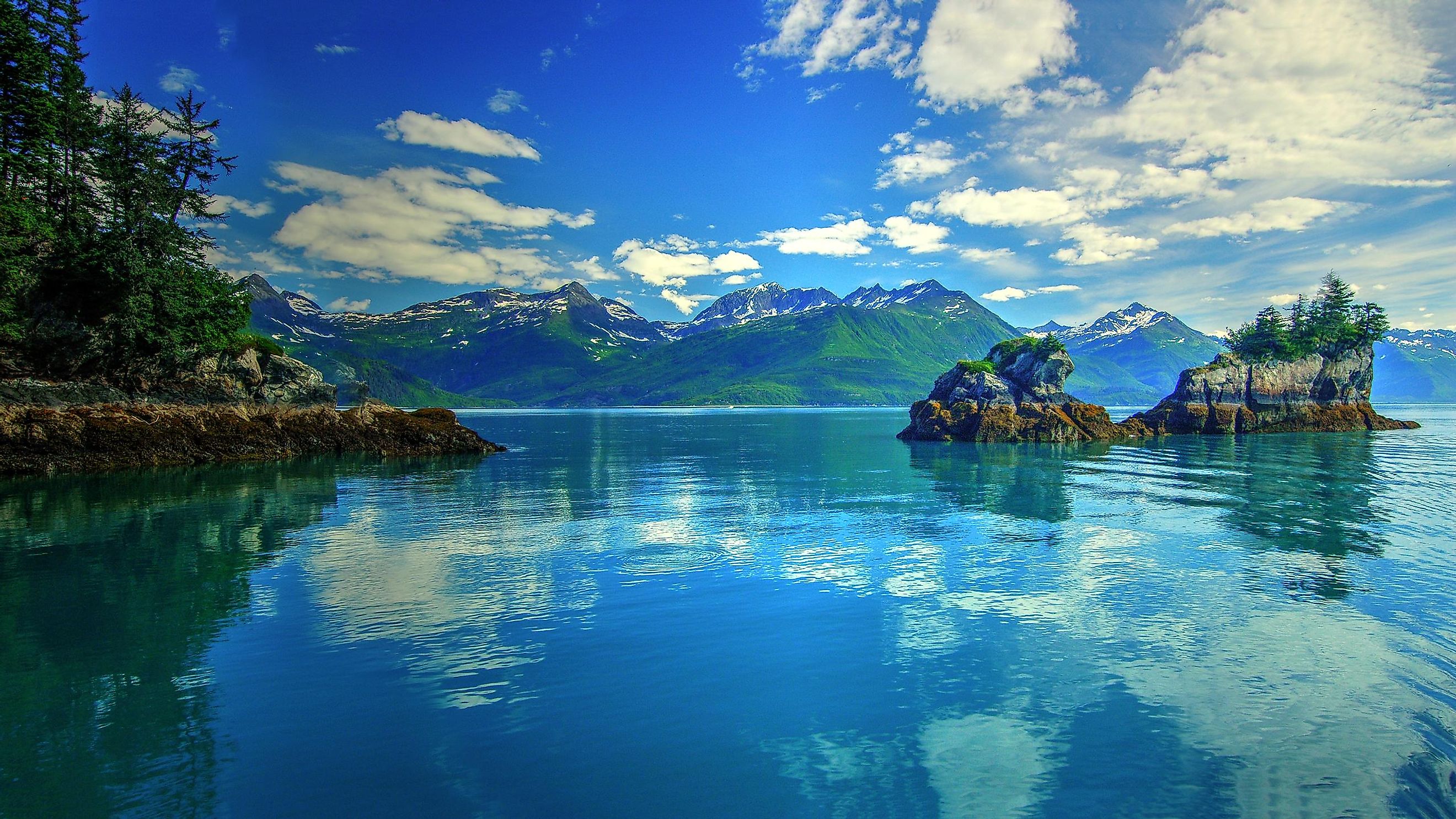
Gulf Of Alaska
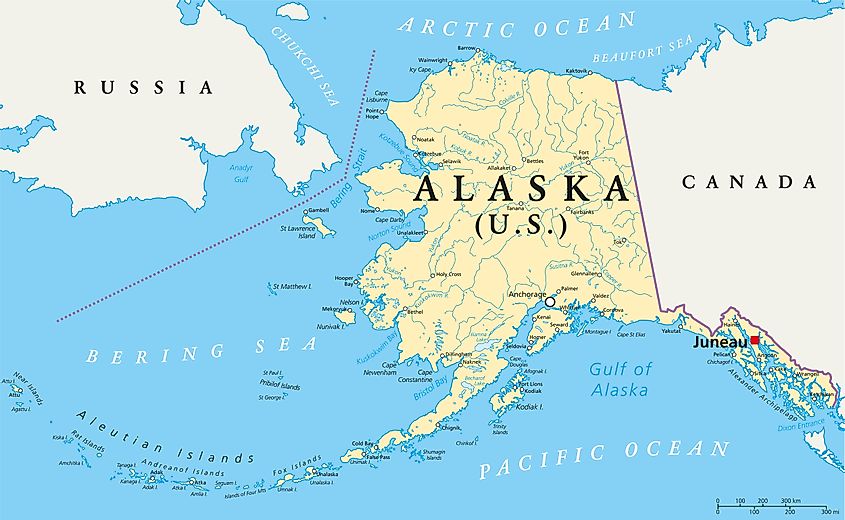
The Gulf of Alaska is an extension of the North Pacific Ocean located along the southern shores of the US state of Alaska. The gulf extends from Kodiak Island and the Alaska Peninsula in the west to the Alexander Archipelago in the east. It is separated from Bristol Bay by the Alaska Peninsula. The Danish explorer Vitus Bering was the first European to enter the Gulf of Alaska region in 1741.
Geography
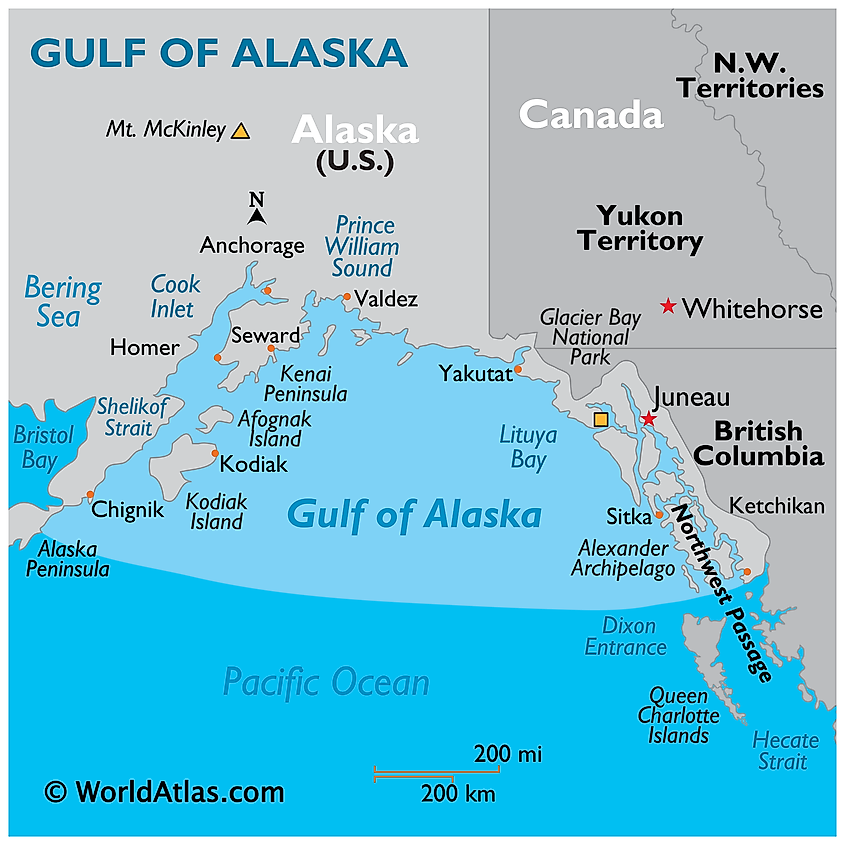
The gulf covers an area of 1,533,000 km2. The rugged coastline of the Gulf of Alaska is composed of mountains, forests, and many tidewater glaciers. The two most massive glaciers of Alaska, namely the Bering Glacier and the Malaspina Glacier, are located along the shores of the gulf. The coastal region of the Gulf of Alaska is deeply indented by fjords and other sea inlets such as the Cook Inlet and the Prince William Sound which are situated on the western and eastern sides of the Kenai Peninsula. It also consists of the Cross Sound, Lituya Bay, and Yakutat Bay. The high snow-capped Alaskan mountains of St. Elias, Chugach, Fairweather, and Kenai are found along the shores of the gulf.
The Susitna and the Copper Rivers flow into the Gulf of Alaska. During the summer season, the river waters loaded with heavy sediments along with melted waters of the glaciers flow into the gulf. Due to the differences in the density of water, they do not easily mix at first. This creates an observable line with the natural blue waters on one side and the sediment-rich water on another as they slowly mix.
Several islands are located in the Gulf of Alaska. These include Montague Island, Middleton Island, Aiaktalik Island, the Alexander Archipelago, and the Kodiak Archipelago. With an area of 9,239 km2, Kodiak Island is the United States’ second-largest island. The 480 km-long Alexander Archipelago comprises about 1,100 islands which include Chichagof Island, Admiralty Island, Etolin Island, and Prince of Wales Island, among others.
Climate
The Gulf of Alaska experiences a subarctic climate. The gulf serves as the source of a high amount of seasonal rain and snowfall in the southwestern part of the United States and the Pacific Northwest. When huge chunks of glaciers get detached from the coast, they become icebergs that are then carried out to the Pacific Ocean by the strong ocean currents. The warm Alaska Current together with the Aleutian Low generates severe storms in the Gulf of Alaska region. This low-pressure system also influences the circulation pattern in the Gulf of Alaska which features an anti-clockwise cyclonic gyre.
Economy

The Gulf of Alaska has been regarded as a Class I productive ecosystem. The gulf is home to many deep-water corals including the notable red tree coral. Several commercially important fishes are found in the Gulf of Alaska. These include the Pacific cod, mackerel, Alaska pollock, Alaska salmon, pink salmon, halibut, and sockeye. Many crustacean species like shrimp, king crab, and tanner crab are also found here.
Oil reserves have been discovered underneath Controller Bay and along the Cook Inlet. The major ports along the Gulf of Alaska are Anchorage, Seward, and Valdez. Constructed in 1977, the 1,300 km-long Trans-Alaska pipeline transports vast quantities of crude oil from the Northern Slope of Alaska and the Prudhoe Bay to the ice-free port of Valdez in southern Alaska.