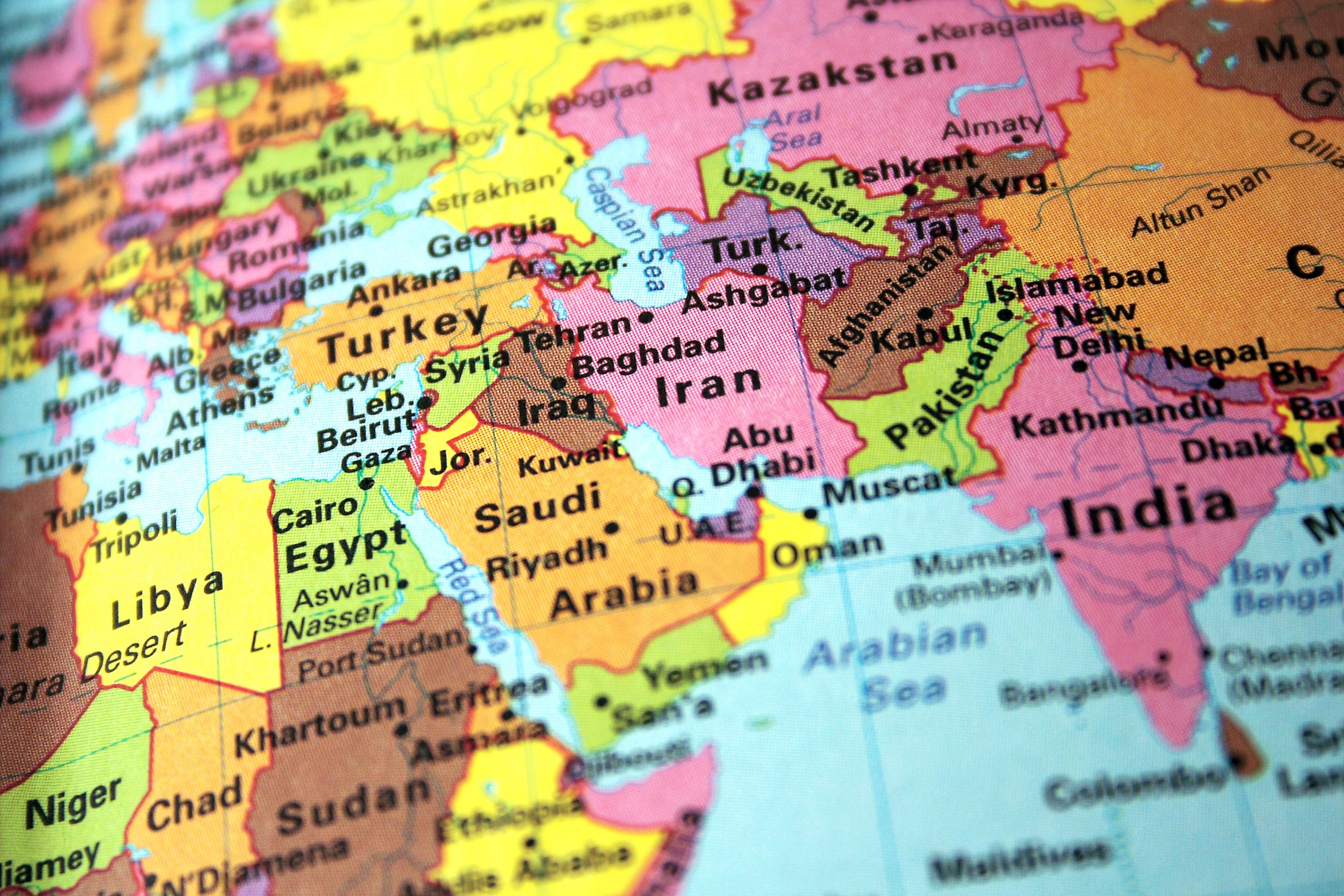
The Middle East is a geographically and culturally diverse region made up of 17 countries spanning northern Africa and western Asia. The region is home to nearly half a billion people with a population of 493 million inhabitants. The Middle East has become widely known as the “Cradle of Civilization,” with the world’s earliest civilizations originating in the Fertile Crescent and Nile Valley.
Bahrain

Bahrain is an island country located in the Persian Gulf, situated west of the Qatar Peninsula along the edge of the Gulf of Bahrain. The country is comprised of the main island, Al Bahrayn (which accounts for the vast majority of Bahrain’s land area), and a small archipelago of 50 natural islands and 33 artificial islets.
Bahrain is the smallest country in the Middle East, covering 764 square kilometers. Despite its size, Bahrain plays a crucial role in the region's financial and economic landscape, being a major hub for banking and investment in the Gulf. The country is home to 1.6 million people. Bahrain’s population is ethnically diverse, with nearly a dozen different ethnic groups of Bahraini citizens.
Cyprus

Cyprus is an island situated in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. The country is the third largest island in the Mediterranean, covering about 9,250 square kilometers, as well as the third most populous, with over 1.2 million people.
The island was first settled around 9000 BCE. From 2000 BCE, Mycenaean-Achaean Greeks began to arrive and settle on the island. During the Ottoman Empire’s conquest of the island in the early 1570s, Turkish settlers were granted land to settle. Cyprus’s strategic location has made it a crossroads of civilizations for millennia, from Mycenaean Greeks to Ottomans, leaving the island with a rich cultural mosaic.
Today, the culture of Cyprus is divided between Turkish and Greek influences, though both contribute to the rich handicraft and folk art traditions alive on the island today.
Egypt
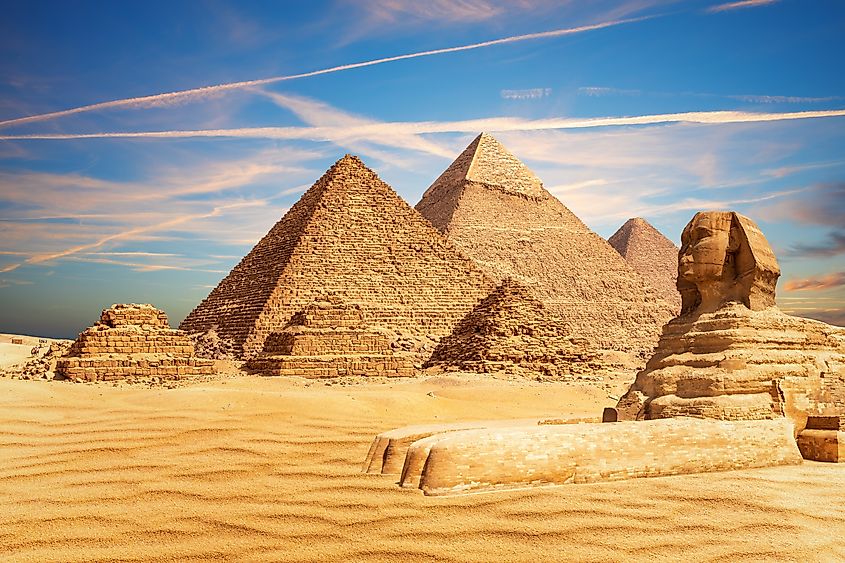

Egypt is located in the northeasternmost corner of Africa, with coastlines along the Mediterranean and Red Seas. The Nile River valley and delta have provided aliment to the arid landscapes for millennia. Present-day Egypt has been at the site of the most prominent human settlements throughout history. These lands were under the rule of Pharaonic Egypt for more than 3,000 years before Alexander the Great’s conquest of the region in the early 4th century BCE. By 30 BCE, much of what is now Egypt had been conquered by the Roman Empire and remained a part of the Byzantine Empire until the Arab Muslim armies gained control in the 7th century.
Today, Egyptian culture is a combination of ancient traditions that have been influenced by societies in Europe, Africa, and the Middle East throughout history. Modern Egypt is home to 111 million people, with 95% of the population living along the Nile River.
Iran
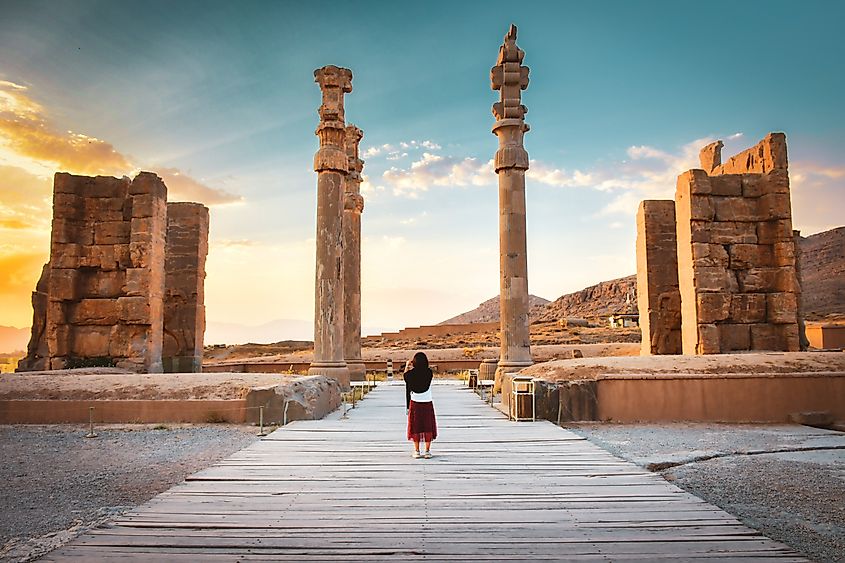

Iran is the second largest and second most populous country in the Middle East. The country cover over 1.6 million square kilometers, and has a population of about 88.55 million people. Iran’s terrain largely consists of deserts and shrublands, with a fertile coast in the north bordering the Caspian Sea. Beyond its deserts and shrublands, Iran is home to striking mountain ranges like the Alborz and Zagros, which are not only significant for their natural beauty but also as sites of ancient human habitation and trade routes
Iran is one of the most continuously inhabited ancient civilizations in the world, with urban settlements dating back to 4000 BCE.
Iraq

Iraq is a topographically diverse country, with deserts in the west and south, highlands in the north, and fertile, alluvial plains in the central and southeastern regions of the country. Mesopotamia, a region that encompasses all of present-day Iraq, comprises the eastern half of the Fertile Crescent, a historically significant region that supported the rise of human civilization. As the birthplace of writing, law, and urbanization, Iraq’s ancient cities such as Ur and Babylon were at the heart of early human civilization, making it a key player in world history.
Today, Iraq is home to 44.5 million people. The two largest ethnic groups in the country are Arabic and Kurdish. Other prominent ethnic groups include Turkic, Persian, Armenian, Assyrian, and Chaldean.
Israel
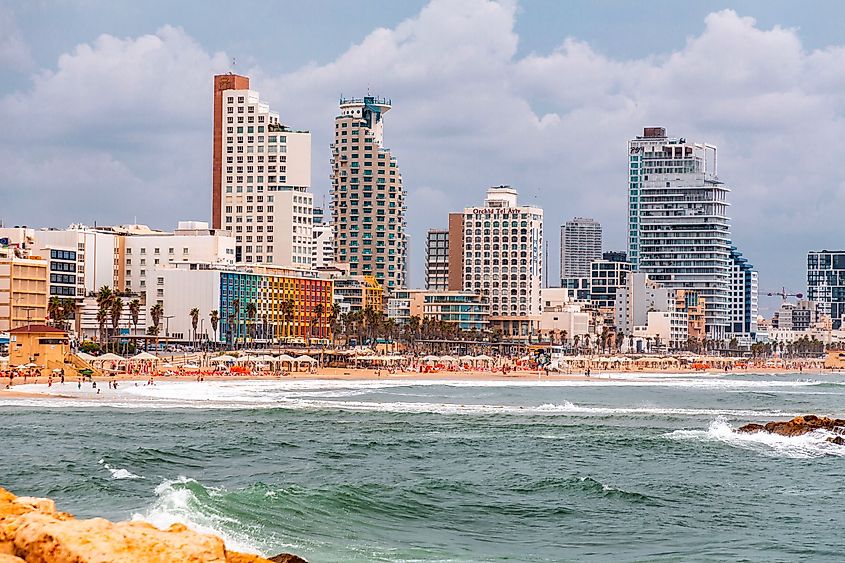

In the western half of the Fertile Crescent, Israel is characterized by its border with the Mediterranean Sea on the western border, fertile coastal plains in the east, mountainous north and central regions, and desert landscapes in the south.
Israel borders the western coast of the Dead Sea, which is 427 meters below sea level, the lowest elevation in the world.
Israel has a population of 9.56 million, with nearly a million living in its proclaimed capital and largest city, Jerusalem. The State of Israel and the State of Palestine both claim it as their capital, which is why the status of Jerusalem remains one of the core issues in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Jordan

Jordan is located in the heart of the Middle East and shares borders with Iraq and Saudi Arabia to the east, Syria to the north, and Israel and Palestine to the west. Jordan is home to 11.29 million people, with the vast majority residing in the northwest. Amman is the capital and home to 4 million residents.
The terrain of Jordan consists largely of a flat desert plateau, with high mountains in the west reaching to heights over 1,700 meters. However, near the Dead Sea, the terrain plummets to over 400 meters below sea level. The country has coastlines with the Gulf of Aqaba and the Dead Sea. In total, Jordan has 26 kilometers of coastline.
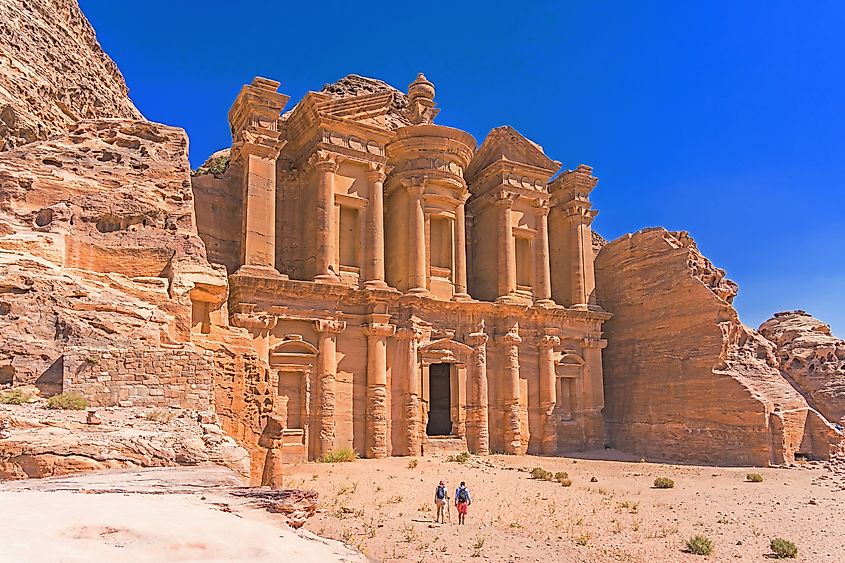
Jordan is home to the ancient city of Petra, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, was once a thriving trading hub for the Nabataean Kingdom, renowned for its intricate rock-cut architecture and water management systems.
Kuwait
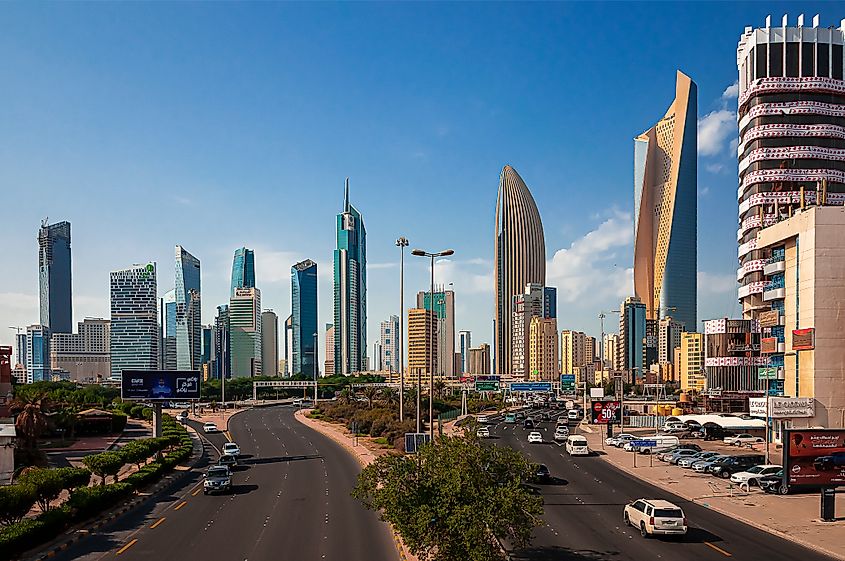

Kuwait is situated in the northwestern corner of the Persian Gulf, sharing borders with Iraq and Saudi Arabia. Kuwait’s wealth is deeply tied to its vast oil reserves, but its cultural institutions like the Kuwait National Museum reflect a commitment to preserving its rich history. The country covers about 17,800 square kilometers, with the land mostly dominated by arid, Arabian Desert aside from the Al-Jahra Oasis. Kuwait is home to 4.27 million people, with 3.29 million (or 77 percent) of people living in the coastal city of Kuwait City.
Kuwait was founded on Arab cultures and traditions influenced by Islam and has developed an architectural style that reflects the nation’s deep connection with its modern design and traditional art.
Lebanon
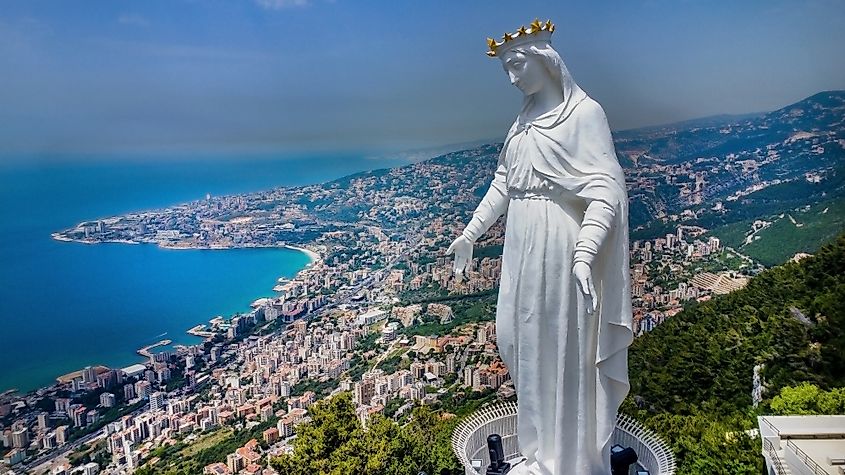

Lebanon is a country of 5.49 million people and is located along the eastern Mediterranean Sea, north of Israel and west of Syria. The country is a diverse Arab culture with origins in Islam and Christianity, with some Western influences. While the official language of Lebanon is Arabic, it is not uncommon for the French or English languages to be used, being that around half of the Lebanese population speaks French fluently, and 40% also speak English well.
Lebanon's dramatic landscapes are complemented by its vibrant urban life, particularly in Beirut, which has long been a cultural capital in the Arab world. Lebanon's terrain ranges from low coastal plains in the west along the Mediterranean Sea to a mountainous pine-forested east reaching over 3,000 meters.
Oman
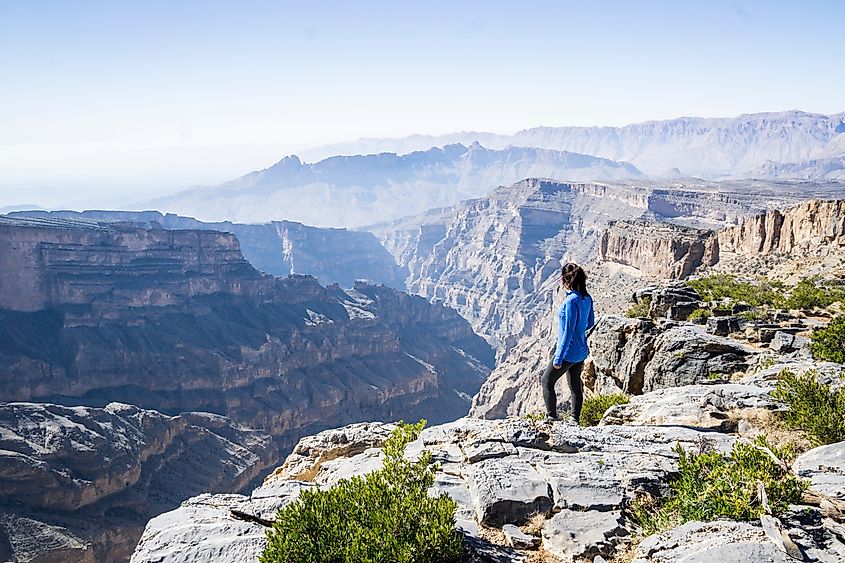

Oman is a country situated on the southeastern portion of the Arabian Peninsula, sharing borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. The country’s terrain is dominated by desert plains and rocky mountains reaching beyond 3,000 meters in elevation. Most of Oman’s population lives in the north near the nation’s capital, Muscat. Though dominated by the vast Rub' al Khali (Empty Quarter), Saudi Arabia also has stunning oases and dramatic mountain ranges like the Asir Mountains, which support unique flora and fauna and break up the desert landscape. People have dwelled in the Muscat region of the country since the 1st century CE. Today, the urban area has over 1.7 million residents.
Oman’s culture is shaped by a mix of traditions, with influences from both modern and tribal society. Omani artisans are renowned for their woodcarving and weaving, as well as jewelry from silver and gold.
Palestine
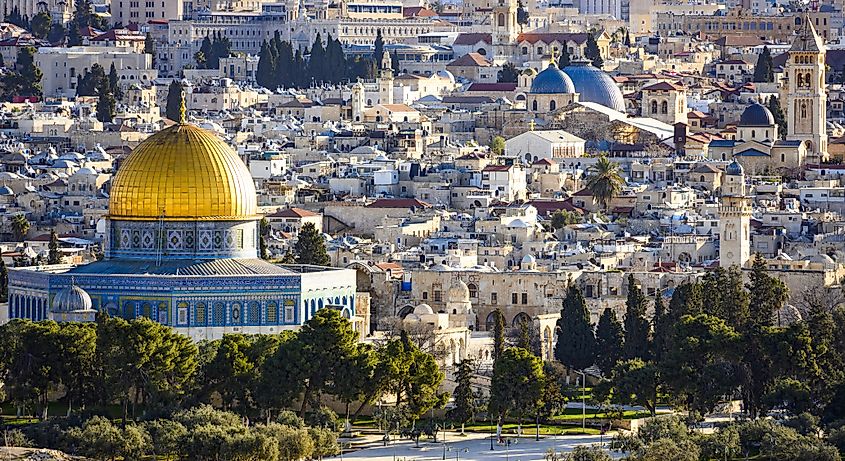

Palestine is a nation comprised of two regions east of the Mediterranean Sea: The West Bank (including East Jerusalem) and the Gaza Strip. The West Bank borders Israel to the west and Jordan to the east and has shores along the Dead Sea and Jordan River. The Gaza Strip is situated about 40 kilometers southwest of the West Bank along the Mediterranean Sea, bordering Israel to the east and Egypt to the south.
Palestine's landscape is not only historically significant, but the region is also home to some of the oldest cities in the world, such as Jericho, which dates back over 10,000 years. Palestine’s terrain in the West Bank is mainly made up of mountainous desert, with vegetation in the western half of the region. The Gaza Strip’s terrain consists of a coastal plain with low, rolling sand dunes near the shore.
The Gaza Strip is home to more than 2.1 million people, which is about 5,500 per square kilometer. In the more expansive West Bank, over 2.9 million people inhabit the region - mostly in the West, with 1,800 per square kilometer.
Qatar

Qatar is a country that occupies the Qatar Peninsula, a landmass in the Persian Gulf that is connected to the much larger Arabian Peninsula. The country shares one land border with Saudi Arabia. The terrain of Qatar is mostly flat, with some rocky outcrops and hills that reach up to a hundred meters above the surface.
In the 18th century, the Bedouin tribes migrated to the Qatar region. Today, the Bedouin people make up about 10 percent of Qatar’s population and have a significant impact on the nation’s culture, with many social etiquettes and traditions originating from the Bedouin people’s lifestyle.
Saudi Arabia
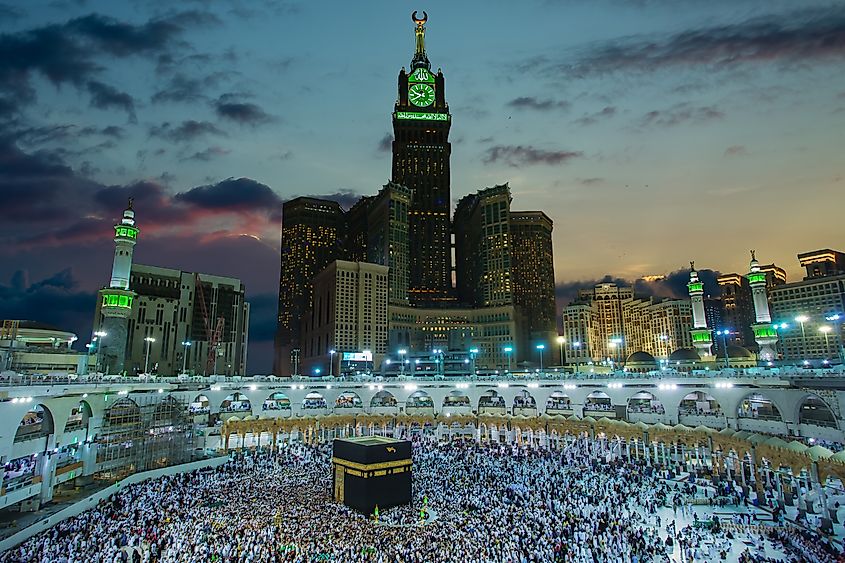

Saudi Arabia is located on the Arabian Peninsula - the largest peninsula in the world - and occupies about 80 percent of the peninsula’s land area. Saudi Arabia’s terrain consists almost entirely of arid, dry landscapes, with about 95 percent of the land covered by desert.
Historically, Saudi Arabia’s population consisted of nomads and people residing in villages. The nation’s culture has been largely influenced by Islam and Arab cultures. Two of the most holy sites of Islam, Mecca and Medina, are located in Saudi Arabia. Much like neighboring countries, Saudi Arabia has a rich culture influenced by the tribes that inhabited the region.
Today, Saudi Arabia is home to more than 36.4 million people, with about 7.8 million of those residents living in the capital city, Riyadh. There are five other cities in the country with a population of over a million residents, including Jeddah, Mecca, Medina, Al-Ahsa, and Ta’if.
Syria
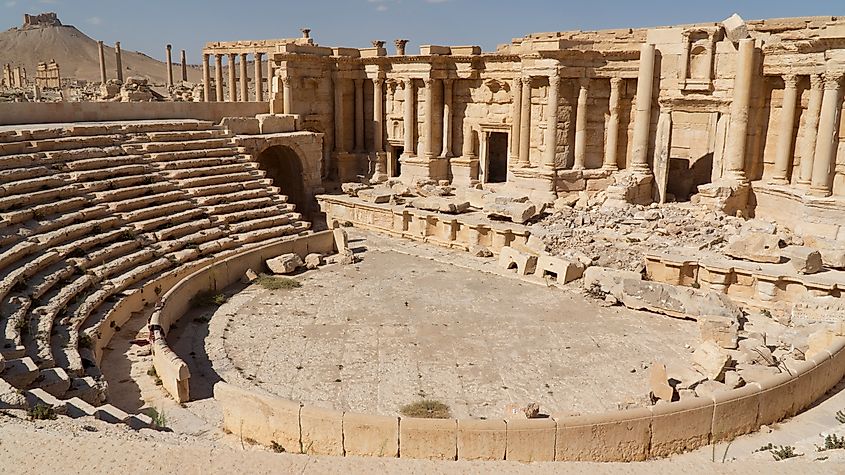

Syria is a culturally rich nation with diverse influences originating from the various societies the nation has been a part of throughout history. The country is located along the east coast of the Mediterranean Sea and shares borders with Türkiye to the north, Iraq to the east, and Lebanon, Israel, and Jordan to the south. The terrain of Syria consists of fertile coastal plains in the west, and arid, dry desert in the east. The ancient Euphrates River flows through the northeastern region of the country.
Syria is the site of many ancient cities, including Palmyra and Damascus. Damascus, one of the world’s oldest continuously inhabited cities, has served as a center of trade, culture, and religion for millennia, while Palmyra, once an oasis city, flourished as a key stop along ancient trade routes. Today, Syria is home to 22.1 people, with the vast majority of people living in urban areas in the west and along the Euphrates. The capital and largest city is Damascus, which has a population of 2.5 million.
Türkiye
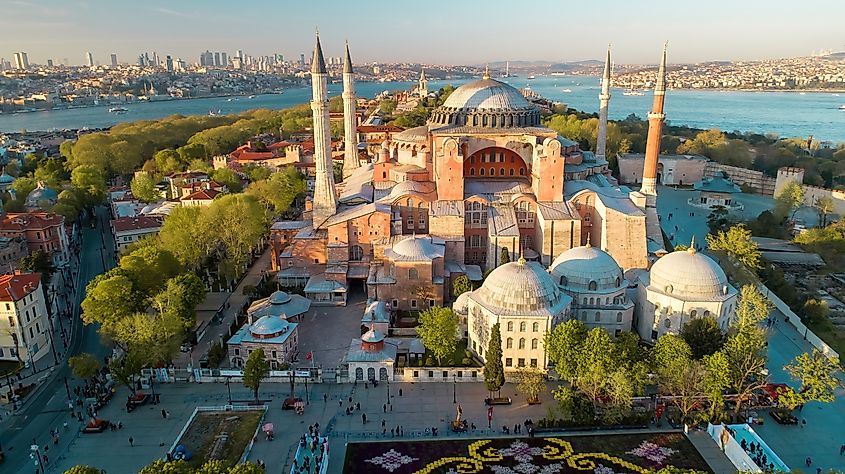

Türkiye, commonly referred to as Turkey, is one of the most geographically diverse countries in the Middle East. The country’s terrain consists of plains, forests, lakes, and coastlines along the Mediterranean Sea, the Black Sea, and the Aegean Sea. Türkiye’s overall landscape features various extensive mountain ranges, including the Taurus Mountains, Pontic Mountains, and Armenian Highlands. The nation also has stretches of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, two bodies of water that supported the earliest human civilization in Mesopotamia.
Türkiye is world renowned for a variety of sites with global, historical, and cultural significance. The country is often seen as the bridge between the continents of Europe and Asia at the ancient city of Istanbul. Türkiye is also well-known for Anatolia, which includes Cappadocia and Çatalhöyük - the world’s oldest known city that dates back about 9,000 years.
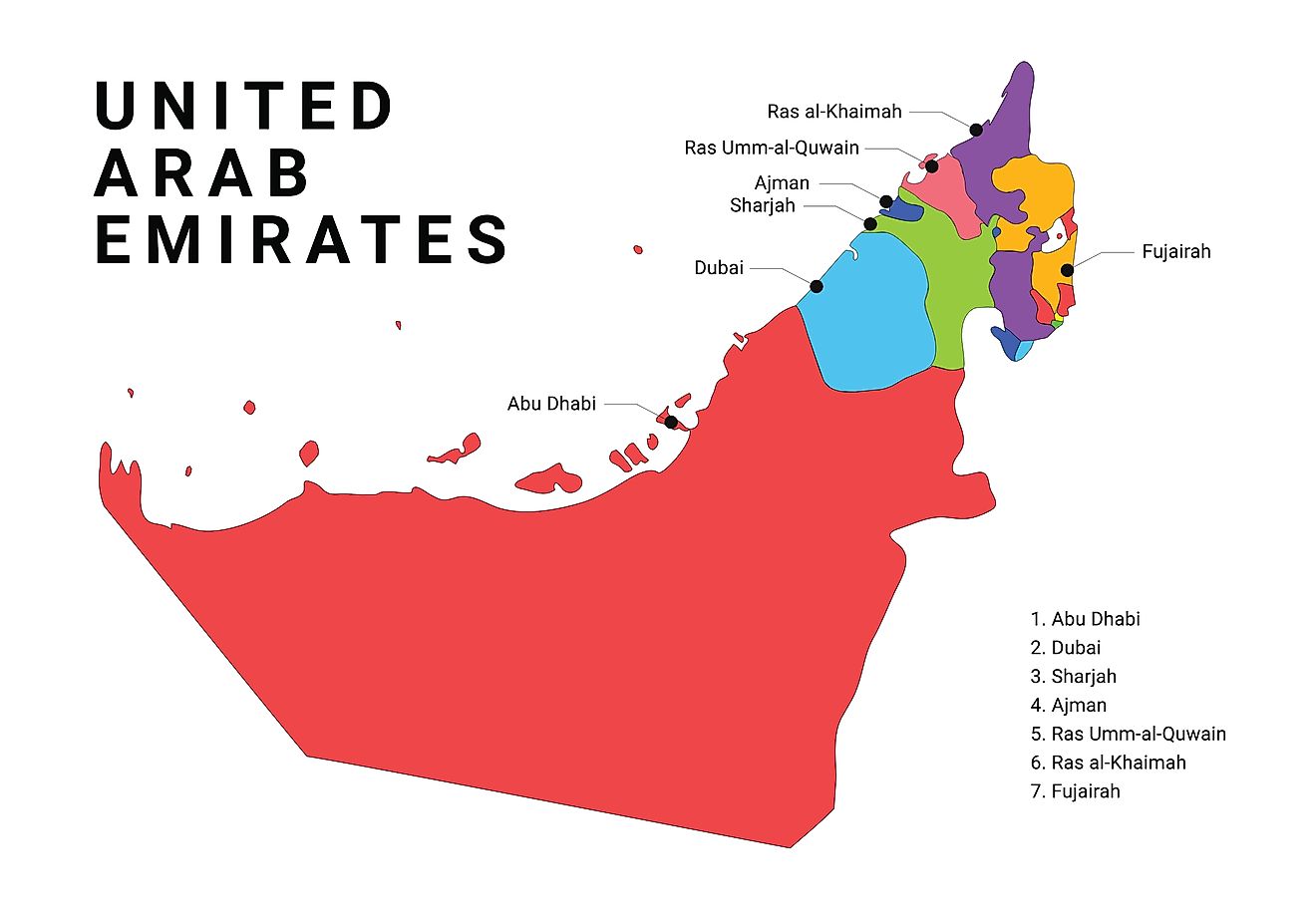
United Arab Emirates
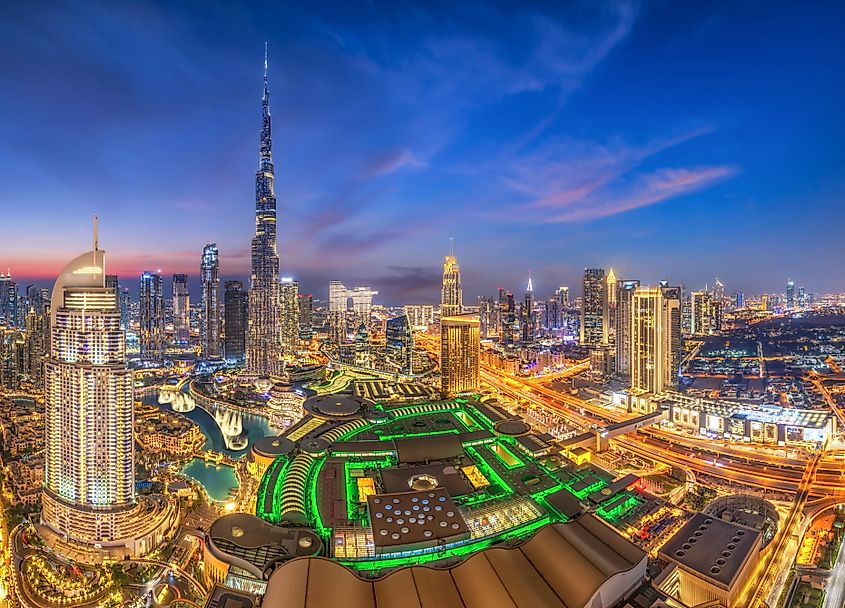

The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is located along the coast of the Persian Gulf (Arabian Gulf) and shares borders with Oman and Saudi Arabia. The terrain of the UAE is made up of a desert coastal plain with sand dunes spanning much of the land area. In the east, the Al Hajar Mountains rise above the sands and reach up to 3,000 meters.
Similar to other countries throughout the Middle East and Northern Africa, the UAE culture is rooted in politeness, courtesy, and hospitality - originating from historical influences of the Bedouin people.
The capital of the UAE is Abu Dhabi, a city of over 1.5 million residents along the central west coast of the country. Abu Dhabi, known for its impressive modern skyline and massive Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque, also houses cultural treasures like the Louvre Abu Dhabi, representing the UAE’s ambition to blend tradition with cutting-edge innovation. The largest and one of the world’s most famous of cities, Dubai, is home to more than 3.6 million people. Together, these urban areas account for about 70 percent of the nation’s total population.
Yemen
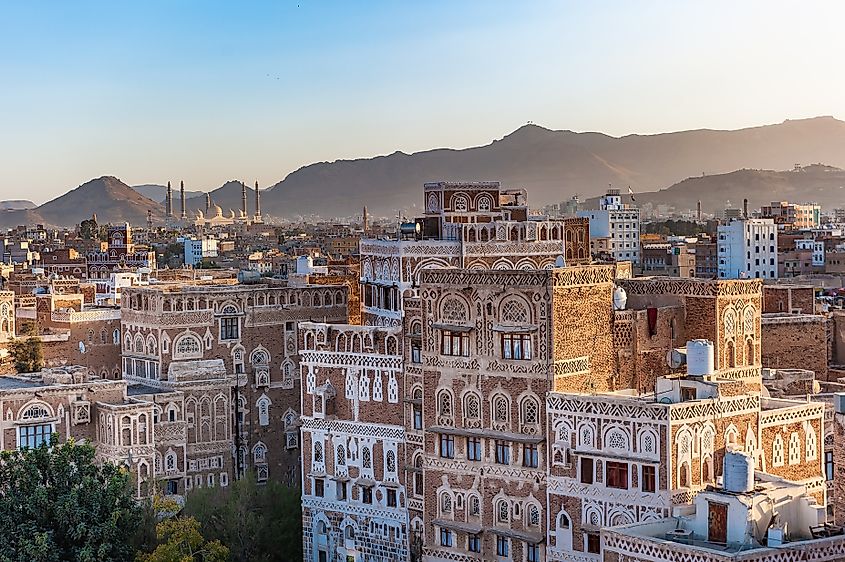

Yemen is situated on the southern corner of the Arabian Peninsula, bordered by Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the east. The country has coasts along the Red Sea to the west, the Gulf of Aden to the south, and the Arabian Sea to the southeast. The southern stretch of the dramatic Sarawat Mountains extends through the southern regions of Yemen, reaching heights of more than 3,000 meters. In the northern and central regions of the country, sand dunes of the Arabian Desert meet the base of the Yemen Highlands. Along the southern and eastern coastlines, the country’s landscape consists of a narrow coastal plain.
Because of Yemen’s location at the southern-most point of the Red Sea, the country has been at the heart of trade networks throughout the course of history, influencing the trade of many historically important commodities. Yemen’s ancient cities like Sana’a and Shibam, often referred to as the ‘Manhattan of the Desert’ for its mudbrick skyscrapers, are architectural wonders that testify to the country’s rich history and strategic importance. To this day, Yemen’s geographical situation is important for maritime trade routes passing through the Rea Sea and to the Suez Canal.
Yemen has a population of about 33.7 million people, most of whom live in the western half of the country. Sanaa is the nation’s capital and largest city, home to more than 3.4 million residents.
Historical Legacy and Ongoing Influence of the Middle East
The Middle East region of the world, commonly referred to as the “Cradle of Civilization,” is a tapestry of flourishing culture, rich history, and geographic diversity. The region is significant to the world’s historical timeline as the site of origin for some of the world’s earliest civilizations. These 17 countries share similarities - though each has a distinct culture - and continue to have an essential role in influencing the world through its history, culture, and traditions - much like the ancient societies that came before.